Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relative Clauses
Uploaded by
Jackie RiveraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Relative Clauses
Uploaded by
Jackie RiveraCopyright:
Available Formats
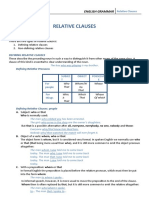
RELATIVE CLAUSES Las Oraciones de Relativo RELATIVE CLAUSES
RULE who / that refer to people which / that refer to objects whose refers to possession when refers to a moment in time where refers to a particular place In non-dening sentences, the word that cannot replace who or which. EXAMPLE They caught the man who / that spied for China. I lost the map which / that she gave me. She complained to the man whose dog bit her. Christmas Day is a day when people are happy. We visited the house where our father was born. Mata Hari, who was a famous female spy, was born in Holland. Buckingham Palace, which is in London, is a favourite tourist site.
Las oraciones de relativo van introducidas por un pronombre o un adverbio relativo: who, which, that, whose, when, where.
oracin principal They caught the man I lost the map
oracin subordinada de relativo who / that spied for China. which / that she gave me. whose dog bit her.
She complained to the man
Hay dos tipos de oraciones de relativo:
Dening Relative Clauses y Non-dening Relative Clauses
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO
DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
Las oraciones de relativo especicativas se llaman as porque aportan informacin esencial sobre su antecedente, de tal manera que sin ellas el sentido de la frase quedara incompleto. Los pronombres relativos son: THAT (que) se usa cuando el antecedente es tanto una persona como una cosa. WHO (que, quien, quienes) se reere slo a personas. WHICH (que) se reere excusivamente a cosas. Ejemplos:
They caught the
man
who / that spied for China.
antecedente persona
I lost the
map
which / that she gave me.
antecedente cosa
Tanto that como who y which se pueden omitir si van seguidos de un nombre o pronombre, es decir, si no son el sujeto de la oracin de relativo. Ejemplos: These are all the clues (that) they left behind. John is the man (who) we saw yesterday at the restaurant. Ive bought the CD (which) Laura recommended to me.
WHOSE indica posesin y signica cuyo/a/os/as. Nunca acta como sujeto y no se puede omitir. She complained to the man whose dog bit her.
WHEN (cuando, en que) hace referencia a un tiempo. Se puede utilizar that en su lugar u omitirse. Do you remember the day (when / that) we met?
WHERE (donde, en el que) indica lugar. We visited the house where our father was born.
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO
RELATIVE + PREPOSITION Cuando el relativo lleva preposicin, which se sigue usando si el antecedente es una cosa; pero si es una persona, en lugar de who se emplea whom, sobre todo en la lengua escrita. Lo ms comn en todos los casos es poner la preposicin al nal de la oracin de relativo y omitir el pronombre. The lm in which he appears was a great success > The lm he appears in was a great success The person to whom I had to talk wasnt there > The person I had to talk to wasnt there.
NON-DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
Estas son oraciones explicativas porque aaden informacin adicional sobre el antecedente. Sin ellas el sentido de la frase se mantiene igual, por lo que no son indispensables. Por eso siempre van entre comas. James Bond , who is a famous spy , was created by the writer Ian Fleming.
Con las Oraciones de Relativo Non-dening no se puede utilizar that, sino who y which para personas y cosas respectivamente. Adems nunca se puede omitir el pronombre o adverbio relativo. That document , which was found in his car , didnt prove his identity. The detective , who you met yesterday , is following the suspects trail. Este tipo de oraciones no es muy frecuente en el ingls hablado, donde se usan mucho ms las oraciones de relativo especicativas.
You might also like
- Relative Clauses Unit 8 PDFDocument3 pagesRelative Clauses Unit 8 PDFtworiversNo ratings yet
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarFrom EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Relatives Teoría Spanish PDF PDFDocument3 pagesRelatives Teoría Spanish PDF PDFAlberto Del Rio MejiaNo ratings yet
- Word Fugitives: In Pursuit of Wanted WordsFrom EverandWord Fugitives: In Pursuit of Wanted WordsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (11)
- Relative Clauses Las Oraciones de RelativoDocument3 pagesRelative Clauses Las Oraciones de RelativoMonikaki1978No ratings yet
- Inglés 2bat GrammarDocument13 pagesInglés 2bat GrammarLaTana LOLNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Relative ClausesDocument6 pagesUnit 4 - Relative ClausescaachuulooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Adjective Clauses PowerPoint ILI MD, Chapter 12, E4 GrammarDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Adjective Clauses PowerPoint ILI MD, Chapter 12, E4 GrammarPaul NicklasNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses: (Oraciones de Relativo)Document12 pagesRelative Clauses: (Oraciones de Relativo)alvarorondaNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Explanation and Steps To Make ThemDocument18 pagesRelative Clauses Explanation and Steps To Make Themcarla adriana hinojosa ramalloNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechRogelio Cueto CubillasNo ratings yet
- Relative Clause PresentationDocument23 pagesRelative Clause PresentationMaria Jose CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Part 1 Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 45046Document18 pagesRelative Clauses Part 1 Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 45046mona bahiNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Explanation and Steps To Make Them - Lesson No. 2Document18 pagesRelative Clauses Explanation and Steps To Make Them - Lesson No. 2Camilo Antolinez AcostaNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument12 pagesRelative Clausesjohann worbisNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Part 1Document18 pagesRelative Clauses Part 1Franco ScarlettNo ratings yet
- Relative - Pronouns - 11º Rules Exercises Students Version 2024Document3 pagesRelative - Pronouns - 11º Rules Exercises Students Version 2024tichaaNo ratings yet
- 3 Relative ClausesDocument19 pages3 Relative ClausesIvekaNo ratings yet
- 1 Alberto Relative Clauses TheoryDocument2 pages1 Alberto Relative Clauses Theoryyvonne carlileNo ratings yet
- Exemples - Relative Pronouns - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument10 pagesExemples - Relative Pronouns - English Grammar Today - Cambridge Dictionaryclotildeta100% (1)
- Adjective Clause: Presented To You by The Writing CenterDocument9 pagesAdjective Clause: Presented To You by The Writing CenterIntan PutriNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument4 pagesRelative ClausesYOLANDA GARCIA MORENONo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument3 pagesRelative ClausesOANA MARIA MARINNo ratings yet
- Chia Lee Shan Sunarti Binti Jasnan 1 Pismp Bm/Pj/Ps Institut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Temenggong IbrahimDocument26 pagesChia Lee Shan Sunarti Binti Jasnan 1 Pismp Bm/Pj/Ps Institut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Temenggong IbrahimMatt NooxNo ratings yet
- Pragmatics 2Document30 pagesPragmatics 2Miro MiroNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Chapter 5Document5 pagesHandouts in Chapter 5Jasmin Ditual PapataNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument4 pagesRelative ClausesRoxana BalcescuNo ratings yet
- Pro NumeleDocument7 pagesPro NumelealidachanduviNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Grammar3ºesoDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Grammar3ºesopepeNo ratings yet
- The Noun PhraseDocument5 pagesThe Noun PhrasePetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns PDFDocument6 pagesRelative Pronouns PDFaljchidz100% (1)
- INFORMEDocument15 pagesINFORMEYesseniaMedinaTerronesNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns: WhoDocument10 pagesRelative Pronouns: WhoLenni KurniaNo ratings yet
- Relatives PronounsDocument16 pagesRelatives PronounsIrem Parla UsukNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument4 pagesRelative ClausesOlivia-A. Tudoran (Cretu)100% (2)
- Noun PhrasesDocument24 pagesNoun PhrasesFaiza ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech: Written by Heather MacfadyenDocument17 pagesPart of Speech: Written by Heather MacfadyenanneNo ratings yet
- Relative PronounsDocument8 pagesRelative PronounsRutNo ratings yet
- Where's The PatisDocument27 pagesWhere's The PatisLovely Shayne Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Noun, Pronoun, AdjectiveDocument24 pagesNoun, Pronoun, AdjectiveZhiHui TayeNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument12 pagesRelative ClausesTấn DũngNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument7 pagesConditionalsMyleni IshidaNo ratings yet
- mệnh đề quan hệDocument8 pagesmệnh đề quan hệHà TrangNo ratings yet
- Luciana Oviedo Castillo.Document15 pagesLuciana Oviedo Castillo.ander oviedoNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns and Expressions in Spanish - Docx1Document4 pagesRelative Pronouns and Expressions in Spanish - Docx1sandra_501001380No ratings yet
- PronoundsDocument10 pagesPronoundsAbigail GoloNo ratings yet
- Pronominal and Reference: BY: Faiza Hassan Lady Jaisa Jainuddin Don Jayeko TayabasDocument40 pagesPronominal and Reference: BY: Faiza Hassan Lady Jaisa Jainuddin Don Jayeko TayabasLj KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 RAW Relative PronounDocument15 pagesLesson 5 RAW Relative PronounMerlito BabantoNo ratings yet
- DEFINING AND NON DEFINING CLAUSES (Spanish)Document4 pagesDEFINING AND NON DEFINING CLAUSES (Spanish)merceNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument17 pagesRelative Clausesantia sobralNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Relative Clauses Theoretical Framework.Document13 pagesUnit 5 - Relative Clauses Theoretical Framework.Vicky RivaderaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech: PronounDocument18 pagesPart of Speech: PronounanneNo ratings yet
- WHOM, WHOSE and WHO'SDocument8 pagesWHOM, WHOSE and WHO'SBondfriendsNo ratings yet
- Defining - Non Defining Relative Clauses - Blackboard SynopsisDocument2 pagesDefining - Non Defining Relative Clauses - Blackboard Synopsisvr.anaclaraNo ratings yet
- Grammar Rules SAT TestDocument17 pagesGrammar Rules SAT TestJBErminyNo ratings yet
- RELATIVE PRONOUNS - ConceptoDocument2 pagesRELATIVE PRONOUNS - ConceptoKiara SifuentesNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses (Revision) : Omission of WHO / WHICH / THAT in Defining Relative ClausesDocument2 pagesRelative Clauses (Revision) : Omission of WHO / WHICH / THAT in Defining Relative ClausesNicole D, HaleNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses: English GrammarDocument10 pagesRelative Clauses: English GrammarDr MontyNo ratings yet
- Arctic PenguinsDocument43 pagesArctic PenguinsJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported Speechjrb759No ratings yet
- Free Crochet Pattern Lion Brand Vanna's Choice - Vanna's Glamour Happy ReindeerDocument4 pagesFree Crochet Pattern Lion Brand Vanna's Choice - Vanna's Glamour Happy ReindeerJackie Rivera100% (1)
- Free Crochet Pattern Lion Brand Vanna's Choice - Vanna's Glamour Happy ReindeerDocument4 pagesFree Crochet Pattern Lion Brand Vanna's Choice - Vanna's Glamour Happy ReindeerJackie Rivera100% (1)
- Phrasal Verbs ListDocument16 pagesPhrasal Verbs ListJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- 72 Some Anything PDFDocument5 pages72 Some Anything PDFJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Resumen de Tiempos VerbalesDocument5 pagesCuadro Resumen de Tiempos VerbalesCancerbero CancerbeNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument3 pagesRelative ClausesJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Regulars VerbsDocument2 pagesRegulars VerbsJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- 72 Some Anything PDFDocument5 pages72 Some Anything PDFJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- 72 Some Anything PDFDocument5 pages72 Some Anything PDFJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- ErrorDocument34 pagesErrorJackie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument55 pagesParts of SpeechMarva GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Gender in Romanian and in EnglishDocument9 pagesGender in Romanian and in Englishonutchka8479No ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument11 pagesTypes of PronounsReynaldo Aluyen Guinoden Jr.No ratings yet
- Key Understan Ding To Be Developed Learning ObjectivesDocument118 pagesKey Understan Ding To Be Developed Learning ObjectivesJaymar Tuatis100% (1)
- The Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesThe Passive VoiceTheShqiprimNo ratings yet
- Anaphoric Nouns Labelling Discourse PDFDocument6 pagesAnaphoric Nouns Labelling Discourse PDFjoe1974No ratings yet
- Radio BroadcastDocument18 pagesRadio BroadcastmariuspalafoxNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns: Albert Einstein The President My Mother A GirlDocument5 pagesTypes of Nouns: Albert Einstein The President My Mother A GirlaudyNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing - Unit 5 - Tn1Document1 pageReading and Writing - Unit 5 - Tn1Romario JCNo ratings yet
- English Page - Simple PresentDocument3 pagesEnglish Page - Simple Presentsander10No ratings yet
- Taro Kageyama (Ed) Transitivity and Valency Alternations Studies On Japanese and BeyondDocument506 pagesTaro Kageyama (Ed) Transitivity and Valency Alternations Studies On Japanese and BeyondMaxwell Miranda100% (2)
- Think l2 Grammar Reference PDFDocument6 pagesThink l2 Grammar Reference PDFIsrael SánchezNo ratings yet
- Definite Articles FamilyDocument2 pagesDefinite Articles Familydido83No ratings yet
- Seminarski Iz EngleskogDocument12 pagesSeminarski Iz EngleskogAleksandar JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Deixis and DistanceDocument43 pagesDeixis and DistanceRaquel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Examen de InglesDocument5 pagesExamen de IngleshumbertocainNo ratings yet
- Speak French, A Book For The Soldiers, 1917Document128 pagesSpeak French, A Book For The Soldiers, 1917natasha0304No ratings yet
- Order of The AdjectivesDocument2 pagesOrder of The Adjectivesgabriel sanchez moraNo ratings yet
- UNIT 01 Extra Grammar ExercisesDocument4 pagesUNIT 01 Extra Grammar ExercisesMeliza Nogales80% (5)
- Past Simple Form With Other Verbs Yes No QuestionsDocument3 pagesPast Simple Form With Other Verbs Yes No QuestionsAnthony LokitoNo ratings yet
- Genre of TextDocument22 pagesGenre of TextRomi AdibiNo ratings yet
- Corner Stores and SupermarketsDocument3 pagesCorner Stores and SupermarketsGlo HernándezNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be GOOD GOOD 8Document1 pageVerb To Be GOOD GOOD 8donaldoNo ratings yet
- PTEG Test TipsDocument65 pagesPTEG Test Tipsamella78No ratings yet
- Consolidate Writing SkillsDocument33 pagesConsolidate Writing Skillsapi-111151704No ratings yet
- SanskritDocument37 pagesSanskritJunaid Siddiqui100% (1)
- Atg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFDocument2 pagesAtg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFALF_1234No ratings yet
- Pra Penulisan Bi Karangan UpsrDocument111 pagesPra Penulisan Bi Karangan Upsropheliaviolet100% (1)
- Straightforward 2e Beg SB-11Document129 pagesStraightforward 2e Beg SB-11Julio Gonzalez LopezNo ratings yet
- English BuilderDocument191 pagesEnglish Buildershwaap100% (3)