Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface To Surface Contact
Uploaded by
scribddisantoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface To Surface Contact
Uploaded by
scribddisantoCopyright:
Available Formats
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 1 di 13
Home > Examples > 31. Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Surface to Surface Contact Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
31.
A clip made of solid elements will come into contact with a fixed base and move through a range of motion based on enforced displacements using surface to surface contact. For this example the clip and the base have already been created. Also, permanent constraints and the contact segments have also been created to focus the example on performing the analysis. The analysis process includes: creating the Connection Property and defining the Connector for surface to surface contact in NX Nastran. creating a functionally-dependent Enforced Displacement to bring the Clip into contact with the Base defining the analysis parameters to aid in convergence of the Nonlinear solution (Analysis Set manger) analyzing the model with NX Nastrans Advanced Nonlinear Solution (SOL 601) viewing the multi-set animation of the analysis sets to understand the contact between the objects.
z z z z z
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 2 di 13
Importing the Neutral File
What Import a FEMAP neutral file containing the Nodes, Elements, Properties, Materials, Permanent Constraints, and Connection Regions How Step 1. UI Command/Display File, New
2.
File, Import, FEMAP Neutral
3.
Read Model from FEMAP Neutral dialog box: FEMAP_INSTALL_FOLDER/Examples/Advanced_Nonlinear/snap601.neu
4.
Locate snap601.neu Click Open Neutral File Read Options dialog box: Click OK
These Elements are solid 3-D elements.
Creating the Contact Conditions
In order for surface to surface contact to occur during analysis with NX Nastran Advanced Nonlinear Method
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 3 di 13
(SOL 601), several parameters must be defined. In general, Connection Regions are created, a Connection Property is defined, and then a Connector (contact pair) is created to define the contact relationship between the two Connection Regions. First, Connection Regions must be created using the Connect, Connection Region command. While this dialog box is open, elements and element faces can be chosen to represent the areas on different parts in the model that will come into contact with one another. The process consists of choosing all elements around the outside edge of a part that may possibly come into contact with another part. Once these elements are chosen, an element face must be chosen to allow NX Nastran to know what face of the element will be part of a contact surface. When all the elements have be chosen and faces selected, the Connection Region will, by default, be shown as orange colored plate elements with thick orange edges on the screen. For this model, the Connection Regions have been created to save modeling time and focus on the use of the NX Nastran Advanced Nonlinear solution sequence (SOL 601). Viewing the Connection Regions will show how these regions should be created. The regions in this model were created by choosing the Elements radio button then clicking the Multiple button in the Define Connection Region dialog box. Multiple allows a number of elements around the edge of the part to be chosen at the same time, then element faces are selected using the Adjacent Faces option in the Face Selection for Elemental Loads dialog box. What Viewing the Connection Regions How Step 1. UI Command/Display Click View Visibility icon (on View Toolbar) OR Press Crtl+Q 2. Visibility dialog box: Choose the Entity/Label tab Click All Off button 3. CHECK Region box located in the Connections section, then...
4.
Click Done This will make only the Connection Regions visible on the screen. These regions will be used along with a connection property to create a connector, used for surface-to-surface contact. Rotate the View to be able to see the element faces which make up the connection regions.
After the Connection Regions have been created and visually confirmed, the next step in creating a Connector (contact pair) is creating the Connection Property. Because this type of property is unique, it will only be found as command on the Connect menu. There are three type of contact Method, or Rigid Target. Along define the behavior of the parts of problem trying to be solved. used by SOL 601 which FEMAP supports: Constraint Function, Segment with each type of contact there a number of parameters which can be set to that will come into contact. The contact type is usually determined by the type Also, birth time and death time for Connection Regions can be defined. For
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 4 di 13
more information on the options see Section 4.4 Creating Connections (NX Nastran Contact Properties) of the FEMAP Commands manual or the Theory and Modeling guide of SOL 601. In this case, the Constraint Function type of contact will be used with the default values assigned. What Create the Connection Property How Step 1. UI Command/Display Connect, Connection Property
Tip: You can also create a new Connection Property using the New command on the context sensitive menu located on the Connection Property branch in the Model Info tree (simply click to highlight the top level of the Connection Properties branch or any existing Connection Property, then right mouse click to see the context sensitive menu). 2. Define Connection Property dialog box: Title: Contact 3. Click the NX Adv Nonlin tab in the
4.
Make sure that 0..Constraint Function is selected from the Contact Type dropdown list in the General section. Also, make sure that Connect Type is set to 0..Contact (This drop-down list is located in the upper right corner of the Define Connection Property dialog box)
5.
Click OK, then...
Click Cancel Finally, once the Connection Property has been defined, the Connector (contact pair) can be created. In order to create a Connector, a Master Connection Region and a Slave Connection Region must be chosen from available Connection Regions. In this model, the Connector will be created in a certain manner to minimize convergence time during the solution. What Create the Connector (contact pair) How Step 1. UI Command/Display Connect, Connector...
2.
Define Contact Connector - Select Connection Regions dialog box: Choose 1..Contact from the Property drop-down list.
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 5 di 13
Choose 1..Deformable from the Master drop-down list. Choose 2..Rigid from the Slave drop-down list. 3. Click OK, then... Click Cancel 4. Click View Visibility icon (on View Toolbar) OR Press Crtl+Q 5. CHECK Element box located in the Mesh section, then... CHECK Connector box located in the Connections section, then... CHECK Constraints.... header box (checks all constraint types)
CHECK Loads.... header box (checks all load types)
6.
Click Done This will show the elements and contact segments only. A single line element will be shown from contact segment to contact segment to represent a contact pair exists between the segments.
7.
Crtl-R OR F8 key
This will bring up View Rotate dialog box:
8.
Click XY Top, then... Click OK Tip: You can also use the View Orient Toolbar to have one click access to several frequently used views. You can turn on this toolbar using Tools, Toolbars, View Orient
The Model should now look like this:
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 6 di 13
Creating the loads and constraints
What Apply constraints to the bottom of the Clip to not allow translation in the Y direction, and fix the nodes which will be loaded with the functionally-dependent Enforced Displacement in the X-direction as well. How Step 1. UI Command/Display Model, Constraint, Create/Manage Set
2.
Constraint Set Manager dialog box: Click New Constraint Set, then...
3.
New Constraint Set dialog box: Title: Constraints
4.
Click OK, then... Constraint Set Manager dialog box: Click Done Tip: You can also create a new Constraint Set using the New command on the context sensitive menu located on the Constraints branch in the Model Info tree (simply click to highlight the top level of the Constraints branch or any existing Constraint Set, then right mouse click to see the context sensitive menu).
5.
Model, Constraint, Nodal
6.
Entity Selection Enter Node(s) to Select dialog box: Select the 6 nodes shown at the bottom of the Clip using a box pick: (Nodes 74-76 and 730-732)
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 7 di 13
7.
Click OK
8.
Create Nodal Constraints/DOF dialog box: CHECK TY box
9.
Click OK
10.
Entity Selection Enter Node(s) to Select dialog box: Select the 2 nodes on the right side of the bottom of the Clip: (Nodes 73 and 729)
11.
Click OK
12.
Create Nodal Constraints/DOF dialog box: CHECK TX and TY boxes
13.
Click OK, then Click Cancel
What Apply functionally dependant Enforced Displacements to the nodes constrained in both the X and Y Translation directions in the last step. The function will be used to step the displacement load up as the analysis progresses. How Step 1. UI Command/Display Model, Function
2.
Function Definition dialog box:
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 8 di 13
Title: Loading Function 3. Select 1..vs. Time from Type drop-down list.
4.
Choose Linear Ramp radio button
5.
Enter the following values in the corresponding fields: X = 0.0 To X = 1 Delta X = 0.01 Y = 0.0 To Y = 1
6. Click Add button X and Y Values will be created for the function. 7. Click OK, then Click Cancel 8. Model, Load, Nodal
9.
Because no Load sets exist in the model, FEMAP will prompt you to create one New Load Set dialog box: Title: Displacements
10.
Click OK
11.
Entity Selection Enter Node(s) to Select dialog box: Select the 2 nodes on the right side of the bottom of the Clip: (Nodes 73 and 729)
12.
Click OK
13.
Create Loads on Nodes dialog box: Highlight Displacement from the selection list
14.
Enter 2.25 in TX field (units: Inches)
15.
Select 1..Loading Function from Time/Freq Dependence drop-down list.
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 9 di 13
16.
Click OK, then Click Cancel
THE MODEL IS NOW READY TO BE ANALYZED!
Running the Nonlinear Static Analysis
What Create an analysis case for Advanced Nonlinear Static Analysis using the FEMAP Analysis Set Manager How Step 1. UI Command/Display Model, Analysis
2.
Analysis Set Manager dialog box: Click New button
3.
Analysis Set dialog box: Title: Snapfit 601
4.
Select 36..NX Nastran from the Analysis Program drop-down list, then Select 22..Advanced Nonlinear Static from the Analysis Type drop-down list
5.
Click Next button 5 times
6.
NXSTRAT Solver Parameters dialog box: Enter 100 in the Number of Steps field in the Time Steps section
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 10 di 13
Enter 0.01 in the Time Increment field in the Time Steps section 7. Click Next button 1 time
8.
NXSTRAT Iteration and Convergence Parameters dialog box: Select 1..On from the Auto Increment drop-down list in the Analysis Control section.
9.
Click OK, then Analysis Set Manager dialog box: Click Analyze Upon Completion of the Analysis, FEMAP will ask OK to read Nonlinear Stresses and Strains?...Click Yes
Post-Processing the Surface to Surface Contact Results
The Advanced Nonlinear Static Analysis has been completed. The best way to view the deformation and stress results of the plastic part is a contour plot. After the contour Plot of the final step is viewed, watch the contact progress with a contoured Multi-set Animation. What View the results in a FEMAP contour plot of a deformed model How Step 1. UI Command/Display View, Select or Press the F5 Key or choose the view select icon 2. View Select dialog box: Choose Deform radio button in Deformed Style section Choose Contour radio button in Contour Style section 3. Click Deformed and Contour Data button from the View Toolbar
4.
Select PostProcessing Data dialog box: Select Last Analysis Step, Time 1 (may differ based on machine set-up) from drop-down list located in the Output Set section Select 1..Total Translation from Deform drop-down list located in the Output Vector section
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 11 di 13
Select 60031..Solid Von Mises Stress from Contour drop-down list located in the Output Vector section 5. Click OK, then View Select dialog box: Click OK 6. Tools, Toolbars, Post (If the Post Toolbar is already visible just click the icons shown below) This will bring up the Post Toolbar.
Click the Post Options icon from the Post Toolbar and select Actual Deformation from the drop-down list (Must have a check mark next to it in the menu) If the Undeformed model is currently NOT visible, skip this portion of the step: Click the Post Options icon from the Post Toolbar again and select Undeformed from the drop-down list (Must NOT have a check mark next to it in the menu) The deformation and stress results should look like this:
What View the results in a FEMAP Animation of all the analysis sets How
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 12 di 13
Step 1.
UI
Command/Display View, Select or Press the F5 Key or choose the view select icon Toolbar from the View
2.
View Select dialog box: Choose Animate Multi-Set radio button in Deformed Style section
3.
Click Deformed and Contour Data button
4.
Select PostProcessing Data dialog box: Select 1..Case 1 Time 0.01 from Initial drop-down list located in the Output Sets section Select Last Analysis Step (may differ based on machine set-up) from Final drop-down list located in the Output Sets section or leave it Blank and FEMAP will use the Final Analysis Set in the model automatically.
5.
Click OK, then View Select dialog box: Click OK, then Press Ctrl-A to Autoscale the Model Tip: You can use the Model Info tree to quickly create a multi-set animation. Simply expand the Results branch so all the Output Sets in the model are visible in a list. Highlight the Output Set you want to use as the first step in the multi-set animation in the list, then hold down the Shift Key and highlight the Output Set you want to use as the final step in the multi-step animation. Now click the right mouse button on one of the highlighted Output Sets and choose MultiSet Animate from the context sensitive menu for Results.
The Contact between the Clip and the Base can be viewed in this mode as the objects come into contact. How Step 1. UI Command/Display View, Select or Press the F5 Key or choose the view select icon Toolbar 2. View Select dialog box: Choose None-Model Only radio button in Deformed Style and Contour Style sections to stop the animation 3. Click OK from the View
This concludes the Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601) example. It is
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
Examples - Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonlinear (SOL 601)
Pagina 13 di 13
recommended to save the model file.
FEMAP
Product Info: http://www.femap.com Customer Support: http://support.ugs.com Phone: (714) 952-5444 or : (800) 955-0000 (US and Canada)
mk:@MSITStore:C:\FEMAPv1101\help\Help.chm::/FEMAPExamples/Snap601/Sna...
02/07/2013
You might also like
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)No ratings yet
- MSC - Software Corporation: Dynamic Analysis Using MSC - Patran and MSC - NastranDocument8 pagesMSC - Software Corporation: Dynamic Analysis Using MSC - Patran and MSC - NastranroylmechNo ratings yet
- Workshop 5 Direct Frequency Response Analysis: WS5-1 NAS122, Workshop 5, January 2004 © 2004 MSC - Software CorporationDocument18 pagesWorkshop 5 Direct Frequency Response Analysis: WS5-1 NAS122, Workshop 5, January 2004 © 2004 MSC - Software CorporationmasatusNo ratings yet
- Total NAS102Document363 pagesTotal NAS102Alejandro Palacios MadridNo ratings yet
- Ws03 DirecttransientDocument20 pagesWs03 DirecttransientswiftthrillsNo ratings yet
- RBE2Document20 pagesRBE2zakir78No ratings yet
- MSC - Software Corporation: Dynamic Analysis Using MSC - Patran and MSC - NastranDocument4 pagesMSC - Software Corporation: Dynamic Analysis Using MSC - Patran and MSC - NastranroylmechNo ratings yet
- Femap Free Body Section Cuts PDFDocument9 pagesFemap Free Body Section Cuts PDFManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- 02 Radioss SEAT BELT ANCHORAGE RADIOSS PAPER Eicher Polaris PDFDocument6 pages02 Radioss SEAT BELT ANCHORAGE RADIOSS PAPER Eicher Polaris PDFsurya prakashjNo ratings yet
- Sec4 Optimization of Composites 021712Document34 pagesSec4 Optimization of Composites 021712FradjNo ratings yet
- Practical Finite Element Modeling Techniques Using MSC - NastranDocument4 pagesPractical Finite Element Modeling Techniques Using MSC - NastranHumayun NawazNo ratings yet
- Patran ExampleDocument18 pagesPatran ExampleKarthick MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Linear Static, Normal Modes, and Buckling Analysis Using MSC - Nastran and MSC - PatranDocument4 pagesLinear Static, Normal Modes, and Buckling Analysis Using MSC - Nastran and MSC - PatranHumayun NawazNo ratings yet
- 5 Mscfatigue TutorDocument24 pages5 Mscfatigue TutorFadzrul Hisyam BadarudinNo ratings yet
- Normal Mode Analysis of PlateDocument26 pagesNormal Mode Analysis of Plateselva1975No ratings yet
- Lingap Oct2001 Update 3398Document21 pagesLingap Oct2001 Update 3398Oreste PrincipeNo ratings yet
- 06 Frame Surf Analy PAT301Document44 pages06 Frame Surf Analy PAT301Muhammad LutfiNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Gap Elements With Coincident NodesDocument12 pagesNonlinear Gap Elements With Coincident Nodesaiyubi2100% (1)
- A New Generation of Crash Barrier Models For LS-DYNADocument22 pagesA New Generation of Crash Barrier Models For LS-DYNAKaran AroraNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Fem Analysis of The Postbuckling Behaviour of Composite PDF E1094Document4 pagesAbaqus Fem Analysis of The Postbuckling Behaviour of Composite PDF E1094FabricioNo ratings yet
- Nas113 Composites Workbook 3Document12 pagesNas113 Composites Workbook 3selva1975No ratings yet
- BoltmodelnastranbearingDocument24 pagesBoltmodelnastranbearingcbryant1990No ratings yet
- Nas113 Composites Workbook 2Document24 pagesNas113 Composites Workbook 2selva1975No ratings yet
- OffsetDocument22 pagesOffsetvinandaraNo ratings yet
- Modal FRA With NastranDocument13 pagesModal FRA With Nastran5colourbalaNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Gap Elements With Non Coincident NodesDocument14 pagesNon Linear Gap Elements With Non Coincident Nodesjjpr814367No ratings yet
- Workshop 11 PDFDocument22 pagesWorkshop 11 PDFJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- Buckling and Postbuckling Analysis of A CFRP Stiffened Panel For ADocument7 pagesBuckling and Postbuckling Analysis of A CFRP Stiffened Panel For AOSCARDELTANo ratings yet
- Workshop 14 Radiation Enclosures: WS14-1 NAS104, Workshop 14, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software CorporationDocument24 pagesWorkshop 14 Radiation Enclosures: WS14-1 NAS104, Workshop 14, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software Corporationaiyubi2No ratings yet
- Simulating The Impact Behaviour of CompositeDocument15 pagesSimulating The Impact Behaviour of CompositeSchmetterling TraurigNo ratings yet
- 11.1.1 Topology Optimization of An Automotive Control Arm Products: Abaqus/Standard Abaqus/CAEDocument5 pages11.1.1 Topology Optimization of An Automotive Control Arm Products: Abaqus/Standard Abaqus/CAEIrandokht NikshabaniNo ratings yet
- Modul-Stiffness MethodDocument18 pagesModul-Stiffness MethodMohamad Zahir RazakNo ratings yet
- Postbuckling and Collapse AnalysisDocument8 pagesPostbuckling and Collapse AnalysisAtsis Papadopoulos100% (1)
- Workshop 4b Nonlin BucklingDocument30 pagesWorkshop 4b Nonlin BucklingRon RaeNo ratings yet
- Franc3D V6 Nastran TutorialDocument52 pagesFranc3D V6 Nastran TutorialSandeep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Failure Criteria CompositesDocument12 pagesAdvanced Failure Criteria CompositesrichardjoliverNo ratings yet
- COMSOL Cohesive Zone DebondingDocument22 pagesCOMSOL Cohesive Zone DebondingAaqib AliNo ratings yet
- Frame Surface Model AnalysisDocument37 pagesFrame Surface Model AnalysisManasses juniorNo ratings yet
- Marc 2017.1 Training 120 Workbook 636522147316424295 PDFDocument340 pagesMarc 2017.1 Training 120 Workbook 636522147316424295 PDFManasses junior100% (1)
- Sec2 Solid Composites 021712Document35 pagesSec2 Solid Composites 021712Jamshid PishdadiNo ratings yet
- Hybrid and 2D DICDocument13 pagesHybrid and 2D DICNguyễn Văn ThườngNo ratings yet
- ABAQUS Tutorial 2Document41 pagesABAQUS Tutorial 2morad_cryNo ratings yet
- ABAQUS IntroDocument46 pagesABAQUS IntroMaroua MahouachiNo ratings yet
- 2004-03-01 Actual vs. Effective Involute Tooth SizeDocument6 pages2004-03-01 Actual vs. Effective Involute Tooth Sizebee140676No ratings yet
- MSC Nastran 2020 Demonstration Problems Manual-Linear AnalysisDocument83 pagesMSC Nastran 2020 Demonstration Problems Manual-Linear AnalysiskadoNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Answers Spring 1997Document4 pagesAbaqus Answers Spring 1997zmchen100% (1)
- LingapsDocument10 pagesLingapsGowtham ReddyNo ratings yet
- NASTRAN Nonlinear ElementsDocument90 pagesNASTRAN Nonlinear Elementssons01No ratings yet
- Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part NoticeDocument20 pagesDefense Technical Information Center Compilation Part NoticeBala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Workshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software CorporationDocument24 pagesWorkshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software Corporationaiyubi2No ratings yet
- Introduction To MSC - Patran ExercisesDocument714 pagesIntroduction To MSC - Patran ExercisesAlex da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Response Spectrum Analysis Using Femap and NX NastranDocument40 pagesResponse Spectrum Analysis Using Femap and NX NastranGana C Rover100% (1)
- Hyper SizerDocument16 pagesHyper SizerKamlesh Dalavadi100% (1)
- 5 - Force VibrationDocument53 pages5 - Force VibrationReem GheithNo ratings yet
- Contact Element TutorialsDocument15 pagesContact Element TutorialsSushil DhunganaNo ratings yet
- Give Example A TitleDocument15 pagesGive Example A Titleapi-3833671No ratings yet
- AMI Mesh Editing TutorialDocument29 pagesAMI Mesh Editing TutorialWoong KimNo ratings yet
- w1 Spherical Indentation IaDocument13 pagesw1 Spherical Indentation IaDaniele Rossi100% (1)
- Tehnical University Gheorghe Asachi From Iasi Faculty of Civil Engineering Master IseDocument26 pagesTehnical University Gheorghe Asachi From Iasi Faculty of Civil Engineering Master IseIon IovitaNo ratings yet
- Creating Connectors 1Document14 pagesCreating Connectors 1Vinoth BalasubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Draft ListDocument3 pagesDraft ListscribddisantoNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument23 pagesDesignscribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Materials Stud Bolts: ASTM A197 B7Document5 pagesMaterials Stud Bolts: ASTM A197 B7scribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Seamless Lap Joint Stub EndsDocument1 pageSeamless Lap Joint Stub Endsscribddisanto100% (1)
- Long Welding Neck Flanges 1500Document1 pageLong Welding Neck Flanges 1500scribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Long Welding Neck Flanges 900Document1 pageLong Welding Neck Flanges 900scribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Long Welding Neck Flanges 600Document1 pageLong Welding Neck Flanges 600scribddisantoNo ratings yet
- BS EN 1515-4:2009 Flanges BoltingDocument22 pagesBS EN 1515-4:2009 Flanges BoltingAlexDdd123100% (1)
- Stainless Steel Material PropertiesDocument4 pagesStainless Steel Material PropertiesMohammed RiyazNo ratings yet
- Long Welding Neck Flanges 150Document1 pageLong Welding Neck Flanges 150scribddisantoNo ratings yet
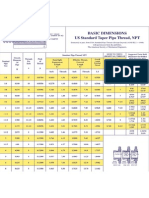
- S E S S U e ,: BA Ic Dim N S Standard Taper Thread NPTDocument1 pageS E S S U e ,: BA Ic Dim N S Standard Taper Thread NPTscribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Control Card HyperMesh and BatchMesher PDFDocument33 pagesControl Card HyperMesh and BatchMesher PDFscribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Unit Systems PDFDocument2 pagesUnit Systems PDFscribddisantoNo ratings yet
- Femap Basic - Day 1Document129 pagesFemap Basic - Day 1spylogo3No ratings yet
- Price of FEA Software - Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFDocument11 pagesPrice of FEA Software - Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFnaraNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Truss Using Autocad Femap Algor PDFDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Truss Using Autocad Femap Algor PDFJohn NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19 - XY Plotting Using The Charting Pane - Rev BDocument18 pagesLesson 19 - XY Plotting Using The Charting Pane - Rev BManu MachadoNo ratings yet
- Compare FEA CodesDocument27 pagesCompare FEA Codesdesibanda73No ratings yet
- Borrowing Setup For Femap 2020.2: Before You BeginDocument2 pagesBorrowing Setup For Femap 2020.2: Before You Beginantonio carlos peixoto de miranda gomesNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: Hardware/Software RequirementsDocument13 pagesInstallation Guide: Hardware/Software RequirementsΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουNo ratings yet
- Using The FEMAP Beam Calculator: Patrick KriengsiriDocument29 pagesUsing The FEMAP Beam Calculator: Patrick KriengsiriMohanned Saleh MahdiNo ratings yet
- Sr. Engineer: Professional InformationDocument8 pagesSr. Engineer: Professional InformationAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manuale FemapDocument594 pagesManuale FemapStefano MilaniNo ratings yet
- Stress and Fatigue Analysis of ASME Pressure Vessels Using PDFDocument30 pagesStress and Fatigue Analysis of ASME Pressure Vessels Using PDFnapinnvoNo ratings yet
- 507 - An Introduction To FEA Via Solid Edge and FEMAP - Mark ShermanDocument51 pages507 - An Introduction To FEA Via Solid Edge and FEMAP - Mark ShermanIbsonhNo ratings yet
- FEMAP PostprocessingDocument18 pagesFEMAP PostprocessinghedpalNo ratings yet
- Femap Free Body Section Cuts PDFDocument9 pagesFemap Free Body Section Cuts PDFManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Feamp Contact Modeling PDFDocument5 pagesFeamp Contact Modeling PDFajroc1515No ratings yet
- Exercise 14 - Bearing LoadDocument38 pagesExercise 14 - Bearing LoaddevNo ratings yet
- Femap 10 3 Mass Property PDFDocument2 pagesFemap 10 3 Mass Property PDFMeaganNo ratings yet
- Advances in ASME Section VIII Division 2 Pressure Vessel Design and Analysis PDFDocument10 pagesAdvances in ASME Section VIII Division 2 Pressure Vessel Design and Analysis PDFkuselanmlNo ratings yet
- Siemens PLM Femap Brochure 2019Document16 pagesSiemens PLM Femap Brochure 2019Ion PopescuNo ratings yet
- SpaceClaim 3D Simulation Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesSpaceClaim 3D Simulation Brochure PDFSahil JawaNo ratings yet
- FEMAP Student GuideDocument338 pagesFEMAP Student Guidec_e_z_a_r100% (3)
- ReadmeDocument170 pagesReadmeaskarahNo ratings yet
- CommandsDocument893 pagesCommandsΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουNo ratings yet
- ZbirkicaDocument520 pagesZbirkicaVladimir MilovanovicNo ratings yet
- NX NastranDocument20 pagesNX Nastranswift100% (1)
- Adina ModelisationDocument240 pagesAdina ModelisationSafia SoufiNo ratings yet
- Making Efficient Connections With RBE2 RBE3 Constraint Equations and CBUSH ElementsDocument24 pagesMaking Efficient Connections With RBE2 RBE3 Constraint Equations and CBUSH ElementsVignesh WaranNo ratings yet
- !commands Femap 11Document707 pages!commands Femap 11msariousNo ratings yet
- 01 - List of NASTRAN SOL Numbers and DescriptionDocument1 page01 - List of NASTRAN SOL Numbers and DescriptionffontanaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument98 pagesReadmejuand_121No ratings yet