Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Exercise No.1
Uploaded by
Shela Lebasnon CaballeroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Exercise No.1
Uploaded by
Shela Lebasnon CaballeroCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Number
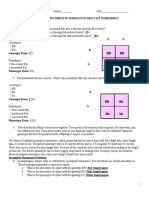
Laboratory Exercise No.1 Scientific Method Introduction Objective 1. Identify and characterize questions that can be answered through scientific investigation. 2. Define hypothesis and explain what characterizes a good scientific hypothesis. 3. Identify and describe the components of a scientific experiment. 4. Summarize and present results in tables and graphs. 5. Discuss results and critique experiments. 6. Design a scientific experiment. 7. Interpret and communicate results. Procedure 1. Read the following example and answer the questions that follow. 2. Prepare to discuss your answers. INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF SULPHUR DIOXIDE ON SOYBEAN REPRODUCTION Agricultural scientists were concerned about the effect of air pollution, sulfur dioxide in particular, on soybean production in fields adjacent to coal-powered power plants. Based on initial investigations, they proposed that sulfur dioxide in high concentrations would reduce reproduction in soybeans. They designed an experiment to test this hypothesis (Figure 1). In this experiment, 48 soybean plants, just beginning to produce flowers, were divided into two groups, treatment and no treatment. The 24 treated plants were divided into four groups of 6. One group of 6 treated plants was placed in a fumigation chamber and exposed to 0.6 ppm of sulfur dioxide for 4 hours to simulate sulfur dioxide emissions from a power plant. The experiment was repeated on the remaining three treated groups. The no-treatment plants were placed similarly in groups of 6 in a second fumigation chamber and simultaneously exposed to filtered air for 4 hours. Following the experiment, all plants were returned to the greenhouse. When the beans matured, the number of bean pods, the number of seeds per pod, and the weight of the pods were determined for each plant.
Figure 1. Experimental Design for soybean experiment. The experiment was repeated four times. Soybeans were fumigated for 4 hours. Supplementary Question Set 1 1. What is/are the Dependent Variables/s? 2. What is/are the Independent Variable/s? 3. Can you suggest other variables that the investigator might have changed that would have had an effect on the dependent variable/s? 4. Why is it important to have only one independent variable? 5. Why is it acceptable to have more than one dependent variable? 6. What are the controlled variables in this experiment? What variables other than those you may have already listed can you now suggest? 7. What was the level of treatment in the soybean experiment? 8. Describe replication in the soybean experiment. 9. What was the control treatment?
You might also like
- Unit 1 HW - Scientific Method1Document8 pagesUnit 1 HW - Scientific Method1cmejdi jNo ratings yet
- 3 Experimental Variables-S PDFDocument5 pages3 Experimental Variables-S PDFDonna NNo ratings yet
- Lab01 Scientific InvestigationDocument9 pagesLab01 Scientific InvestigationdanaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Bio150 Laboratory GuidelinesDocument11 pages1.0 Bio150 Laboratory GuidelinesNUR AISHAH MOHAMADNo ratings yet
- Effectsof Gamma Radiationon Seed Germinationand GrowthDocument3 pagesEffectsof Gamma Radiationon Seed Germinationand GrowthStephan ChiariniNo ratings yet
- Writing A Conclusion ParagraphDocument1 pageWriting A Conclusion ParagraphDebdoot GhoshNo ratings yet
- Observing A Yeast PopulationDocument2 pagesObserving A Yeast PopulationasdofiajseofijaweofjapoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Guidelines OCT 2022Document17 pagesLab Manual Guidelines OCT 2022ANIS NURALYSA AFFENDINo ratings yet
- SARAH ABRAHAM - 3 Experimental Variables-SDocument5 pagesSARAH ABRAHAM - 3 Experimental Variables-SSARAH ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in YeastDocument11 pagesCellular Respiration in YeastxshelyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual March 2023Document23 pagesLab Manual March 2023MASYITAH MOHD PADZILNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Scientific MethodDocument26 pagesUnit 1 The Scientific Methodbonillajosue943No ratings yet
- Sci. Method Student NotesDocument5 pagesSci. Method Student NotesChristian TocioNo ratings yet
- The Helix Charter HS Lab ReportDocument19 pagesThe Helix Charter HS Lab ReportChristian AlvarezNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE V 2nd RatingDocument90 pagesSCIENCE V 2nd RatingMichael Joseph SantosNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Biology Sem 1 23 - 24Document25 pagesLab Manual Biology Sem 1 23 - 24Ahmad AmirulNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design Diagram and Independent VariablesDocument4 pagesExperimental Design Diagram and Independent Variablesalain presillasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - The Practicals 16 APRIL 2014 Lesson DescriptionDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis - The Practicals 16 APRIL 2014 Lesson DescriptionKeneilweNo ratings yet
- M1 Scientific InvestigationDocument35 pagesM1 Scientific InvestigationLyn mae OdiasNo ratings yet
- Strand1: SA1, SA2, SA3Document6 pagesStrand1: SA1, SA2, SA3Mico Angelo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- A. Study The Scenario Described Below That Illustrates What An Experiment IsDocument4 pagesA. Study The Scenario Described Below That Illustrates What An Experiment IsRezel C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Print - Science and Health 6Document10 pagesLesson Plan For Print - Science and Health 6Aldrin Paguirigan100% (1)
- Branches of BiologyDocument3 pagesBranches of BiologyDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- Science Fun Grade 6 AnswersDocument4 pagesScience Fun Grade 6 AnswersbinduNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Prelim ExperimentsDocument18 pagesPharmacognosy Prelim ExperimentsMello Diax100% (1)
- Discussion and Conclusions 1Document18 pagesDiscussion and Conclusions 1api-290657090100% (3)
- Analyzing The Enzymatic Activity of CatalaseDocument9 pagesAnalyzing The Enzymatic Activity of CatalaseZainab BunajmahNo ratings yet
- HW Packet 1 - The Study of Life (KEY) PDFDocument2 pagesHW Packet 1 - The Study of Life (KEY) PDFDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Values: Cooperation, Industriousness: Science and Health VDocument2 pagesValues: Cooperation, Industriousness: Science and Health VRichardDumlaoNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 1Document8 pagesBio Lab 1Adriana Isabel PeñaNo ratings yet
- AP Bio EssaysDocument34 pagesAP Bio EssayshyacyntheNo ratings yet
- 1 Scientific MethodDocument17 pages1 Scientific MethodViviane O. BaylonNo ratings yet
- Name: Lululs Windarto: NIM: 210301161200056 Class: CDocument2 pagesName: Lululs Windarto: NIM: 210301161200056 Class: CadrianNo ratings yet
- Pre Ap Bio Sci Met One Free Response PromptDocument1 pagePre Ap Bio Sci Met One Free Response Promptapi-26963416No ratings yet
- Scientific Method: The Involves A Series of Steps That Are Used To Investigate A Natural OccurrenceDocument30 pagesScientific Method: The Involves A Series of Steps That Are Used To Investigate A Natural OccurrenceKazuya SenseiNo ratings yet
- Eb61188c 18c7 42df 8b31 6266f6a7de19 613de4af679baf0b813c9242 1631446410 Week 1. Components of Scientific InvestigationDocument4 pagesEb61188c 18c7 42df 8b31 6266f6a7de19 613de4af679baf0b813c9242 1631446410 Week 1. Components of Scientific InvestigationMoshiNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodsDocument7 pagesScientific MethodsMochamad Yusup FaturohmanNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument30 pagesScientific MethodRyan Christian JacintoNo ratings yet
- Biology Remedial Module PDFDocument185 pagesBiology Remedial Module PDFBetseha Merawi67% (3)
- Rate of Photosynthesis LabDocument2 pagesRate of Photosynthesis Labapi-251390921100% (2)
- The Scientific MethodDocument16 pagesThe Scientific MethodJeona Kiel DominguezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quarter 1 Common LabDocument4 pagesChemistry Quarter 1 Common LabLynsey WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Research 2: Quarter 1 MODULE 5 (Week 5 &6) : GUIDED EXPERIMENTSDocument5 pagesResearch 2: Quarter 1 MODULE 5 (Week 5 &6) : GUIDED EXPERIMENTSChelsea BialaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab Practical Guide A Lab Practical or Exam Tests ...Document4 pagesAP Biology Lab Practical Guide A Lab Practical or Exam Tests ...marisa corderoNo ratings yet
- Planning and Designing LabsDocument3 pagesPlanning and Designing LabsAlicia HaughtonNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Concepts of Biology 3rd Edition by Mader ISBN 0073525537 9780073525532Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Concepts of Biology 3rd Edition by Mader ISBN 0073525537 9780073525532benjaminwolfprdiyajkcz100% (28)
- Writing Conclusion Paragraphs in A Science Lab ReportDocument1 pageWriting Conclusion Paragraphs in A Science Lab ReportHazel CordanoNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument18 pagesScientific Methodδαι δαιNo ratings yet
- Lab YeastDocument5 pagesLab Yeastlaliberte68100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5MELANIE R. DIAMANo ratings yet
- Sci 7 Q1 WK1 Scientific Investigation Lea TomasDocument7 pagesSci 7 Q1 WK1 Scientific Investigation Lea TomasJoyce CarilloNo ratings yet
- Reading. First PeriodDocument6 pagesReading. First PeriodLupita GuzmánNo ratings yet
- K01582 - 20180302121452 - Lab ManualDocument32 pagesK01582 - 20180302121452 - Lab ManualNur Hana SyamsulNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method QuizDocument5 pagesScientific Method QuizRialyn Kate BinagNo ratings yet
- Chem Int CC CH 01 - Introduction To Chemistry - Answers (09.15)Document12 pagesChem Int CC CH 01 - Introduction To Chemistry - Answers (09.15)JhonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Module 1 CombinedDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Module 1 Combinedapi-293001217No ratings yet
- Biology EssaysDocument35 pagesBiology Essayst rex422No ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument48 pagesScientific Methodlovelyaquino189No ratings yet
- 0537 - Memorandum-DEC-12-16-464Document1 page0537 - Memorandum-DEC-12-16-464Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- 1629 2676 1 SMDocument9 pages1629 2676 1 SMShela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lab Exer 2Document2 pagesLab Exer 2Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Part2 Chemical Basis of LifeDocument5 pagesPart2 Chemical Basis of LifeShela Lebasnon Caballero100% (1)
- Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCourse SyllabusShela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Determining The VariablesDocument2 pagesDetermining The VariablesShela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- ECOL 1 Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesECOL 1 Course SyllabusShela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Individual Project No1Document1 pageIndividual Project No1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document3 pagesLecture 1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Individual Project No1Document1 pageIndividual Project No1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 2Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- BIOL3Document4 pagesBIOL3Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- 121 Tutorial How Det Formal Charges SP 2006Document4 pages121 Tutorial How Det Formal Charges SP 2006KasunBuddikaNo ratings yet
- 11th NGS FlyerDocument2 pages11th NGS FlyerShela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Physiology of BacteriaDocument9 pagesMorphology and Physiology of Bacteriaprashantshukla8280No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument8 pagesGeneral BiologyJanine RomanoNo ratings yet
- Biocomputers: Biochemical ComputersDocument3 pagesBiocomputers: Biochemical ComputersAjinkyaJadNo ratings yet
- Error Recognition: ToeicDocument47 pagesError Recognition: ToeicNargis Maulina17No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Soluble Reactive PhosphorusDocument4 pagesSoluble Reactive Phosphorusmahfi222juNo ratings yet
- NitroglycerinDocument6 pagesNitroglycerinPapaindoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - Homology and Analogy of Plants and AnimalsDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - Homology and Analogy of Plants and AnimalsAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Jurnal: PERBANYAKAN AKASIA HIBRIDA (Acacia Mangium × AcaciaDocument14 pagesJurnal: PERBANYAKAN AKASIA HIBRIDA (Acacia Mangium × AcaciaTT ZmDESNo ratings yet
- Activity - Camera and Human EyeDocument5 pagesActivity - Camera and Human EyeVincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Eugenics HistoryDocument9 pagesEugenics HistoryLuis AmaralNo ratings yet
- Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Serous Fluids - Shidham & AtkinsonDocument9 pagesCytopathologic Diagnosis of Serous Fluids - Shidham & Atkinsonvshidham100% (1)
- Witamina C W Medycynie I KosmetologDocument20 pagesWitamina C W Medycynie I KosmetologmochisrtNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of The Circulatory SystemFatima Zehra YusefNo ratings yet
- 5.1.3. Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsDocument2 pages5.1.3. Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsMonika BontongNo ratings yet
- Test Request Form - (Name Laboratory) : Patient Details Requester DetailsDocument1 pageTest Request Form - (Name Laboratory) : Patient Details Requester DetailsMisty Collings100% (1)
- 29 BAJR Guide: An Introduction To Archaeological Fish RemainsDocument9 pages29 BAJR Guide: An Introduction To Archaeological Fish RemainsDavid Connolly88% (8)
- Boy Scout Beekeeping Merit Badge PamphletDocument31 pagesBoy Scout Beekeeping Merit Badge PamphletWorkerBeester100% (2)
- Dwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFmariputwashercy4ca100% (15)
- List of Video Lectures Available in Our Video BankDocument25 pagesList of Video Lectures Available in Our Video Bankzeeshannajeeb80% (10)
- Plant Biotechnology Multiple Choice Test 1Document1 pagePlant Biotechnology Multiple Choice Test 1shoyou9100% (1)
- Activity 3 - The Human ReflexDocument2 pagesActivity 3 - The Human ReflexGOOKIEBOONo ratings yet
- ddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddDocument9 pagesddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddjoao victorNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review On The Pre-Clinical Study of Cephalandra Indica and Gymnema Sylvestre in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 pagesA Systematic Review On The Pre-Clinical Study of Cephalandra Indica and Gymnema Sylvestre in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Organic Chemistry: Amino Acids & ProteinsDocument9 pagesIntroduction in Organic Chemistry: Amino Acids & ProteinsMariellaIsabelCasuyonNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 3Document19 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 3Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Soal Bhs Ing Xi GenapDocument5 pagesSoal Bhs Ing Xi GenapArdiWirawanNo ratings yet
- 4a Lesson PlanDocument10 pages4a Lesson PlanPauline E. BinarabaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report IDocument11 pagesLab Report IElle B.No ratings yet
- Agri 32 2 NarrativeDocument1 pageAgri 32 2 NarrativeRaizza Anna AlforjaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (109)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (595)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)