Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 - Biodiversity
Uploaded by
Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 - Biodiversity
Uploaded by
Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Form 2 note
CHAPTER 3: BIODIVERSITY
3.1 THE VARIETY OF LIVING ORGANISM 1. 2. 3. 4. The living things found on Earth are humans, animals and plants. A living things is known as an organism. Animals and plants have various shapes, sizes and habitats. The differences that exist between the same species of living things are called variations/diversity of life or biodiversity.
HABITAT OF LIVING THINGS 1. 2. 3. A natural place where plants and animals live is called a habitat. Different animals and plants live in different habitats. A habitat is important to an organism because a. it provides the organism with food, b. protection c. space for breeding. habitat of living things Animals Animal Bir d Snak e Amoeba Whal e Cam el Termite habitat tre e bush es pon d se a dese rt woo d plants plant lotu s mushroom Durian tree duckweed Coconut tree cact us habitat lak e woo d orchard pon d seashore dese rt
Science Form 2 note
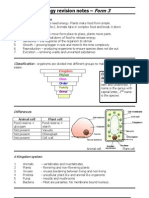
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Go to http://anthro.palomar.edu/animal/animal_1.html describe the Linnaeuss system of classification used in Science to classify all living organisms. For easy access, go to www.icd.com.my 1. 2. Classification can be classified based on common characteristics. Examples of classification of animal based on their habits and their breathing organs are shown below. classification of animals Habitat breathing organs water moist water gills lungs and land skin Examples prawn crab Turtle horse frog whale seahorse crocodile duck ToadPMR10 crab eel FrogPMR10 cow ? PMR 04 PMR 2010
(classification of animals)
land eagle chicken snake
3.2 CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS
http://www.indianchild.com/animal_kingdom.htm
Go to http://animaldiversity.ummz.imich.edu. To learn about animal, type the name of the animal into the sites own search engine. 1. 2. 3. 4. Animals can be classified into two big groups: a. Animals with backbones. b. Animals without backbones. Animals with backbones are known as vertebrates. Animals without backbones are known as invertebrates. Vertebrates are divided into five main groups. The five groups are : a. Fish PMR 07 b. Bird c. mammal PMR 06 d. reptile PMR 04, 07 e. amphibian PMR 04, 07 Classification of vertebrates and their characteristic; PMR 2010
5.
http://www.kidport.com/Reflib/Science/Animals/Animalindexlnv.htm Salin/photostat dari m/s 64-65
Science Form 2 note
6.
Invertebrates can be broadly classified into two groups. The groups are: a. with jointed legs b. without jointed legs.
two
http://www.kidport.com/Reflib/Science/Animals/Animalindexlnv.htm Invertebrates invertebrates with jointed legs invertebrates without jointed legs Examples crab, spider, earthworm, flatworm, sea centipede, millipede, anemone, starfish, snail 3.3 CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS Go to www.perspective.com/nature/plantae/index.html observe the description of the classification and the divisions in the plant kingdom. For easy access, go to www.icd.com.my 1. 2. Plants can be divided into groups based on some common features. Plants can be divided into two groups. The two group are those which a. produce flowers, flowering plants b. do not produce flowers, non flowering plants. salin m/s 67 3. Flowering plants are divided into dicotyledons and monocotyledon. a. Flowering plants i. this type of plants produces flowers, seeds and fruits. The flowers normally become fruits. ii. This type of plants produces flowers for reproduction. iii. Examples of dicotyledons are rubber trees, durian trees, hibiscus plants and rambutan trees. iv. Characteristics of dicotyledons: leaves with network veins have taproot system
Science Form 2 note
v. oil vi.
stems are usually woody seeds have two cotyledons Examples of monocotyledons are paddy plants, grass and palm. Characteristics of monocotyledons: leaves with parallel veins have fibrous root system have soft stem seeds with one cotyledon lukis dan salin m/s 68
b. Non-flowering plants http://www.zephyrus.co.uk/nonfloweringplants.html i. Non-flowering plants do not produce flowers, fruit and seeds. ii. These plants reproduce by spores or binary fission. iii. Non-flowering plants are divided into four groups: algae moss fungus ferns 3.4 THE IMPORTANT OF BIODIVERSITY TO THE ENVIRONMENT. Go to http://www.journeymalaysia.com/m_rain.htm Gather information about Malaysian wild jungles, rainforest, ecotourism, nature travel, forest and wildlife guided tours. For easy access, go to www.icd.com.my
Buat nota sendiri m/s 69 text book
tamat
Science Form 2 note
You might also like
- Science NAT 6 - 2Document16 pagesScience NAT 6 - 2Vangie G Avila80% (5)
- Integrated Science NotesDocument16 pagesIntegrated Science NotesannmarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BiodiversityDocument5 pagesChapter 3 BiodiversityxzaipangxNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz in ScienceDocument3 pagesLong Quiz in ScienceDaisy Joy LacandazoNo ratings yet
- Folio Science Aku!!!!Document26 pagesFolio Science Aku!!!!guzer_wan9595% (21)
- Science Report (Kris & Bry)Document60 pagesScience Report (Kris & Bry)Bryan Mallen IsnaniNo ratings yet
- The Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationDocument9 pagesThe Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationliugirmayNo ratings yet
- Site Introductio1Document5 pagesSite Introductio1api-249592469No ratings yet
- Biology Exam GuideDocument16 pagesBiology Exam GuideKe-Deidra DaleyNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument29 pagesBiodiversityGhoulispogNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Carnivorous Plants: Answer These Questions As Best You CanDocument5 pagesCarnivorous Plants: Answer These Questions As Best You CanBMelly11No ratings yet
- F3biol Revision NotesDocument5 pagesF3biol Revision NotesVinitha MenonNo ratings yet
- Makalah Animal and PlantDocument17 pagesMakalah Animal and PlantMuhammad FuadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 3 NotesDocument75 pagesBiology Form 3 NotesFar taNo ratings yet
- Bio Note9Document4 pagesBio Note9Debela mendaraNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Mozac E-FusionDocument31 pagesBiodiversity Mozac E-FusionAreKimz CyberzNo ratings yet
- Std07 I MSSS EM 3Document48 pagesStd07 I MSSS EM 3Karthick KumarNo ratings yet
- Revised Form 2 NotesDocument68 pagesRevised Form 2 Notestegokate008No ratings yet
- SCINCE NOTES Part IIDocument6 pagesSCINCE NOTES Part IISANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- C H A P T e R VA IDocument8 pagesC H A P T e R VA IArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- Read The Text Quickly and Sign The Difficult WordsDocument4 pagesRead The Text Quickly and Sign The Difficult WordsFirdaus Dwi Yulian 74934No ratings yet
- Biodiversity or Biological Diversity STU COPDocument13 pagesBiodiversity or Biological Diversity STU COPcbseiscNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PDFDocument67 pagesBiodiversity PDFTanaya BorseNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of BiologyDocument15 pagesKingdom Plantae: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of BiologySalar BasherNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - EcosystemsDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - EcosystemsIndah FitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Plant Classification DegreeDocument57 pagesPlant Classification Degreejohnsonsamuel090677746No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: BiodiversityDocument2 pagesChapter 3: BiodiversityAlexander Noah A MNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living OrganismDocument60 pagesVariety of Living OrganismThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Short Questions and AnswersDocument17 pagesKingdom Plantae: Short Questions and AnswersNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- Class Five L Science NotesDocument10 pagesClass Five L Science NotesALI JAMILNo ratings yet
- 11 VI Science Le 11 Habitats of OrganismsDocument7 pages11 VI Science Le 11 Habitats of OrganismsKumarNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringDocument5 pagesEssential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringChloe Troulan100% (1)
- Objectives: Week 7: Day 1-2 Lesson 2: Plant AdaptationsDocument17 pagesObjectives: Week 7: Day 1-2 Lesson 2: Plant AdaptationsMaam JurieNo ratings yet
- Las Sci6 Q2 Week6Document9 pagesLas Sci6 Q2 Week6Gianna BaldoradoNo ratings yet
- Viability of Organism: By: Aidil Adhani Biology Ix GradeDocument22 pagesViability of Organism: By: Aidil Adhani Biology Ix GradeAidil AdhaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology and DiversityDocument10 pagesPlant Morphology and Diversityalyssa mae antonioNo ratings yet
- Annelida Written ReportDocument11 pagesAnnelida Written ReportIrish MaireignNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- The 7 Characteristics That Distinguish Living Things From Non-Living Objects AreDocument34 pagesThe 7 Characteristics That Distinguish Living Things From Non-Living Objects AreTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument3 pagesBab IiiVenty HabibieNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi: Addis Hiwot SchoolDocument5 pagesKingdom Fungi: Addis Hiwot Schoolleul habtamuNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesDiversity in Living Organismssumendra singhNo ratings yet
- Focus Questions: Week 1Document5 pagesFocus Questions: Week 1api-238747348No ratings yet
- Kingdoms ClassifiedDocument24 pagesKingdoms ClassifiedDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hari's - PaperDocument34 pagesHari's - PapermuhammadkdrNo ratings yet
- F2C3 - BiodiversityDocument11 pagesF2C3 - BiodiversitytankiuNo ratings yet
- Diversity: ClassificationDocument19 pagesDiversity: Classificationmurari_sahuNo ratings yet
- Science Animal and EcosytemDocument5 pagesScience Animal and EcosytemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- 5th Class ScienceDocument6 pages5th Class ScienceM Saadat SaeediNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Class 11 Unit 1Document21 pagesRajkumar Class 11 Unit 1asuhassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andummahputeriNo ratings yet
- Adaptation For SurvivalDocument16 pagesAdaptation For SurvivalSalma LabaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Ecosystem EnvisciDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Ecosystem EnvisciMarie FeNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Zonal PlantDocument6 pagesClass 8 Zonal PlantRitesh SNo ratings yet
- (Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Document18 pages(Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Bekele GonfaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Absorption of Digested FoodDocument14 pages2.4 Absorption of Digested FoodNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Document62 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 5qq23585% (41)
- 2.3 Digestive System 2003Document7 pages2.3 Digestive System 2003Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument13 pages2.1 Classes of FoodNoraslina Binti Abdul Wahab0% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 7Document32 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 7qq23582% (11)
- 2.2 The Important of Balanced DietDocument8 pages2.2 The Important of Balanced DietNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Reabsorption Water N 2.6 Eating HabitsDocument7 pages2.5 Reabsorption Water N 2.6 Eating HabitsNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 4 - Interpendence Among Living Organisms & Environment PDFDocument55 pagesNotes Chapter 4 - Interpendence Among Living Organisms & Environment PDFNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Expressnotes Scienceform2Document11 pagesExpressnotes Scienceform2Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document46 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1qq23589% (66)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 2)Document28 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 2)qq23592% (38)
- Notes Chapter 3 - Biodiversity PDFDocument15 pagesNotes Chapter 3 - Biodiversity PDFNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Air PressureDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Air PressureNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2Document63 pagesSains Tingkatan 2Sekolah Portal95% (37)
- Chapter 4 - Interpendence Among Living Organisms and The EnvironmentDocument6 pagesChapter 4 - Interpendence Among Living Organisms and The EnvironmentNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - NutritionDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - NutritionNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Water and Solution: Form 2Document18 pagesWater and Solution: Form 2Nur A'ainNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineDocument23 pagesNotes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineNoraslina Binti Abdul Wahab100% (2)
- Chapter 3 - BiodiversityDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - BiodiversityNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2Document63 pagesSains Tingkatan 2Sekolah Portal95% (37)
- Chapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Expressnotes Scienceform2Document11 pagesExpressnotes Scienceform2Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 7 1Document5 pagesWorksheet Chapter 7 1jhezooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - The World Through Our SensesNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Chapter 2 - NutritionDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - NutritionNoraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Name List T 2 2013Document10 pagesName List T 2 2013Noraslina Binti Abdul WahabNo ratings yet