Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Written Report "Osteoarthritis": Catanduanes State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing
Uploaded by
Mezil NazarenoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Written Report "Osteoarthritis": Catanduanes State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing
Uploaded by
Mezil NazarenoCopyright:
Available Formats
CATANDUANES STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF NURSING
WRITTEN REPORT OSTEOARTHRITIS
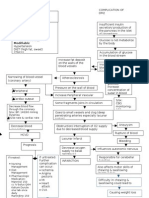
OSTEOARTHRITIS Definition: Osteoarthritis (OA), also known as degenerative joint disease or osteoarthrosis, is the most common joint disorder. It is a chronic, non-inflammatory and slowly progressing disorder that causes the deterioration of articular cartilage. It affects weight bearing joints(hips and knees), as well as the distal interphalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers. Besides age, risk factors for OA include female gender, generic predisposition, obesity, mechanical joint stress, joint trauma, congenital and developmental disorders of the hips, previous bone and joint disorders, inflammatory joint diseases, and endocrine and metabolic diseases.
Pathophysiology: 1. Changes in articular cartilage occur first; secondary soft tissue changes may occur later. 2. Progressive wear and tear on cartilage leads to the thinning of joint surfaces and ulceration into the bone. 3. Inflammation of the joint and increased blood flow and hypertrophy of subchondral bone. 4. New cartilage and bone formation of at joint margins results in osteophytosis (bone spurs), altering the size and shape of bone. 5. Generally affects ages 50-90. 6. Cause is unknown, but aging and obesity are contributory factors. Previous trauma may cause secondary osteoarthritis. Clinical Manifestation: Pain Stiffness Functional impairment due to pain on movement and limited joint motion when structural changes develop. Bony nodes may be present (painless unless inflamed)
Diagnostic Examination: No specific laboratory examination. X-rays of affected joint show joint space narrowing, osteophytes and sclerosis. Radionuclide imaging (bone scan) shows increased uptake in affected bones. Analysis of synovial fluid differentiates OA from RA.
Management:
Management focuses on slowing and treating symptoms because there is no treatment available that stops the degenerative joint disease process.
Prevention: Weight reduction Prevention of injuries Perinatal screening for congenital hip disease Ergonomic modifications
Pharmacologic Theraphy: Acetaminophen; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) if joint symptoms persist. The newer Cox-2 inhibitors(for patient with increased risk for GIbleeding). This blocks prostaglandins involved in inflammation. Topical analgesic such as capsaicin and methylsalicylates. The newer therapeutic approaches: glucosamine and chondroitin are common alternative remedies that that have potential cartilage-rebuilding effects. Viscosupplementation- intra-articular of hyaluronic acid Intra- articular injections of corticosteroids for acute joint inflammation (short term only)
Conservative Measures: Heat,weight reduction, joint rest and avoidance of joint overuse Orthostatic devices to support inflamed joints (splints, braces) Isometric and postural exercise, and aerobic exercise Occupational and physical therapy
Surgical Management: Osteotomy
Debridement Joint Fusion Arthroscopy Arthroplasty (joint replacement) is used with patient with end-stage disease.
Nursing Diagnosis: Pain related to joint degeneration and muscle spasm Impaired physical mobility related to pain and limited joint movement Self-care deficits related to pain and limited joint movement
You might also like
- Handout Medical-Surgical Nursing Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument13 pagesHandout Medical-Surgical Nursing Fluid and ElectrolytePaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (10)
- Histology For RetardsDocument57 pagesHistology For RetardsDavid Degaetano100% (1)
- Autism EnglishDocument129 pagesAutism EnglishRaí Caetano de JesusNo ratings yet
- Without Grain 100 Delicious Recipes For Eating A Grain-Free - Gluten-Free - Wheat-Free Diet PDFDocument211 pagesWithout Grain 100 Delicious Recipes For Eating A Grain-Free - Gluten-Free - Wheat-Free Diet PDFChuôngGió100% (1)
- Vortex Laser Reiki 1Document17 pagesVortex Laser Reiki 1Volkan VVolkan100% (3)
- Arm:Leg Fracture PDFDocument11 pagesArm:Leg Fracture PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritisDharti PatelNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method ValidationDocument86 pagesAnalytical Method ValidationRambabu komati - QA100% (12)
- BrainwashingDocument2 pagesBrainwashingSahnoune MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3:osteoarthritis (2007 Powerpoint)Document54 pagesLecture 3:osteoarthritis (2007 Powerpoint)j.doe.hex_87100% (1)
- Braddom RheumatologyDocument22 pagesBraddom RheumatologynesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Good Clinical Practice in Clinical Trials (1998)Document49 pagesGuidelines For Good Clinical Practice in Clinical Trials (1998)analyn123No ratings yet
- BONESDocument73 pagesBONESsafa_sabaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of BonesDocument3 pagesDisorders of BonesAnonymous 0pSLjJYNo ratings yet
- OSOM Regs 08Document12 pagesOSOM Regs 08Aymen ElatrashNo ratings yet
- Restraint CompetencyDocument6 pagesRestraint CompetencyFrederick RyanNo ratings yet
- Cmo 14Document125 pagesCmo 14pirmiadi100% (1)
- Nordic Questionnaire For Low Back PainDocument5 pagesNordic Questionnaire For Low Back Painbubbly_bea83% (6)
- Colonic Carcinoma Case StudyDocument24 pagesColonic Carcinoma Case StudyAudi Kyle Saydoven100% (4)
- OsteoarthritisDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritisprincess0fdeathNo ratings yet
- Drug Design Using BioinformaticsDocument13 pagesDrug Design Using BioinformaticsAniqah Zulfa100% (3)
- Review Injeksi Intraartikular Pada OA LututDocument12 pagesReview Injeksi Intraartikular Pada OA LututUmmu Qonitah AfnidawatiNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis AapmrDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritis AapmrBiandaNo ratings yet
- Typical Clinical Symptoms Are Pain, Particularly After ProlongedDocument12 pagesTypical Clinical Symptoms Are Pain, Particularly After Prolongedifa afifahNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint Disease: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Professor Department of MedicineDocument27 pagesDegenerative Joint Disease: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Professor Department of MedicinedrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritisVanessa Da CruzNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint DiseasesDocument30 pagesDegenerative Joint DiseasesBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument23 pagesOsteoarthritisGoutham VGouthamNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis NotesDocument11 pagesOsteoarthritis Notesjesmitha2740No ratings yet
- Review Sistem GerakDocument63 pagesReview Sistem GerakDanur AdiNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis - Dont EraseDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritis - Dont EraseLynlyn AlforqueNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument61 pagesOsteoarthritisTony HermawanNo ratings yet
- Refratt OsteoartritisDocument24 pagesRefratt OsteoartritisSulung Ade PratamaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument10 pagesAnatomyapi-3845840No ratings yet
- Bilateral OsteoarthritisDocument58 pagesBilateral OsteoarthritisMaya VilNo ratings yet
- Understanding Medical PaperDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Medical Paperrhn 5b1coolNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitacion ReumatologicaDocument22 pagesRehabilitacion ReumatologicaRosa M. AlcaláNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Knee OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Knee Osteoarthritiseyewhyvkg100% (1)
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument16 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisDeepak GhimireNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument60 pagesOsteoarthritis & Rheumatoid ArthritisSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument15 pagesOsteoarthritisMichael BanksNo ratings yet
- Osteonecrosis: Avascular NecrosisDocument8 pagesOsteonecrosis: Avascular NecrosisJezreel BonaNo ratings yet
- 08 Brandt EtiologyOA Review RheumClinNADocument29 pages08 Brandt EtiologyOA Review RheumClinNAPrincessDianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Defining Arthritis: Arth + It IsDocument82 pagesDefining Arthritis: Arth + It IsRofi IrmanNo ratings yet
- Rol - PDF Final.Document17 pagesRol - PDF Final.Muskan khaziNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 2018Document45 pagesOsteoarthritis 2018Rizcky Naldy Eka PutraNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Approach To The Tratament Osteoartrit TMJ 2020Document24 pagesInterdisciplinary Approach To The Tratament Osteoartrit TMJ 2020PauloNo ratings yet
- Paget DiseaseDocument11 pagesPaget DiseaseFrancesco MazzarellaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument2 pagesOsteoarthritisDwipratiwi 2003No ratings yet
- Group 3 Fact Sheet Degenerative Joint Disease OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesGroup 3 Fact Sheet Degenerative Joint Disease OsteoarthritisJoe Aire SalvediaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisorderDocument90 pagesMusculoskeletal Disordernhice19No ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis ImagingDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis ImagingAgus TriwiNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: BackgroundDocument9 pagesOsteoarthritis: BackgroundNathania LongkutoyNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Pathomechanisms of Osteoarthritis: Christian Egloff, Thomas Hügle, Victor ValderrabanoDocument14 pagesBiomechanics and Pathomechanisms of Osteoarthritis: Christian Egloff, Thomas Hügle, Victor ValderrabanobertouwNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint DiseaseDocument5 pagesDegenerative Joint DiseaseskittypieNo ratings yet
- BMJ 2006 p639Document5 pagesBMJ 2006 p639Wahab RasyidNo ratings yet
- Mi OsteoartritisDocument23 pagesMi OsteoartritisJULISSA MARICIELO GONZALEZ DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lect 6Document37 pagesLect 6eslambasuony98No ratings yet
- 3 Oa RMDocument15 pages3 Oa RMAhmad Nur Fikri AbrorNo ratings yet
- Group 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Document8 pagesGroup 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Jezreel BonaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument26 pagesOsteoarthritisRidwan MuttaqinNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument57 pagesArthritisSella Septi EkasariNo ratings yet
- OA LamonganDocument57 pagesOA LamonganruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Arthritis - Osteoarthritis, Gout, & Amp Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument23 pagesChapter 24 - Arthritis - Osteoarthritis, Gout, & Amp Rheumatoid ArthritisHarris GhifaryNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic Test AssessmentDocument10 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic Test AssessmentAl-Mansor MoayadNo ratings yet
- Introduction OADocument3 pagesIntroduction OAMae UsquisaNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument39 pagesOsteoporosisSri MahadhanaNo ratings yet
- Disease of Skeletal Muscle and JointsDocument7 pagesDisease of Skeletal Muscle and JointsNur Amirah FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Management of OADocument15 pagesManagement of OARudy HsNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Major Cause of Morbidity and InabilityDocument10 pagesOsteoarthritis: Major Cause of Morbidity and Inabilitymanuel124No ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument23 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitispatel divya100% (1)
- Osseous and Periosteal PainDocument34 pagesOsseous and Periosteal PainABE UPSKILLSNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesChronic Renal FailureMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesVii. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Under The General Supervision of The Chief, UN Joint Medical Service (UNJMS)Document2 pagesUnder The General Supervision of The Chief, UN Joint Medical Service (UNJMS)Mezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument4 pagesFetal DistressMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- The Pancreas: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument5 pagesThe Pancreas: Anatomy and FunctionsMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics: Status EpilepticusDocument1 pageDiagnostics: Status EpilepticusAlvin Tyantyan TayasNo ratings yet
- NajszdkDocument1 pageNajszdkMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- SNXKDZMDocument1 pageSNXKDZMMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- NcjalokxDocument25 pagesNcjalokxMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentDocument2 pagesLab EquipmentMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- NcwiowwDocument5 pagesNcwiowwAlvin Tyantyan TayasNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Our Lady of Sorrows PicDocument6 pagesA Brief History of Our Lady of Sorrows PicMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- A Personal Reflection On My Experience As A Mental Health Nurse in New ZealandDocument5 pagesA Personal Reflection On My Experience As A Mental Health Nurse in New ZealandMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive HVCD, DM2, CVD InfarctDocument1 pageComprehensive HVCD, DM2, CVD Infarctrexale riaNo ratings yet
- A Personal Reflection On My Experience As A Mental Health Nurse in New ZealandDocument5 pagesA Personal Reflection On My Experience As A Mental Health Nurse in New ZealandMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- CHN Report GoyetaDocument24 pagesCHN Report GoyetaMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesAbbreviationsMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Health InformaticsDocument7 pagesHealth InformaticsMezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Morality & DemocracyDocument16 pagesMorality & DemocracyMezil Nazareno100% (1)
- Man & Self - Lec2Document52 pagesMan & Self - Lec2Mezil NazarenoNo ratings yet
- F629 15Document3 pagesF629 15masoudNo ratings yet
- BLUE Protocol 2Document1 pageBLUE Protocol 2Syed Shahrul Naz SyedNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Cover LetterDocument1 pagePortfolio Cover Letterapi-301522421No ratings yet
- Application of Pharmaceutical GelatinDocument4 pagesApplication of Pharmaceutical GelatinShakrie AbdullahNo ratings yet
- N12 HO1 Health & Wellness T2SY201112Document10 pagesN12 HO1 Health & Wellness T2SY201112Ronzy BarreraNo ratings yet
- Global Epidemiology of Oral and Oropharyngeal CancerDocument8 pagesGlobal Epidemiology of Oral and Oropharyngeal CancerArpit JainNo ratings yet
- Magnesium ReplacementDocument4 pagesMagnesium ReplacementArvenaa SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Inheritance of Antibody Specificity II. Anti - (4-Hydroxy-5-Bromo-3-Nitrophenyl) Acetyl in The MouseDocument15 pagesInheritance of Antibody Specificity II. Anti - (4-Hydroxy-5-Bromo-3-Nitrophenyl) Acetyl in The MouseVenkata Suryanarayana GorleNo ratings yet
- Elements of MorphologyDocument16 pagesElements of MorphologySyrk12No ratings yet
- Apamarga Kshara SwitraDocument6 pagesApamarga Kshara SwitraSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiNo ratings yet
- HaematologyReport PDFDocument78 pagesHaematologyReport PDFhamody662002No ratings yet
- SAQ123 NursesUserGuide V6Document30 pagesSAQ123 NursesUserGuide V6LisaBrook100% (1)
- 3 Perubahan Fisiologis Pada LansiaDocument5 pages3 Perubahan Fisiologis Pada Lansiaalbert fernandoNo ratings yet
- Apollo Case Study StrategyDocument16 pagesApollo Case Study StrategyKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Griffith 1898 PlatesDocument180 pagesGriffith 1898 PlateshaleliNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management of TB and HIVDocument154 pagesClinical Management of TB and HIVapi-3781623100% (3)
- Report On DR.B.R.K.R Govt - Ayurvedic College & Hospital, Erragadda, HyderabadDocument22 pagesReport On DR.B.R.K.R Govt - Ayurvedic College & Hospital, Erragadda, HyderabadRavindra Singh PalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Implant Devices MarketDocument15 pagesCardiac Implant Devices MarketITIndustryARCNo ratings yet