Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Breathing Lab
Uploaded by
iheartfoodCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Breathing Lab
Uploaded by
iheartfoodCopyright:
Available Formats
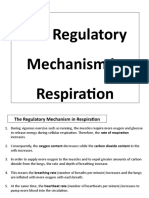
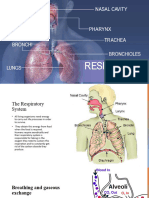
Controlling Rate of Respiration Discussion Post-lab questions: 1.
The average number of breaths per minute can be determined by counting the number of breaths during a three-minute period and then dividing the resulting value by three. In comparison to counting the actual number of breaths in a minute, finding an average is a more accurate representation of respiratory rate. If we were to count the number of breaths in a minute, the value could be easily skewered by slight breathing changes or other disturbances that may occur during that short period of time. A small error would end up having a large impact on the calculated rates. 2. Holding breath increases the level of carbon dioxide and decreases the level of oxygen in the body. Hyperventilating decreases the level of carbon dioxide and increases the level of oxygen in the body. Breathing into a paper bag increases the level of carbon dioxide and decreases the level of oxygen in the body. According to my results in both trials, after holding my breath for 45s, my breathing rate increased due to the lack of oxygen and the build-up of carbon dioxide. The increased breathing rate allows for greater intake of oxygen and quicker removal of excess carbon dioxide in the tissues. After hyperventilating, my breathing rate decreased in the first trial due to the high concentration of oxygen and low concentration of carbon dioxide in the body. In the second trial, my breathing rate increased because I changed my hyperventilating form. Instead of focusing on inhaling deeply followed by a shallow exhalation, I focused on shallow inhalation and forceful exhalation. Consequently, the intake of oxygen decreases in comparison to the first trial, causing an increase in breathing rate. During both trials, after breathing into a paper bag, my breathing rate increased and deepened due to the decrease of available oxygen in the paper bag and the increase in concentration of carbon dioxide as I exhaled into the bag. 3. Workers in a crowded, poorly ventilated office building have higher breathing rates. Under such conditions, the concentration of oxygen in the surrounding is low due to higher intake of by the crowd, and the concentration of carbon dioxide is high due to exhalation; hence, the workers have to inhale more frequently to obtain the oxygen needed by the body tissues, and exhale to expel the build-up of carbon dioxide in the body. 4. Both my classmates and my breathing rates increased after holding our breaths in order to increase the intake of oxygen and to expel the build-up of carbon dioxide in our body. However, our breathing rates increased by different amounts. This may be due to the difference in lung capacity. Greater lung capacity enables a person to take in more oxygen and expel more carbon dioxide in one breath, resulting in a smaller increase in breathing rates after holding breath as the body can quickly replenish the need for oxygen and remove excess carbon dioxide. In addition, after hyperventilating, some classmates have higher breathing rates while some have lower breathing rates. The increase or decrease is affected by the form of hyperventilation. Inhaling deeply followed by a shallow exhalation will increase the
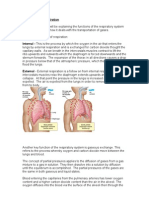
concentration of oxygen and decrease the concentration of carbon dioxide, resulting in decreased breathing rates. Shallow inhalation and forceful exhalation decreases the overall intake of oxygen, resulting in increased breathing rates. ___________________________________________________________________________ The purpose of this lab was to determine the effects of oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations on the rate of respiration, by comparing the resting breathing rate of a person to the resulting rate of breathing after holding breath, after hyperventilating and while breathing into a paper bag. The purpose was met by this experiment. Before the experiment, my class predicted that the concentration of carbon dioxide will have a greater control over the rate of respiration in comparison to the concentration of oxygen. We failed to reject our hypothesis. According to the general results of the class, breathing rates are most affected after holding breath and while breathing into a paper bag. These two conditions greatly increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in the body. Hyperventilating increases the concentration of oxygen in the body and therefore, has less impact on the change in breathing rates. Due to the higher concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere, oxygen is mostly present in abundance in the body regardless of whether a person holds his/her breath, is hyperventilating or is breathing into a paper bag. In addition, each breath provides an overabundance of oxygen. Consequently, the change in concentration of oxygen does not cause a drastic change in breathing rates. However, since carbon dioxide is present is small amounts both in the atmosphere and the human body, a slight change in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the body stimulates a greater response. Breathing rates increase more drastically to remove the build-up of carbon dioxide. Despite the precautions taken, there are a few sources of errors. Firstly, while breathing into a paper bag, air from the bag may leak out and air from the surrounding may enter the paper bag if it is held loosely against a persons mouth and nose. The mixing of air will cause the air breathe in from the paper bag to have similar concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide as air from the surroundings. This will hinder us from measuring the effect of increased concentrations of carbon dioxide on breathing rates as breathing rates will return to normal resting rates. Secondly, the form of hyperventilation affects the accuracy of the results. Inhaling deeply followed by a shallow exhalation decreases breathing rates. On the other hand, shallow inhalation and forceful exhalation increases breathing rates. Thirdly, the calculated breathing rates for each condition may not be the same as a persons natural breathing rates. While focusing on counting our breathing rates, we may subconsciously alter our rate of breathing, causing it to differ from actual breathing rates. The effects of oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations on breathing rates are related to the real world. During vigorous exercises, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the body increases, causing the depth and rate of breathing to increase. Moreover, similar to breathing into a paper bag, under poorly ventilated or crowded conditions, the concentration of carbon dioxide inhaled into the body increases as time passes due to the increased amount of exhaled air in the surroundings, causing an increase in breathing rates. Next, the partial pressure of
oxygen is lower at high altitudes; hence, humans hyperventilate to maximise the intake of oxygen and also to remove excess carbon dioxide. This lab can be extended by analysing the effects various types of music, such as jazz, rock, blues and dramatic music, have on breathing rates. In addition, for future experiments, the form of hyperventilation should be unified for more consistent results among students.
You might also like
- Health: How to get it and keep it: The hygiene of dress, food, exercise, rest, bathing, breathing, and ventilationFrom EverandHealth: How to get it and keep it: The hygiene of dress, food, exercise, rest, bathing, breathing, and ventilationNo ratings yet
- The Power of Breathing Techniques - Breathing Exercises for more Fitness, Health and RelaxationFrom EverandThe Power of Breathing Techniques - Breathing Exercises for more Fitness, Health and RelaxationNo ratings yet
- Respi ConclusionDocument1 pageRespi ConclusionMoira LarinNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)Document3 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)SkefadiutoNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Mechanism in RespirationDocument12 pagesRegulatory Mechanism in RespirationandrewadrianNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)Document3 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)Skefadiuto100% (2)
- Process of BreathingDocument3 pagesProcess of BreathingssmaddiNo ratings yet
- B. Inggris Kel 1Document9 pagesB. Inggris Kel 1davina mandaNo ratings yet
- 6 Human Respiration 2Document10 pages6 Human Respiration 2Harlee QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesRespiratory System Structure and FunctionRavi BhollahNo ratings yet
- Ideally It Is Shown You Should Breathe Lightly, in A Calm Fashion, and Only Through The Nose, Not MouthDocument10 pagesIdeally It Is Shown You Should Breathe Lightly, in A Calm Fashion, and Only Through The Nose, Not MouthS KNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory During ExerciseDocument3 pagesAssignment Respiratory During Exercisedomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Buteyko Theory: A Breathing DiscoveryDocument3 pagesButeyko Theory: A Breathing DiscoveryMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pages4.2 - Respiratory SystemBenJenkinsNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologySophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- 11 Lung PhysiologyDocument14 pages11 Lung PhysiologyGlen UrbaniNo ratings yet
- 10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeDocument33 pages10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesRespiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument5 pagesGas Exchange in HumansRAGHU RAM SAKAMURINo ratings yet
- Evens RespiortyDocument4 pagesEvens RespiortyamyhowarthNo ratings yet
- Forum Fisiologi SenamDocument3 pagesForum Fisiologi SenamErwan Sha HabinullahNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 - External RespirationDocument32 pagesExercise 15 - External RespirationAldrin LozanoNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ReportDocument19 pagesLab 6 Reportapi-311215267100% (2)
- Respiration SystemDocument15 pagesRespiration Systemapi-283243804No ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemSophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- BONUS CHAPTERS To THE BREATHING CURE by Patrick McKeown HUMANIX BOOKS 04 22 2021Document77 pagesBONUS CHAPTERS To THE BREATHING CURE by Patrick McKeown HUMANIX BOOKS 04 22 2021Charles Mitchell100% (1)
- Breathing: Breathing Is The Process That Moves Air in and Out of The LungsDocument5 pagesBreathing: Breathing Is The Process That Moves Air in and Out of The LungsArief Rachman WiladisastraNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationMemona KhalidNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Altitude PhysiologyDocument49 pagesMicrosoft Word - Altitude PhysiologyMetinee AngsutorntakNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Human (Word)Document4 pagesGaseous Exchange in Human (Word)Technical NihalNo ratings yet
- Buteyko Manual PDFDocument130 pagesButeyko Manual PDFPauloCarvalho92% (12)
- S H S, H: Indhi IGH Chool EbbalDocument23 pagesS H S, H: Indhi IGH Chool EbbaljyotiNo ratings yet
- Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Respiratory SystemRachelHatcher123No ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument18 pagesRESPIRATIONNur Rezki OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces: The Alveolus Is The Gas Exchange Surface in HumansDocument9 pagesFeatures of Gas Exchange Surfaces: The Alveolus Is The Gas Exchange Surface in HumansM. ShayanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument25 pagesOxygen TherapyIsaiah AmolatoNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (B3.1) Tuesday 30TH JanuaryDocument11 pagesBio Notes (B3.1) Tuesday 30TH JanuaryNeema Sarah MUTWIRINo ratings yet
- Name: Cauilan, Darwin C. Score: Year and Section: Bs Pharma 1-A Set A DateDocument3 pagesName: Cauilan, Darwin C. Score: Year and Section: Bs Pharma 1-A Set A DateDarwin CauilanNo ratings yet
- 6.4 QuestionsDocument18 pages6.4 QuestionsAurelija GardžiulytėNo ratings yet
- Biology QuizDocument8 pagesBiology Quizkathy abreuNo ratings yet
- Biology G - 9 Notes &practice Questions 2012Document41 pagesBiology G - 9 Notes &practice Questions 2012elroe wubshetNo ratings yet
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- Emsp 1355 !!! Co2Document17 pagesEmsp 1355 !!! Co2acctsacctsNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument15 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggrisfera kartikaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesBiology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10biologyDocument8 pagesChapter 10biologyAleena kazmiNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review NotesDocument36 pagesNCLEX Review NotesKyla Patricia RibanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument48 pagesLecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMZara16No ratings yet
- Pranayam 25Document1 pagePranayam 25B Prakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument46 pagesBreathingRamnaresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Breathing ExercisesDocument58 pagesBreathing Exerciseszafarmecan6137100% (3)
- Prana Shakti KriyaDocument8 pagesPrana Shakti KriyaAdeep SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Textbuk DiscussionDocument5 pagesTextbuk Discussionapi-3717941No ratings yet
- Assignment Gaseous ExchangeDocument10 pagesAssignment Gaseous ExchangefetramyraNo ratings yet
- English ChillaDocument8 pagesEnglish ChillaChilla Adis ViolitaNo ratings yet
- Safety Stations G1902: Guardian EquipmentDocument2 pagesSafety Stations G1902: Guardian Equipmenteisenbarger5607No ratings yet
- Softening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Document11 pagesSoftening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Thamilaarasan SonOf Nathan29% (7)
- Common Gain StageDocument37 pagesCommon Gain StageVincent ClaesNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT Heat BalanceDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT Heat BalanceYogesh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Input-Output Tracking System For Process MeasurementDocument4 pagesInput-Output Tracking System For Process MeasurementVipen MahajanNo ratings yet
- PERFORMANCEDocument4 pagesPERFORMANCEKorong KapampanganNo ratings yet
- TWT Twta HandbookDocument133 pagesTWT Twta HandbookMudassar RafiqNo ratings yet
- Infineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enDocument15 pagesInfineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enAbohicham AbhNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communications: Systems, Modulation, and Noise, 7Document2 pagesPrinciples of Communications: Systems, Modulation, and Noise, 7Rahul MenonNo ratings yet
- Manual Book 500XDocument72 pagesManual Book 500XDadung PrakosoNo ratings yet
- What Is Virtualization AssignmentDocument27 pagesWhat Is Virtualization Assignmentedscott66No ratings yet
- RDMC - Cairo Metro Line-3 Checklist 03-02: Rail - Greasy Status Check PreventiveDocument1 pageRDMC - Cairo Metro Line-3 Checklist 03-02: Rail - Greasy Status Check PreventiveMina AlbertNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportDocument51 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportAvay SinghNo ratings yet
- 014 A5.2 Floor FinishesDocument1 page014 A5.2 Floor FinishesqgfytzvqabzqrxyilmNo ratings yet
- TorquesDocument108 pagesTorquesnaruxzNo ratings yet
- Optimize Magnetic GapDocument45 pagesOptimize Magnetic GapteomondoNo ratings yet
- Non-Concurrent Space ForcesDocument2 pagesNon-Concurrent Space ForcesJessica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To The Design of Super-DirectiveDocument12 pagesA New Approach To The Design of Super-DirectiveAnonymous P2ZN8X100% (1)
- Ford Explorer CodigosDocument183 pagesFord Explorer Codigosjose gabriel0% (1)
- The Chattering Problem in Sliding Mode SystemsDocument8 pagesThe Chattering Problem in Sliding Mode SystemsBhaskar BiswasNo ratings yet
- Get Going With Ibank 4: © For Site UsersDocument100 pagesGet Going With Ibank 4: © For Site UserstxtgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Asterix Adsbtr Cat021 Part12 v2 6Document91 pagesAsterix Adsbtr Cat021 Part12 v2 6DAI XUANLINGNo ratings yet
- The CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors ExaminationDocument5 pagesThe CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors Examinationgreg mNo ratings yet
- Draft SOP For Usage of Tree PrunerDocument2 pagesDraft SOP For Usage of Tree PrunerAkhilesh Kumar Singh100% (1)
- HDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtDocument20 pagesHDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtsetavietnamNo ratings yet
- Weinig Rondamat 960 PDFDocument16 pagesWeinig Rondamat 960 PDFCimpean AlexandruNo ratings yet
- P091 067 UmDocument208 pagesP091 067 UmBojan MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Goals of True Broad Band's Wireless Next Wave (4G-5G)Document5 pagesGoals of True Broad Band's Wireless Next Wave (4G-5G)alokcena007No ratings yet
- DM Automatic Irrigation System SpecsDocument56 pagesDM Automatic Irrigation System SpecsSarfraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dynamic (Vibration) Testing: Design-Certification of Aerospace SystemDocument16 pagesDynamic (Vibration) Testing: Design-Certification of Aerospace SystemCamelia MunteanuNo ratings yet