Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labs Drug Study 1
Uploaded by
Drei LanuzoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Labs Drug Study 1
Uploaded by
Drei LanuzoCopyright:
Available Formats
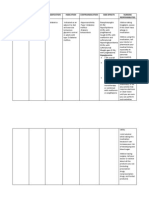
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Lanoxin (Digoxin)
Cardiac glycoside / Cardiotonic / Pregnancy: Category C
Lanoxin is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate heart failure. It increases left ventricular ejection fraction and improves heart failure symptoms as evidenced by exercise capacity and heart failure-related hospitalizations and emergency care, while having no effect on mortality. Where possible, Lanoxin should be used with a diuretic and an angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, but an optimal order for starting these three drugs cannot be specified. Atrial Fibrillation: Lanoxin is indicated for the control of ventricular response rate in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation.
ADULT DOSAGE:
- Extra beats - anorexia, Loading dose, - nausea and 0.751.25 mg vomiting. PO or 0.125 -Diarrhea in 0.25 mg IV. elderly - confusion Maintenance - dizziness, dose, 0.125 -drowsiness, 0.25 mg/day PO. -restlessness, - nervousness, Lanoxicaps -agitation capsules -amnesia, -visual Loading dose, disturbances, 0.40.6 mg PO. -local irritation (IM/SC inj), Maintenance -rapid IV admin dose, 0.1 0.3 may lead to mg/day PO. vasoconstrictio n and transient hypertension. Potentially Fatal: Cardiac arrhythmias in combination with heart block.
-Before taking digoxin, tell the doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to similar drugs (such as digitoxin); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. -Talk to your pharmacist for more details. Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: kidney problems, thyroid problems (underactive or overactive).The balance of certain natural minerals in
-Assess history of: Allergy to digitalis preparations, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, heart block, sick sinus syndrome, IHSS, acute MI, renal insufficiency, decreased K+, decreased Mg2+ increased Ca2+, pregnancy, lactation Physical: Weight; orientation, affect, reflexes, vision; P, BP, baseline ECG, cardiac auscultation, peripheral pulses, peripheral perfusion, edema WARNING: Monitor apical pulse for 1 min before administering; hold dose if pulse < 60 in adult or < 90 in infant; retake pulse in 1 hr. If adult pulse remains < 60 or
your blood (calcium, magnesium, potassium) can affect how this drug works in your body. Certain drugs such as "water pills" (diuretics) may affect the normal balance of these minerals. Digitalis toxicity, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillati on, obstructive cardiomyopathy. Arrhythmias due to accessory pathways (e.g. WolffParkinson-White syndrome).
infant < 90, hold drug and notify prescriber. Note any change from baseline rhythm or rate. Take care to differentiate Lanoxicaps from Lanoxin; dosage is very different. Check dosage and preparation carefully. Avoid IM injections, which may be very painful. Follow diluting instructions carefully, and use diluted solution promptly. Avoid giving with meals; this will delay absorption. Have emergency equipment ready; have K+ salts, lidocaine, phenytoin, atropine, and cardiac monitor readily available in case toxicity develops. WARNING: Monitor for therapeutic drug levels: 0.52 ng/mL.
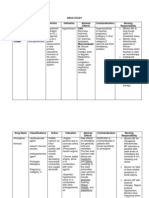
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects Side effects of spironolactone include -headache -diarrhea -cramps -drowsiness -rash -nausea -vomiting -impotence -irregular menstrual periods -irregular hair growth. -Fluid and electrolytes imbalance (for example, low sodium, low magnesium, and high potassium) may occur, so patients should be monitored carefully. Enlargement of
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Aldactone (Spironolactone)
Potassiumsparing diuretic /Aldosterone antagonist
Diagnosis and maintenance of primary hyperaldosteronism. Adjunctive therapy in edema associated with CHF, nephrotic syndrome, hepatic cirrhosis when other therapies are inadequate or inappropriate Treatment of hypokalemia or prevention of hypokalemia in patients who would be at high risk if hypokalemia occurred: Digitalized patients, patients with cardiac arrhythmias Essential hypertension, usually in combination with other drugs Unlabeled uses: Treatment of hirsutism due to its antiandrogenic properties, palliation of symptoms of PMS, treatment of familial male precocious puberty, shortterm treatment of acne vulgaris
Spironolactone may be taken with or without food. The dosage range is 25-400 mg daily in single or divided doses.
-Anuria -hyperkalemia, -Acute or progressive renal insufficiency -Addisons disease.
-Check blood pressure before initiation of therapy and at regular intervals throughout therapy. Lab tests: Monitor serum electrolytes (sodium and potassium) especially during early therapy; monitor digoxin level when used concurrently. Assess for signs of fluid and electrolyte imbalance, and signs of digoxin toxicity. Monitor daily I&O and check for edema. Report lack of diuretic response or development of edema; both may indicate tolerance to drug.
the breasts (gynecomastia) may also occur and is related to dose and duration of therapy. It usually reverses upon discontinuation of spironolactone.
Weigh patient under standard conditions before therapy begins and daily throughout therapy. Weight is a useful index of need for dosage adjustment. For patients with ascites, physician may want measurements of abdominal girth.
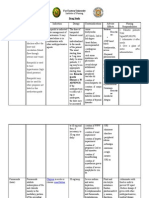
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Fluimucil (Acetylceistein)
Mucolytic agent
Treatment of respiratory aff ections characterized by thic k and viscoushypersecretion s: acute bronchitis, chronic b ronchitis and its exacerbatio ns; pulmonaryemphysema, mucoviscidosis and bronchiectasis. Exerts mucolytic action through its free sulfhydryl group which opens up the disulfide bonds in the mucoproteins thus lowering mucous viscosity. The exact mechanism of action in acetaminophen toxicity is unknown. It is thought to act by providing substrate for conjugation with the toxic metabolite
ADULT DOSAGE:
Hypersensitivit y reactions 1 sachet of have been Acetylcysteine reported in 200 mg or 2 patients sachets of receiving Acetylcysteine1 acetylcysteine, 00 mg, 2-3 times including a day1 bronchospasm, Acetylcysteine angioedema, 600 rashes and mg effervescent pruritus, may tablet daily ( occur. preferably in the evening) Other adverse effects For the reported prevention of include nausea exacerbation, and vomiting, the use of fever, syncope, FLUIMUCIL 200 sweating, mg sachets is arthralgia, recommended. blurred vision, disturbances of liver function.
MAO inhibitor thera py within 14 days ini tiating therapy; severe hypertension; severe. Coronary artery disease, hypersensitivity to p seudoedephrine,acri vastine or any component; renal impairment.
Fluimicil contains the active ingredient Acetylecystein. It is generally used to reduce the extent of liver injury after an overdose of Acetaminophen. Due to the high doses required, the patient should be watched for an overdosage of this medication, signs may include nausea and vomiting. You should also watch for increased blood pressure and hypoxia. Monitor effectiveness of therapy and advent of a dverse/allergic effects. Instruct patient in appropriate use and adverse effects to report.
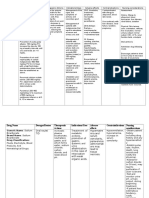
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects Side effects are infrequent and usually reversible upon discontinuance of the drug. They include drowsiness, gastrointestinal intolerance, cutaneous eruptions, gynaecomastia, mild androgenic effects. Thiazides when used alone have been reported to decrease glucose tolerance and to induce hyperuricaemia . Periodic estimation of serum electrolytes is
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Aldazide
Diuretics / Spironolactone
Spironolactone promotes diuresis in patients with oedema or ascites. Spironolactone acts in the distal portion of the renal tube by competitive inhibition of aldosterone, a sodium-retaining, potassium-excreting hormone. Isobutylhydrochlorothiazide promotes sodium and water excretion by inhibiting sodium and chloride reabsorption in the kidney tubule. The combination of spironolactone and isobutylhydrochlorothiazide provides an effective treatment for many patients who would not respond to either drug alone. The combination results in an additive diuretic effect since both drugs will increase sodium and water excretion
The average daily dose is 2 4 tablets. For edema it is recommended that therapy should be started with four tablets a day. After the disappearance of edema, the dose can be reduced according to the patient's needs. If adequate diuresis does not occur after three days of treatment, the dose can be increased up to 8 tablets daily. For hypertension, the initial dose
Acute renal insufficiency, rapid deterioration of renal function, anuria, hyperkalaemia or sensitivity to thiazides. Lactating mothers should not receive the combination as thiazides appear in milk.
ducate patient to avoid hazardous activity such as driving until response to drug is known.
Take with meals or milk; avoid excessive ingestion of food high in potassium or use of salt substitutes
Diuretic effect may be delayed 2-3 days and maximum hypertensive may be delayed 2-3weeks; monitor I and O ratios and daily weight, BP, serum electrolytes (K, Na) and renal function
by acting in different parts of the renal tubule.
of four tablets a day should be continued for at least two weeks, since the response to ALDAZIDE may be delayed. The dose can then be adjusted according to the patient's needs.
desirable. The administration of potassium supplements or of other potassium sparing agents is not recommended as it may induce hyperkalaemia.
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Aspirin
Antipyretic / Analgesic
Aspirin also has an antiplatelet effect by inhibiting the production of thromboxane, which under normal circumstances bind platelet molecules together to repair damaged blood vessels. This is why aspirin is used in long-term, low doses to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clot formation in people at high risk for developing blood clots. It has also been established that low doses of aspirin may be given immediately after a heart attack to reduce the risk of another heart attack or of the death of cardiac tissue.
ADULT DOSAGE:
ACUTE ASPIRIN Contraindicated TOXICITY: with allergy to salicylates or Minor aches and Respiratory NSAIDS (more pains: 325-650 alkalosis, common with nasal mg q 4 hr hyperpnea, polyps, asthma, tachypnea, chronic (uticaria) Arthritis and hemorrhage, allergy to tatrazine rheumatic excitement, (cross-sensitivity to conditions: 3.2- confusion, aspirin in common); 6g/day in pulmonary hemophilia, divided doses. edema, bleeding ulcers, metabolic hemorrhagic states, TIAS in men: acidosis, blood coagulation, 1300 mg/day in seizures, vitamin K deficiency. divided doses tetany, fever, (650 mg bid or coma, CV Use cautiously with 325 mg qid) collapse, renal impaired renal and respiratory function; chicken MI prophylaxis: failure. pox, influenza. 75-325 mg/day ASPIRIN INTOLERANCE: Exacerbation of bronchospasm rhinitis (with nasal polyps, asthma, rhinitis)
.Give drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs Give drug with full glass of water to reduce risk of tablet or capsule lodging in the esophagus. Do not crush, and ensure that patient does not chew the preparations. Use drug only as suggested; avoid overdose. Do not cut, crush or chew sustained release products. Report ringing in the ears, dizziness, confusion, abdominal pain, rapid or difficult breathing, nausea, vomiting, bloody stools
GI Nausea, dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric discomfort, anorexia, hepatotoxicity
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects Hypersensitivit y Reactions: Rash, pruritus and feverhave been reported Gastrointestina l Effects:melen a, gastritis Hepatic Effects: Transientincrea ses in aspartateamin otransferase (AST),alanine aminotransfera se(ALT), alkalinephosph atase and bilirubin can occur. Renal Effects: Increases in serum concentrations of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Piptaz (Piperacillin)
Enzyme inhibitor
Treatment of infections in the lower resp tract eg severe community-acquired pneumonia & healthcare pneumonia; uncomplicated & complicated skin & skin structure infections; intraabdominal infections w/peritonitis eg complicated appendicitis; complicated & uncomplicated UTI; gynecologic infection eg postpartum endometritis or pelvic inflammatory disease; bacterial infection in neutropenic patients; bone & joint infections; bacterial sepsis.
Piptaz is administered by IV infusion over 30 min. Adults: Usual Dose: 4.5 g every 8 hrs. Total daily dose of piperacillin 12 g and tazobactam 1.5 g. The usual duration of treatment is 710 days. The duration of treatment is based on the type and severity of the infection being treated and on the patient's clinical and bacteriological progress.
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to any of the penicillins, cephalosporins or lactamase inhibitors or to any of the ingredient of Piptaz.
Piptaz should not be added to blood products or albumin hydrolysates and should not be mixed with other drugs in a syringe or infusion bottle due to possible problems with compatibility. Piptaz is not chemically stable in solutions that contain only sodium bicarbonate and solutions that significantly alter pH. Lactated Ringer's Solution is not compatible with Piptaz. Piptaz is stable in glass and plastic containers (plastic syringes, IV bags and tubing) once used with compatible diluents
may be observed. Effect on the Central Nervous System: Headache, Malaise Local Reactions: pain, inflammation, thrombophlebi tis and edema.
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Imdur (Isosorbide mononitrate)
Nitrates / antianginal
Imdur (isosorbide mononitrate) is in a group of drugs called nitrates. It dilates (widens) blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through them and easier for the heart to pump. Imdur is used to prevent angina attacks (chest pain). Imdur will not treat an angina attack that has already begun. Imdur may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
The recommended adult dose of isosorbide-5mononitrate is 1 tablet (60 mg) taken once daily in the morning after getting up. Your doctor may increase the dose to 2 tablets (120 mg) once daily in the morning if necessary. To reduce the risk of headache, your doctor may suggest starting with one-half tablet (30 mg) once daily each morning for the first 2 to 4 days
Abdominal pain constipatio n diarrhea dizziness or lightheaded ness, especially when rising from a lying or sitting position flushing of face and neck gas headache increased s weating nausea restlessnes s sensation of spinning trouble sleeping
Headache may be a marker for drug activity; do not try to avoid by altering treatment schedule; aspirin or acetaminophen may be used for relief Dissolve SL tablets under tongue; do not crush, chew, or swallow Do not crush chewable tablets before administering Avoid alcohol Make changes in position slowly to prevent fainting
Give sublingual preparations under the tongue or in the buccal pouch; discourage the patient from swallowing. Create a nitrate-free period to minimize tolerance. Give oral preparations on an empty stomach, 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals; take with meals if severe, uncontrolled headache occurs.
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Champix (varenicline)
Belongs to the class of drugs used in the management of nicotine dependence.
Champix tablets contain the active ingredient varenicline, which is a medicine used to help people who are addicted to nicotine to give up smoking. It acts in the brain, but is not the same as nicotine replacement therapy. Varenicline is a type of medicine called a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. This means that it acts on the same receptors in the brain as nicotine. Varenicline works by stimulating the nicotinic receptors in the brain. This produces an effect that relieves the craving and withdrawal symptoms you can get when you stop smoking. At the same time,
1 mg twice Nausea. daily, following Headache. a 1-wk titration. Difficulty Days 1-3: 0.5 mg sleeping once daily. Days (insomnia). 4-7: 0.5 mg Abnormal twice daily. Day dreams. 8 - End of treatment: 1 mg twice daily. Start fatigue. dosing 1-2 wk before a date to stop smoking. taste. Duration: 12 wks. of the gut such Patients who as cannot tolerate constipation, adverse diarrhoea, effects 0.5 mg vomiting, twice daily. abdominal discomfort or Severerenal bloating, impairment 1 indigestion, mg once daily. wind (flatulence).
Explain how to take - This medicine varenicline might make you feel dizzy or sleepy and Set a date to stop smoking and start so could impair your varenicline 12 weeks ability to perform before (to reduce potentially craving and hazardous tasks withdrawal such as driving or symptoms). operating Don't use nicotinemachinery. You containing therapies should avoid driving while using or operating varenicline; using machinery until you nicotine replacement know how this at the same time may medicine affects you cause nausea, and are sure that it headache, dyspepsia, wont affect your fatigue and dizziness. ability to perform Follow the smokingsuch activities cessation program safely. recommended by their health professional, as this decreased kidney can increase their function. chance of quitting for good. Advise them disease involving about additional the heart and blood smoking-cessation vessels services available in
varenicline blocks nicotine from acting on the nicotinic receptors. This prevents any nicotine inhaled in tobacco smoke from having a rewarding and enjoyable effect.
appetite.
(cardiovascular disease).
their area and how to access them if necessary.
history of Advise about common psychiatric illness, side effects and eg depression, schiz concerns ophrenia, bipolar Varenicline disorder. frequently causes Epilepsy (this nausea that may medicine has not settle over time. been studied in Advise patients to people with take varenicline with epilepsy). food and a full glass of water, which may help reduce nausea. Ask them to tell their doctor if nausea is severe or prevents them from taking their medication.
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects High blood potassium level (hyperkalaemia ) in people with diabetes.
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Aprovel
Angiotensin II
Aprovel tablets contain the active ingredient irbesartan, which is a type of medicine called an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. (Irbesartan tablets are also available without a brand name, ie as the generic medicine.) Irbesartan lowers blood pressure by preventing the action of a hormone in the body called angiotensin II. Blocking the actions of angiotensin II also increases the amount of fluid removed from the blood by the kidneys. This decreases the amount of fluid in the blood vessels, which also lessens the resistance and pressure in the blood vessels.
The usual recommended initial and maintenance dose is 150 mg once daily, with or without food. Aprovel at a dose of 150 mg once daily generally provides a better 24 hour blood pressure control than 75 mg. However, initiation of therapy with 75 mg could be considered, particularly in haemodialysed patients and in the elderly over 75 years
with low fluid volume or salt levels in the body, eg due to diuretic therapy, low-sodium diet, diarrhoea, vomiting or dehydration. years of age. decreased kidney function. haemodialysis for kidney failure.
Monitor patients BP regularly. Monitor patients electrolytes. Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug therapy. Give with a diuretic if drug is needed to control blood pressure. Place in supine position and give an IV infusion of NSS if patient becomes hypotensive. Tell patient that drug may be taken once daily with or without food. Instruct client to avoid driving and hazardous activities
blood pressure that occurs when moving from a lying or sitting position to sitting or standing, which results in dizziness and lightheadednes s (postural hypotension). vomiting.
muscles or bones (musculoskelet al pain).
narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys (renal artery stenosis). Heart disease caused by inadequate blood flow to the heart (ischaemic heart disease). characterised by
thickening of the internal heart muscle and a blockage inside the heart (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy). heart failure. Heart valve disease (mitral valve stenosis). narrowing of the main artery that leaves the heart to supply blood to the body (aortic stenosis).
until CNS effects of drug are known.
Name of the drug
Classification
Indications
Dosage
Side / Adverse Effects
Contraindication and Precaution
Nursing Responsibilities
Mucosta
Anatacids, antireflux, agents and anti ulcerants
Rebamipide isa mucosal protective agent and is postulated to increase gastric blood flow, prostaglandin biosynthesis and decrease free oxygen radicals.
Dosage: Oral Peptic ulcer, Gastritis Adult: 100mg tid, in the morning, evening and before bed
Rash pruritus constipation diarrhea nausea
Lactation
Monitor for any adverse reaction
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- A Guide to Diabetes: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionFrom EverandA Guide to Diabetes: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDocument3 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument58 pagesCardio DrugsMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument27 pagesDrugspeterjongNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument11 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Dizziness Low Blood Pressure Triglycerides Blood Cholesterol EPS Dry MouthDocument2 pagesDizziness Low Blood Pressure Triglycerides Blood Cholesterol EPS Dry MouthMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexDocument6 pagesDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyjazmine_caritos100% (2)
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDocument5 pagesACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNo ratings yet
- Drus Study AaaaaaDocument6 pagesDrus Study AaaaaamarkharoldNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- OB Med SheetDocument12 pagesOB Med SheetSam DanaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesChristine AlavazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- Ify Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesIfy Drug StudiesifyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument64 pagesPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- Bell 2010Document8 pagesBell 2010RosarioBengocheaSecoNo ratings yet
- 4 6048890192880730833Document332 pages4 6048890192880730833Rin4lNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Barrier Nursing 168 - June 2012Document2 pagesIsolation and Barrier Nursing 168 - June 2012tharakaNo ratings yet
- Al HijamahTherapyDocument6 pagesAl HijamahTherapyNarendra DadhichNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Dysphagia by DR TilahunDocument32 pagesApproaches To Dysphagia by DR TilahunAhmed AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Medical para Health-1Document504 pagesMedical para Health-1Yordanos AsmareNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 2 (Phbs 107) Midterm Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE: Each of The Questions, Statements, or Incomplete Statements Can Be CorrectlyDocument17 pagesPharmacology 2 (Phbs 107) Midterm Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE: Each of The Questions, Statements, or Incomplete Statements Can Be CorrectlyT'amo HanashNo ratings yet
- DISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)Document9 pagesDISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)jenn212No ratings yet
- Adult-2, Unit 1, Metabolic and EndocrineDocument157 pagesAdult-2, Unit 1, Metabolic and EndocrineBav VAansoqnuaetzNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument4 pagesIntussusceptionlovethestarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Electro Physiological TestingDocument22 pagesClinical Electro Physiological TestingPaul VkNo ratings yet
- Dissertation: Dr.M.Arunkumar. 1st Year Postgraduate Department of Community Medicine, SRMC & RiDocument27 pagesDissertation: Dr.M.Arunkumar. 1st Year Postgraduate Department of Community Medicine, SRMC & Rirajforever17No ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency SyndromePankaj YadavanNo ratings yet
- 03.1 PHD Personality DisordersDocument8 pages03.1 PHD Personality DisordersDump AccNo ratings yet
- "Ecstasy of St. Teresa": A. B. C. DDocument3 pages"Ecstasy of St. Teresa": A. B. C. DRalphNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Used in DentistryDocument53 pagesEmergency Drugs Used in Dentistryasmita1989No ratings yet
- Fcps SurgeryDocument75 pagesFcps SurgeryLANKAPATRUDU6772No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Minor Disorders During Pregnancy Its Management 1Document20 pagesLesson Plan On Minor Disorders During Pregnancy Its Management 1Bhawna Joshi100% (6)
- Menopause Related Symptoms and Their Correlates: A Community Based Cross Sectional Study in Kollam District, KeralaDocument129 pagesMenopause Related Symptoms and Their Correlates: A Community Based Cross Sectional Study in Kollam District, Keraladhaya georgeNo ratings yet
- Addtional List Dissertation 040117Document6 pagesAddtional List Dissertation 040117Sagar Kansara100% (2)
- Writing SOAP Notes NYCCDocument7 pagesWriting SOAP Notes NYCCmassagekevin100% (2)
- Xango: Scientific Comparison of Xango and MonavieDocument4 pagesXango: Scientific Comparison of Xango and MonavieJahaziel OrtizNo ratings yet
- Sickness Body PartsDocument13 pagesSickness Body Partsmaharajkumar100% (1)
- Peripheral Neuropathies in Clinical PracticeDocument398 pagesPeripheral Neuropathies in Clinical PracticeIka Gultom100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAisha FakhryNo ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases: DR Rashmi NazarethDocument49 pagesGlomerular Diseases: DR Rashmi NazarethRohit RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Childhood Anaemia: Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist Deparment of Paediatrics & Child Health MustDocument34 pagesChildhood Anaemia: Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist Deparment of Paediatrics & Child Health MustSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Listening Sample Test 2 Audio ScriptDocument12 pagesListening Sample Test 2 Audio ScriptCCCAXANo ratings yet
- Equip Second ManualDocument76 pagesEquip Second ManualArjun SutharNo ratings yet
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483No ratings yet