Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 Seconds
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne SupnetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 Seconds
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne SupnetCopyright:
Available Formats
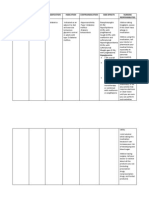
DRUG NAME Brand Name: Imdur Generic Name: Isosorbide Mononitrate 60mg/tab 1x a day at bedtime
DRUG CLASSIFICATION Antianginal Nitrate Vasodilator
THERAP Imdur will not treat an angina attack that has already begun.
Indications Treatment and prevention of Angina Pectoris.
Contraindication Severe Anemia, Head Trauma, Cerebral Hemorrhage, Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Orthostatic Hypotension. Use Cautiously: Acute MI, Heart Failure
Adverse Effects CNS: Headache, apprehension, restlessness, weakness, bvertigo, dizziness, faintness CV: Tachycardia, palpitation, hypotension, syncope, collapse, orthostatic hypotension, angina, rebound hypertension, atrial fibrillation Dermatologic: Rash, expoliative dermatitis, cutaneous vasodilation with flushing GI: Nausea, vomiting, incontinence of faces, abdominal pain, ulcer, diarrhea
Nursing Responsibilities -Caution: hypovolemia, mild hypotension. - Monitor BP frequently during therapy . -Give 1 hr before/2 hr after meals. -Can experience daily headaches from vasodilatation. -Abrupt D/C can cause angina, increase risk of MI. Patient Teaching: -Teach s/s of angina (chest pain, fullness, nausea)
GU: Dysuria, impotence, urinary frequency Other: muscle twitching, pallo, perspiration, cold, sweat, athralgia, bronchitis, thrombocytopenia
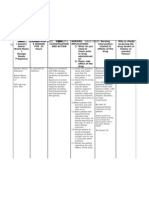
Drug Name Brand Name: Coreg Generic Name: Carvidelol 25mg tab 2x a day hold if BP <100 <60
Drug Classification Alpha and beta adrenergic blocker Antihyperten sives
Therapeutic Action Competitively blocks alpha-, beta, and beta2adrenergic receptors and has some sympathomimetic activity at beta2receptors. Both alpha and beta blocking actions contribute to the BP-lowering effect; beta blockade prevents the reflex tachycardia seen with most alphablocking drugs and decreases plasma renin activity. Significantly reduces plasma renin activity. -
Indications Hypertension, alone or with other oral drugs, especially diuretics Treatment of mild to severe CHF of ischemic or cardiomyopat hic origin with digitalis, diuretics, ACE inhibitors Left ventricular dysfunction Unlabeled uses: Angina (20-50mg BID)
Contraindication Contraindicated with decompensated CHF, bronchial asthma, heart block, cardiogenic shock, hypersensitivity to carvedilol, pregnancy, lactation. Use cautiously with hepatic impairment, peripheral vascular disease, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, anesthesia, major surgery
Adverse Effects CNS: Dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, fatigue, emotional depression, paresthesias, sleep disturbances CV:Bradycardia, orthostatic hypertension, CHF, cardiac arrhythmias, pulmonary edema, hypotension GI: Gastric pain, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, hepatic failure Respiratory:Rhin itis, pharyngitis, dyspnea Other: Fatigue, back pain, infections
Nursing Responsibilities Assessment History: CHF, bronchial asthma, heart block, cardiogenic shock, hypersensitivity to carvedilol, pregnancy, lactation, hepatic impairment, peripheral vascular disease, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, anesthesia or major surgery Physical: Baseline weight, skin condition ,neurologic status, P,BP, ECG, respiratory status, LFTs, renal and thyroid function tests, blood and urine glucose
WARNING: Do not discontinue drug abruptly after chronic therapy
(hypersensitivity to catecholamines may have developed, causing exacerbationof angina, MI, and ventricular arrhythmi as); taper drug gradually over 2wk with monitoring. Give with food to decrease orthostatic hypotension and adverse effects. Monitor for orthostatic hypotension and provide safety precautions. Monitor diabetic patient closely; drug may mask hypoglycemia or worsen hyperglycemia. WARNING: Monitor patient for any sign of hepatic impairment (pruritus, dark urine or stools,
anorexia, jaundice, pain); arrange for LFTs and discontinue drug if tests indicate liver injury. Do not re start carvedilol Teaching points Take drug with meals. Do not stop taking drug unless instructed to do so by a healthcare provider. Advise the diabetic patient to promptly report changes in glucose. You may experience these side effects: Depression, dizziness, light-headedness (avoid driving or performing dangerous activities; getting up and changing positions slowly may help ease dizziness).
Report difficulty breathing, swelling of extremities, changes in color of stool or urine, very slow heart rate, continued dizziness
Drug Name
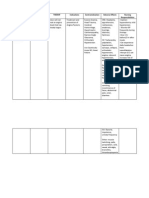
Brand Name: Digoxin Generic Name: Lanoxin 0.25 mg tab every other day
Drug Classificati on Cardiac Glycoside Cardiotonic
Therapeutic Action
Indications
Contraindication
Adverse Effects CNS: Headache, weakness, drowsiness, visual disturbances, mental status change CV: Arrhythmias GI: GI upset, Anorexia
Nursing Responsibilities
Inhibits sodiumHeart Failure potassium activated Atrial fibrillation adenosine triphosphate, promoting movement of calcium from extracellular to intracellular cytoplasm and strengthening myocardial contraction. Also acts on CNS to enhance vagal tone, slowing conduction through the SA node and AV nodes.
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with digitalisinduced toxicity, ventricular tachycardia unless caused by heart failure. Use with extreme caution in elderly patients and in those with acute MI, incomplete AV block, sinus bradycardia, cardiomyopathy and renal insufficiency.
1 . Drug induced arrhythmias may increase the severity of heart failure and hypotension. 2 . Before giving loading dose obtain baseline date. (BP, HR and electrolytes) and ask patient about use of cardiac glycoside with the previous 2 to 3weeks. 3 . Before g i v i n g d r u g t a k e apical-radial pulse for 1 minute. Record and notify physician of significant changes (sudden increase or decrease in pulse rate, pulse deficit, irregular beats). 4 . ALERT: excessive slowing of pulse rate may be a sign of digitalis toxicity. Withhold the drug and notify physician. 5 . Monitor potassium carefully.
Drug Name Brand Name: Lipitor Generic Name: Atorvast atin Calcium 40 mg/ tab once a day at bedtime
Drug Classificatio n Antihyperlip idemic HMG-Coa Reductase inhibitor
Therapeutic Action Inhibits HMGCoAreductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the cholesterolsynth esis pathway, resulting in a decrease in serum cholesterol, serum LDLs (associated with increased risk of CAD), and increases serum HDLs (associated with decreased risk of CAD); increases hepatic LDL recapture sites, enhances reuptake and catabolism of LDL; lowers triglyceride levels
Indications
Contraindication
Adverse Effects CNS: Headache, asthenia GI: Flatulence, abdominal pain, cramps, constipation, nausea, dyspepsia, heartburn, liver failure Respiratory: Sinusitis, pharyngitis Other: Rhabdomyoly sis with acute renal failure, arthralgia, myalgia
Nursing Responsibilities 1. Monitor patient s lipid and liver function levels at baseline and periodically thereafter. 2. Take this drug once a day, at about the same time each day, preferably in the evening; may be taken with food. Do not drink grapefruit j uice while taking this drug. 3. Monitor patients lipid and liver function levels at baseline and periodically thereafter.
Adjunct to diet in treatment of elevated total cholesterol, serum triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia (types IIa and IIb)and mixed dyslipidemia, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, and homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia whose response to dietary restriction of saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures has not been adequate To increase HDL-Cin patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia Adjunct to diet to treat elevated serum triglyceride levels Prevention of CV disease in adults without clinically evident coronary disease but with multiple risk factors for CAD such as age> 55 yr, smoking, hypertension, low HDL-C, family history of early CAD; to reduce the risk of MI and risk for revascularization procedures and angina
Contraindicated with allergy to atorvastatin, fungal by products ,active liver disease or unexplained and persistent elevations of transaminase levels, Use cautiously with impaired endocrine function, history of liver disease, alcoholism
Drug Name
Drug Classification
Therapeutic Action
Indications
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
Brand Name: Aceon Generic Name: Perindopril erbumine 5mg/tab 1x a day in the morning
Ace Inhibitor Antihypertensives
NOTE: potassiu
Perindopril erbumine tablets are a pro-drug for Perindoprilat, which inhibits ACE in human subjects and animals. The mechanism through which Perindoprilat lowers blood pressure is believed to be primarily inhibition of ACE activity. ACE is a peptidyl dipeptidase that catalyzes conversion of the inactive decapeptide, angiotensin I, to the vasoconstrictor, angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent peripheral vasoconstrictor, which stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex, and provides negative feedback
Treatment of hypertension and mild to moderate congestive heart failure. Treatment of patient with stable coronary artery disease to reduce the risk of CV mortality and nonfatal MI. Can be used with conventional treatment for management of coronary artery disease, such as antiplatelet, antihypertensive or lipid-lowering therapy.
Perindopril Erbumine Tablets are contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive (including angioedema) to this product or to any other ACE inhibitor. Perindopril Erbumine Tablets are also contraindicated in patients with hereditary or idiopathic angioedema.
CNS: Headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, paresthesias CV: Orthostatic Hypotension, tachycardia, angina pectoris, MI, Raynauds syndrome, Heart Failure GI: gastric Irritation, nausea, diarrhea, aphthous ulcers, peptic ulcers, dysgeusia, cholestatic jaundice, heaptocellular injury, anorexia,consti pation GU: Proteinuria, renal
Monitor BR and HR carefully following initial dose for several hours until stable, especially in patients using concurrent diuretics, on salt restriction, or volume depleted. Place patient immediately in a supine position if excess hypotension develops. Lab tests: Monitor serum potassium, serum sodium, BUN and creatinine, ALT, blood glucose lipid profile, and WBC with differential periodically. Monitor kidney function in patients with CHF closely. Monitor serum lithium levels and
on renin secretion. Inhibition of ACE results in decreased plasma angiotensin II, leading to decreased vasoconstriction, increased plasma renin activity and decreased aldosterone secretion. The latter results in diuresis and natriuresis and may be associated with a small increase of serum potassium. ACE is identical to kininase II, an enzyme that degrades bradykinin. Whether increased levels of bradykinin, a potent vasodepressor peptide, play a role in the therapeutic effects of Perindopril
insufficiency, renal failure, plyuria, oliguria, frequency of urination Hematologic: Neutropenia, agranulocytosis , thrombocytope nia, hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia Other: Angioedema (face, extremities, lips, tongue, larynx death has been reported cough, muscle cramps, impotence
assess for S&S of lithium toxicity frequently when used concurrently; increased caution is needed when diuretic therapy is also used.
erbumine tablets remains to be elucidated. While the principal mechanism of Perindopril in blood pressure reduction is believed to be through the reninangiotensinaldosterone system, ACE inhibitors have some effect even in apparent lowrenin hypertension. Perindopril has been studied in relatively few black patients, usually a low-renin population, and the average response of diastolic blood pressure to Perindopril was about half the response seen in nonblack patients, a finding consistent with
previous experience of other ACE inhibitors.
Drug Name Brand Name: Lasix Generic Name: Furosemide 40mg/tab 1x a day
Drug Classification Loop Diuretic
Therapeutic Action Inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the proximal and distal tubules and ascending limb of the loop of Henle, leading to a sodium rich dieresis.
Indications Edema associated with heart failure, cirrhosis, renal disease, hypertension
Contraindication Anuria, severe renal failure, hepatic coma Use cautiously with SLE, gout, DM
Nursing Responsibilities CNS: dizziness, vertigo, Monitor weight, paresthesias, xanthopsia, blood pressure, weakness, and pulse rate headache, drowsiness, routinely with fatigue, blurred vision, long term use tinnitus, irreversible hearing and during rapid loss diuresis. Furosemide can CV: orthostatic hypotension, lead to profound volume depletion, cardiac and electrolyte arrythmias, thrombophlebitis depletion. Dermatologic: Photosensitivity, rash, pruritus, urticaria, purpura, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme GI: vomiting, nausea, anorexia, oral and gastric irritation, constipation, diarrhea, acute pancreatic, jaundice GU: polyuria, nocturia, glycosuria, urinary blader spasm HEMA: leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, fluid and electrolyte imbalances, hyperglycemia, Monitor fluid intake and output and electrolyte, BUN, and carbon dioxide level frequently. Watch for signs of hypokalemia such as muscle weakness and cramps Advise patient to immediately report ringing ears, severe abdominal pain, or sore throat
Adverse Effects
hyperuricemia Other: muscle cramps and muscle spasms
and fever which may indicate furosemide toxicity
Drug Name Brand Name: Aldactone Generic Name: Spinolactone 25mg/tab 1x a day at noon
Drug Classification Aldosterone antagonist Potassium Sparing Diuretic
Therapeutic Action Competitively blocks the effects of aldosterone in the renal tubule, causing loss of sodium and water and retention of potassium.
Indications Edema Hypertension Diuretic-induced hypokalemia
Contraindication Contraindicated to patients hypersensitive to drug.
Adverse Effects CNS: headache, drowsiness, lethargy, confusion, ataxia GI: diarrhea, gastric bleeding, ulceration, cramping, gastritis, vomiting GU: inability to maintain erection Hematologic: agranulocytosis Metabolic: hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, dehydration, mild acidosis Skin: urticaria, hirsutism, maculopapular eruptions. Other: drug fever, anaphylaxis
Nursing Responsibilities To enhance absorption, give drug with meals. Protect drug from light. Monitor electrolyte levels, fluid intake and output, weight and blood pressure. Monitor elderly patients closely, who are more susceptible to excessive diuresis. Inform laboratory that patient is taking spironolactone because drug may interfere with tests that measure digoxin level. Maximum hypertensive
Contraindicated in those with anuria, To detect primary acute or hyperaldosteronism progressive renal insufficiency, or To manage primary hyperkalemia. hyperaldosteronism Use cautiously in Heart failure, as patients with fluid adjunct to ACE and electrolyte inhibitor or loop imbalances, diuretic, with or impaired renal without function, or cardiacglycoside hepatic disease. Acne vulgaris Familial male precociouspuberty Use with extremecaution in pregnantwomen
response may be delayed for up to 2weeks. Watch out for hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, which may occur during therapy, especially in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Instruct patient to take drug in morning to prevent need to urinate at night. If second dose is needed, tell him to take it with food in the early afternoon. Alert: to prevent serious hyperkalemia, warn patient to avoid excessive ingestion of potassium-rich foods, potassiumcontaining salt substitutes, and
potassium supplements.
8. Insulin 9. feso4 10. Folic Acid 11. flumucil 12. tramadol 13. nystatin gargle 14. iselpin 15. ompeprazole 16. lactulose 17. calmoseptine
Drug name Arixtra
Drug Classification
Anticoagulants, Antiplatelets & Fibrinolytics
Therapeutic action
Mechanism of Action: Fondaparinux is a synthetic and selective inhibitor of
Indications
Prevention of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in patients
Contraindication Adverse effects
Hypersensitivity. Active clinically significant bleeding, acute bacterial Anemia, bleeding, purpura; edema.
Nursing Responsibilities
Do not administer IM. Do not give 24 hr prior to CABG surgery & may be restarted 48 hr post-op. STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI for reperfusion. Monotherapy in
(Thrombolytics)
activated factor X (Xa). The antithrombotic activity of fondaparinux is the result of antithrombin III (ATIII)-mediated selective inhibition of factor Xa. By binding selectively to ATIII, fondaparinux potentiates (about 300 times) the innate neutralization of factor Xa by ATIII. Neutralization of factor Xa interrupts the blood coagulation cascade and inhibits both thrombin formation and thrombus development. Fondaparinux does not inactivate thrombin (activated factor II) and has no known effect on platelet function. Pharmacodynamic Effects: At the 2.5 mg dose, fondaparinux does not have a clinically relevant effect on routine coagulation tests eg, activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), activated clotting time (ACT) or prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR) tests in plasma, nor bleeding time or fibrinolytic activity.
undergoing major orthopedic surgery of the lower limbs eg hip fracture including extended prophylaxis, knee & hip replacement surgery; abdominal surgery at risk of thromboembolic complications, restricted mobility during acute illness who are at risk of thromboembolic complications. Treatment of acute DVT & pulmonary embolism (PE), unstable angina or non-ST segment elevation MI (UA/NSTEMI) acute coronary syndrome for the prevention of death, MI & refractory ischemia; ST segment elevation MI (STEMI) acute coronary syndrome for the prevention
endocarditis.
UA/NSTEMI & STEMI patients undergoing non-primary PCI. Increased risk of hemorrhage eg congenital or acquired bleeding disorders, active ulcerative GI disease, recent intracranial hemorrhage, shortly after brain, spinal or ophth surgery. Low body wt <50 kg; spinal/epidural anesth or spinal puncture. History of heparininduced thrombocytopenia & latex allergy. Renal (CrCl <20 or 30 mL/min) or severe hepatic impairment. Close monitoring is recommended in patients concomitantly taking products enhancing the risk of hemorrhage. Pregnancy & lactation. Childn <17 yr. Elderly 75 yr.
However, rare spontaneous reports of elevated aPTT have been received at the 2.5 mg dose. Fondaparinux does not cross-react with sera from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) type II.
of death & myocardial reinfarction in patients who are managed w/ thrombolytics or who initially are to receive no other form of reperfusion therapy.
Drug name Humulin R insulin (regular)
Drug Classification Insulin Preparations
Therapeutic action
Pharmacology: The time course of action of any insulin may vary considerably in different individuals or at different times in the same individual. As with all insulin preparations, the duration of action of Humulin is dependent on dose, site of injection, blood supply, temperature and physical activity. Humulin N (NPH): Vial: Humulin N (NPH) contains isophane human insulin of recombinant DNA origin. It is an intermediate-acting preparation; onset of action is approximately 1 hr, with a duration of about 14 hrs and peak activity at 2-8 hrs.
Indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus for the control of hyperglycemia.
Contraindication Adverse effects
Hypoglycemia. Lipodystrophy, insulin resistance. Local & generalised allergic reactions.
Nursing Responsibilities
Transferring from other insulins. Emotional distress. Infection. Pregnancy.
Cartridge: Humulin N (NPH) is a sterile, crystalline suspension of human insulin with protamine and zinc, providing an intermediate-acting insulin with a slower onset of action and a longer duration of activity (up to 24 hrs) than that of regular insulin. Humulin R (Regular): Humulin R (Regular) is a neutral human insulin of recombinant DNA origin. It is a shortacting preparation; onset of action occurs at approximately 30 min, with a duration of about 5 hrs and peak activity at 1-3 hrs. Humulin 70/30: Humulin 70/30 is an intermediateacting insulin combined with the more rapid onset of action of regular insulin. The duration of activity may last up to 24 hrs following injection.
Drug name Ferrous Sulfate
Drug Classification
Belongs to the class of oral iron bivalent preparations. Used in the treatment of anemia.
Therapeutic action
Antianemic.
Indications
Prophylaxis & treatment of simple Fedeficiency disorders & Fe-
Contraindication Adverse effects
Anemia not due to Fe deficiency, intolerance to Fe, inability to absorb Fe, regional GI irritation.
Nursing Responsibilities
Should be taken on an empty stomach. Best taken on an empty stomach. May be taken w/ meals to reduce GI discomfort.
deficiency anemia.
enteritis, colostomy, ileostomy or hemochromatosis.
Drug name Folic Acid
Drug Classification
Vitamins & Minerals (Pre & Post Natal) / Antianemics
Therapeutic action
Indications
Treatment & prevention of folate deficiency state. Protection against neural tube defects in the offspring of pregnant & women of childbearing potential.
Contraindication Adverse effects
Rarely, GI disturbances & hypersensitivity reactions.
Nursing Responsibilities
Undiagnosed megaloblastic anemia alone or in conjunction w/ inadequate amounts of vit B12. May be taken with or without food.
Drug name Fluimucil
Drug Classification
acetylcysteine ; Belongs to the class of mucolytics. Used in the treatment of
Therapeutic action
Indications
Acute & chronic resp tract infections w/ abundant mucus
Contraindication Adverse effects
Effervescent tab/Oral soln: Phenylketonurics. Rarely, urticaria, bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting. Inhalant: Rhinitis, stomatitis.
Nursing Responsibilities
Asthmatic patients. Patients w/ history of peptic ulceration. Should be taken with food.
wet cough.
secretions due to acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis & its exacerbations, pulmonary emphysema, mucoviscidosis & bronchiectasis.
You might also like
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- How Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidDocument1 pageHow Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLee JennyNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- LactuloseDocument2 pagesLactuloseGrace Iloreta RN82% (11)
- Febuxostat lowers uric acid for goutDocument2 pagesFebuxostat lowers uric acid for goutJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Clopidogrel - Drug StudyDocument1 pageClopidogrel - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- Therabloc Antihypertensive Drug Atenolol Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesTherabloc Antihypertensive Drug Atenolol Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Losartanhahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Humulin RDocument1 pageHumulin RZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument2 pagesGliclazideReinell GoNo ratings yet
- SimvastatinDocument3 pagesSimvastatinLonnieAllenVirtudes100% (1)
- AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesAtorvastatinJasmin T LarizaNo ratings yet
- Mannitol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMannitol Drug StudyNo Vem BerNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Besylate Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Besylate Drug StudyKrissy Java100% (1)
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Lansoprazole Drug Study SummaryDocument2 pagesLansoprazole Drug Study SummaryGeorley Lobrido100% (1)
- Vitamin B ComplexDocument2 pagesVitamin B ComplexCar_Mi_3606No ratings yet
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- AeknilDocument2 pagesAekniljaycey24No ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageDrug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Drug study details effects of amlodipineDocument1 pageDrug study details effects of amlodipineaagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SitagliptinDocument2 pagesDrug Study SitagliptinAl Theó0% (1)
- XareltoDocument2 pagesXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Irbesartan (Avapro)Document1 pageIrbesartan (Avapro)ENo ratings yet
- Cordarone for Arrhythmias: Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing CareDocument1 pageCordarone for Arrhythmias: Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing CarejaybamanNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Cholestyramine (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCholestyramine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blocker AmlodipineDocument2 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker AmlodipineRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Nebivolol for BP Lowering (BystolicDocument1 pageNebivolol for BP Lowering (BystolicshaeNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCebu Normal University College of Nursing Drug StudyFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Fondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesFondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Senna Concentrate Drug Study: Senokot Forte LaxativeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate Drug Study: Senokot Forte LaxativeTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Lactulose DrugDocument3 pagesLactulose DrugjangzieNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameMichael PalmaNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetoprolol Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- MorphineDocument1 pageMorphineKenny Nadela67% (3)
- CatapresDocument1 pageCatapres去約翰No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricJhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Memantine, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Rivastigmine, Losartan, Aspirin, ClopidogrelDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Memantine, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Rivastigmine, Losartan, Aspirin, ClopidogrelCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SUMMARYDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY SUMMARYEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Bisoprolol FumarateDocument3 pagesBisoprolol Fumarateapi-37979410% (1)
- Requirements in Basic Skills TrainingDocument1 pageRequirements in Basic Skills TrainingJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- University Evansville nursing drug sheetDocument2 pagesUniversity Evansville nursing drug sheetJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Registered Nurses Philippines Health Service ApplicationDocument1 pageRegistered Nurses Philippines Health Service ApplicationNica NixNo ratings yet
- NPIDocument12 pagesNPIJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsDocument23 pagesImdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- 2-Library - IJLSR - Information - SumanDocument10 pages2-Library - IJLSR - Information - SumanTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- ESSAYSDocument5 pagesESSAYSDGM RegistrarNo ratings yet
- Character Interview AnalysisDocument2 pagesCharacter Interview AnalysisKarla CoralNo ratings yet
- Barnett Elizabeth 2011Document128 pagesBarnett Elizabeth 2011Liz BarnettNo ratings yet
- Simple Future Vs Future Continuous Vs Future PerfectDocument6 pagesSimple Future Vs Future Continuous Vs Future PerfectJocelynNo ratings yet
- MES - Project Orientation For Night Study - V4Document41 pagesMES - Project Orientation For Night Study - V4Andi YusmarNo ratings yet
- Safety Moment Manual LiftingDocument1 pageSafety Moment Manual LiftingEvert W. VanderBerg100% (1)
- Walter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 - 30 July 1894) Was An English EssayistDocument4 pagesWalter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 - 30 July 1894) Was An English EssayistwiweksharmaNo ratings yet
- Business Planning Process: Chapter-Four Operations Planning and ControlDocument12 pagesBusiness Planning Process: Chapter-Four Operations Planning and ControlGemechis BussaNo ratings yet
- Decision Support System for Online ScholarshipDocument3 pagesDecision Support System for Online ScholarshipRONALD RIVERANo ratings yet
- Bioethics: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument6 pagesBioethics: Bachelor of Science in NursingSherinne Jane Cariazo0% (1)
- FIITJEE Talent Reward Exam 2020: Proctored Online Test - Guidelines For StudentsDocument3 pagesFIITJEE Talent Reward Exam 2020: Proctored Online Test - Guidelines For StudentsShivesh PANDEYNo ratings yet
- The Secret Path Lesson 2Document22 pagesThe Secret Path Lesson 2Jacky SoNo ratings yet
- Fill in The BlanksDocument38 pagesFill in The Blanksamit48897No ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud QuotesDocument7 pagesSigmund Freud Quotesarbeta100% (2)
- Term2 WS7 Revision2 PDFDocument5 pagesTerm2 WS7 Revision2 PDFrekhaNo ratings yet
- Category Theory For Programmers by Bartosz MilewskiDocument565 pagesCategory Theory For Programmers by Bartosz MilewskiJohn DowNo ratings yet
- Napolcom. ApplicationDocument1 pageNapolcom. ApplicationCecilio Ace Adonis C.No ratings yet
- Price and Volume Effects of Devaluation of CurrencyDocument3 pagesPrice and Volume Effects of Devaluation of Currencymutale besaNo ratings yet
- Corti Et Al., 2021Document38 pagesCorti Et Al., 2021LunaNo ratings yet
- Executive Support SystemDocument12 pagesExecutive Support SystemSachin Kumar Bassi100% (2)
- School of Architecture, Building and Design Foundation in Natural Build EnvironmentDocument33 pagesSchool of Architecture, Building and Design Foundation in Natural Build Environmentapi-291031287No ratings yet
- 02 Activity 1 (4) (STRA)Document2 pages02 Activity 1 (4) (STRA)Kathy RamosNo ratings yet
- Ivan PavlovDocument55 pagesIvan PavlovMuhamad Faiz NorasiNo ratings yet
- Structuring Your Novel Workbook: Hands-On Help For Building Strong and Successful StoriesDocument16 pagesStructuring Your Novel Workbook: Hands-On Help For Building Strong and Successful StoriesK.M. Weiland82% (11)
- Kargil Untold StoriesDocument214 pagesKargil Untold StoriesSONALI KUMARINo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Elements of A Concept PaperDocument4 pagesLesson 12 Elements of A Concept PaperTrending Now100% (2)
- Inver Powderpaint SpecirficationsDocument2 pagesInver Powderpaint SpecirficationsArun PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Common Application FormDocument5 pagesCommon Application FormKiranchand SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Senarai Syarikat Berdaftar MidesDocument6 pagesSenarai Syarikat Berdaftar Midesmohd zulhazreen bin mohd nasirNo ratings yet