Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roller Conveyor
Uploaded by
zainonayraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roller Conveyor
Uploaded by
zainonayraCopyright:
Available Formats
HANDLING MACHINES
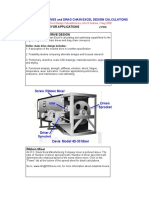
Application Notes: Roller Conveyor
Machine purpose
To move isolated loads of sufficient size with minimum friction but with very small changes of level. Optimized flow for gain in time and/or personnel. Production, assembly, erection, packing and conditioning lines, work-station supply, transport, handling, distribution, storage, intermediate storage, accumulation storage, sorting, order preparation, picking, shipping, heating and cooling of elements.
Theory of operation
A roller conveyor is used for routing isolated loads (pallets, containers, boxes, cartons, others). The rollers are driven by flat or cylindrical belts or by chains. The machine can accommodate switches. Rail and air freight in-feed, automatic postal package sorting, hospital logistics, transport and storage of documents and files, transfer of television sets on assembly line, routing of orders to shipping point, sorting of cartons by customer and round, weighing and labeling station, dynamic carton stock, manual work-station, food product packaging line (deep-frozen foods) and storage of books, handling of bags and containers, reception of pallets (docks), deep freezing by blowing red berries and peas, automobile body conveying, preparation of orders for mail order sales. Pallet conveyor, pressureless accumulation conveyor. Roller conveyor, roller table, heavy conveyor, light conveyor.
Several examples of use
Names of machines related to application Names used
Rollers Stopper Guiding strand
Drive motor
Drive chain
Detection, identification Control Flat angle iron feet for attaching to floor
2003 Schneider Electric
All rights reserved. Doc. # 0105DB0301
HANDLING MACHINES
Main types
Conveyor with plastic, steel or aluminum rollers, free or motorized roller conveyor, telescopic roller conveyor, roller conveyor for heavy loads, roller conveyor, 2-chain roller conveyor, fixed and flexible curves, taper roller curve, inclined roller conveyor. Conveyor belt, belt conveyor, belt curve, chain conveyor (parallel or supporting), telescopic roller or belt conveyor, flexible conveyor, turntable, turn-over, elevator, chain transfer, belt transfer. Generally roller conveyors are located indoors. However, for agro-food applications, it can operate at negative temperatures (-40C) with high relative humidity or harsh environments (dust, corrosive agents). Washing with a jet (or a high pressure jet) with or without detergents is a practice that imposes a specific choice of material. Some applications call for electrostatic discharging of the conveyed parts. For a system, the electrical cabinet is generally isolated. For an isolated machine, the electric equipment must be designed to allow for the environment and if necessary for explosive atmosphere. Guides, guide strand, guide disk, link attachment, stop or buffer, stopper, pneumatic stop, retracting lock, brake roller for mobile conveyor, flat angle foot for floor attachment, conveyor-turntable link, stepper feed, roller or motor, disengagable, self-driven rollers, brake roller, brake plate, switch, automatic linear switch, automatic angle switch, parallel single output grouper, pusher, selection pusher, centering pusher, pushing shoe, pop-up, turn-over finger, bin orientation device (pivot), automatic empty bin stacker, gate, weight control unit (static or dynamic), gauge tester, load identification (bar or magnetic code), test bench, electro-zinc finish or stainless steel for agro-food, anti-static belt, blower, fan, air conditioner, flow control software, PC, printer. Conveyors of all types, chain or belt transfer at 45 or 90, transfer truck, turntable, turntable with transfer, shuttle, turn-over, vertical, multiple level elevator, continuous vertical elevator, elevator table, scissors elevator table, elevator platform, transfer elevator, distribution cart (with or without friction wheel drive mechanism), wire guided cart, magazine, empty pallet magazine, transtorage, rotary storage. Assembly, sorting, weighing, grading, counting, identification, packing, conditioning, palletizing, deepfreezing, treatment, painting, baking.
Other typical machines or family
Situation in environment
Associated systems
Upstream and downstream machines
Related professions
Table position, D1 Shipping of specific products Automatic palletizing Process control and display station (if necessary). Process cabinet
Passage of load, D1 Jamming, D3
E
Turn- Roller table conveyor Belt Transfer
Distribution box or cabinet
E
Chain transfer
Load counting, D2 Positioning of load for stoppage, D5 Identification of the load, D6 Lack of product, D4 Package return defective labeling Incoming products from all production sources
Machine located within a process
Page 2
HANDLING MACHINES
Electrical equipment associated with conveyor
Item D D D E E E E E E E E E/M1 E/M1 E/M1 E E E/M1 E E E E E E D1 D2 D2 D3 D2 D2 D2 E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E E Functions Distribution Mobile electric distribution of roller conveyor General distribution Mechanical protection of distribution Equipment Mechanical protection of equipment and control Attaching electrical equipment Routing cables Distributing power Connecting cables Control power supply Power control Roller conveyor energizing Movement supply and safety cut-off Starting motor(s) (if possible on load) Changing motor running direction Changing motor speed Energizing variable speed controller power Brake release control Positioning the load Protection Protecting motor(s) against short-circuits Protecting motor(s) against overloads Protecting the brake(s) Protecting control power supply transformer Lighting circuit, 220 V outlet and control circuit Protecting and monitoring network and motor Detection Top and bottom table position Passage of load (presence, absence) Load counting Jamming on conveyor Product run-out Positioning of load for stoppage Load identification (automatic sorting) Opening of electric equipment access door Signalling (dialogue) Voltage presence on roller conveyor Energizing roller conveyor Roller conveyor in motion Displaying coded messages, conveyor status Displaying plain messages: maintenance, production Displaying process, exchanges underway Resetting roller conveyor Process supervision Control (dialog) Starting and stopping roller conveyor Emergency stop Selecting automatic or manual modes Manual rotation control (maintenance) Selecting desired speed direction Resetting roller conveyor after fault Sending variable speed controller setpoint Processing Start order sequence Time delays Power adaptation Switching variable speed controller setpoints Positioning of load Flow and stock management Isolated machine Machine integrated into a process Monitoring of emergency stop buttons Solutions* KN, KS C60, NS, Masterpact, GS1, FA, KA, LA AA, AM, ACM AA, AM, ACM, ACP, LG., XAP, DE8-B AM3, AM1, DZ6, LG. AK2-G, AK2-L, LG. AB3, AK5 AB1, DB6, DZ5, ABS, ABE, LG., 9080G 9070T/TF LS1D, GS1, Vario, NS, Compact, LG., FA, KA LC1, LP1, LU LC1, LC3, LD1, ATV6, LG., LU, ATV28/11 LC2, LG8, LU, ATV28/11 LC1, ATV6, LU LC1, LU LC1, LU MSP, AV28/11 LS1D, GS1, GV2M-L, GV., LB1L, NS, LG., LU LRD, LT3, GV2M-P, GV7, LB1L, LG., ATV28/11 GV2, LU DF6, GB2RT, GB2CB, C60, GV. DF6, GB2CB, C60, Vigi C60, GV2 RH328AP, SM21, EM9T Q. x 1 1 1 x x x x 1 1 1 1 1 x 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 x x x x x x x x 1 1 1 1 x 1 1 1 1 1, 2 1 1 x 2, 1 1 1 x 1 x x 1 x x x 1
Page 3
XC, XS, XU depending on load type, XCW XC, XS, XU depending on load type, XCW XC, XS, XU depending on load type, XCW XC, XU depending on load type, XCW XC, XU depending on load type, XCW XGV, XC, XS, XU, XGS, XCW XC XB4B XB4B XVB, audible signalling unit XBLA, XB4B XBT TSX, XBT-N/G XB4B XBT XB4B XB2B, XA2B, Vario, XY2C, XB4B, XALD XB4B XAD, XBT, XB4B, 9001K XAD, XBT, XB4B XB4B SZ1RV, XBT, XB4B CAD, LA1, RU, RX, RH, micro TSX RE4, RE5, LAD, Twido, micro TSX RU, RX, RH LA1, RU, RX, RH, Twido, microTSX TSX7, micro TSX TSX7, micro TSX, XBT-N/G micro TSX, Momentum micro TSX, XBT-N/G XPS-A
*refer to general catalog for complete details.
HANDLING MACHINES
Criteria for choice of machine user Critical points to be solved by manufacturer/know-how
Mechanical Guidance of loads, loss of adhesion of loads during acceleration, noise, transportation of fragile products, transportation of atypical shaped products. Electric Detection of jamming and anomalies, detection in difficult environments (cold: mist), identification of products, synchronization with other conveyors, positioning of loads, speed of logic control components in automatic sorting application (load follow-up). Motor dimensioning 90% of light roller conveyors (<5 lb.) use a range of motors with power from 1/3 hp to 3/4 hp. Conveyor belts for the same loads require power ranging from 1 hp to 4 hp (high speed table). The weight of the loads (influencing the choice of material and the diameter of the rollers): ultra light, <4 lbs. ; light, <110 lbs.; medium, <220 lbs.; heavy up to 2 T. Size and shape of loads. Speed of movement of loads : 3.2 feet/min to 393 feet/min The length of the conveyor: up to several miles; generally in lengths of 20 to 32 feet. Conveyor width 4 inch to 6.5 feet. Conveyor height. Topology, logistics and transit conditions. Environment/Applications : steel grades (stainless), route, accumulation, load identification, etc.
Cost of roller conveyor
A roller conveyor for light loads (<220 lbs.), 20 feet long, costs $46K before tax. A system can cost between $500K and $30 million. A roller conveyor is cheaper than a belt conveyor (belt guidance). The mechanism is simpler and the drive power is reduced compared to a conveyor belt of the same capacity. The belt conveyor becomes essential as soon as elevation is necessary.
CE marking
Low voltage directive 73/23/CEE of 19/2/73, amended by directive 93/68/CEE of 22/7/93. Safety This machine is covered by machine directive No 89/392/CEE, amended. Generally, this is one of the elements in an automated installation for which safety is incorporated. When this machine is accessible to the personnel, it is necessary to install emergency stop devices every 30 feet or trip wire emergency stop switches monitored by a Preventa module. EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) 89/336/CEE + amendments. When a variable speed controller is used, the radio perturbations must be attenuated by VW3A input filters, if necessary with VW3A line coils or SinWave active compensators (MG) to reduce harmonic current. Schneider services consulting, training, research assistance, checks and measurements on site. It is advisable to use interference supressors for contactors (LA4).
Several application references in Europe
Germany: Mannesmann Demag Austria : Belgium : Denmark: Spain : Finland : France : Savoye, Samovie, Sydel, Atecmi, Matflex, NTS , Manumeca, Greece : Italy: Conveyors, Peem, Papa, Montini Norway: Netherlands: Caljan Portugal: Sweden: Switzerland: UK : Shuttle worth
Page 4
HANDLING MACHINES
Roller Conveyor
Motor Starter Detection
main functions (...) optional
M2 M2 D2 M1 M2 M3
product that may be critical
D1
M2 M3 M2 D3 M2
Mark
M1
Qty
1
Motor starter function
Forward/backward movement of the chain conveyor on load: avoiding mechanical shocks, stopping at foreseen position.
Recommended product
ATV28 ATV11 Type ATV28/11 starter with two running directions, low and high speed with acceleration, and deceleration ramp times. P<1.5kW / 2 hp. Type ATV28/11 starter with two running directions, low and high speed with acceleration and deceleration ramp times. P<1.5kW / 2 hp. The reverse motion is used during maintenance operations. P<1.5kW / 2 hp. U-Line control
Remarks
The changing from low to high speed with acceleration and delay or detection of the table position. @ 460 / 575 VAC ------@ 115 / 230 VAC The changing from low to high speed can be realized by a time delay or detection of the table position. @ 460 / 575 VAC ------@ 115 / 230 VAC Standard motor switching with overload protection Provide solid state overload protection and communications capability.
>1 M2
Forward/backward movement of the pallet on the conveyor elements.
ATV28 --------ATV11
2 M3
Lifting/lowering of chain transfer
LC2 LU
Mark
D1
Qty 2
per element
Detection needs
Recommended product
Type XS1 inductive proximity sensor, diameter 12 mm, XCK angular position switch with roller lever. Type XUL photo-electric sensor with background suppression.
Remarks
Alternative: cylinder mounted sensors XS7-V12 on PADE cylinders.
Detecting the top and bottom position XS of the table to authorize: or the arrival or the exit of the pallet, XC the backward or forward movement of the pallet on the arrival and exit conveyor. Detecting the pallet position on the arrival and exit conveyor. XU
>1 D2
per element
For more precise sensing a thru-beam system should be used, For brilliant materials a sensor with background suppression or a polarized reflex sensor should be used. Generally the sensors are mounted between the rollers and detect towards the top.
2 D3
per element
Detecting the passage and presence of the pallet on the table.
XU
Type XUL photo-electric sensor with background suppression.
Page 5
HANDLING MACHINES
Roller Conveyor
Motor Starter Detection
main functions (...) optional
M2 M1 M2 V2
product that may be critical
D3 V M1 D2 D4 M2 D1
Mark
M1
Qty
1
per element
Motor starter function
Recommended product
Starter with one running direction, P < 0.75 kW / 1 hp. Type ATV28/11 starter with two running directions with variable speed, P < 3 kW / 4 hp. The reverse motion is used during maintenance operations.
Remarks
See M3
Forward movement of products on the LC1 ------product separation element. LU Forward/backward movement of products on the conveyor elements. ATV-28 ------ATV-11
1 M2
per element
The conveyor rotation speed can depend on the jamming detection and only initiate the stopping of the conveyor after the time delay is elapsed. @ 460 / 575 VAC ------@ 115 / 230 VAC
Mark
D1
Qty 2
per stopper
Detection needs
Detecting the top and bottom position of the table to authorize: the arrival or the exit of products. Detecting the product position on the arrival and exit conveyor.
Recommended product
XS or XC XU Type XS1 inductive proximity sensor, diameter 12 mm. XCM angular position switch with roller lever. Type XUL photo-electric sensor with reflex system. Type XU photo-electric sensor with standard or delayed reflex system.
Remarks
Alternative: cylinder mounted sensors XS7-V12 on PADE cylinders. Generally the sensors are mounted between the rollers and detect towards the top. For a more precise sensing a thru-beam system should be used. For brilliant materials a sensor with background suppression or a polarised reflex sensor should be used.
>1 D2
per stopper
1 D3
per element
Detecting a product jamming after the XU switching.
1 D4
per element
Detecting a product jamming before the switching.
XU
Type XU photo-electric sensor with background suppression.
Page 6
You might also like
- Conveyor Belt CalculationDocument14 pagesConveyor Belt CalculationIman SatriaNo ratings yet
- Chain ConveyorDocument172 pagesChain Conveyorhengki wibowoNo ratings yet
- Dunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual PDFDocument17 pagesDunlop Conveyor Belt Design Manual PDFMuthuvel VivekNo ratings yet
- Conveying MasterDocument90 pagesConveying MasterYen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Slat ConveyorDocument8 pagesSlat ConveyorpkjddjsydNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Belt Scale Data SheetDocument2 pagesConveyor Belt Scale Data SheetEDUARDONo ratings yet
- O&M Instruction of Screw UnloaderDocument84 pagesO&M Instruction of Screw Unloadertienhunght100% (1)
- Roller Conveyor CatalogueDocument50 pagesRoller Conveyor CatalogueAbudo Paixao100% (2)
- Appendix A1Document5 pagesAppendix A1Thomas Stephen100% (1)
- Steel Cord Conveyor Belts PDFDocument2 pagesSteel Cord Conveyor Belts PDFnicolasNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor Design-Dunlop 1Document161 pagesBelt Conveyor Design-Dunlop 1Andrew PotterNo ratings yet
- Catalogue R I Tang Đ NG Cơ Rulmeca PDFDocument8 pagesCatalogue R I Tang Đ NG Cơ Rulmeca PDFRulmeca Việt Nam100% (1)
- Roller Conveyor Design ReportDocument21 pagesRoller Conveyor Design Reportabdallah391No ratings yet
- Mato Belt Cleaner CatalogueDocument12 pagesMato Belt Cleaner Catalogueleeyod100% (1)
- Conveyor Screws PDFDocument9 pagesConveyor Screws PDFldavilaluceralNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor Vertical CurvesDocument1 pageBelt Conveyor Vertical CurvesmlacordNo ratings yet
- Conveyor CalculationsDocument10 pagesConveyor CalculationsCristhian PortocarreroNo ratings yet
- High Performance Bucket Elevator CatalogDocument12 pagesHigh Performance Bucket Elevator CatalogcachorrexNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of Roller Conveyor SystemDocument5 pagesDesign and Optimization of Roller Conveyor SystemAnkit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Imososa Mining Company Crushing Plant ReportDocument14 pagesImososa Mining Company Crushing Plant ReportTawanda NyambiyaNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator ManualDocument37 pagesBucket Elevator ManualEdwin MarsigliaNo ratings yet
- PDF BeltConveyorsCalculationsCEMA5 EngDocument46 pagesPDF BeltConveyorsCalculationsCEMA5 EngfelramNo ratings yet
- 3 Date 2 1 0 R e V I S I o N Checked by Checked by Approve DbyDocument2 pages3 Date 2 1 0 R e V I S I o N Checked by Checked by Approve DbyidilfitriNo ratings yet
- Pan Conveyors PDFDocument20 pagesPan Conveyors PDFChristian Makande100% (2)
- Line-by-line conveyor code for material handling parameters and calculationsDocument4 pagesLine-by-line conveyor code for material handling parameters and calculationskmats2No ratings yet
- Chain ConveyorsDocument4 pagesChain Conveyorsarup11nvNo ratings yet
- Ceylan Telescopic Conveyor Belt ManualsDocument24 pagesCeylan Telescopic Conveyor Belt ManualsFarshad MahmoudiNo ratings yet
- SiloDocument285 pagesSiloantiacidoNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Design-DraftDocument42 pagesConveyor Design-Draftmkchy1295% (21)
- Belt Conveyor Take Up DesignDocument4 pagesBelt Conveyor Take Up DesignKroya HunNo ratings yet
- Bulk Material Handling Belt-Conveyor-CatalogDocument21 pagesBulk Material Handling Belt-Conveyor-CatalogjayNo ratings yet
- Belt Drive SystemDocument15 pagesBelt Drive Systemafsana_rajNo ratings yet
- M 275 ContentDocument40 pagesM 275 ContentAnonymous DQ4wYUmNo ratings yet
- ConveyorsDocument17 pagesConveyorsmissy forlajeNo ratings yet
- DTS - Belt Bucket Elevator - DatasheetDocument3 pagesDTS - Belt Bucket Elevator - DatasheetBRUNA NASCIMENTONo ratings yet
- Textile Conveyor BeltsDocument24 pagesTextile Conveyor BeltsShrinivas Bartakke100% (1)
- Actuators Cat Andco f10 08Document52 pagesActuators Cat Andco f10 08Thalavai Balamurugan100% (1)
- Vertical Screw Elevators PDFDocument10 pagesVertical Screw Elevators PDFtamil vaananNo ratings yet
- Num g01 Bin DesignDocument48 pagesNum g01 Bin DesignfranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pipe Conveyor Belts: With Steel Cord and Fabric ReinforcementDocument5 pagesPipe Conveyor Belts: With Steel Cord and Fabric ReinforcementEugenepaccelli Kolandai SamyNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyors PDFDocument23 pagesBelt Conveyors PDFNitesh Singh100% (1)
- Bucket ElevatorsDocument6 pagesBucket Elevatorskingathur26681No ratings yet
- Conveyor Chain SelectionDocument2 pagesConveyor Chain SelectionAmeya Datrange100% (2)
- Design, Fabrication and Testing of A Low Headroom Conveyor Transfer ChuteDocument132 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Testing of A Low Headroom Conveyor Transfer ChuteJakesNo ratings yet
- Conveyor DesignDocument73 pagesConveyor DesignAl Hisadin95% (22)
- Mathews Roller ConveyorsDocument136 pagesMathews Roller ConveyorsSergio Fernandes PereiraNo ratings yet
- Belt Jointing ProcedureDocument5 pagesBelt Jointing ProcedureproxywarNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ConveyorDocument36 pagesPneumatic ConveyorA.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Conveyor SelectionDocument14 pagesConveyor SelectionDr_M_Soliman100% (2)
- Roller DesignDocument34 pagesRoller DesignAnonymous z4Fe39j100% (1)
- Shaftless Screw ConveyorsDocument2 pagesShaftless Screw Conveyorshenker21No ratings yet
- Sedis Conveyor Chains Catalogue PDFDocument236 pagesSedis Conveyor Chains Catalogue PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Sorting SystemsDocument5 pagesSorting Systems25 Hitesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bag Palletizer Up To 30 Picks Per MinuteDocument2 pagesBag Palletizer Up To 30 Picks Per MinutetintucinbNo ratings yet
- Complete CatalogueDocument41 pagesComplete CatalogueRad AlexNo ratings yet
- GIS Electric Chain Hoists For 1001 Jobs: Lifting TechnologyDocument12 pagesGIS Electric Chain Hoists For 1001 Jobs: Lifting TechnologyJoao PereiraNo ratings yet
- Escalator & Travelator PDFDocument17 pagesEscalator & Travelator PDFasyrafmuhddNo ratings yet
- SH E096qDocument24 pagesSH E096qkanstopthankNo ratings yet
- Role of MH Equipments Working & SafetyDocument31 pagesRole of MH Equipments Working & SafetyRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Overhead ConveyorsDocument9 pagesOverhead ConveyorsFederico MejiaNo ratings yet
- An Academic Research Publishing Checklist: Brian WhitworthDocument12 pagesAn Academic Research Publishing Checklist: Brian WhitworthzainonayraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Math Form 1Document11 pagesFinal Exam Math Form 1zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Toyota in Variable NvironDocument621 pagesToyota in Variable NvironzainonayraNo ratings yet
- HTTP WWW - Emeraldinsight.com - Ezaccess.library - Uitm.edu - My Insight ViewContentServlet Contenttype Article&Filename Published Emeraldfulltextarticle PDF 0220250204Document21 pagesHTTP WWW - Emeraldinsight.com - Ezaccess.library - Uitm.edu - My Insight ViewContentServlet Contenttype Article&Filename Published Emeraldfulltextarticle PDF 0220250204zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Ebert Griffin PP04Document28 pagesEbert Griffin PP04zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Identify and Inspect Solenoid Valve: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2Document12 pagesIdentify and Inspect Solenoid Valve: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Identify and Inspect Solenoid Valve: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2Document12 pagesIdentify and Inspect Solenoid Valve: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Destructive and Non Destructive Testing of MaterialDocument33 pagesChapter 7 - Destructive and Non Destructive Testing of MaterialzainonayraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3zainonayraNo ratings yet
- L5 Laws of Logarithms WorksheetDocument2 pagesL5 Laws of Logarithms WorksheetzainonayraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5zainonayraNo ratings yet
- IllusionsDocument7 pagesIllusionszainonayraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Identify Air Compressor: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2Document12 pagesIdentify Air Compressor: Basic Hydraulic & Pneumatic System 2zainonayraNo ratings yet
- D.Riche, A.Franklin - Watercolor Fairies - Creating The Fairy World PDFDocument131 pagesD.Riche, A.Franklin - Watercolor Fairies - Creating The Fairy World PDFSangeeta BastodkarNo ratings yet
- 2013 CalendarDocument1 page2013 Calendar8610261830No ratings yet
- MKT 232 Exam 2 Study QuestionsDocument2 pagesMKT 232 Exam 2 Study QuestionszainonayraNo ratings yet
- Premises Corporate StrategyDocument18 pagesPremises Corporate StrategyzainonayraNo ratings yet
- The Business Case For Process SafetyDocument24 pagesThe Business Case For Process SafetyzainonayraNo ratings yet
- Architecture: The Art and Design That Goes Into Making Buildings Is Known As ArchitectureDocument3 pagesArchitecture: The Art and Design That Goes Into Making Buildings Is Known As ArchitecturezainonayraNo ratings yet
- 10.3 MomentsDocument7 pages10.3 MomentszainonayraNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument80 pagesLenseszainonayraNo ratings yet
- UT Austin Small Business Subcontracting ProgramDocument28 pagesUT Austin Small Business Subcontracting ProgramzainonayraNo ratings yet
- Topic 22 Perpendicular LinesDocument4 pagesTopic 22 Perpendicular LineszainonayraNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document49 pagesCH 12zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Strategy and Competitive Dynamics: Chapter EightDocument41 pagesEntrepreneurial Strategy and Competitive Dynamics: Chapter EightJose Luis AlamillaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document31 pagesPhysics Form 4evrex0% (2)
- Physics430 Lecture01Document26 pagesPhysics430 Lecture01zainonayraNo ratings yet
- Free Enterprise Test AnswersDocument6 pagesFree Enterprise Test AnswersSupriyasingh16No ratings yet
- A Force That Opposes - Acts Parallel To The: Motion Surfaces in ContactDocument37 pagesA Force That Opposes - Acts Parallel To The: Motion Surfaces in ContactzainonayraNo ratings yet
- LG Therma V Split Rukovodstvo PolzovatelyaDocument30 pagesLG Therma V Split Rukovodstvo Polzovatelyagheorghe tabaraNo ratings yet
- IRMCF312: Dual Channel Sensorless Motor Control IC For AppliancesDocument35 pagesIRMCF312: Dual Channel Sensorless Motor Control IC For AppliancesMeselao Meselao MeselaoNo ratings yet
- 2 WaydistributorDocument53 pages2 WaydistributormbhaditNo ratings yet
- New Denon PMA-510AE Integrated AmplifierDocument2 pagesNew Denon PMA-510AE Integrated AmplifierKaushik SinghaNo ratings yet
- TRAX Automatic Switch Box Reduces Transformer Test TimeDocument4 pagesTRAX Automatic Switch Box Reduces Transformer Test TimeEduardo ToroNo ratings yet
- Passport P250 ManualDocument15 pagesPassport P250 ManualJoe BauerNo ratings yet
- P0011 - P0012Document8 pagesP0011 - P0012jeremih alhegnNo ratings yet
- Jacobsen F305Document216 pagesJacobsen F305Lady Marcela RodriguezNo ratings yet
- M 1Document59 pagesM 1KEEP CALM studiosNo ratings yet
- Operator Manual HL MODELO 90-5000 Ingerson-IntermediaDocument37 pagesOperator Manual HL MODELO 90-5000 Ingerson-IntermediaRafael Agustin Menchaca MarinNo ratings yet
- Rotulado FotovoltaicasDocument1 pageRotulado FotovoltaicasMauricio GalloNo ratings yet
- TM1115 - STM32F103ZE - Chapter 6 (I2C - LCD)Document23 pagesTM1115 - STM32F103ZE - Chapter 6 (I2C - LCD)Safwat KhairNo ratings yet
- BVR2220GBDocument4 pagesBVR2220GBFerdhy EdhyNo ratings yet
- Canon Pixma MP600 Service ManualDocument71 pagesCanon Pixma MP600 Service ManualAnonymous egTruyVdxvNo ratings yet
- Assemble GEMO D-04 Contactless Ignition System in Under 40 StepsDocument9 pagesAssemble GEMO D-04 Contactless Ignition System in Under 40 StepsManuel Ćulibrk100% (1)
- H2 Power Bank ManualDocument19 pagesH2 Power Bank ManualMarcantonio Infascelli100% (1)
- Epsonvs 43 ADocument15 pagesEpsonvs 43 AInna C HernándezNo ratings yet
- Cargo Securement Guide 2017Document76 pagesCargo Securement Guide 2017vegeta1984No ratings yet
- Go Green With APT: UL Listed To UL 1449-3 Photovoltaic StandardDocument2 pagesGo Green With APT: UL Listed To UL 1449-3 Photovoltaic Standarddnps2011No ratings yet
- Marantz pm4000Document9 pagesMarantz pm4000cucu_spywareNo ratings yet
- 1995 KLX650 CarburetorDocument3 pages1995 KLX650 CarburetorPedro VegaNo ratings yet
- E74h IbmDocument37 pagesE74h IbmJose BerrospiNo ratings yet
- PT Burden Calculations 01 PDFDocument4 pagesPT Burden Calculations 01 PDFArunava Basak100% (2)
- Reutech - Electric Gun DrivesDocument2 pagesReutech - Electric Gun DrivesOsorio LuisNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Brazing Pipe and TubingDocument6 pagesProcedures For Brazing Pipe and Tubingphankhoa83No ratings yet
- Gemini Videocaster ManualDocument4 pagesGemini Videocaster ManualjimdigrizNo ratings yet
- SMC8508T Ug R01Document27 pagesSMC8508T Ug R01Epure LiviuNo ratings yet
- Grupo Electrogeno Kohler 14 20RESADocument6 pagesGrupo Electrogeno Kohler 14 20RESAUrs SantellanNo ratings yet
- Apl 1117Document19 pagesApl 1117Oscar R. Cárdenas CéspedesNo ratings yet
- 416b Elec - TransDocument9 pages416b Elec - TransFelix CruzNo ratings yet