Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JT15D Ata 73
Uploaded by
Egor85Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JT15D Ata 73
Uploaded by
Egor85Copyright:
Available Formats
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
Page 1 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
0 TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 5 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Fuel system Purpose Fuel system components Fuel additives and limitations Input requirement Fuel pump Purpose Description Typical pump capacity @ 100% N2 Inlet filter Outlet filter Filter bypass valve Maintenance FCU (hydraulic section) Purpose High pressure relief valve Metering valve Bypass valve Motive flow valve FCU (pneumatic section) Purpose Bellows Governor Enrichment valve Back-up valve T2 temperature compensation sensor Step modulator (JT15D-1 and 4 series) Flight idle solenoid (JT15D-5 series) Operation Flow divider Purpose Fuel shut-off and wind milling bypass valve Minimum pressurising and flow divider valve Spill valve Dump valve Operation 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8 8 8 9 9 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 11 11 13 13 13 13 14 14 15
Page 2 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
6 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 7 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Automatic shut-off valve Purpose Construction Operation Maintenance Fuel nozzles Purpose Construction Operation Maintenance 19 19 19 19 19 20 20 20 20 20
Page 3 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 1
1.1
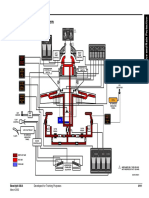
FUEL SYSTEM
Purpose The fuel system provides the engine with clean fuel at the required flow rate to permit control of engine power Supply high pressure fuel to the bleed valve actuator (JT15D-5 series)
1.2
Fuel system components Fuel pump Motive flow valve Bleed valve actuator (Ref ATA 72 Sect 6.4 JT15D-5 series) FCU Flow meter (airframe supplied) Fuel cooled oil cooler Flow divider valve Automatic shut-off valve Fuel nozzles
Page 4 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
1.3 Fuel, additives and limitation Refer to SB 7144 for complete listing of approved fuel and additives Use of AVGAS limited to 50 hours between any TBO amount of AVGAS Hours operating = average fuel consumption 1.4 Input requirements Power lever position P3, compressor discharge pressure N2, high pressure rotor speed
Page 5 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 2
2.1
FUEL PUMP
Purpose Provide clean fuel under pressure to the fuel control unit.
2.2
Description: The pump is a one stage gear-type pump (JT15D-1 and 4 series) The fuel pump is a two-stage pump consisting of a centrifugal first stage, and a gear-type second stage (JT15D-5 series) Two filter elements protect downstream components against contamination A bypass valve allows unfiltered fuel to flow to the engine in the event of filter blockage by allowing fuel to bypass the filter
2.3
Typical pump capacity @ 100% N2 3935 pph @ 580 psi (JT15D-1 and 4 series) 4100 pph @ 580 psi (JT15D-5 series)
2.4
Inlet filter 74 micron metallic type Self bypassing at 9 -12 psid Cleanable
Page 6 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
2.5 Outlet filter 10 micron Paper type filter Disposable 2.6 Filter bypass valve Ball type bypass valve Open at 40 - 60 psid if filter is restricted 2.7 Maintenance Inspect and clean inlet filter electrosonicaly every minor airframe inspection Inspect and replace outlet filter every minor airframe inspection Replace pump if fuel leakage is detected
Page 7 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 3
3.1
FCU (HYDRAULIC SECTION)
Purpose Provide the engine with the required fuel flow according to the power lever position and P3 pressure.
3.2
High pressure relief valve Prevents build up of excess P1 and P2 pressure in the fuel system. This valve is normally closed until P1 pressure overcomes the spring tension and allows P1 fuel to dump into Po. It opens at 1260 psid.
3.3
Metering valve The metering valve travels between a maximum and a minimum fuel flow position and determines the amount of fuel going to the engine fuel nozzles. The metering valve is mechanically linked to the pneumatic bellows in the FCU by torque tubes; spring loaded upwards to W f (min.). JT15D-1 and 4 series Wf (min) Wf (max) JT15D-5 series Wf (min) Wf (max) POSITION UP DOWN POSITION UP DOWN FUEL FLOW 155-160 pph 1600-1640 pph FUEL FLOW 160-165 pph 2170-2260 pph
Page 8 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
3.4 By-pass valve The bypass valve returns fuel in excess of engine requirements to Po. Actuated by means of a diaphragm and spring, the valve maintains a constant P 1 - P2 differential (delta P) of 15-24 psid. 3.5 Motive flow valve Open at 120 psid supply P1 pressure to the airframe fuel ejector pump (JT15D-1 and 4 series). Open at 240 psid to supply P1 pressure to the airframe fuel ejector pump (JT15D-5 series).
Page 9 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 4
4.1
FCU (PNEUMATIC SECTION)
Purpose The function of the N2 governor is to vary engine compressor speed (N2) in order to obtain the desirable thrust (target N1 speed).
4.2
Bellows Senses Px and Py air pressures. Movement of the bellows assembly is transmitted to the metering valve assembly via torque tube assembly.
4.3
Governor Sense N2 speed in order to control the amount of bleed of Px and Py pressure.
4.4
Enrichment valve Allows optimisation of engine acceleration. Above 85% N2 speed, Px and Py pressure are boost in order to increase acceleration rate.
4.5
Back-up valve Allow bleeding Py pressure when actual N2 is higher than selected N2 (approx 9%).
4.6
T2 Temperature Compensation Sensor Modify the fuel schedule to maintain acceleration constant under any ambient temperature. constant when engine anti-ice is selected in order to maintain acceleration time constant. It is energised when ignition is ON.
4.7
Step modulator (JT15D-1 and 4 series) Fitted to all JT15D-4 and JT15D-1 POST SB 7124. It keeps the P3 pressure
Page 10 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
4.8 Flight idle solenoid (JT15D-5 series) Provide higher idle speed (flight idle) to give better respond time on acceleration. NOTE: The T2 compensator is matched with the FCU and must be changed as a set.
4.9
Operation As the pilot move the power lever, this puts tension on the governor spring. It causes the governor lever to pivot and restricting Py bleed. Py increases in the bellows, causing the bellows section to go down. This downward motion causes the metering valve to move down, therefore increasing W f. As W f increases, the engine accelerates, increasing rotation of the governor drive shaft. An increase in drive shaft rotation causes the flyweights to spread, which lifts the drive shaft table. As it lifts, the governor spring is overcome, pivoting the governor lever to open the governor orifice again. Once equilibrium between flyweight force and spring tension is obtained, the engine speed is maintained constant.
Page 11 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
Above 85% N2 the enrichment lever pivots, which opens the enrichment valve. This boosts Px pressure going to the bellows, therefore increase the rate of acceleration. If N2 is higher than selected power lever setting (approx. 9%), the governor force opens a back-up valve in addition to opening the governor orifice. This rapid bleed of Py causes the bellows to travel upwards, which in turn causes the metering valve to reduce W f and therefore limit an over speed condition. A variable orifice, controlled by bimetallic disks in the sensor, controls the quantity of Px air bleed to atmosphere. This sensor effectively modifies the fuel schedule to maintain engine acceleration constant throughout various outside temperatures. The T2 compensator is located under the engine nacelle.
Page 12 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 5
5.1
FLOW DIVIDER
Purpose Divide flow between primary and secondary fuel manifolds and dumps fuel from the manifolds on shutdown.
5.2
Fuel shut-off and wind milling bypass valve Prevent fuel to flow to nozzles on cut-off position. Permit fuel to bypass if engine is wind milling.
5.3
Minimum pressurising and flow divider valve In the absence of metered fuel pressure, the minimum pressurising valve prevents flow to the fuel nozzles Ensures proper operating fuel pressures within the fuel system during the starting sequence Divides the metered fuel flow between the primary and secondary fuel manifolds
Page 13 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
5.4 Spill valve Reduces FCU minimum fuel flow to a level suitable for the starting sequence 5.5 Dump valve Purges fuel remaining in fuel nozzles and manifolds during shutdown
Page 14 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
5.6 Operation
5.6.1 Starting position As the power lever is moved from cut-off to the start/run position, the shut-off and wind milling valve allow metered fuel from the FCU to flow inside the flow divider. When the metered fuel reaches 75 psid, the minimum pressurising valve opens and allows fuel to flow to the dump valve and spill valve. Metered fuel pressure causes the dump valve to close at 5 psi and fuel flows to the primary fuel manifold and the bleed jet. A bleed jet allows a small amount of metered fuel to prime the secondary manifold.
Page 15 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
The spill valve opens and diverts a certain amount of metered fuel into the bypass system. This reduction of fuel to the primary manifold is necessary to optimise the starting characteristics of the engine. Once combustion takes place, the engine begins to accelerate towards idle, the spill valve closes under the influence of the increasing P3 air pressure (30 psi).
Page 16 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
5.6.2 Running position When the pilot sets N2 above 60%, increased fuel pressure causes the flow divider to open and allow fuel flow to the secondary fuel manifold.
Page 17 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
5.6.3 Shut-off position As metered fuel pressure is cut-off by the shut-off and wind milling valve, spring tension acting upon the minimum pressure valve causes it to close off the primary and secondary manifold inlet ports. The lack of fuel pressure within the flow divider also allows the dump valve to open. This connects the primary and secondary manifold to the fuel dump port. Fuel remaining in the fuel manifold system drains out of the dump port, which is connected to the airframe waste fuel system.
Page 18 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 6
6.1
AUTOMATIC SHUT-OFF VALVE
(JT15D-1, 4 and 5 series) Purpose Automatically cut off fuel in the event low pressure rotor shafts decoupling.
6.2
Construction Actuator rod and bell crank Wire rope Tripper mechanism Shut-off valve
6.3
Operation In the event of low pressure rotor shafts decoupling, the turbine shaft moves rearward and contacts the automatic shut-off valve plunger located in the no. 4 bearing cover. This causes the shut-off valve to trip and shut-off the supply of fuel to the nozzles. NOTE: An axial displacement of the low pressure turbine shaft of 0.070" is required to trip valve.
6.4
Maintenance Set gap between tripper and housing, and between bell crank and no. 4 bearing cover Reset the tripper mechanism when system tripped
Page 19 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL 7
7.1
FUEL NOZZLES
(JT15D-1, 4 and 5 series) Purpose Deliver and atomise fuel into the combustion chamber.
7.2
Construction Dual orifice type 12 nozzle adapters 12 nozzle sheaths 12 nozzle tips 24 transfer tubes
7.3
Operation Two offset slots on the nozzle distributor impart a swirl motion to the fuel which emerges as a finely atomised spray in the combustion chamber. Slots in the sheath allow compressor discharge air to pass through the sheath and over the nozzle tip for cooling the tip and atomisation of the fuel.
7.4
Maintenance Flow test at 22 and 60 psi Pressure test for cross manifold leakage at 170 - 200 psi Leak test at 500 psi once installed on low turbine support case
Page 20 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
Page 21 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
Pratt & Whitney JT15D Series (CAT C)
ATA 73 ENGINE FUEL AND CONTROL
PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
Page 22 of 22
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
JT15D - ISSUE 1, 2009
You might also like
- Aircraft Engine Illustrated Parts Catalog: For Reference OnlyDocument48 pagesAircraft Engine Illustrated Parts Catalog: For Reference OnlyBartNo ratings yet
- MM Tpe-331-12Document1,714 pagesMM Tpe-331-12Cristhian342100% (6)
- TFE 731 Chap 74Document6 pagesTFE 731 Chap 74Egor85No ratings yet
- AP Research Survival Guide - RevisedDocument58 pagesAP Research Survival Guide - RevisedBadrEddin IsmailNo ratings yet
- TFE 731 Chap 73Document34 pagesTFE 731 Chap 73Egor85100% (2)
- JT15D Ata 79Document10 pagesJT15D Ata 79Egor85100% (1)
- TFE 731 Chap 70Document18 pagesTFE 731 Chap 70Egor85100% (1)
- JT15D Ata 74Document6 pagesJT15D Ata 74Egor85No ratings yet
- Cessna 550-551-560 (PWC JT15D) Initial Aircraft Type Rating CourseDocument27 pagesCessna 550-551-560 (PWC JT15D) Initial Aircraft Type Rating CourseNitsuga50% (2)
- Jt15d Ata 71 IntroDocument10 pagesJt15d Ata 71 IntroEgor85100% (1)
- Cessna 550 551 560 PWC JT15DDocument1 pageCessna 550 551 560 PWC JT15DJuantorres1No ratings yet
- Type Acceptance Report for Cessna 500-550-560 Series AircraftDocument15 pagesType Acceptance Report for Cessna 500-550-560 Series AircraftZapopano Ducas100% (1)
- SB 1803 R2 Operating TBO & HSI FrequencyDocument22 pagesSB 1803 R2 Operating TBO & HSI FrequencyDade Sobarna100% (4)
- Electronic Instrument SystemsDocument49 pagesElectronic Instrument SystemsEgor85No ratings yet
- PT6A-27 HSI Check SheetDocument10 pagesPT6A-27 HSI Check SheetSantosh SahNo ratings yet
- PrattWhitney Book 2Document393 pagesPrattWhitney Book 2luis Minaya100% (7)
- Ice and Rain Protection System: Beechjet 400A 4H-1Document10 pagesIce and Rain Protection System: Beechjet 400A 4H-1Miguel Angel MartinNo ratings yet
- EASA Part 66 Module 3Document130 pagesEASA Part 66 Module 34587560100% (8)
- Pratt and Whitney JT15D-4 Engine: 4K-1 Citation I/II/SIIDocument12 pagesPratt and Whitney JT15D-4 Engine: 4K-1 Citation I/II/SIIHasni Chawi100% (1)
- FAA Type Certificate Data Sheet for Williams International FJ44 Turbofan EnginesDocument19 pagesFAA Type Certificate Data Sheet for Williams International FJ44 Turbofan EnginesAsthaSingh100% (1)
- 15 PowerplantDocument26 pages15 PowerplantBlueSkyMaster100% (4)
- Easa b1 Module 11Document170 pagesEasa b1 Module 11Mh Huan91% (11)
- Service BulletinDocument14 pagesService Bulletinlocoboeing100% (1)
- Powerplant King 350Document22 pagesPowerplant King 350stive100% (2)
- Workbook - EEng (Part A) Marking GuideDocument40 pagesWorkbook - EEng (Part A) Marking GuideEgor85No ratings yet
- JT15D Borescope Report PC-E 71122Document12 pagesJT15D Borescope Report PC-E 71122Santos Junnior Hipolito Sandoval100% (1)
- Aircraft engine systems overviewDocument8 pagesAircraft engine systems overviewKevin ArteagaNo ratings yet
- JT15D Ata 75Document12 pagesJT15D Ata 75Egor8550% (2)
- Apu 36 Gulfstream 150 G ApuDocument2 pagesApu 36 Gulfstream 150 G ApuEstevam Gomes de Azevedo100% (1)
- JT15D Ata 78Document6 pagesJT15D Ata 78Egor85No ratings yet
- TFE 731 Head IndexDocument4 pagesTFE 731 Head IndexEgor85No ratings yet
- TFE 731 Head IndexDocument4 pagesTFE 731 Head IndexEgor85No ratings yet
- PT6 KitDocument1 pagePT6 Kit060533No ratings yet
- Cheyenne - Pressurization SystemDocument3 pagesCheyenne - Pressurization Systemtumb100% (1)
- Jt15d Ata 72 MaintDocument12 pagesJt15d Ata 72 MaintEgor85100% (1)
- TFE 731 Chap 77Document12 pagesTFE 731 Chap 77Egor85No ratings yet
- TFE 731 Chap 79Document24 pagesTFE 731 Chap 79Egor8550% (2)
- TFE 731 Chap 79Document24 pagesTFE 731 Chap 79Egor8550% (2)
- Complete 100-hour inspection kit for PT6A enginesDocument1 pageComplete 100-hour inspection kit for PT6A enginesLuz Analía Valdez CandiaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft PropulsionDocument148 pagesAircraft Propulsionkhalid1983No ratings yet
- TFE 731 Chap 72Document38 pagesTFE 731 Chap 72Egor85100% (1)
- Tr7-8fi ManualDocument82 pagesTr7-8fi ManualClint CooperNo ratings yet
- TFE 731 MaintenanceDocument34 pagesTFE 731 MaintenanceEgor85100% (2)
- Paxman SpecsDocument9 pagesPaxman Specsbastech100% (2)
- JT15D Ata 77Document8 pagesJT15D Ata 77Egor85100% (1)
- JT15D Series Head IndexDocument4 pagesJT15D Series Head IndexEgor85No ratings yet
- The Williams FJ44 Is A Family of SmallDocument44 pagesThe Williams FJ44 Is A Family of SmallXavier Diaz75% (4)
- TFE 731 Chap 76Document42 pagesTFE 731 Chap 76Egor85100% (4)
- Cessna Citation 500/501 Pilot's Technical Examination: CandidateDocument16 pagesCessna Citation 500/501 Pilot's Technical Examination: Candidatealvaro2005100% (1)
- 1002 R29Document13 pages1002 R29LUCASDOURADO18100% (1)
- Jt15d Ata 73 MaintDocument14 pagesJt15d Ata 73 MaintEgor85100% (1)
- TFE731-40 Turbofan Engine Publication Collection PDFDocument17 pagesTFE731-40 Turbofan Engine Publication Collection PDFYousefh Pineda100% (1)
- MM PT6T-3B 70-00Document32 pagesMM PT6T-3B 70-00Panca Xp100% (2)
- Slick Mag Overhaul ManualDocument64 pagesSlick Mag Overhaul Manualleather_nun100% (1)
- PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA PROPELLER GOVERNOR MANUALDocument12 pagesPRATT & WHITNEY CANADA PROPELLER GOVERNOR MANUALMichael Quintero100% (1)
- PW100 Conference Presentation Jakarta 2018Document115 pagesPW100 Conference Presentation Jakarta 2018Rehana Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- JT15DDocument3 pagesJT15DDamian Cuenca50% (2)
- Bendix Fuel Injection Training Manual 15-812 - BDocument25 pagesBendix Fuel Injection Training Manual 15-812 - Bkjdhiman100% (2)
- Organic Evolution (Evolutionary Biology) Revised Updated Ed by Veer Bala RastogiDocument1,212 pagesOrganic Evolution (Evolutionary Biology) Revised Updated Ed by Veer Bala RastogiTATHAGATA OJHA83% (6)
- TES Engine Datapack (April 10)Document49 pagesTES Engine Datapack (April 10)Ibraheem Sadiq100% (1)
- Engines-Tpe331 10Document2 pagesEngines-Tpe331 10Hasan Basri Azis75% (4)
- PW615F A PDFDocument7 pagesPW615F A PDFValBMSNo ratings yet
- Racial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesRacial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceYony Gutierrez100% (1)
- JT8 E Ngine, Part 2 Training PDFDocument100 pagesJT8 E Ngine, Part 2 Training PDFalfonsofelipesaravia100% (1)
- Q400 PropellerDocument10 pagesQ400 PropellerMoshiurRahman100% (1)
- BAe Jetstream Series 3100-3200Document14 pagesBAe Jetstream Series 3100-3200Mark100% (1)
- Asset Valuation: Debt Investments: Analysis and Valuation: 1 2 N M 1 2 N MDocument23 pagesAsset Valuation: Debt Investments: Analysis and Valuation: 1 2 N M 1 2 N MSirSmirkNo ratings yet
- PQ of Vial Washer Ensures Removal of ContaminantsDocument25 pagesPQ of Vial Washer Ensures Removal of ContaminantsJuan DanielNo ratings yet
- M250-B17 O+mmDocument14 pagesM250-B17 O+mmturboshaftNo ratings yet
- Turbine Engine Starting SystemDocument30 pagesTurbine Engine Starting SystemAishah HanisNo ratings yet
- Sil IndexDocument162 pagesSil IndexBenjamin Strickland100% (1)
- JT8D Fuel SystemDocument8 pagesJT8D Fuel SystemTrifi AJe JaenuriNo ratings yet
- ESD Handling GuideDocument7 pagesESD Handling GuideEgor85No ratings yet
- Fibre OpticsDocument23 pagesFibre OpticsEgor85100% (1)
- ElectronicDocument187 pagesElectronicEgor85No ratings yet
- Logic CircuitsDocument33 pagesLogic CircuitsEgor85No ratings yet
- Engineering: 1 Electronic DisplaysDocument33 pagesEngineering: 1 Electronic DisplaysEgor85No ratings yet
- ServomechanismsDocument25 pagesServomechanismsEgor85No ratings yet
- Data ConversionDocument13 pagesData ConversionEgor85No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic EnvironmentDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic EnvironmentEgor85No ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardsDocument5 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardsEgor85No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument23 pagesTransistorsEgor85100% (1)
- Data BusesDocument35 pagesData BusesEgor85No ratings yet
- Module 4 MasterDocument120 pagesModule 4 MasterEgor85No ratings yet
- DiodesDocument33 pagesDiodesEgor85No ratings yet
- Workbook - EEng (Part A)Document27 pagesWorkbook - EEng (Part A)Egor85No ratings yet
- Integrated CircuitsDocument29 pagesIntegrated CircuitsEgor85No ratings yet
- Bristol Physics NotesDocument66 pagesBristol Physics NotesEgor85No ratings yet
- Workbook - EEng (Part A) Answers EWB TasksDocument5 pagesWorkbook - EEng (Part A) Answers EWB TasksManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1versineNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Part A) MasterDocument133 pagesModule 3 (Part A) MasterEgor85No ratings yet
- Bristol Physics Notes OlderDocument66 pagesBristol Physics Notes OlderEgor85No ratings yet
- !1 Jet Engine Principles Definitions LawsDocument49 pages!1 Jet Engine Principles Definitions LawsEgor85No ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Charateristics of Model WingDocument4 pagesAerodynamic Charateristics of Model WingEgor85No ratings yet
- Mumbai Tourist Attractions.Document2 pagesMumbai Tourist Attractions.Guru SanNo ratings yet
- Nidhi Investment Consultant: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. AB Prafulbhai (Age 18)Document2 pagesNidhi Investment Consultant: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. AB Prafulbhai (Age 18)jdchandrapal4980No ratings yet
- Arts and Culture An Introduction To The Humanities Combined Volume 4th Edition Benton Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument22 pagesArts and Culture An Introduction To The Humanities Combined Volume 4th Edition Benton Test Bank Full Chapter PDFoutscoutumbellar.2e8na100% (15)
- 10 Compactness in Function Spaces: Ascoli-Arzel A TheoremDocument5 pages10 Compactness in Function Spaces: Ascoli-Arzel A TheoremronalduckNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Computer MCQ: 1. A. 2. A. 3. A. 4. A. 5. A. 6. ADocument17 pagesFundamental of Computer MCQ: 1. A. 2. A. 3. A. 4. A. 5. A. 6. AacercNo ratings yet
- UNIT- 5 IRSDocument78 pagesUNIT- 5 IRSganeshjaggineni1927No ratings yet
- CONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESDocument4 pagesCONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESSHIVAM BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Document9 pagesChapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Khaerul UmamNo ratings yet
- 2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolDocument50 pages2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolZtolenstarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemDocument14 pagesChapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemCharis AbadNo ratings yet
- NT140WHM N46Document34 pagesNT140WHM N46arif.fahmiNo ratings yet
- Viviana Rodriguez: Education The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP)Document1 pageViviana Rodriguez: Education The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP)api-340240168No ratings yet
- Nortek Quick Guide: - To Vectrino ProfilerDocument4 pagesNortek Quick Guide: - To Vectrino ProfilerAndresFelipePrietoAlarconNo ratings yet
- Doohap supplier and customer segmentationDocument2 pagesDoohap supplier and customer segmentationPriyah RathakrishnahNo ratings yet
- BS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsDocument26 pagesBS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsBorn ToSinNo ratings yet
- Remembering Manoj ShuklaDocument2 pagesRemembering Manoj ShuklamadhukarshuklaNo ratings yet
- Declarative and Procedural Knowledge (Lêda's Final Paper) 2010 01Document13 pagesDeclarative and Procedural Knowledge (Lêda's Final Paper) 2010 01Jair Luiz S. FilhoNo ratings yet
- Living in a digital age unit review and digital toolsDocument1 pageLiving in a digital age unit review and digital toolsLulaNo ratings yet
- Cross-Sectional Tomography: Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyDocument7 pagesCross-Sectional Tomography: Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyPhanQuangHuyNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter 1Document7 pagesResearch Chapter 1Aryando Mocali TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Mod. 34 Classic Compact T06Document4 pagesMod. 34 Classic Compact T06Jaime Li AliNo ratings yet
- Simple Present 60991Document17 pagesSimple Present 60991Ketua EE 2021 AndrianoNo ratings yet
- 1 FrameworkDocument26 pages1 FrameworkIrenataNo ratings yet
- LEONI Dacar® 110 enDocument1 pageLEONI Dacar® 110 engshock65No ratings yet
- Dinflo DFCSDocument2 pagesDinflo DFCSvictorharijantoNo ratings yet