Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Haemodynamic Pocket Guide
Uploaded by
Darryl BettsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Haemodynamic Pocket Guide
Uploaded by
Darryl BettsCopyright:
Available Formats
hemo_mont.
qxd
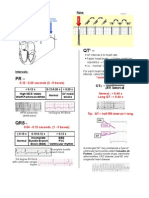
(sec) Hemodynamic Monitoring Determining the Accuracy of Hemodynamic Values
0.1 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 Parameter Normal Importance Steps Technique How often should it
Value be done?
REF
PR, QRS, and QT interval
SvO2 60-70% The SvO2 helps identify which Level the trans- Place any stopcock at the phle- Only if the patient has
Indicates adequacy of blood pressue and cardiac ducer to the phle- bostatic axis. Patient should moved from the origi-
tissue oxygenation, the output are acceptable for bostatic axis be supine. Elevation can be nal position. Relevel if
11/1/00
primary reason many each patient. from flat to 45 degrees reading has unexplain-
30
ably changed.
MM
patients receive hemo-
dynamic monitoring
Zero the With the stopcock off to the Must zero on initial
Stroke Index (SI) 25-45 Used in conjunction with cardiac Transducer/amplifier patient and open to air, cap setup. Rezero if read-
1
How much blood is ml/m2 pressures to diagnose and removed and leveled at the phle- ings have unexplain-
Heart rate at 25 mm/sec (Measure two cardiac cycles from the reference arrow)
pumped with each beat evaluate treatment. bostatic axis, activate the moni- ably changed.
35
8:03 AM
referenced against body tor’s zero function. Close trans-
Hemodynamic size. ducer to air and open to patient
2
and then recap stopcock.
Cardiac Index 2.5-4.0 Not as early an indicator of a
Monitoring How much blood is L/m/m2 hemodynamic problem as stroke Perform a square Activate the fast flush device Prior to obtaining
40
pumped during one index due to the compensating wave test. The and release. Interpret the readings
3 minute reference role of heart rate when stroke square wave test response.
Page 1
against body size. It is index is low. checks the accura- See illustration below It is better way of
45
a product of stroke cy of the tubing/ verifying the arterial
index and heart rate catheter system. line accuracy than
4
the blood pressure
50
Pulmonary artery About Useful in assessing response to cuff comparison.
pressure (PAP) 25/10 therapies for pulmonary
55
mmHg hypertension. Normally not a
Performing Square Wave Test
5
primary parameter in assessing
60
hemodynamics. Characteristics Illustration How to correct? Clinical Result
Pulmonary artery About When the stroke index is low,
Waveforms are
70
occlusive pressure 8-12 the PAOP helps differentiate left Optimal Dampening No necessary
6
(PAOP or wedge) mmHg ventricular dysfunction 1) Should have a small correction accurately
overshoot, followed by reproduced
100 90 80
(PAOP>12mmHg) and
hypovolemia (PAOP< 8mmHg). a small overshoot
(about 1/3 the distance
7
Central venous pressure About When stroke index is low, the of the undershoot)
(CVP) 2-6 mmHg CVP helps differentiate right ven- 2) Should have 1-2 blocks
Right atrial pressure. A tricular dysfunction (CVP> 6 between oscillations
reflection of right ven- mmHg) and hypovolemia (CVP is
Under Dampening 1) Remove
8
200 150
tricular end diastolic normal or < 2 mmHg.
pressure. The CVP is an 1) Either extra oscillations excess tubing.
estimation of preload. are present or 2) Insert
2) Prolonged distance dampening
Blood Pressure Varies with A common less invasive form of (more than 2 blocks device
9
400 300
Reflects pressure in sys- site, size, estimating blood flow. With between bounces.
temic arterial system. age and hemodynamic monitoring
sex. available (SvO2, SI, CI), blood Over Dampening Find source of Systole is artifi-
cially depressed,
10
pressure is less useful. 1) Obstruction in line problem.
REF prevents oscillation 1) Air in line diastole may be
A supplement to CRITICAL CARE NURSE® Systemic Vascular 900-1300 Often used to assess the 2) Note slurring on 2) Blood in line higher than
Resistance (SVR) dynes/sec/ response of arterial dilators. downstroke. 3) Kink in tub- actual.
cm5 ing/catheter Use mean
values if unable
to correct.
5968-6249E Printed in the USA, July 1999
hemo_mont.qxd
How to read a CVP waveform How to read a Right Ventricular & PA waveform Avoiding Respiratory Artifact
Method Technique Indications Waveform Characteristics Example Types of How to Read Example
Artifact
Pre C wave Find the c Theoretically the Right Ventricular 1) Rapid upstroke to
wave on the most sound waveform systole. Systole found Patient initiated - 1) Locate where the
downstroke of method. Use this after the QRS but before includes baseline drops
the a wave method if possible the T-wave. spontaneous 2) Read the last
11/1/00
(usually near 2) Terminal diastolic breathing and clear wave before
the end of the rise-diastole found near patient initiated the drop occurs
QRS complex) the end of the QRS ventilator breaths
complex
Pulmonary 1) Rapid upstroke to
Artery waveform systole. Systole found
8:03 AM
after the QRS but before
the T-wave.
2) Progressive diastolic
runoff-diastole found Mechanical 1) Locate where the
Average of the Find the a Often the easiest near the end of the Ventilation baseline moved
a-c waves wave in the to use since the c QRS complex. upward
Page 2
PR interval. waves are not 3) A dicrotic notch (closure 2) Read the last
Locate top always visible. Use of the pulmonic valve) is clear wave before
and bottom this method if c sometimes visible during the baseline
of a-c wave. wave is not the progressive diastolic elevates.
Average the present. runoff.
two values.
How to read a PAOP waveform
Avoiding Abnormal Waveforms
Method Technique Indications
Clinical How to Read Example
Average of the Find the a wave Often the easiest Situation
a-c waves after the QRS to use since the c
complex. Locate waves are not Large V wave Locate the pre c point
top and bottom always visible. Common with or the mean of the a-c
Z point Draw a line Use this method CHF wave before the large V
down from when no clear a of a-c wave. Use this method
Average the if c wave is not wave.
the end of or c wave present.
the QRS (e.g. atrial two values. present
complex. fibrillation and
Where the paced rhythms)
line hits the
baseline, is
the CVP
reading. Large or absent a Use the Z point method.
Z point Draw a line down Use this method
from about .08 to when no clear a wave
.12 seconds after or c wave present
the QRS complex. (e.g. atrial fibrilla-
Where the line hits tion and paced
the baseline, is the rhythms)
PAOP reading.
You might also like
- Respiratory Therapy Formulas and Values GuideDocument1 pageRespiratory Therapy Formulas and Values Guidelizzy59683% (6)
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (17)
- Critical Care Survival GuideDocument2 pagesCritical Care Survival Guidetringalama100% (4)
- ABG InterpretationDocument1 pageABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocument1 pageTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (2)
- Critical Care Intravenous DrugsDocument1 pageCritical Care Intravenous DrugsMarynel Dixie Izon Brao89% (9)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- Cheatsheet 5Document1 pageCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocument1 page(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Electrolyte CompleteDocument6 pagesElectrolyte CompleteTofan Ana100% (2)
- Cheatsheet 4Document1 pageCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNo ratings yet
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (25)
- DRUG TITRATION GUIDEDocument2 pagesDRUG TITRATION GUIDEEgi Munandar100% (1)
- CCRN PulmonaryDocument107 pagesCCRN PulmonaryCzarina Charmaine Diwa100% (4)
- MAP, CO, and SV+HRDocument11 pagesMAP, CO, and SV+HRjenwiley318096% (73)
- Role of Critical Care Nurses in Caring for Critically Ill PatientsDocument10 pagesRole of Critical Care Nurses in Caring for Critically Ill PatientsHanis Rozib99% (69)
- Hemodynamic Assessment ParametersDocument2 pagesHemodynamic Assessment ParametersalexNo ratings yet
- Icu GuidebookDocument43 pagesIcu Guidebookdrimran570100% (4)
- Critical Care NotesDocument18 pagesCritical Care NotesjulieNo ratings yet
- CCRN CardiacDocument39 pagesCCRN CardiacMike100% (5)
- ABG Made EasyDocument10 pagesABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocument1 pageCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Respiratory Therapy Pocket Reference: Ifnopt TriggerDocument2 pagesRespiratory Therapy Pocket Reference: Ifnopt TriggermohamedkorieshNo ratings yet
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- Critical Care Calculations Study GuideDocument6 pagesCritical Care Calculations Study GuideAja Blue100% (2)
- Boot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument37 pagesBoot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringTinaHo100% (7)
- EKG ExamplesDocument9 pagesEKG ExamplesMayer Rosenberg99% (235)
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasNo ratings yet
- The Ventilator BookDocument126 pagesThe Ventilator BookAlberto David100% (22)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Hemodynamic Monitoring in ICUDocument111 pagesHemodynamic Monitoring in ICUManjunath Gemini100% (2)
- Haemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideFrom EverandHaemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideNo ratings yet
- Ccrn Certification Examination Practice Questions and Answers with Rationale: First EditionFrom EverandCcrn Certification Examination Practice Questions and Answers with Rationale: First EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Surviving the ICU: A Toolkit for the Critical Care NurseFrom EverandSurviving the ICU: A Toolkit for the Critical Care NurseNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyFrom EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Adult CCRN Exam Flashcards, Second Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAdult CCRN Exam Flashcards, Second Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!From EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!No ratings yet
- Respiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesFrom EverandRespiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Outline of Critical Care Nursing: 250 Review QuestionsFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Critical Care Nursing: 250 Review QuestionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Advanced Practice in Critical Care: A Case Study ApproachFrom EverandAdvanced Practice in Critical Care: A Case Study ApproachSarah McGloinNo ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasFrom EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Basic Plastic Surgery Techniques and Principles: How To SutureDocument3 pagesBasic Plastic Surgery Techniques and Principles: How To SutureDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- HPCSA Clinical Practice Guidelines 2016 - Request For CommentDocument218 pagesHPCSA Clinical Practice Guidelines 2016 - Request For CommentDarryl Betts50% (2)
- Riding The Waves Handout R6Document35 pagesRiding The Waves Handout R6Darryl Betts100% (2)
- Muscle PhysioDocument11 pagesMuscle PhysioDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- Esophageal PressuresDocument10 pagesEsophageal PressuresDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- CE/Gunshot Wounds: A PrimerDocument10 pagesCE/Gunshot Wounds: A PrimerDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- Skin CancerDocument16 pagesSkin CancerDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- Esophageal PressuresDocument10 pagesEsophageal PressuresDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck ExaminationDocument25 pagesHead and Neck ExaminationDarryl Betts100% (1)
- Welcome To The IV TherapyDocument21 pagesWelcome To The IV TherapyDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- ECGsDocument30 pagesECGsDarryl Betts100% (1)
- Key Terms: Chapter 19: Coagulation DisordersDocument16 pagesKey Terms: Chapter 19: Coagulation DisordersDarryl Betts100% (1)
- Comparison of BenzodiazepinesDocument8 pagesComparison of BenzodiazepinesDarryl BettsNo ratings yet
- Breast Disease and Examination: Dr. Tim CoughlinDocument34 pagesBreast Disease and Examination: Dr. Tim CoughlinDarryl Betts100% (3)
- ALS ProtocolsDocument134 pagesALS ProtocolsDarryl Betts71% (24)
- Pulse Oximetry and The Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve: I. II. Iii. IV. A. B. C. D. V. VI. Vii. A. B. C. D. Viii. IX. XDocument11 pagesPulse Oximetry and The Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve: I. II. Iii. IV. A. B. C. D. V. VI. Vii. A. B. C. D. Viii. IX. XDarryl Betts50% (2)
- The Vascular Examination: DR Karan WadhwaDocument21 pagesThe Vascular Examination: DR Karan WadhwaDarryl Betts100% (1)
- Technical Bro A4 UK LR NEW v2Document45 pagesTechnical Bro A4 UK LR NEW v2Roxana NegoitaNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument2 pagesClassification of Matterapi-280247238No ratings yet
- Tipolo WH Gantt ChartDocument15 pagesTipolo WH Gantt ChartMayeterisk RNo ratings yet
- Karan Chawla and Joshua Lee November 21, 2016 MEDS 3020 - Fall 2016 Dr. Rosevear, Dr. Cartwright, Dr. LiebermanDocument2 pagesKaran Chawla and Joshua Lee November 21, 2016 MEDS 3020 - Fall 2016 Dr. Rosevear, Dr. Cartwright, Dr. LiebermanJeremy DelaneyNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Unit 9 - Probability: Lesson 1: "Sample Spaces, Subsets, and Basic Probability"Document87 pagesMath 2 Unit 9 - Probability: Lesson 1: "Sample Spaces, Subsets, and Basic Probability"Anonymous BUG9KZ3100% (1)
- EVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFDocument80 pagesEVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFgibonulNo ratings yet
- Clinnic Panel Penag 2014Document8 pagesClinnic Panel Penag 2014Cikgu Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareDocument14 pagesUser Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareComputershastriNoproblem0% (1)
- JC Metcalfe - The Power of WeaknessDocument3 pagesJC Metcalfe - The Power of Weaknesschopin23No ratings yet
- Roxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaDocument2 pagesRoxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaJennilyn omnosNo ratings yet
- How To Use Hyper-V Snapshot Revert, Apply, and Delete OptionsDocument15 pagesHow To Use Hyper-V Snapshot Revert, Apply, and Delete OptionsKaran MishraNo ratings yet
- Biology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument10 pagesBiology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeRicky MartinNo ratings yet
- 60Hz Axial-Fan Centrifugal-Fan AC EN (2009) PDFDocument136 pages60Hz Axial-Fan Centrifugal-Fan AC EN (2009) PDFRodrigo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Critical Thin...Document7 pagesChapter 1 Critical Thin...sameh06No ratings yet
- 341SAM Ethical Leadership - Alibaba FinalDocument16 pages341SAM Ethical Leadership - Alibaba FinalPhoebe CaoNo ratings yet
- OJT Form 03 Performance EvaluationDocument2 pagesOJT Form 03 Performance EvaluationResshille Ann T. SalleyNo ratings yet
- Catalogue MinicenterDocument36 pagesCatalogue Minicentermohamed mahdiNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Wood WasteDocument14 pagesUtilization of Wood WasteSalman ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Otis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallDocument20 pagesOtis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallveersainikNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual 11-3000psi Shear Ram BopDocument30 pagesOperation Manual 11-3000psi Shear Ram BopBoedi SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Nanofil Manual PDFDocument5 pagesNanofil Manual PDFJuliana FreimanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDiego S. FreitasNo ratings yet
- What Are Your Observations or Generalizations On How Text/ and or Images Are Presented?Document2 pagesWhat Are Your Observations or Generalizations On How Text/ and or Images Are Presented?Darlene PanisaNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument28 pagesColor TheoryEka HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Mpce 24Document39 pagesMpce 24Sachin Mehla0% (1)
- Cognitive Clusters in SpecificDocument11 pagesCognitive Clusters in SpecificKarel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Amity Online Exam OdlDocument14 pagesAmity Online Exam OdlAbdullah Holif0% (1)
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadAnonymous ffje1rpaNo ratings yet
- 42U System Cabinet GuideDocument68 pages42U System Cabinet GuideGerman AndersNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Penggunaan Refrigeran R22 Dengan R407 Pada Performa ACDocument15 pagesPerbandingan Penggunaan Refrigeran R22 Dengan R407 Pada Performa ACYuli RahmawatiNo ratings yet