Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compressor Power Estimation Calcs
Uploaded by
tedfdfeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compressor Power Estimation Calcs
Uploaded by
tedfdfeCopyright:
Available Formats
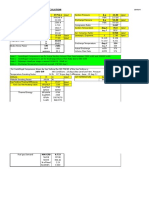
Thermodynamic Equations for gas compressor calculations Adiabatic compression: Changes of state P2/P1 = (V1/V2) = (T2/T1) Power P, kW Theoretical
disch. temperature, T2
k k-1/k
{(k / k - 1)* P1*100000*Q1*[ (P2/P1)(k - 1/k) - 1 ]}/1000 T1*[P2/P1](k - 1/k)
Isothermal compression: Changes of state P2/P1 = (V1/V2) Power P, kW
{P1*100000*Q1*ln(P2/P1)}/1000
ISOTHERMAL COMPRESSION IS FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSE ONLY. CHEMICAL PROCESS INDUSTRY COMPRESSION APPLICATIONS ARE GENERALLY NOT CONSIDERED AS ISOTHERMAL. Where: P1 = Gas pressure before compression (inlet), barA P2 = Gas pressure after compression (outlet), barA V1 = Gas volume at pressure P1, m3 V2 = Gas volume at pressure P2, m3 Q1 = Gas volume flow rate at inlet of compressor, m3/s T1 = Gas temperature at inlet of compressor, K T2 = Gas temperature at outlet of compressor (adiabatic process), K k = Ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to specific heat at constant volume, C p/Cv P = Theoretical power requirement of compressor, kW Example of adiabatic compression of air: P1, barA P2, barA T1, C T1, K Q1, m3/s T2, K T2, C k P, kW 1.4 1 2 20 293.15 1 76.65 357.35 84.20 1.4 1 3 20 293.15 1 129.06 401.25 128.10 1.4 1 4 20 293.15 1 170.10 435.62 162.47 1.4 1 5 20 293.15 1 204.34 464.30 191.15 Note: k is both a function of temperature and pressure. At highly elevated temperatures & pressures, k values will be different than those given at standard conditions of 15C & 1-atm pressure and require to be computed. Example of isothermal compression of air: P1, barA P2, barA T1 & T2, C Q1, m3/s 1 2 20 1 1 3 20 1 1 4 20 1 1 5 20 1
P, kW 69.31 109.86 138.63 160.94
Note: Actual power requirement of driver is a function of the efficiency of the type of compressor & the speed transmission mechanical device.
Pmotor = P/(hmachine*htr)
Efficiency Type of compressor Rotary Reciprocating (Lobe, Centrifugal (piston) Vane) (Dynamic) 0.85-0.9 0.7-0.75 0.7-0.75
hmachine
Note: Efficiency values are given as a range and as a general guideline and may differ from the values given in the table. User is cautioned to check from other resources (compressor manufacturer's literature, handbooks etc.) for the realistic values of efficiency for the given type of compressor. Efficiency worm Type of speed transmission Hydro 0.8 Gear 0.85 Belt 0.97 Direct coupling 1
htr
0.7
Where: Pmotor = rating of the driver, kW hmachine = compression efficiency of the compressor htr = efficiency of the speed transmission device. Specific heat ratio of various gases @15C and 1-atm pressure: k Argon 1.668 Helium 1.66 Air 1.4 Methane 1.31 Oxygen 1.4 Nitrogen Hydrogen Ethane 1.4 1.41 1.22
Prepared by:
Ankur Srivastava Chemical Engineer e-mail: ankur_2061@hotmail.com
Disclaimer : The information and methods included within this spreadsheet are presented for 'compressor power' calculations. It is intended to be used by technically skilled persons at their own discretion. I do not warrant the suitability or accuracy of these methods.
r 'compressor power' I do not warrant the suitability or
You might also like
- Rotary Screw CompressorsDocument22 pagesRotary Screw Compressorsganeshdhage100% (2)
- Polytropic CompressionDocument22 pagesPolytropic CompressionSonal Power Unlimitd50% (2)
- Compressor Selection Process IndDocument15 pagesCompressor Selection Process IndadoptvnNo ratings yet
- Assessment of CompresorsDocument14 pagesAssessment of CompresorsranveerNo ratings yet
- Compressor Sizing CalDocument2 pagesCompressor Sizing Calcanada_198020008918100% (1)
- Compressor Sizing and CalculationDocument6 pagesCompressor Sizing and CalculationOghale B. E. Omuabor100% (6)
- Compressor Sizing CalDocument2 pagesCompressor Sizing CalSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Compressor Capacity CalculationDocument4 pagesCompressor Capacity CalculationHoney Tiwari100% (1)
- Rotary CompressorsDocument59 pagesRotary Compressorsguru_519572100% (3)
- Plant Air SystemDocument7 pagesPlant Air SystemAnuj ShahiNo ratings yet
- Blower Power CalculDocument4 pagesBlower Power Calculm_stasys9939No ratings yet
- 6 Compressed Air Systems 2-1Document29 pages6 Compressed Air Systems 2-1Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sizing Calculations For Pressure Relief Valves - Chemical Engineering (2013)Document8 pagesSizing Calculations For Pressure Relief Valves - Chemical Engineering (2013)Jim WesnorNo ratings yet
- Sizing Air Receiver TankDocument3 pagesSizing Air Receiver TankDennis DanielNo ratings yet
- Velocity of Compressed AirDocument1 pageVelocity of Compressed AirLucky Karunia Setyawan PratamaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Selection of Strainers August 2006 EditionDocument10 pagesGuidelines For Selection of Strainers August 2006 EditionEver Briceño100% (1)
- Selection of Gas CompressorsDocument4 pagesSelection of Gas CompressorsDiegoNo ratings yet
- Compressor Selction and Design Course Program OutlineDocument5 pagesCompressor Selction and Design Course Program OutlinePrasanna kumar subudhiNo ratings yet
- CAGI ElectHB ch8Document112 pagesCAGI ElectHB ch8rcangeliNo ratings yet
- Compressor Air CalculationDocument3 pagesCompressor Air CalculationmohamedbadawyNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument27 pagesCompressorsoxal100% (1)
- Selección de CompresoresDocument23 pagesSelección de CompresoresjowarNo ratings yet
- Compressor GATE Mechanical EngineerDocument45 pagesCompressor GATE Mechanical Engineersap2279100% (1)
- Lobe Blower TheoryDocument6 pagesLobe Blower TheoryAnonymous CMS3dL1TNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical and Practical Guide To The Basics of Designing Air Flow SystemsDocument40 pagesA Theoretical and Practical Guide To The Basics of Designing Air Flow SystemsKagitha TirumalaNo ratings yet
- RG Integrally Geared Compressors PDFDocument6 pagesRG Integrally Geared Compressors PDFJaswindersingh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Centrifugal Compressor Capacity ControlsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Centrifugal Compressor Capacity Controlsjuancgr77100% (1)
- Reciprocating Air Compressors: Compression RatioDocument25 pagesReciprocating Air Compressors: Compression RatioRichardt LootsNo ratings yet
- Gas Compressor Calculations Tutorial PDFDocument7 pagesGas Compressor Calculations Tutorial PDFHaARSIMRAn100% (1)
- TGI Sabana Gas Transport: Operating Conditions Normal D E F A B CDocument3 pagesTGI Sabana Gas Transport: Operating Conditions Normal D E F A B Chernan plazasNo ratings yet
- A Guideline For Design Pressure - Part 2Document4 pagesA Guideline For Design Pressure - Part 2Said Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- Comp Gas Flow FormulaDocument10 pagesComp Gas Flow FormulajamestppNo ratings yet
- Calculate Compressed Air ReceiversDocument2 pagesCalculate Compressed Air ReceiversYYo YudiNo ratings yet
- Calculate Saturated-Gas Loads For Vacuum SystemsDocument3 pagesCalculate Saturated-Gas Loads For Vacuum SystemsFred FaberNo ratings yet
- SOP CalculationDocument8 pagesSOP Calculationmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Balistic SeperatorDocument36 pagesBalistic SeperatorAhmetNo ratings yet
- Tube Rupture (Two Phase-Omega Method)Document1 pageTube Rupture (Two Phase-Omega Method)Saeid Rahimi MofradNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compresor CalculationDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Compresor CalculationgrabettyNo ratings yet
- Fan Performance CurveDocument4 pagesFan Performance CurvemuddogNo ratings yet
- A03 Hydrocarbon Dew Point Control Rev 07-10Document2 pagesA03 Hydrocarbon Dew Point Control Rev 07-10Arif MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Compressor Air Intake Quality ImportanceDocument12 pagesCompressor Air Intake Quality Importanceanup_nairNo ratings yet
- 2K Method PDFDocument5 pages2K Method PDFMiguel Antonio Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Surge Control Dynamic Simulation Centrifugal CompDocument3 pagesSurge Control Dynamic Simulation Centrifugal CompAnil B YadavNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument28 pagesPressure Drop Calculationshicham100% (2)
- Step by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredDocument5 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredkarthickNo ratings yet
- Control Valve DPDocument8 pagesControl Valve DPAmit SawantNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor SizingDocument11 pagesAir Compressor Sizingalquin08No ratings yet
- Acceleration Head For Reciprocating PumpsDocument2 pagesAcceleration Head For Reciprocating PumpsEng Alf100% (2)
- Dynamic Modeling of Heat Exchanger Tube RaptureDocument20 pagesDynamic Modeling of Heat Exchanger Tube RaptureRajesh NimmakayalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Reciprocatng Compressors: StructureDocument26 pagesUnit 8 Reciprocatng Compressors: StructureRakeshKrNo ratings yet
- (MEA) CO2 Capture PFDsDocument95 pages(MEA) CO2 Capture PFDsfNo ratings yet
- Calculate Compressed Air ReceiversDocument1 pageCalculate Compressed Air ReceiverssgrsthNo ratings yet
- Key Parameters For Air Cooled Condenser DesignDocument12 pagesKey Parameters For Air Cooled Condenser DesignmohantyomNo ratings yet
- Memoria de Cálculo CompresoresDocument6 pagesMemoria de Cálculo CompresoresEstuardo Javier Gan Rodríguez100% (1)
- Compressor Power Estimation CalcsDocument4 pagesCompressor Power Estimation Calcsronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- BlowersDocument58 pagesBlowersmahmad61100% (1)
- PressorsDocument8 pagesPressorsManoj MisraNo ratings yet
- 7 CompressorsDocument49 pages7 Compressorsparvin.f100% (1)
- Turbo Machinery, Lecture Notes Physics Prof T P HynesDocument71 pagesTurbo Machinery, Lecture Notes Physics Prof T P HynesPunit GuptaNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Perf Curves To Evaluate Behavior of Cent CompDocument8 pagesHow To Use The Perf Curves To Evaluate Behavior of Cent CompAnonymous yLPPdPwNo ratings yet
- Crane Technical Paper 410Document144 pagesCrane Technical Paper 410tedfdfe0% (1)
- Industrial InsulationDocument9 pagesIndustrial Insulationahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- 128 CTI Test Code For Sound MeasurementDocument24 pages128 CTI Test Code For Sound MeasurementyohayjoNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower 6MWDocument6 pagesCooling Tower 6MWtedfdfeNo ratings yet
- Elastomer CompareDocument1 pageElastomer ComparetedfdfeNo ratings yet
- Inverted T Bent Cap Design ExampleDocument88 pagesInverted T Bent Cap Design ExampletedfdfeNo ratings yet
- Jis To Other STDDocument2 pagesJis To Other STDtedfdfeNo ratings yet
- API 610 Centrifugal Pump Types - OH, BB & VSDocument17 pagesAPI 610 Centrifugal Pump Types - OH, BB & VSDANISH ALINo ratings yet
- Atkinson Cycle EnginesDocument8 pagesAtkinson Cycle EnginesMichael Louise Decena GleanNo ratings yet
- Material Receiving Inspection Rep0Rt: Shell Dt1 & Dt2 Project SKPDocument4 pagesMaterial Receiving Inspection Rep0Rt: Shell Dt1 & Dt2 Project SKPAqeel aslamNo ratings yet
- Ec460b 09Document6 pagesEc460b 09Khinmg Aye 554No ratings yet
- Checklist Fire PDFDocument1 pageChecklist Fire PDFMadan TiwariNo ratings yet
- Plastic Recycling - Injection Molding Auxiliaries Catalog - SV TechnologiesDocument26 pagesPlastic Recycling - Injection Molding Auxiliaries Catalog - SV TechnologiesSV TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- ASC Presentation PDFDocument89 pagesASC Presentation PDFAhmadHussain09No ratings yet
- Danfoss GUY60NRb R134a 115 60Document5 pagesDanfoss GUY60NRb R134a 115 60Jhon Freddy Roldan NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Me B 3 Engines With Variable Exhaust Valve TimingDocument3 pagesMe B 3 Engines With Variable Exhaust Valve TimingJatin JainNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Test and Production Separation Production Separation PresentationDocument73 pagesWelcome To The Test and Production Separation Production Separation PresentationhamdiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Subpart 76.13-Steam Smothering Systems: 46 CFR Ch. I (10-1-09 Edition) 76.13-1Document1 pageSubpart 76.13-Steam Smothering Systems: 46 CFR Ch. I (10-1-09 Edition) 76.13-1sachin2010No ratings yet
- Mitsui Wall Type Series On-Off MVE - Technical SpecificationDocument1 pageMitsui Wall Type Series On-Off MVE - Technical SpecificationBruno Faria CotaNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantsDocument2 pagesTypes of Power Plantsrexdindigul0% (1)
- Industrial Steam ProcessDocument1 pageIndustrial Steam ProcessPryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Turbine Prestartup ChecklistDocument4 pagesTurbine Prestartup ChecklistSCE SOLAPURNo ratings yet
- كتاب اساسيات محرك الديزل وشرح أجزاءه PDFDocument52 pagesكتاب اساسيات محرك الديزل وشرح أجزاءه PDFabdallah badrNo ratings yet
- E426 1 Mynute JDocument12 pagesE426 1 Mynute JAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- GEIT-65027US Remote Visual InspectionDocument16 pagesGEIT-65027US Remote Visual InspectionvrapciudorianNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Exploration and Production Activities in South AfricaDocument1 pagePetroleum Exploration and Production Activities in South AfricaEthan van DiemenNo ratings yet
- Equipment Master (R) - TemplateDocument137 pagesEquipment Master (R) - TemplateruchitlpatelNo ratings yet
- 101 - 200 KVA » Silent » LOVOL Genset Silent 100 Kva • Penjualan & Service Aneka Generator Set _ Genset - Perkins, Cummins, Deutz, MWM, FG Wilson, MAN, MTU, YANMAR, Mitsubishi, PRAMAC, Stamford, Leroy Somer, LovolDocument2 pages101 - 200 KVA » Silent » LOVOL Genset Silent 100 Kva • Penjualan & Service Aneka Generator Set _ Genset - Perkins, Cummins, Deutz, MWM, FG Wilson, MAN, MTU, YANMAR, Mitsubishi, PRAMAC, Stamford, Leroy Somer, LovolGIGsantonNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 1 ESYBOX MAX 85 120 TDocument4 pagesData Sheet 1 ESYBOX MAX 85 120 TAjie McNo ratings yet
- Piso Techo Nuevo Uca VerticalDocument4 pagesPiso Techo Nuevo Uca VerticalfacturacionductairesNo ratings yet
- 1308172866-Broshure BT GIDocument20 pages1308172866-Broshure BT GIcatch_samNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Technology: Types of Refrigeration Systems AND Principles of OperationDocument3 pagesRefrigeration Technology: Types of Refrigeration Systems AND Principles of OperationJoseph Francis GalleraNo ratings yet
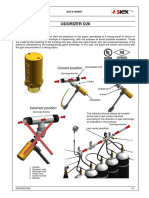
- Odorizer D20: Correct Position Correct PositionDocument3 pagesOdorizer D20: Correct Position Correct PositionEMMA VIDALNo ratings yet
- Dyke Calculation and TechnicalDocument17 pagesDyke Calculation and Technicalsiva_aelNo ratings yet
- ABS Guide For Enhanced Fire Protection ArrangementsDocument100 pagesABS Guide For Enhanced Fire Protection ArrangementsIsa KumNo ratings yet
- Fmea of Co Air Conditioning Systems: by Dr.-Ing. Ulrich Hussels Risa Sicherheitsanalysen GMBH, GermanyDocument13 pagesFmea of Co Air Conditioning Systems: by Dr.-Ing. Ulrich Hussels Risa Sicherheitsanalysen GMBH, GermanykaimanwatsoNNo ratings yet
- Internalcombustionenginevtuatdnotes 160625105955Document6 pagesInternalcombustionenginevtuatdnotes 160625105955Islam SahafayatNo ratings yet