Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intoduction To Electrical Engineering Tut 2
Uploaded by
Naveen BabuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intoduction To Electrical Engineering Tut 2
Uploaded by
Naveen BabuCopyright:
Available Formats
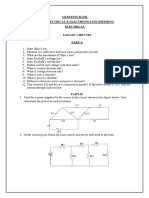
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
Tutorial 2 (AC Circuits and 3 Phase)
1. For the oscilloscope display:
a. Determine the period of each waveform. b. Determine the frequency of each waveform. c. Find the rms value of each waveform. d. Determine the phase shift between the two waveforms and which leads or lags.
2. The voltage across a 1-mF capacitor is 30 sin 200t. What is the sinusoidal expression for
the current? 3. Determine the sinusoidal expression for the source voltage and for currents i1 and i2
4. Perform the following operations and give your answer in rectangular form for a,b and c
and in polar form for d and e
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 1
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
5. Find the sinusoidal expression for the voltage va if
ein =120 sin(wt+30) Vb= 30 sin (wt+60) Vc=40sin (wt+120)
6. Find the sinusoidal expression for the current i1 for the system, if
is=0.018sin (377t+180) i2=0.008sin (377t-180) i3=2i2
7.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 2
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
8.
9. a. Find the total admittance YT in polar form.
b. Draw the admittance diagram. c. Find the value of C in microfarads and L in henries. d. Find the voltage E and currents IR, IL, and IC in phasor form. e. Draw the phasor diagram of the currents Is, IR, IL, and IC, and the voltage E. f. Verify Kirchhoffs current law at one node. g. Find the average power delivered to the circuit. h. Find the power factor of the circuit, and indicate whether it is leading or lagging. i. Find the sinusoidal expressions for the currents and voltage.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering Page 3
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
j. Plot the waveforms for the currents and voltage on the same set of axes.
10.
a.
Calculate E, IR, and IL in phasor form. b. Calculate the total power factor, and indicate whether it is leading or lagging. c. Calculate the average power delivered to the circuit. d. Draw the admittance diagram. e. Draw the phasor diagram of the currents Is, IR, and IL, and the voltage E. f. Find the current IC for each capacitor using only Kirchhoffs current law. g. Find the series circuit of one resistive and reactive element that will have the same impedance as the original circuit.
11. Find the element or elements that must be in the closed container of Fig to satisfy the
following conditions. (Find the simplest parallel circuit that will satisfy the indicated conditions.) a. Average power to the circuit is 3000 W. b. Circuit has a lagging power factor.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 4
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
12.
13.
Find the unknown quantities marked in the circuit diagram.
14. Find I1, V1 and average power delivered to network
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 5
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
15.
a. Find the total impedance ZT and the admittance YT. b. Find the source current Is in phasor form. c. Find the currents I1 and I2 in phasor form. d. Find the voltages V1 and Vab in phasor form. e. Find the average power delivered to the network. f. Find the power factor of the network, and indicate whether it is leading or lagging.
16. a. Find the total impedance
b. Find V1, I1 and Is
17. Find I1
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 6
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
18.
19.
a. Find total P, Q and S, Power factor. b. Draw the power Triangle and find Is.
20.
a. Find the average, reactive, and apparent power for the 20 ohm resistor. b. Repeat part (a) for the 10 ohm inductive reactance. c. Find the total number of watts, volt-amperes reactive, and volt-amperes, and the power factor Fp. d. Find the current Is.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 7
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
21.
a. Find the average power delivered to each element. b. Find the reactive power for each element. c. Find the apparent power for each element. d. Find the total number of watts, volt-amperes reactive, and volt-amperes, and the power factor of the circuit. e. Sketch the power triangle. f. Find the energy dissipated by the resistor over one full cycle of the input voltage. g. Find the energy stored or returned by the capacitor and the inductor over one halfcycle of the power curve for each.
22.
23. a. Find the total number of watts, volt-amperes reactive, and volt-amperes, and pf.
b. Find the current Is. c. Find the type of elements and their impedance in each box. (Assume that the elements within each box are in series.)
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 8
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
24.
a. Find the total number of watts, volt-amperes reactive, and volt-amperes, and pf. b. Find the voltage E. c. Find the type of elements and their impedance in each box. (Assume that the elements within each box are in series.)
25.
The phase sequence for the Y-Y system of Fig. is ABC. a. Find the angles 2 and 3 for the specified phase sequence. b. Find the voltage across each phase impedance in phasor form. c. Find the current through each phase impedance in phasor form. d. Draw the phasor diagram of the currents found in part (c), and show that their phasor sum is zero. e. Find the magnitude of the line currents. f. Find the magnitude of the line voltages.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 9
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
26.
Find the magnitude of the unknown voltages and currents.
27.
a.
Find the magnitude and angle associated with the voltages EAN, EBN, and ECN. b. Determine the magnitude and angle associated with each phase current of the load: Ian, Ibn, and Icn. c. Find the magnitude and phase angle of each line current: IAa, IBb, and ICc. d. Determine the magnitude and phase angle of the voltage across each phase of the load: Van, Vbn, and Vcn.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 10
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
28.
For the Delta-connected load of Fig: a. Find the magnitude and angle of each phase current Iab, Ibc, and Ica. b. Calculate the magnitude and angle of each line current IAa, IBb, and ICc. c. Determine the magnitude and angle of the voltages EAB, EBC, and ECA.
29.
Find the total watts, Volt amperes reactive, volt amperes and power factor.
30. For the three wire system, properly connect a second wattmeter so that two measure the
total power delivered to the load.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 11
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
31. Find the magnitude and angle of the phase currents, line currents. Determine reading of
each wattmeter and the total power delivered to load.
Shiv Nadar University, School of Engineering, Department of Electrical Engineering
Page 12
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- EED 101 - Tut 1Document5 pagesEED 101 - Tut 1GaneshKannaNo ratings yet
- BEEE - Unit - I - QBDocument8 pagesBEEE - Unit - I - QBSweetlineSoniaNo ratings yet
- Elektroteknik SorularDocument21 pagesElektroteknik Sorularserkan1234No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3DavidNo ratings yet
- Physics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaDocument5 pagesPhysics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaGAME DEVNo ratings yet
- Physics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1Document4 pagesPhysics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1ChetanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering ElectricalDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering Electricalcsvtu notesNo ratings yet
- EEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Document8 pagesEEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Arpit ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question BankDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question BankRacherla Mega RaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 2marksDocument6 pagesUnit 1 2marksKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Module2 Qbank 2023-24Document3 pagesModule2 Qbank 2023-24Aqsa MohammadiNo ratings yet
- IEE Tutorial 1Document6 pagesIEE Tutorial 1wwinnerNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Document3 pagesClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrinceNo ratings yet
- EEE SyllabusDocument11 pagesEEE Syllabussamarpit_anandNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions EmtDocument9 pagesImportant Questions EmtDinesh PeterNo ratings yet
- Questions Chap 7 Alternating Current - 77504 - 2023 - 01 - 14 - 22 - 53Document4 pagesQuestions Chap 7 Alternating Current - 77504 - 2023 - 01 - 14 - 22 - 53Abhay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2billy bobNo ratings yet
- Ee201 - Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument14 pagesEe201 - Electric Circuit AnalysisFLOWERNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits and Networks (EE)Document5 pagesElectric Circuits and Networks (EE)EDENINo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AcDocument4 pagesPhysics Ch6&Ch7 EMI&AclkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Kaushik BorahNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Electrical Engineering: 2013-14 (1 Sem) Question Bank From My PortionsDocument7 pagesElements of Electrical Engineering: 2013-14 (1 Sem) Question Bank From My PortionsWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- IEEE Unit 2 QBDocument3 pagesIEEE Unit 2 QBjyuvarajeeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15ADocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15AG46Anand P KNo ratings yet
- ELC 131 Exam 1a 9-12-23Document8 pagesELC 131 Exam 1a 9-12-23tcosteenNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Module 1Document2 pagesAssignment-Module 1الجيش اليمنى الالكترونى YemenNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Vel's University: Unit 1Document6 pagesVel's University: Unit 1Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityDocument17 pages2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityAziz BakarNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument107 pagesElectric CircuitsKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Bee 1701 PS2Document3 pagesBee 1701 PS2KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions PhysicsDocument12 pagesImportant Questions PhysicsNaziaParveenNo ratings yet
- Sumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Document5 pagesSumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Manongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument9 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurNiranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsDocument50 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiNo ratings yet
- Apeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsDocument4 pagesApeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsabhilashagoelNo ratings yet
- WWW Universityquestions inDocument63 pagesWWW Universityquestions inRajgir Raj100% (1)
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADocument8 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Circuiy Theory IDocument8 pagesCircuiy Theory Ivincent.olorunbe3No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument45 pagesQuestion BankSaritha Reddy100% (1)
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- D.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Document5 pagesD.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Pritam Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Question PaperDocument7 pagesSample Question PaperSaravanan KNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS SyllabusDocument8 pagesELECTRICAL CIRCUITS SyllabusShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & Networks Question BankDocument6 pagesElectrical Circuits & Networks Question BankMATHANKUMAR.S100% (1)
- IEE Tutorial 1Document6 pagesIEE Tutorial 1wwinnerNo ratings yet
- Boylestad - Formula SheetDocument2 pagesBoylestad - Formula SheetZain AliNo ratings yet
- Ch08 3d Technology (Not Much Use)Document35 pagesCh08 3d Technology (Not Much Use)Naveen BabuNo ratings yet
- Onsjn 123Document1 pageOnsjn 123Naveen BabuNo ratings yet
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 16, 311-331, 2009Document22 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 16, 311-331, 2009Naveen BabuNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructurePavan GoudNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment Grade 10Document7 pagesPhysics Assessment Grade 10Steven ShemdoeNo ratings yet
- Ugular Adv Mechanics AppendixDocument57 pagesUgular Adv Mechanics AppendixFiras DiknashNo ratings yet
- NozzelsDocument47 pagesNozzelsraghu.entrepreneurNo ratings yet
- Section-A (Multiple Choice Questions) : (A) Z (B) Z (C) ZDocument3 pagesSection-A (Multiple Choice Questions) : (A) Z (B) Z (C) ZSasikalaNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics: 10/11/2017 Dynamic Analysis 1Document110 pagesStructural Dynamics: 10/11/2017 Dynamic Analysis 1Mohammed Essam ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Dielectric MaterialsDocument52 pagesDielectric MaterialsHarinn Hizhadi MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Soil Axial Resistance of A PipelineDocument3 pagesSoil Axial Resistance of A PipelineFemi Richard FakoyaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Board Exam Questions: Power and Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument9 pages2017 Board Exam Questions: Power and Industrial Plant Engineeringdominique100% (1)
- Slope Stability ImprovementDocument43 pagesSlope Stability Improvementomar cNo ratings yet
- Planck 'S ConstantDocument4 pagesPlanck 'S ConstantgeetishaNo ratings yet
- Heliyon: H.M. Shahadat Ali, M.A. Habib, M.Mamun Miah, M. Ali AkbarDocument12 pagesHeliyon: H.M. Shahadat Ali, M.A. Habib, M.Mamun Miah, M. Ali AkbarAndry WirawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1 Review SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Unit 1 Review Sheetapi-330460747No ratings yet
- Example Problems ConductionDocument9 pagesExample Problems ConductionAJ100% (1)
- Strength of Materials - IDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials - IJosephNo ratings yet
- Science of Spirit Excerpt For ScribdDocument86 pagesScience of Spirit Excerpt For ScribdRobert Donald TonelliNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Sample ProblemsDocument17 pagesDynamics Sample ProblemsLou Berwel Domingo71% (7)
- Lesson 7a Sample COT PhysicsDocument4 pagesLesson 7a Sample COT PhysicsRona Liee PelaezNo ratings yet
- Distillation DesignDocument30 pagesDistillation Designfdc20062340100% (2)
- A Study of The Eigenvalue Analysis Capabilities ofDocument9 pagesA Study of The Eigenvalue Analysis Capabilities ofNedim HadžiaganovićNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms: NEET/JEE: 2020-21Document2 pagesStructure of Atoms: NEET/JEE: 2020-21shantinath123gmailcoNo ratings yet
- TLWDocument39 pagesTLWCandida DhasonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 5 - Ohm's Law SimulationDocument4 pagesLaboratory Work No. 5 - Ohm's Law SimulationJoyce CañaveralNo ratings yet
- Pipe Segment: Subsea Piping: Connections Inlet StreamDocument16 pagesPipe Segment: Subsea Piping: Connections Inlet StreamRaseuki MahadinaNo ratings yet
- Soil CompositionDocument36 pagesSoil CompositionElla Clent moralesNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Shallow Foundations On Jointed Rock MassDocument89 pagesBehaviour of Shallow Foundations On Jointed Rock MasscenapNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument5 pagesTransformerJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- RC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryDocument9 pagesRC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryOsang Ekeh Bush TitusNo ratings yet
- Fetch PDFDocument5 pagesFetch PDFPatricio Castillo ManquecoyNo ratings yet