Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus Summary
Uploaded by
Jay JayCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculus Summary
Uploaded by
Jay JayCopyright:
Available Formats
Tom Penick tom@tomzap.com www.teicontrols.
com/notes 6/11/2001
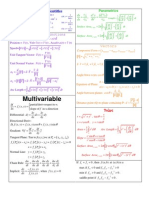
CALCULUS SUMMARY
A quick reference on Exponents, Logarithms, Differentiation, Integration, Power Series
Exponents
b
x
> 0 b b
x y
if and only if x y
b b b
x y x y
+
( ) b b
x y xy
b b b
x y x y
/
a e
x x a
ln
Logarithms
Natural Logarithmic Function f x x x
e
( ) log ln The
natural number e 2 71828182846 . . To get this
number on the calculator, press 1 INV lnx.
log
e
x is written ln x (read "el - en - ex")
1/
0
lim(1 )
x
x
e x
+ ln x b if and only if e x
b
lim ln
x
x
+
0
limln
x
x
.
lne x
x
e b
a b a ln
ln ln ln xy x y + ln ln ln
x
y
x y
ln ln x y x
y
Logarithms to other bases:
y x
a
log if and only if
y
a x
log log log
a a a
xy x y +
log log log
a a a
x
y
x y
log log
a
y
a
x y x
log
log
log
a
b
b
x
x
a
A calculator can be used to evaluate an expression such as
log
2
14 by virtue of the fact that it is equivalent to ln14/ ln 2 .
RULES OF DIFFERENTIATION
(where u is a function of x)
The derivative of a constant is 0.
The power rule: the derivative of
n
x is
1 n
nx
.
The general power rule*:
d
dx
n n
u nu u
1
The constant multiple rule:
d
dx
c u c u ( )
The sum and difference rule:
d
dx
u v u v ( ) t t
*The General Power rule is a special case of the Chain rule.
The product rule:
d
dx
u v u v u v ( ) +
The quotient rule:
d
dx
u
v
v u u v
v
_
,
2
The chain rule*: ( ) ( )
d d d
dx du dx
f u f u u
The absolute value rule: , 0
d
dx
u
u u u
u
Exponential functions: ( ) ( )
d
dx
x x
a a a ln
( ) ( )
d
dx
u u
a a a u ln
The natural number e:
d
dx
u u
e e u ( )
The natural log:
d
dx
x
x
(ln )
1
d
dx
u
u
u
(ln )
d
dx
u x
u
x
x u ( ln ) ln +
Logarithms to other bases: ( )
d
dx a
x
a x
log
(ln )
1
( )
d
dx a
u
a u
u log
(ln )
1
Trigonometric formulas:
(sin ) cos
d
u u u
dx
(cos ) sin
d
u u u
dx
( )
2
tan sec
d
u u u
dx
(sec ) sec tan
d
u u u u
dx
2
(cot ) csc
d
u u u
dx
(csc ) csc cot
d
u u u u
dx
2
[arcsin ]
1
d u
u
dx
u
d
dx
u
u
u
[arccos ]
1
2
2
[arctan ]
1
d u
u
dx u
+
2
[arccot ]
1
d u
u
dx u
+
2
[arcsec ]
1
d u
u
dx
u u
2
[arccsc ]
1
d u
u
dx
u u
( ) sinh cosh
d
u u u
dx
( ) cosh sinh
d
u u u
dx
Example of the general power rule with trigonometric functions:
d
dx
x
d
dx
x x x x x (sin ) (sin ) (sin ) cos sin cos
3 3 2 2
3 3
Tom Penick tom@tomzap.com www.teicontrols.com/notes 6/11/2001
RULES OF INTEGRATION
The basic formula: x dx
x
n
C
n
n
+
+
+
1
1
Constants: 0 dx C
dx x c +
k dx kx C +
k f x dx k f x dx ( ) ( )
The sum and difference rule:
[ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( ) f x g x dx f x dx g x dx t t
Fractional functions:
1
x
dx x C +
ln
1
u
du u C +
ln
u
u
dx u C ln
Exponential functions: a dx
a
a C
x x
_
,
+
1
ln
The natural number e: e dx e C
x x
+
e dx
u
e C
u u
1
xe dx x e C
x x
+
( ) 1
2
( 1)
ax
ax
e
xe dx ax C
a
+
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( )
2
1 / 2
0
/ 2 1 / 2
1 / 2 !
for odd
2
1 3 5 1
for even
2
n
n ax
n n
n
n
a
x e dx
n
n
a
a
+
+
1
]
L
Composite function where u is a function of x:
f u u dx F u C ( ) ( ) +
The general power rule: u u dx
u
n
C
n
n
+
+
+
1
1
Integration by parts; try letting dv be the most
complicated portion of the
integrand that fits an
integration formula:
The definite integral where f(x) is the derivative of F(x):
[ ] f x dx F b F a F x
a
b
a
b
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
Second degree polynomials for p x Ax Bx C ( ) + +
2
:
p x dx
b a
p a p
a b
p b
a
b
( ) ( ) ( )
_
,
+
+
_
,
+
1
]
1
6
4
2
Trigonometric formulas:
1
sin cos u dx u C
u
+
1
cos sin u dx u C
u
+
sec lnsec tan udu u u C + +
sec tan
2
udu u C +
sec tan sec u udu u C +
csc ln csc cot u du u u C + +
csc cot
2
udu u C +
csc cot csc u udu u C +
tan ln cos udu u C +
cot ln sin udu u C +
du
a u
u
a
C
2 2
arcsin
du
a u a
u
a
C
2 2
1
+
+
arctan
du
u u a
a
arc
u
a
C
2 2
1
sec
sin sin
2
1
2
1
4
2 udu u u C +
cos sin
2
1
2
1
4
2 udu u u C + +
sin ( sin ) cos
3 2
1
3
2 udu u u C + +
+ + C u u du u sin ) cos 2 (
3
1
cos
2 3
Definite Integrals
Natural Number e:
/
0
x
e dx
/ 2
0
x
xe dx
2 / 3
0
2
x
x e dx
/ 1
0
!
n x n
x e dx n
Probability Integrals
For the form
2
0
n ax
n
I x e dx
1/ 2
0
2
I a
1
1
2
I
a
3/ 2
2
4
I a
2
3
1
2
I a
5/ 2
4
3
8
I a
3
3
I a
for odd n:
( )
( ) 1 / 2
1 / 2 !
2
n
n
n
I
a
+
1
]
for even n:
( )
( ) ( ) / 2 1 / 2
1 3 5 1
2
n
n n
n
I
a a
+
L
Complex Trigonometric Identities
) ( cos
2
1
+
j j
e e +
sin cos j e
j
) ( sin
2
1
j j
j
e e
udv uv v du
Tom Penick tom@tomzap.com www.teicontrols.com/notes 6/11/2001
Quadratic Equation
Given the equation
0
2
+ + c bx ax : x
b b ac
a
t
2
4
2
Power Series Representation
...
! 3 ! 2
1
!
3 2
0
+ + + +
x x
x
n
x
e
n
n
x
cos
( )
( )! ! !
... x
x
n
x x
n n
n
1
2
1
2 4
2
0
2 4
sin
( )
( )! ! !
... x
x
n
x
x x
n n
n
+
+
+
1
2 1 3 5
2 1
0
3 5
cosh
( )! ! !
... x
x
n
x x
n
n
+ + +
2
0
2 4
2
1
2 4
sinh
( )! ! !
... x
x
n
x
x x
n
n
+
+ + +
+
2 1
0
3 5
2 1 3 5
ln( )
( )
... 1
1
2 3
1
0
2 3
+
+
+
x
x
n
x
x x
n n
n
... 1
1
1
3 2
0
+ + + +
x x x x
x
n
n
2 2 4 6
2
0
1
1 ..., 1
1
n
n
x x x x x
x
+ + + + <
1
1 , 1
1
x x
x
+
=
1
1 1 , 1
2
x x x + + =
You might also like
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- Basic Calculus FormulaeDocument4 pagesBasic Calculus FormulaeAkshay Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Integration TechniquesDocument18 pagesIntegration Techniquesஏம்மனுஎல்லெ செலேச்டினோNo ratings yet
- qc2 LogsDocument17 pagesqc2 LogsSherangi SilvaNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- PRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabDocument2 pagesPRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabPamela Ricaforte100% (1)
- Integration Key FactsDocument7 pagesIntegration Key FactsAhmad Hussain100% (1)
- CQF January 2014 Maths Primer Calculus ExercisesDocument2 pagesCQF January 2014 Maths Primer Calculus ExercisesShravan VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Econometrics HomeworkDocument11 pagesEconometrics HomeworkkmbibireddyNo ratings yet
- Financial Engineering and Risk Management: Martin Haugh Garud IyengarDocument5 pagesFinancial Engineering and Risk Management: Martin Haugh Garud IyengarAlejandro SanhuezaNo ratings yet
- Answers For Stochastic Calculus For Finance I Steven Shreve Vjul 15 2009Document7 pagesAnswers For Stochastic Calculus For Finance I Steven Shreve Vjul 15 2009tlanggyNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument7 pagesFormulaMàddìRèxxShìrshírNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Derivatives and IntegralsDocument1 pageFormulas For Derivatives and IntegralsAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Algebra PDFDocument4 pagesMathematics Algebra PDFHarmanjot Singh RiarNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Formula Sheet - 0Document4 pagesIntegral Calculus Formula Sheet - 0Sriraghuraman Gopal RathnamNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometry Theory - eDocument20 pagesInverse Trigonometry Theory - ethinkiitNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Finance Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMathematical Finance Cheat SheetMimum100% (1)
- RES9 Phys Flash CardsDocument5 pagesRES9 Phys Flash CardsnoobharvestorNo ratings yet
- List of Logarithmic IdentitiesDocument7 pagesList of Logarithmic IdentitiesMuhammedNayeemNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry-3 JEE MAIN AND ADVANCED PDFDocument4 pagesTrigonometry-3 JEE MAIN AND ADVANCED PDFNirmal yadav s channelNo ratings yet
- Algebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesDocument20 pagesAlgebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesHiren Mistry100% (1)
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsDocument17 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarNo ratings yet
- Trignometry Basic QuestionsDocument18 pagesTrignometry Basic Questionsdev1996100% (1)
- WQU - Econometrics - Module2 - Compiled ContentDocument73 pagesWQU - Econometrics - Module2 - Compiled ContentYumiko Huang100% (1)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet AllDocument11 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet AllDr Milan Glendza Petrovic NjegosNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument102 pagesDifferentiationChisei MeadowNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument21 pagesComplex NumbersAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Actuarial Science - ElementaryDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Actuarial Science - ElementaryPolelarNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Formula Sheet CondensedDocument1 pageDerivatives Formula Sheet CondensedintegralCALCNo ratings yet
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Magic of Definite IntegralDocument88 pagesMagic of Definite IntegralsagarNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Math Exam NotesDocument13 pagesGrade 11 Math Exam Notespkgarg_iitkgpNo ratings yet
- Final Notes For AB and BCDocument16 pagesFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012No ratings yet
- MCR3U Final Exam Review (June2010)Document6 pagesMCR3U Final Exam Review (June2010)Erin Guerrero100% (1)
- Solving Transportation Problem Using Vogel's Approximation Method, Stepping Stone Method & Modified Distribution MethodDocument38 pagesSolving Transportation Problem Using Vogel's Approximation Method, Stepping Stone Method & Modified Distribution MethodChadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- CQF January 2014 Maths Primer Differential Equations ExercisesDocument5 pagesCQF January 2014 Maths Primer Differential Equations ExercisesShravan VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- CQF January 2014 Maths Primer Exercises and SolutionsDocument16 pagesCQF January 2014 Maths Primer Exercises and SolutionsladykryaNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at InfinityDocument11 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at Infinityapi-1192241886% (7)
- Some Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesSome Basic Formulae:: Quadratic FormulaBlazingStudiosNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx UxvyDocument8 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 7.2 1 of 8: Yx Uxvymasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- EE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008Document26 pagesEE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008doomachaleyNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDocument28 pagesTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianNo ratings yet
- Resolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2Document11 pagesResolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2ChevronelleNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integral FormulasDocument4 pagesIndefinite Integral FormulasJessrell MalacoraNo ratings yet
- Formule Ploce I LjuskeDocument18 pagesFormule Ploce I LjuskeAmar MušovićNo ratings yet
- M 4u Integration FatmuscleDocument14 pagesM 4u Integration Fatmuscleapi-36563676No ratings yet
- Integration PDFDocument11 pagesIntegration PDFJaymour Cris FiestaNo ratings yet
- Tabular IntegrationDocument21 pagesTabular IntegrationArsalan JumaniNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasDocument12 pages2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasMaylalaine AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Spe 174023 MSDocument29 pagesSpe 174023 MSJay JayNo ratings yet
- Reservoir 1Document3 pagesReservoir 1Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Text Book - Exam Preparation - ToeflDocument1 pageText Book - Exam Preparation - ToeflJay JayNo ratings yet
- Reservoir 1Document3 pagesReservoir 1Jay JayNo ratings yet
- 03 VolumetricsDocument20 pages03 VolumetricsJay JayNo ratings yet
- Approved Technical Electives 14-16Document1 pageApproved Technical Electives 14-16Jay JayNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Grad Application Essay GuidesDocument6 pagesGrad Application Essay GuidesJay JayNo ratings yet
- SPE Strategic Plan 2013-2017: Approved by The Spe Board of DirectorsDocument10 pagesSPE Strategic Plan 2013-2017: Approved by The Spe Board of DirectorsJay JayNo ratings yet
- Outstanding Chapter RulesDocument2 pagesOutstanding Chapter RulesJay JayNo ratings yet
- Grad School Seminar NotesDocument5 pagesGrad School Seminar NotesJay JayNo ratings yet
- E101 Syllabus 29 Aug 2013Document4 pagesE101 Syllabus 29 Aug 2013Jay JayNo ratings yet
- 035Document6 pages035Jay JayNo ratings yet
- 97 PhysDocument143 pages97 Physramx32No ratings yet
- What Is Policy Evaluation?: 1. IdentificationDocument10 pagesWhat Is Policy Evaluation?: 1. IdentificationJay JayNo ratings yet
- 299 Words GreDocument2 pages299 Words GreFarah FazalNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument18 pagesRatio AnalysisJay JayNo ratings yet
- Supplication For ChildDocument2 pagesSupplication For ChildJay JayNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra BookDocument202 pagesLinear Algebra BookArtM16No ratings yet
- LiquidityDocument3 pagesLiquidityJay JayNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment of 30 Students (J.Ss.3) of Suleja Grammar School Suleja, Niger StateDocument7 pagesContinuous Assessment of 30 Students (J.Ss.3) of Suleja Grammar School Suleja, Niger StateJay JayNo ratings yet
- Resistance WeldingDocument1 pageResistance WeldingJay JayNo ratings yet
- Tech Spec 7 Wiring DiagramsDocument6 pagesTech Spec 7 Wiring DiagramsJay JayNo ratings yet
- Chap 01Document20 pagesChap 01Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Ch02 LimitsAndContinuityDocument2 pagesCh02 LimitsAndContinuityJay JayNo ratings yet
- Ans 2Document2 pagesAns 2Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Ch07 ExpAndLogFunctionsDocument2 pagesCh07 ExpAndLogFunctionsJay JayNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Curves in The Plane: V V V V V V V V V VDocument4 pagesVectors and Curves in The Plane: V V V V V V V V V VJay JayNo ratings yet
- Ac 2Document1 pageAc 2Jay JayNo ratings yet
- History Homework Help Ks3Document8 pagesHistory Homework Help Ks3afetnjvog100% (1)
- Bio 104 Lab Manual 2010Document236 pagesBio 104 Lab Manual 2010Querrynithen100% (1)
- STFC-2023 International E - conference-BITDocument6 pagesSTFC-2023 International E - conference-BITRanilprabhu MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 WarehousingDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 WarehousingabbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsAhmad FaidhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document16 pagesChapter 07Elmarie RecorbaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: MSBA7003 Quantitative Analysis MethodsDocument29 pagesTutorial: MSBA7003 Quantitative Analysis MethodsAmanda WangNo ratings yet
- Dady - Piernas LargasDocument12 pagesDady - Piernas LargasSarha NietoNo ratings yet
- Lab Final SolutionDocument18 pagesLab Final SolutionZeeNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Well FoundationDocument40 pagesAnalysis and Design of Well Foundationdhanabal100% (1)
- Barack ObamaDocument3 pagesBarack ObamaVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Time Table & Instruction For Candidate - Faculty of Sci & TechDocument3 pagesTime Table & Instruction For Candidate - Faculty of Sci & TechDeepshikha Mehta joshiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit TeachingDocument39 pagesTeaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit Teachingronna drio100% (1)
- Answer:: Exercise-IDocument15 pagesAnswer:: Exercise-IAishika NagNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DIPDocument33 pagesModule 2 DIPdigital loveNo ratings yet
- LITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesDocument6 pagesLITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesPrachi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Practice Book - Doing Passivation ProcessDocument22 pagesThe Practice Book - Doing Passivation ProcessNikos VrettakosNo ratings yet
- 1974 - Roncaglia - The Reduction of Complex LabourDocument12 pages1974 - Roncaglia - The Reduction of Complex LabourRichardNo ratings yet
- Corometrics 170 Series BrochureDocument3 pagesCorometrics 170 Series BrochureCesar MolanoNo ratings yet
- Design of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesDesign of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerabfstbmsodNo ratings yet
- Sentence Diagramming:: Prepositional PhrasesDocument2 pagesSentence Diagramming:: Prepositional PhrasesChristylle RomeaNo ratings yet
- Hunger Games Mini Socratic Seminar2012Document4 pagesHunger Games Mini Socratic Seminar2012Cary L. TylerNo ratings yet
- Static Power Conversion I: EEE-463 Lecture NotesDocument48 pagesStatic Power Conversion I: EEE-463 Lecture NotesErgin ÖzdikicioğluNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Sample Size For Animal-Based Studies (VetBooks - Ir)Document292 pagesA Guide To Sample Size For Animal-Based Studies (VetBooks - Ir)Jonathan MannNo ratings yet
- Power-Miser 12 Water Heater ManualDocument32 pagesPower-Miser 12 Water Heater ManualClaudeVanDammNo ratings yet
- Citroen CX Manual Series 2 PDFDocument646 pagesCitroen CX Manual Series 2 PDFFilipe Alberto Magalhaes0% (1)
- 3.1 MuazuDocument8 pages3.1 MuazuMon CastrNo ratings yet
- Stevenson Chapter 13Document52 pagesStevenson Chapter 13TanimNo ratings yet
- IDL6543 ModuleRubricDocument2 pagesIDL6543 ModuleRubricSteiner MarisNo ratings yet
- The Invisible SunDocument7 pagesThe Invisible SunJay Alfred100% (1)