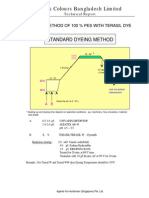
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indigo - Continuous (Modo de Compatibilidad)
Uploaded by
Carlos Rodríguez GandarillasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indigo - Continuous (Modo de Compatibilidad)
Uploaded by
Carlos Rodríguez GandarillasCopyright:
Available Formats
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
DyStar Continuous Dyeing of Indigo
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 1 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
Co te t Content
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8 8. 9. General overview DyStar Product Offer Dyeing machinery and principle Pretreatment Dyeing Metering system Guideline recipes Aft t Aftertreatment t t Conversion factors for caustic soda
Page 2 June 2003
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
1. Ge General ea O Overview e e Indigo d go
Main application is the continuous dyeing of warp yarn for denim fabric. The indigo pigment is a water-insoluble vat dye (no affinity to cotton). Indigo is converted to its water-soluble leuco form by reduction (affinity to cotton). cotton) With DyStar Indigo Granules the reduction process (vatting) takes place in the stock vat. DyStar Indigo Vat 40% Solution and DyStar Indigo Vat 60% Grains have been reduced by hydrogenation process during their manufacture. Preparation of a stock vat is therefore unnecessary with both these products.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 3 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
2. DyStar ySta Product oduct O Offer e
Product D t Indigo Dystar I di G Granules l DyStar Indigo Vat 40 % Solution Characteristics/main application area z Low L d dusting ti z Denim z Prereduced product z No stock vat preparation z Up to 70 % saving in hydrosulfite z Contains 9 % NaOH z Denim DyStar Indigo Vat 60 % Grains z Prereduced product z Contains 15 % NaOH , cottage g industry y applications pp z Wool,
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 4 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3. Dyeing 3 ye g machinery ac e y and a d principle p cpe
Rope dyeing: The yarn is assembled into ropes of about thumb thickness, each containing round 350 ends; 12 36 ropes (1 3 warps) are run through the dyeing range side-by-side side by side. Before sizing sizing, the ropes are opened and the warp ends wound onto section-warp beams.
Slasher dyeing: The ends (approx. 4000) from several section-warp beams are assembled to form a warp warp, which is dyed in the open-width open width form, form sized and then wound onto beams for the loom.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 5 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3.1 Dyeing 3 ye g machinery ac e y Rope ope Dyeing ye g
Advantages z High Hi h rate t of f production d ti z No stoppage with lot changes z No p possibility y of side-to-center shade variations in the finished fabric z Little yarn wastage, provided that leader is used Disadvantages z The Th ropes must t be b opened d after ft dyeing z Lack of flexibility y owing g to the large g dyebath volume (up to 40000 l) z Additional costs for softener to facilitate opening of the ropes
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 6 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3.2 Dyeing 3 ye g machinery ac e y S Slasher as e Dyeing ye g
Advantages z Compact C t range z Fine yarns (shirting materials) can be processed ( p (up p to Ne 40/1) ) z Continuous production from sectionwarp beam (undyed) to sized warp beam (dyed) z Small dyebath volume (1500 8000 l) z Allows flexible change in process z Produces maximum ring dyeing changes
Regional Business Development Denim
Disadvantages z Possibility P ibilit of f side-to-center id t t shade h d variations in the finished fabric z Yarn wastage g from lot changes g z Short immersion times and/or a small number of dips which are particularly likely with older dyeing ranges result in a lower standard of fastness with dark shades z Relatively long stoppages during lot changes
Page 7 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3.3 3 3 Dyeing ye g p principle cpeI
The dyeing process on indigo-dyeing ranges is carried out in a number of dips, usually from 4 8, i. e. the warp yarn is passed through a dyebath several times.
The dyebath can consist of one box only or be made up of several boxes.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 8 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3.3 3 3 Dyeing ye g p principle c p e II
Dipping immersion time 4 20 s reduced indigo exhausts onto the cellulosic fibre
Squeezing 70 80% liquor pick-up contributes to rapid oxidation improves the fastness
Air passage the hydrosulfite and the indigo is oxidized
Page 9 June 2003
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
3.4 Dyeing 3 ye g machinery ac e y a and dp principle cpe
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 10 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
4. Pretreatment et eat e t - Su Survey ey
Process P Prewetting tti Boiling off Causticizing Process Application z Standard St d d process f for slasher l h d dyeing i ranges z Standard process for rope dyeing ranges z Process to obtain extreme ring dyeing and/or special effects (e. g. salt and pepper) z Can be carried out on all dyeing ranges Without pretreatment z Only for slasher dyeing ranges z Gives good ring dyeing z Higher risk of streakiness zAddition of wetting agent to the dyebath necessary
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 11 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
4.1 Prewetting e ett g
3 g/L wetting agent e.g. Primasol NF (BASF) Temperature: room temperature Immersion time: at least 6 s Replenishment: by level control
Rinse cold
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 12 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
4.2 Boiling o g off o
10 15 mL/L NaOH 50% 1-3 2-4 g/L sequesting agent e.g. Kieralon MFB (BASF) g/L complexing agent e.g. Trilon TA (BASF) Temperature: 90 C Immersion time: at least 10 s Replenishment: by level control 2 x rinse hot (approx. 60 C) Rinse cold
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 13 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
4.3 3 Caust Causticizing c g
NaOH 12 - 22 B 4 g/L wetting agent e.g. Leophen MC (BASF)
2 - 4 g/L complexing agent e.g. Trilon TA (BASF) Temperature: room temperature Immersion time: 10 15 s Replenishment: by level control
To maintain a NaOH concentration of 20 B in the causticizing box, the liquor must be replenished with NaOH of 22 B.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 14 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
4.3.1 3 Caust Causticizing c g with/without t / t out neutralization eut a at o
Causticizing without subsequent neutralization Causticize 2 3 x rinse hot (approx. 60 C) Rinse cold several times
g with subsequent neutralization Causticizing Causticize 1 2 x rinse hot ( (approx. pp 60 C) ) Neutralize/acidify 1 2 x rinse cold
Page 15 June 2003
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5. Dyeing 5 ye g
Irregular dyeing results particularly variations within dyeing lots are a problem in denim production. As a rule, the finished denim material is classed into groups according to the dyeing results and the appearance after washdown. Maintaining the dyebath parameters constant reduces the number of these groups and also the proportion of off shades.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 16 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.1 Process 5 ocess Parameters a a ete s I
Parameter R d Reduced di indigo di Nature of the change Ri i Rise in concentration t ti Fall in concentration Indigo pigment content Increase Effect z Increase I in i depth d th of f shade h d z Decrease in depth of shade z Lowers the fastness z Less contrast in wash-down Decrease Immersion time Extending z Improves the fastness z Greater dye penetration z Increase in depth of shade Shortening z More pronounced ring dyeing z Decrease in depth of shade
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 17 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.2 Process 5 ocess Parameters a a ete s II
Parameter Caustic C ti concentration Nature of the change R i i Raising Effect z Raises R i th the pH H z Greater dye penetration z Shade becomes redder, , clearer Lowering z Lowers the pH z More p pronounced ring g dyeing y g z Shade becomes greener, duller z Risk of formation of the vat acid at pH <11.5
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 18 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.2 Process 5 ocess Parameters a a ete s III
Parameter Hydrosulfite H d lfit concentration Nature of the change R i i Raising Effect z Greater dye penetration z Shade becomes greener, clearer z Lowers the pH z More pronounced ring dyeing z Promotes oxidation of the indigo in p g the air passage z Risk of increased formation of indigo pigment in the dyebath z Risk of bronzy dyeings z Shade becomes redder, duller z Raises the pH
Page 19 June 2003
Lowering
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.3 5 3 Examples a p es o of p pH variation a at o deg degree ee o of ring g dyeing dye g
pH 13.2
pH 11.5
Cross-section of a yarn bundle with approx. 200 threads (magnification 7 : 1)
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 20 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.4 Examples 5 a p es o of p pH variation a at o c change a ge in s shade ade
pH 13.2
pH 11.5
Surface view of a yarn bundle
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 21 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
5.4 Examples 5 a p es o of hydrosulfite yd osu te variation a at o c change a ge in s shade ade
0.5 g/L excess hydrosulfite
2.0 g/L excess hydrosulfite
Surface view of a yarn bundle
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 22 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
6.1 Stoc 6 Stock vat at without t out c chemical e ca replenishing ep e s g add additions to s
DyStar Indigo Granules NaOH Hydrosulfite Auxilliaries
Little flexibility when there is a change in the style to be dyed Little flexibility when it is necessary to change the processing parameters instable because of d decomposition iti of f hydrosulfite h d lfit not recommended
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 23 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
6.2 Stoc 6 Stock vat at with t sepa separate ate c chemical e ca replenishing ep e s g add additions to s
DyStar Indigo Granules NaOH Hydrosulfite Auxilliaries NaOH Hd Hydrosulfite lfit
Most frequently used method More flexible than the stock vat method without chemical replenishments Does not allow automatic pH control limited stability of dissolved h d hydrosulfite lfit
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 24 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
6.3 6 3 Stoc Stock vat at with t sepa separate ate c chemical e ca add additions to sa and d metering ete g of the caustic soda
DyStar Indigo Granules NaOH Hydrosulfite Auxilliaries NaOH Hd Hydrosulfite lfit
NaOH
Particularly flexible Processing parameters can be readily changed by altering the setting of the metering pumps Allows automatic pH control Allows several dyeing ranges to be supplied from one mixing station t ti The recipes for the stock vat and chemical replenishment need not be changed limited stability of dissolved hydrosulfite
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 25 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
6.4 DyStar 6 ySta Indigo d go Vat at 40% 0% So Solution ut o with t separate sepa ate c chemical e ca replenishment additions
DyStar Indigo Vat 40 % Solution Storage tank NaOH Hydrosulfite
No stock vat preparation Dye metered direct from the storage tank Particularly flexible Allows automatic pH control
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 26 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
6.5 6 5 DyStar ySta Indigo d go Vat at 40% 0% So Solution ut o with t separate sepa ate c chemical e ca additions and metering of the caustic soda
DyStar Indigo Vat 40 % Solution Storage tank NaOH Hydrosulfite
No stock vat preparation Dye metered direct from the storage tank Does not allows automatic pH control
NaOH
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 27 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.1 Stoc Stock Vat at Preparation epa at o I
80 1 g/L g/L DyStar Indigo Granules wetting agent e.g. Primasol NF (BASF) complexing agent e.g. Trilon TA (BASF) dispersing agent e.g. Setamol WS (BASF)
4 8 g/L 1 70 65 g/L
mL/L NaOH 50% g/L hydrosulfite
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 28 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.1 Stoc Stock Vat at Preparation epa at o II
Fill cold water into the mixing vessel to approx. 75% of the final volume Add auxiliaries Strew in and disperse indigo. Add caustic soda Slowly strew in hydrosulfite. Stirring for 3 5 min dissolves the hydrosulfite. Fill up with water to the final volume. The mix is finally stirred again for 3060 s. Depending on the temperature, vatting of the indigo is completed in 2 3 hours
Page 29 June 2003
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.2 C Chemical e ca replenishment ep e s e t
135 g/L 70 mL/L hydrosulfite NaOH 50%
Temperature: room temperature
Chemical liquors should be stored under cool conditions and protected from exposure to t air. i The Th amounts t prepared d should h ld be b such h that th t they th are consumed within 60 90 min .
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 30 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.3 3 Dyebath yebat p preparation epa at o
40 g/L 2 mL/L salt (common salt or Glauber salt) NaOH 50% hydrosulfite stock vat (cf. 7.1) = 2.0 g/L DyStar Indigo Granules
1.5 g/L 5 mL/L
The dyebath is set cold with salt, caustic soda and hydrosulfite, followed by addition of the stock vat. 12.5 mL/L of the stock vats described in 7.1 corresponds to 1 g/L DyStar Indigo Granules.
Page 31 June 2003
Regional Business Development Denim
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.4 Example a p e ca calculation cu at o I
7 Ne yarn 4000 number of ends 25 m/min running speed 7.4 kg/min yarn throughput 1.8 % indigo concentration based on weight of yarn 0.5 g/L hydrosulfite concentration 11.7 pH 6 dips 75 % liquor pick-up
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 32 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
7.4 Example a p e ca calculation cu at o II
130 g/min 250 g/min 190 mL/min replenishment of DyStar Indigo Granules replenishment of hydrosulfite replenishment of NaOH 50%
Stock vat at : 1 1.6 6 L/min replenishment 80 65 70 g/L Dystar Indigo Granule g/L hydrosulfite mL/L NaOH 50%
Chemical liquor : 0.7 L/min replenishment 135 g/L hydrosulfite 70 mL/L NaOH 50%
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 33 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
8. Aftertreatment 8 te t eat e t
2 3 x rinse hot (up to 50 C) The dyed warp yarns are rinsed at least twice with cold or, better, warm water of up p to 50 C to wash out any y unfixed dye y and chemicals. With rope-dyeing ranges, a softener should be used. The last rinsing bath to facilitate rebeaming rebeaming. Warp yarns dyed on slasher machines are given an intermediate drying to a residual moisture content of approx. 30% and are then sized.
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 34 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
9. Co 9 Conversion e s o factors acto s Caust Caustic c soda I
1 L NaOH 50% 1 L NaOH 50% 1 L NaOH 50% 1 L NaOH 50% % 1 L NaOH 38 B 1 L NaOH N OH 38 B 1 L NaOH 38 B 1 L NaOH 38 B = = = = = = = = 1.74 L NaOH 38 B 1.09 L NaOH 48 B 766 g NaOH 100% 1525 g 0.57 L NaOH 50% 0 63 L NaOH 0.63 N OH 48 B 441 g NaOH 100% 1358 g
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 35 June 2003
Asia Pacific Continuous dyeing of indigo
9. Co 9 Conversion e s o factors acto s Caust Caustic c soda II
1 L NaOH 48 B 1 L NaOH 48 B 1 L NaOH 48 B 1 L NaOH 48 B = = = = 0.91 L NaOH 50% 1.59 L NaOH 38 B 700 g NaOH 100% 1500 g 1.30 L NaOH 50% 2 27 L NaOH 2.27 N OH 38 B 1.43 L NaOH 48 B
1 kg NaOH 100% = 1k kg N NaOH OH 100% = 1 kg NaOH 100% =
Regional Business Development Denim
Page 36 June 2003
You might also like
- Report ON DENIMDocument59 pagesReport ON DENIMEbony Gallagher93% (14)
- Pantone - Color Trend 2021 - Recipes by Fiber V2.0Document15 pagesPantone - Color Trend 2021 - Recipes by Fiber V2.0JUAN SEBASTIAN BUSTOS GARNICA100% (1)
- Types of Sewing Thread Reference ChartDocument6 pagesTypes of Sewing Thread Reference ChartMihiraNo ratings yet
- Oekotex 2021Document90 pagesOekotex 2021Nazmul hasanNo ratings yet
- Salt Alkali Free ReactiveDocument6 pagesSalt Alkali Free ReactiveSaif Rahman100% (1)
- Indigo Dyeing: Prepared By-Rajdeep Singh B-Tech 4 SemDocument20 pagesIndigo Dyeing: Prepared By-Rajdeep Singh B-Tech 4 SemGaurav Dhawan100% (3)
- Remazol Ultra RGBDocument33 pagesRemazol Ultra RGBCarlos Rodríguez Gandarillas100% (2)
- Minimal Application Tech.Document32 pagesMinimal Application Tech.Vaibhav GandhiNo ratings yet
- Textile Processing JuryDocument41 pagesTextile Processing JuryANISHA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Archroma Passion-for-Denim Digital3 PDFDocument10 pagesArchroma Passion-for-Denim Digital3 PDFDewan Ajuad Hossain RifatNo ratings yet
- Warp Dyeing With Indigo DyesDocument12 pagesWarp Dyeing With Indigo DyesMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CHT Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Spin FinishDocument21 pagesCHT Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Spin Finishvb_scribd1234100% (2)
- Clariant Blue MagicDocument9 pagesClariant Blue MagicHrishikesh DhawadshikarNo ratings yet
- Ananto Garments LTD (Intership Report)Document60 pagesAnanto Garments LTD (Intership Report)Batch 27100% (1)
- Recommended Exhaust Dyeing Process For EcoFRESH Yarn V3 00-2015 12 (En)Document5 pagesRecommended Exhaust Dyeing Process For EcoFRESH Yarn V3 00-2015 12 (En)Saidur Rahman SajibNo ratings yet
- Corelation Between Lab and BulkDocument38 pagesCorelation Between Lab and BulkSuraj Raghv0% (1)
- Semi Continuous Dyeing ProcessDocument3 pagesSemi Continuous Dyeing ProcessMonjur MorshedNo ratings yet
- Dye Bath LubricantsDocument23 pagesDye Bath Lubricantshuerta_antonio1181100% (1)
- Aatcc NewletterDocument52 pagesAatcc NewletterlthyaguNo ratings yet
- Finishing Collection and Guide Line RecipeDocument29 pagesFinishing Collection and Guide Line Recipeapi-19663176No ratings yet
- Selected Garments WashingDocument35 pagesSelected Garments WashingTanmoy AntuNo ratings yet
- Textile - Reference Book For SpinningDocument199 pagesTextile - Reference Book For Spinningnour04100% (13)
- Textile Printing ClariantDocument9 pagesTextile Printing ClariantAkmal Javed0% (1)
- Denim & Textile Processing - Anti Back Staining Method For DenimDocument4 pagesDenim & Textile Processing - Anti Back Staining Method For DenimjahirulNo ratings yet
- Textile Dyeing and Printing-IIDocument99 pagesTextile Dyeing and Printing-IIKeshav Dhawan100% (1)
- Textile Yarn Dyed Tips & TechniqueDocument23 pagesTextile Yarn Dyed Tips & TechniqueMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 9 After Print Washing Printing Training 1&2Document55 pages9 After Print Washing Printing Training 1&2yadi haryadiNo ratings yet
- Terasil Standard Dyeing MethodDocument1 pageTerasil Standard Dyeing MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Exhaust DyeingDocument60 pagesExhaust DyeingLieven Verraest50% (4)
- Costing and Sourcing of Jeans ApparelDocument7 pagesCosting and Sourcing of Jeans ApparelchocolateNo ratings yet
- WeavingDocument93 pagesWeavingkernchiaNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Print Paste Using Natural and Indigenous Thickener - MaizeDocument4 pagesFormulation of Print Paste Using Natural and Indigenous Thickener - MaizeFathi MustafaNo ratings yet
- Z&S PesDocument8 pagesZ&S Pesguven44No ratings yet
- FactSheet Dyeing Finishing DyStar IngeoColorationPack PDFDocument53 pagesFactSheet Dyeing Finishing DyStar IngeoColorationPack PDFJose Iniesta PerezNo ratings yet
- Dyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentDocument22 pagesDyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentTooba Anum100% (1)
- Customer Information: A Guide To Pretreatment, Dyeing and FinishingDocument29 pagesCustomer Information: A Guide To Pretreatment, Dyeing and FinishingRickgableNo ratings yet
- Fabric physical test matrixDocument1 pageFabric physical test matrixNazmul hasanNo ratings yet
- Pad BatchDocument7 pagesPad BatchPadmakar29No ratings yet
- Everzol Dyes StructuresDocument9 pagesEverzol Dyes StructuresNestor Mauricio Florian RamirezNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Textile Machinery Webtalk - Powered by VDMA!Document19 pagesWelcome To Textile Machinery Webtalk - Powered by VDMA!Shaikh ShaharuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Finish EbookDocument534 pagesFinish EbookNess DarkNo ratings yet
- Blind DyeingDocument6 pagesBlind Dyeingprabhulean14No ratings yet
- Reactive DyeingDocument23 pagesReactive Dyeingshivkalia8757100% (2)
- Project ReportDocument79 pagesProject ReportranaNo ratings yet
- Employee Turnover: A Summer Training Project Report ONDocument82 pagesEmployee Turnover: A Summer Training Project Report ONIshani Gupta100% (2)
- One Bath One Stage Dyeing of Polyester/Cellulosic Blends Using Disperse and Reactive DyesDocument31 pagesOne Bath One Stage Dyeing of Polyester/Cellulosic Blends Using Disperse and Reactive Dyessanjay shettiNo ratings yet
- Tubifast As 5087 Ff-EnDocument4 pagesTubifast As 5087 Ff-EnrajasajjadNo ratings yet
- Dyeing LabDocument19 pagesDyeing LabFathi MustafaNo ratings yet
- Finishing TextilesDocument202 pagesFinishing TextilesvasilicapNo ratings yet
- Dyefix-CF - Dye Fixing Agent With Excellent Fastness To Chlorine.Document10 pagesDyefix-CF - Dye Fixing Agent With Excellent Fastness To Chlorine.L.N.CHEMICAL INDUSTRYNo ratings yet
- Disperse PrintingDocument20 pagesDisperse PrintingCamila Suarez100% (1)
- 01703Document3 pages01703Shaique SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Denim Fabric Manufacturing (Cap: 5000 Meter Per Day)Document7 pagesProject Report On Denim Fabric Manufacturing (Cap: 5000 Meter Per Day)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Dyeing CalculationDocument6 pagesDyeing CalculationRihan Ahmed RubelNo ratings yet
- Contineous Dyeing of Reactive DyesDocument9 pagesContineous Dyeing of Reactive DyesMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Batch to Batch Reproducibility and how to avoid creases, spots and stainsDocument32 pagesBatch to Batch Reproducibility and how to avoid creases, spots and stainsJohn VasilonikolosNo ratings yet
- Ultratex UHS Hydrophilic Softener: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesUltratex UHS Hydrophilic Softener: Technical Data SheetSon NguyenNo ratings yet
- Textile Internship Report AlokDocument39 pagesTextile Internship Report AlokRahul TelangNo ratings yet
- Printingmethodsstylesetc 160507081424Document32 pagesPrintingmethodsstylesetc 160507081424Pratham JainNo ratings yet
- Wet Processing Technology .Industrial Re PDFDocument153 pagesWet Processing Technology .Industrial Re PDFaauNo ratings yet
- Fabric Dyeing ProcessDocument6 pagesFabric Dyeing ProcessSURUCHI KUMARINo ratings yet
- Denim Finishing: Weko Offers Solutions ..Document8 pagesDenim Finishing: Weko Offers Solutions ..孙兴峰No ratings yet
- International DyerDocument56 pagesInternational DyerAnonymous vhMCGINo ratings yet
- Vishwanath Spinnerz - Given His Elaborated View at Departmentwise, The Causes of BarreDocument3 pagesVishwanath Spinnerz - Given His Elaborated View at Departmentwise, The Causes of BarreDhasaratahi JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Dyeing AND Printing: Assignment-2Document21 pagesDyeing AND Printing: Assignment-2Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Electrolytes for Reactive Cotton DyeingDocument6 pagesAnalyzing Electrolytes for Reactive Cotton DyeingRajeev MehraNo ratings yet
- Faerben Und AusruestenGB PDFDocument28 pagesFaerben Und AusruestenGB PDFRabbial MamunNo ratings yet
- Ijser: Study On Waterless Chemical Effect On Indigo Rope DyeingDocument5 pagesIjser: Study On Waterless Chemical Effect On Indigo Rope DyeingDheerajNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Textile PrintingDocument33 pagesCase Study in Textile PrintingAun Na-DonNo ratings yet
- MI 2008-30e Acid CellulasesDocument3 pagesMI 2008-30e Acid CellulasesCarlos Rodríguez GandarillasNo ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument20 pagesConcreteCarlos Rodríguez GandarillasNo ratings yet
- Basacryl DyesDocument33 pagesBasacryl DyesCarlos Rodríguez GandarillasNo ratings yet
- PA DyeingDocument11 pagesPA DyeingCarlos Rodríguez GandarillasNo ratings yet
- BASF Dyeing - Auxiliary ManualDocument55 pagesBASF Dyeing - Auxiliary ManualCarlos Rodríguez Gandarillas100% (1)
- FOCbookDocument76 pagesFOCbookCarlos Rodríguez GandarillasNo ratings yet
- Ingredient Branding & Supply Chain Transparency in The Jeanswear Industry: The Isko CaseDocument17 pagesIngredient Branding & Supply Chain Transparency in The Jeanswear Industry: The Isko CaseJgcFranNo ratings yet
- Project Term ReportDocument29 pagesProject Term ReportM Hammad KothariNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesReading ComprehensionLissNo ratings yet
- Brochure DenimDocument4 pagesBrochure DenimRickgableNo ratings yet
- SURYALAKSHMI COTTON MILLS LTD DENIM UNIT STOCK RECONCILIATIONDocument11 pagesSURYALAKSHMI COTTON MILLS LTD DENIM UNIT STOCK RECONCILIATIONyadav1990No ratings yet
- Denim Present and Future of Bangladesh (For Selim)Document12 pagesDenim Present and Future of Bangladesh (For Selim)shohagh12133% (3)
- Examen Grammar y Reading A1+Document4 pagesExamen Grammar y Reading A1+Adriana Jimenez CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Trims Details Sourcing Guide S S 22Document11 pagesTrims Details Sourcing Guide S S 22Chelle LimNo ratings yet
- TH MSW Stock NosDocument24 pagesTH MSW Stock Nosqnodop1No ratings yet
- Arvind Textiles Internship ReportDocument107 pagesArvind Textiles Internship ReportDipan SahooNo ratings yet
- Friends Style Wear LTD ProfileDocument21 pagesFriends Style Wear LTD Profiledomaingood0% (1)
- English Comprehension TestDocument129 pagesEnglish Comprehension TestQuang TrầnNo ratings yet
- Raymond DenimDocument1 pageRaymond DenimraquibalamNo ratings yet
- Customer call list for textile companies 07.10.20Document104 pagesCustomer call list for textile companies 07.10.20Abdus Satter HimelNo ratings yet
- Sister Denim Composite Limited vision and strengthsDocument18 pagesSister Denim Composite Limited vision and strengthsIsrafil AlamNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument15 pagesDefinitionsTherescuer RescuedNo ratings yet
- Improve Fabric Properties Through Fibre Blending and Yarn MixingDocument2 pagesImprove Fabric Properties Through Fibre Blending and Yarn MixingVipin Singh KandholNo ratings yet
- BCI Members List ContactsDocument180 pagesBCI Members List ContactsSuggest ErpNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S245222362200092X MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S245222362200092X MainRaquel IanineNo ratings yet
- VISION ArvindDocument26 pagesVISION ArvindPalak MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of Nandan Denim LtdDocument70 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Nandan Denim LtdsejalNo ratings yet
- Billabong SP14 Mens CatDocument170 pagesBillabong SP14 Mens CatFlory CucuNo ratings yet
- Arvind ReportDocument17 pagesArvind Reportaneri31791100% (1)