Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus Maths Xii (I) To (III)
Uploaded by
Akash GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus Maths Xii (I) To (III)
Uploaded by
Akash GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
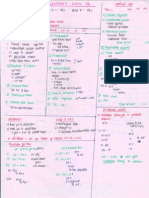
UNIT I
CHAPTER/ TOPIC Relation and Functions.
SYLLABUS OF CLASS XII MATHEMATICS (2013-14) DETIALS Marks Types of Relations: reflexive,transitive and equivalence relations. 10 One to one and onto functions, composite functions, inverse of a function.Binary operations. Definition, range,domain,principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions ALGEBRA II Matrices
Concept,notation,order,equality, types of matrices,zero matrices,transpose of a matrices, symmetric and skew matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication ,non commutative of multiplication of matrices and existence of non zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix(restrict to square matrices of order 2). Concept of elementary row and column operations.Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of Inverse,if it exists;(Here all matrices will have real entities).
13
Determinants
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), Properties of determinants, minors,cofactors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix.Consistency,inconsitency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples,solving system of linear equations in two or three variables(having linear equations by examples,solving system of linear equations in two or three variables(having unique solution)using inverse of a matrix. i
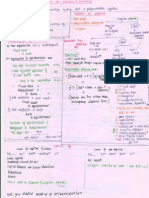
CALCULUS Continuity and differentiability III
Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse functions,derivative of implicit function.Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions and their derivative.Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms,Second order derivatives.Rolles and Lagranges Mean value theorems (without proof) and their geometric interpretations. Applications of derivatives :rate of change ,increasing/deraesing functions, tangents and normals,approximation,maxima nad minima(first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool).Simple problems (that illustrates basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real life situations) Integration as inverse process of differentiation, integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type
44
Applications of Derivatives
Integrals
dx
2
, dx , dx , dx dx , 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 x +a x + a a - x ax + bx +c ax +bx+c
2
(px+q)
Applications of Integrals
Differential Equations
dx, (px+q) dx , a2 + x2 dx and x2 - a2 dx ax2 + bx2 +c ax2 +bx+c to be evaluated Definite integrals as a limit of sum, fundamental theorem of calculus (without proof),basic properties of a definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals Applications in finding the area under simple curves,especially lines, areas of circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only), area between the two above said curves (theregion should be clearly indentifiable) Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a dfferntial equations. Formation of differential equations by method of separation of variables, homogeneus differnatial equations of first order ii
and first degree.Solutions oflinear differential equation of the type: dy/dx+ p(x) y=q(x), where p(x) and q(x) are functions of x. Vectors IV Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector,Direction cosines/ratios of vectors. Types of vectors(equal,unit,zero, parallel and collinear vectors),position vector of a point,negative of a vector,components of a vector,addition of a vector, multiplication of a vector by a scalar,position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio, scalar(dot) product of a vectors, projection of a vector on a line, Vector (cross) product of vectors. Three Dimensional Geometry Direction cosines/ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line,coplanar and skew lines,shortest distance between two lines,Cartesian and vector equation of a plane.Angles between (i) two lines, (ii) two planes (iii) a line and a plane.Distance of a point from a plane. Linear Programming V Introduction, definition of related terminology such as constraints, objective function,optim,ization, different types of linear programming(L.P)problems, mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions,optimal feasible solutions (upto three non trivial constraints) Probability VI Multiplication theorem on probality,conditional probability, independent events, total probalility,Bayes theorem, Random variable and its probality distribution, mena and variance of haphazard variable. Repeated independent (Bernoullli) trials and binomial distribution
17
10
iii
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- EclDocument44 pagesEclAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Respaper CA (Icai) - Ipcc - Model Mock Test Group I Paper 1 AccountingDocument6 pagesRespaper CA (Icai) - Ipcc - Model Mock Test Group I Paper 1 AccountingAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sify Notes For C.S ExcDocument16 pagesSify Notes For C.S ExcAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cs Online Test Sify 1500 Questions MCQDocument110 pagesCs Online Test Sify 1500 Questions MCQcsjournal70% (10)
- Issue and Redemption of DebentureDocument2 pagesIssue and Redemption of DebentureAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class 11th Cbse AccountsDocument2 pagesClass 11th Cbse AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sify Notes For C.S ExcDocument16 pagesSify Notes For C.S ExcAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Co's Bill Highlights 2013Document18 pagesCo's Bill Highlights 2013Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Main Points of Food Security Bill 2013Document2 pagesMain Points of Food Security Bill 2013Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class 11th Economics NotesDocument2 pagesClass 11th Economics NotesAkash Gupta0% (1)
- Sify NotesDocument3 pagesSify NotesAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Investment AccountsDocument1 pageInvestment AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sify NotesDocument2 pagesSify NotesAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cs Online Test Sify 1500 Questions MCQDocument110 pagesCs Online Test Sify 1500 Questions MCQcsjournal70% (10)
- Underwiting of Shares & DebenturesDocument1 pageUnderwiting of Shares & DebenturesAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Self Balancing LedgersDocument2 pagesSelf Balancing LedgersAkash Gupta0% (1)
- Cash Flow StatementDocument2 pagesCash Flow StatementCa Anil DangiNo ratings yet
- Internal ReconstructionDocument1 pageInternal ReconstructionAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Company Final AccountsDocument2 pagesCompany Final AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Branch AccountsDocument4 pagesBranch AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Partnership AccountsDocument8 pagesPartnership AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Departmental AccountsDocument2 pagesDepartmental AccountsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accounts of Electricity CompaniesDocument2 pagesAccounts of Electricity CompaniesAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accounts of Banking CompaniesDocument2 pagesAccounts of Banking CompaniesAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accounts From Incomplete RecordsDocument1 pageAccounts From Incomplete RecordsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solved Answer Accounts CA IPCC May. 2010Document13 pagesSolved Answer Accounts CA IPCC May. 2010Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accountants Formulae BookDocument47 pagesAccountants Formulae BookVpln SarmaNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument2 pagesContentsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers: QuestionsDocument1 pageSuggested Answers: QuestionsAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Data Structures and Algorithms: Lecture Notes 1Document35 pagesData Structures and Algorithms: Lecture Notes 1manasa008No ratings yet
- Convolution and CorrelationDocument11 pagesConvolution and CorrelationSHYAMNo ratings yet
- LCD 03 Exercise 1Document25 pagesLCD 03 Exercise 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Solving exponential equations and evaluating expressions with rational exponentsDocument47 pagesSolving exponential equations and evaluating expressions with rational exponentsKaren GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Algorithms, Assignment 6 SolutionsDocument3 pagesFundamental Algorithms, Assignment 6 SolutionsAashish DNo ratings yet
- CSP Algorithms for Constraint Satisfaction ProblemsDocument57 pagesCSP Algorithms for Constraint Satisfaction Problemssimionesei.loredanaNo ratings yet
- Latex Test PDF RenderingDocument4 pagesLatex Test PDF RenderinglordpersonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1RaghuNo ratings yet
- Sets CDF PointsDocument1 pageSets CDF PointsRen JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Cheat Sheet DraftDocument5 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Cheat Sheet DraftNatasha MuchaiNo ratings yet
- National-Level Science Talent Search Examination (NSTSE) Class 6 PaperDocument6 pagesNational-Level Science Talent Search Examination (NSTSE) Class 6 Paperankur_07gargNo ratings yet
- 1 Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithms: Methodologies, Architectures, and ReviewsDocument17 pages1 Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithms: Methodologies, Architectures, and Reviewsankit407No ratings yet
- Spectral Methods For Time-Dependent ProblemsDocument281 pagesSpectral Methods For Time-Dependent ProblemsLei WangNo ratings yet
- I N Herstein@ PDFDocument9 pagesI N Herstein@ PDFArnold Greenwell ChristianNo ratings yet
- Problem Set of Differential Equation PDFDocument73 pagesProblem Set of Differential Equation PDFJosephNo ratings yet
- Polack Solutions PDFDocument16 pagesPolack Solutions PDFDaniel PiresNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab-01Document28 pagesDSP Lab-01Mekonen AberaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation SolverDocument26 pagesQuadratic Equation SolverMuzaFarNo ratings yet
- Divisibility RulesDocument5 pagesDivisibility RulesNaveen MawatwalNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination TechniquesDocument27 pagesGaussian Elimination TechniquesFahad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Corso - Perego (Complex Algebraic Surface Note)Document208 pagesCorso - Perego (Complex Algebraic Surface Note)kehao chengNo ratings yet
- Terrence Tao - Free ProbabilityDocument32 pagesTerrence Tao - Free ProbabilitycaprioloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Power SeriesDocument55 pagesChapter 4 Power SeriesThalagawali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3/week # 1 Part 2: Learning Activity Sheet (SHS) Basic CalculusDocument12 pagesQuarter 3/week # 1 Part 2: Learning Activity Sheet (SHS) Basic CalculusDominic Dalton CalingNo ratings yet
- Disipline Wise Course List - MathematicsDocument3 pagesDisipline Wise Course List - MathematicsNandhiniNo ratings yet
- Sec. 18 ExercisesDocument2 pagesSec. 18 Exercisesmuhammad ilham suwahyuNo ratings yet
- EC 263 Signals and Systems Lab PDFDocument21 pagesEC 263 Signals and Systems Lab PDFarundhupamNo ratings yet
- Complex Vector Spaces PDFDocument42 pagesComplex Vector Spaces PDFmechmaster4uNo ratings yet
- Piecewise Function: Tr. Kclyn TagayunDocument15 pagesPiecewise Function: Tr. Kclyn TagayunKclynNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesLinear Algebra Cheat SheetNooraniManshadNo ratings yet