Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life of King Arthur
Uploaded by
Michaela KrishiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life of King Arthur
Uploaded by
Michaela KrishiaCopyright:
Available Formats
LIFE OF KING ARTHUR Father King Uther of Pendragon Mother Duchess Igraine (wife of Duke Gorlois of Cornwall) Morgause
se - daughter of Duke Gorlois and Duchess Igraine Half-sister of King Arthur Mother of Mordred/Modred Mordred - son of Morgause and King Arthur, accused Guinevere of adultery
Merlin wizard friend of King Arthur and King Uther Sir Hector foster father of King Arthur Guinevere - wife of King Arthur Camelot - seat of King Arthurs court Excalibur magic sword of King Arthur Sir Lancelot friend and champion knight of King Arthur Sir Bedivere only survivor in the war between Arthur and Mordred Lady of the lake took the Excalibur when it was thrown by Sir Bedivere Avalon - an island where Arthur was brought and healed by Monte Le Fay
MEDIEVAL PERIOD 1066-1485 Characteristics: I. The Normans conquered England by defeating the Anglo-Saxons in the Battle of Hastings in 1066.
II. The Normans introduced a social, economic and political system called Feudalism. * Under this system, land was divided among noble overlords who were served by knights for military protection and serfs who farmed the land and herded the animals. III. The knights tried to live according to the Code of Chivalry which required them to be honorable, courteous, brave and skillful. IV. The concept of Chivalry played an important role in shaping the literature of the Medieval Period. * When chivalry was blended with such magical elements as giants, wizards, sorcerers and dragons, the form of literature romance was created. Romance - a story that presents remote or imaginative incidents rather than ordinary, realistic experiences - filled with fantasy, adventure and courtly love - was originally used to refer to medieval tales of the deeds and loves of noble knights and ladies Characteristics of Medieval Romances: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Embody the ideals of chivalry Set in a remote time and place Emphasize rank and social distinction Convey a sense of the supernatural Present a hero engaged in pure adventure Include love as a major plot element Feature spontaneous, unmotivated fighting
V. Most of the literature of the period reflected the influence of religion. This influence is most noticeable in the two forms of drama: 1. Mystery Play a name given to any of the Biblical plays performed during the Medieval Period - was derived from Latin ministerium not from mysterium
- was performed on pageants (stages built on large wagons)
- based on Bible stories
2. Morality Play a medieval drama in which the characters are personified abstractions: *based on saints lives or apocryphal miracles of the Virgin
Everyman, Good Deeds, Faith, Mercy, Anger, etc.
* was used to inculcate ethical or educational ideals and to provide thinly disguised political commentary or satire Two themes of religious moralities: a. the struggle between good and evil powers for b. the journey or the pilgrimage of life * Everyman the oldest surviving English morality play 1. The fighting nobleman during the Middle Ages was an object of great respect and even of veneration. mans soul
2. The knight was accorded the highest rank of society 3. The knight was not only a warrior but also a lover. 4. The system of knighthood elevated the position of women into one of great importance. (Reasons: religious revival of the Medieval Ages, growing devotion to the Virgin Mary all over Europe) * The knight worshipped women because Mary was a woman. * The knight was bound to womanhood by oath of homage and fealty; he could not be faithless, he had to act according to a set formula, he had to win his ladylove by his faithfulness, patience, manliness and warlike skill. ARTHURIAN ROMANCES The perfection of Knighthood as well as the mystic element was fully represented in the Arthurian Romances. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. was married to Guinevere had a mysterious and magic birth his career a marvelous one he surrounded himself with 12 Knights Sir Gawain Sir Percival Sir Tristan/Tristam Sir Lancelot Sir Lamoracke Sir Galahad 7. Sir Gareth 8. 9. Sir Kay Sir Bors
10. Sir Bedivere 11. Sir Tor 12. Sir Modred
SIR THOMAS MALORY (1449 1471) He grow up in the finest ideals of chivalry He lived and died a knight Author of Le Morte DArthur
*Le Morte D Arthur considered a complete story of Arthur and his knights of the Round Table - this was completed about 1469 - the first edition of the book was published in 1485 by William Caxton, the first English printer *The Round Table the gift received by King Arthur - designed to prevent jealousy - symbolizes the equality of the knights
Run-on Sentence vs. Complete Sentence Complete Sentences A complete sentence has a subject and a predicate that work together to make a complete thought. Run-On Sentences A RUN-ON SENTENCE (sometimes called a fused sentence) has at least two parts, either one of which can stand by itself, but the two parts have been connected together with one or two words instead of becoming two sentences. Run-On Sentences Remember: The length of a sentence really has nothing to do with whether a sentence is a run-on or not; even a very short sentence could be a run-on. Run-On Sentences When two clauses are connected by only a comma, they are a run-on sentence that is called a comma-splice. Run-On Sentences happen when an independent clause gives an order or directive based on what was said in the prior independent clause. Run-On Sentences happen when two clauses are connected by words such as however, moreover, nevertheless. Four Ways to Correct Run-ons 2. Join the clauses with a subordinating conjunction such as because, although, if,when,since,after. -Because the fuse burned too quickly before he could throw it, the explosive blew up between his legs. 3.Make the clauses into separate sentences. 4. Join two independent clauses with a semicolon (;)if they are closely related.
DATA GATHERING TECHNIQUES Sources of Data 1. 2. Primary Source- based on first hand information. Secondary Source- based on completed study, books, and encyclopedia.
METHODS OF COLLECTING DATA
1. Direct 2. Indirect 3. Observation 4. Experiment 5. Registration SAMPLING: Is a method of selecting the sample from a given population.
How is sample determined? Some social researchers adopt the following simple rules regarding the determination of sample size.
1. For heterogeneous groups; Either n=50 or n= 30%of N That is, n= 0.30x N, whichever is higher. 2. For homogeneous groups: N = at least 10% of the population For example, if N =128, then 10%of N= 0.10 x 128= 12.8 or 13. Thus, the sample size n=13 or more. Note: the closer the value of n is to N, the better it approximates the characteristics of the population. 3. Others; Using the formula: n= N 1+Ne2 where e = desired margin of error ( percentage allowed for non-precision because of the use of the sample instead of the population) Example: If the population is 5,000 and the margin of error you allow is 5%, then the representative sample is computed as follows: n= N/ 1+Ne2 n= 5,000 1+5,000(0.05)2 n= 370.37 or simply 370 Sampling Techniques - is a procedure that is used to find out the members of the sample. A. Probability Sampling -wherein every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected as members of the sample. 2. Systematic Sampling -the parent population is finite, the individual maybe numbered and arranged in order. Advantage: Easy to perform Disadvantage: the interval may correspond to a hidden agenda or periodicity.
Example: A systematic sample might yield biased results if one interviewed the residents of every 10th house along a certain route and it so happened that every 10th house selected is a corner house. 3.Stratified Random Sampling -this sampling procedure is used when the population contains different strata or subgroups. Advantage: the different subgroups are represented in the sample. Example: 4. Cluster Sampling -this method selects a sample containing either all, or a random selection, of the elements from clusters that have themselves been selected randomly from a population. It is appropriate when: The population is homogenous but scattered. When the clusters are geographic areas such as subdivisions of a city, this kind of sampling is also called Area Sampling. the research plan requires direct observation of the respondents and their environment or face-to-face interviews. Advantage: It is efficient over simple random sampling and less costly. Nonprobability Sampling Techniques In this method, not all members of the population have an equal chance of becoming a part of the sample. 1. Quota Sampling In this method, a researcher is simply given quotas to be filled from different strata, with few (if any) restrictions on how they are to be filled. The method of selection of the individuals is left to the researchers discretion. It is also known as judgment samples 2. Purposive Sampling In this method, the researcher selects individuals who according to his/her judgment, represent the target population. For example, if one wished to interview the barangay officials of a particular district, the respondents are limited to those who suit the purpose of the interviewer. 3. Accidental Sampling This is the weakest type of nonprobability sampling. The sample usually consists of individuals who are in the vicinity by accident when the researcher gathers information. Exercises 1. 2. 3. Find the sample size from a population of 18, 000 with 1% margin of error. What margin of error was used if the sample size is drawn from a population of 40, 000 is 2, 500? A T.V. journalist would like to know the most favorite noontime show for this month. He decided to conduct a survey on 5 barangays.
Below are the no. of residents in each barangay. Use Stratified random sampling to draw 1,000 residents to be included in the survey. Barangays Mapayapa Maganda Makisig Malinis Mahangin 2,000 1,000 1,500 2,500 1,500 N= 8,500 n = 1,000 No. of Residents
You might also like
- Republic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission ManilaDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission ManilaMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income, Collections and Related TransactionsDocument12 pagesAccounting For Income, Collections and Related TransactionsMichaela Krishia100% (1)
- Internal Factors 2. Swot AnalysisDocument1 pageInternal Factors 2. Swot AnalysisMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- Internal Factors 2. Swot AnalysisDocument1 pageInternal Factors 2. Swot AnalysisMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- Otaku Guild (Form Girl)Document1 pageOtaku Guild (Form Girl)Michaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Mrs. Lorena BolorDocument7 pagesSubmitted To: Mrs. Lorena BolorMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- Business Firm As SystemDocument20 pagesBusiness Firm As SystemMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- History of Computing HardwareDocument5 pagesHistory of Computing HardwareMichaela KrishiaNo ratings yet
- ABC's of Technical WritingDocument6 pagesABC's of Technical WritingMichaela Krishia56% (9)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Thomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFDocument433 pagesThomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFMarcelo Ramos100% (2)
- Complete PDFDocument495 pagesComplete PDFMárcio MoscosoNo ratings yet
- Power and MagicDocument40 pagesPower and MagicSandro AmoraNo ratings yet
- FJ&GJ SMDocument30 pagesFJ&GJ SMSAJAHAN MOLLANo ratings yet
- HW 3 or MethodsDocument5 pagesHW 3 or Methodsaidoutza2101No ratings yet
- Proper AdjectivesDocument3 pagesProper AdjectivesRania Mohammed0% (2)
- ObliCon Digests PDFDocument48 pagesObliCon Digests PDFvictoria pepitoNo ratings yet
- SassigbmentDocument7 pagesSassigbmentFurkaan Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFDocument16 pagesTop 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFmohammed arsalan khan pathan100% (1)
- Focus Group DiscussionDocument13 pagesFocus Group DiscussionSumon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Conrail Case QuestionsDocument1 pageConrail Case QuestionsPiraterija100% (1)
- List de VerbosDocument2 pagesList de VerbosmarcoNo ratings yet
- Hedonic Calculus Essay - Year 9 EthicsDocument3 pagesHedonic Calculus Essay - Year 9 EthicsEllie CarterNo ratings yet
- Biology - Solved ExamDocument27 pagesBiology - Solved ExamlyliasahiliNo ratings yet
- STAFFINGDocument6 pagesSTAFFINGSaloni AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sample Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesSample Midterm ExamRenel AluciljaNo ratings yet
- Trudy Scott Amino-AcidsDocument35 pagesTrudy Scott Amino-AcidsPreeti100% (5)
- Chinese AstronomyDocument13 pagesChinese Astronomyss13No ratings yet
- Contents Serbo-Croatian GrammarDocument2 pagesContents Serbo-Croatian GrammarLeo VasilaNo ratings yet
- Signalling in Telecom Network &SSTPDocument39 pagesSignalling in Telecom Network &SSTPDilan TuderNo ratings yet
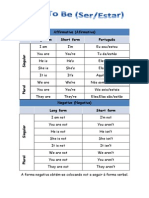
- Affirmative (Afirmativa) Long Form Short Form PortuguêsDocument3 pagesAffirmative (Afirmativa) Long Form Short Form PortuguêsAnitaYangNo ratings yet
- Challenges For Omnichannel StoreDocument5 pagesChallenges For Omnichannel StoreAnjali SrivastvaNo ratings yet
- Simple Future Tense & Future Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesSimple Future Tense & Future Continuous TenseFarris Ab RashidNo ratings yet
- Leg Res Cases 4Document97 pagesLeg Res Cases 4acheron_pNo ratings yet
- Yukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+41Document17 pagesYukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+410191720003 ELIAS ANTONIO BELLO LEON ESTUDIANTE ACTIVONo ratings yet
- Functions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan ADocument29 pagesFunctions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan AsrinivasanaNo ratings yet
- WO 2021/158698 Al: (10) International Publication NumberDocument234 pagesWO 2021/158698 Al: (10) International Publication Numberyoganayagi209No ratings yet
- Problem ManagementDocument33 pagesProblem Managementdhirajsatyam98982285No ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaDocument16 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaSubhro ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Pentecostal HealingDocument28 pagesPentecostal Healinggodlvr100% (1)