Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Bronchitis? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Uploaded by
Melvin Lopez Silvestre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
215 views1 pagebronchitis
Original Title
What is Bronchitis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbronchitis
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
215 views1 pageWhat Is Bronchitis? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Uploaded by
Melvin Lopez Silvestrebronchitis
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
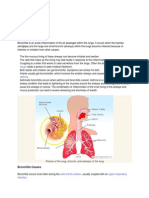
What Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, the airways that connect the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs.
People who are exposed to a lot of secondhand smoke People with weakened immune systems The elderly and infants Those who are exposed to irritants at work, such as chemical fumes from
ammonia, strong acids, chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide or bromine
What are the symptoms of bronchitis?
Signs and symptoms for both acute and chronic bronchitis include: Inflammation or swelling of the bronchi Coughing Production of clear, white, yellow, grey, or green mucus (sputum) Shortness of breath Wheezing Fatigue Fever and chills Chest pain or discomfort Blocked or runny nose
Mucolytics - these thin or loosen mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up sputum. Anti-inflammatory medicines and glucocorticoid steroids - these are for more persistent symptoms. Pulmonary rehabilitation program this includes work with a respiratory therapist to help breathing.
How can bronchitis be prevented?
Bronchitis is a somewhat preventable disease. Prevention methods include: Avoiding tobacco smoke and exposure to second hand smoke Quitting smoking Avoiding people who are sick with colds or the flu Getting a yearly flu vaccine Getting a pneumonia vaccine (especially for those over 60 years of age) Washing hands regularly Avoiding cold, damp locations or areas with a lot of air pollution Wearing a mask around people who are coughing and sneezing
Bronchitis can be acute or chronic
Acute bronchitis describes the inflammation of the bronchi usually caused by a viral infection, although bacteria and chemicals also may cause acute bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis for research purposes is defined as a daily cough with sputum production for at least three months, two years in a row. Chronic bronchitis is a diagnosis usually made based on clinical findings of a long term persistent cough usually associated with tobacco abuse
How to keep bronchitis symptoms under control and relieve symptoms?
Doctors may prescribe: Antibiotics - these are effective for bacterial infections, but not for viral infections. They may also prevent secondary infections. Cough medicine - one must be careful not to completely suppress the cough, for it is an important way to bring up mucus and remove irritants from the lungs. Bronchodilators - these open the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus.
Who gets bronchitis?
People at increased risk of getting bronchitis and increased risk of having more severe symptoms include: Smokers
You might also like
- The Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis GuideDocument5 pagesChronic Bronchitis GuideJemalyn M. Saludar100% (2)
- Bronchitis: Week 5 1Document5 pagesBronchitis: Week 5 1jessNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument19 pagesChronic BronchitisNurdina Afini100% (1)
- Bronchitis Vs BronchiolitisDocument52 pagesBronchitis Vs BronchiolitisUngku Hajar Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- COPD: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, & Pathophysiology: Wyatt E. Rousseau, MD May 11, 2006Document50 pagesCOPD: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, & Pathophysiology: Wyatt E. Rousseau, MD May 11, 2006Mahmmoud Fuqaha100% (1)
- Pediatric Bronchitis Case PresentationDocument28 pagesPediatric Bronchitis Case PresentationJoshua DulayNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument8 pagesPneumoniaNader Smadi100% (2)
- Management of Asthma ExacerbationDocument13 pagesManagement of Asthma ExacerbationAini Shofa HaniahNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Case Study in a ChildDocument43 pagesTyphoid Fever Case Study in a ChildJef Sembrano DiplomaNo ratings yet
- COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument30 pagesCOPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseAmila SirisingheNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines (Nursing) - Indwelling Urinary Catheter - Insertion and Ongoing CareDocument8 pagesClinical Guidelines (Nursing) - Indwelling Urinary Catheter - Insertion and Ongoing CareLeeNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Chronic Inflammatory Airway DiseaseDocument22 pagesAsthma: Chronic Inflammatory Airway DiseaseAnna EmNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem (Main)Document94 pagesViral Exanthem (Main)Starlet Rhonadez Bito-onon OrielNo ratings yet
- PTB Case StudyDocument6 pagesPTB Case StudyTrisha Carolina SottoNo ratings yet
- BRONCHOPNEUMONIA: AN OVERVIEWDocument18 pagesBRONCHOPNEUMONIA: AN OVERVIEWMANEESH MANINo ratings yet
- Women's Pneumonia ReportDocument9 pagesWomen's Pneumonia ReportNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- Bronchospasm PR 1Document41 pagesBronchospasm PR 1teklayNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument11 pagesPneumothoraxManoj RanadiveNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Document17 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Nikka Moreen DagdagNo ratings yet
- BronchiolitisDocument45 pagesBronchiolitisYuusuf MubarikNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesAcute Bronchitis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfCynthia ChezanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy AdministrationDocument15 pagesOxygen Therapy AdministrationMike Faustino Solangon100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology PneumoniaMajkel Benche CustodioNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Evidence and Management of AsthmaDocument19 pagesA Clinical Evidence and Management of Asthmaraajverma1000mNo ratings yet
- Lung Abscess Bronchoectasis PleurisynDocument19 pagesLung Abscess Bronchoectasis Pleurisynmarco luenaNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis PathoDocument3 pagesAcute Bronchitis Pathobanyenye25No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis (40Document5 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis (40George Mikhail Labuguen100% (1)
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument38 pagesRespiratory AssessmentNisha MwlzNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument11 pagesChronic BronchitisNazurah AzmiraNo ratings yet
- Health Info Health Info Medicines Advanced Search Register Login Top of Form User NameDocument24 pagesHealth Info Health Info Medicines Advanced Search Register Login Top of Form User NameAnusha PradhanNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Laryngitis TB 70 TahunDocument21 pagesCase Presentation Laryngitis TB 70 TahunMegan Shanzu100% (1)
- Case Study Asthma Group 2Document17 pagesCase Study Asthma Group 2Kennedy PelicoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study on a Patient with EmphysemaDocument19 pagesA Case Study on a Patient with EmphysemaMajkel Benche CustodioNo ratings yet
- Central Venous PressureDocument10 pagesCentral Venous PressureAngelo ArquizaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument71 pagesPneumoniafrancis00090100% (1)
- Oxygen Therapy: by DR Finny Theo, MBBS, (DNB)Document59 pagesOxygen Therapy: by DR Finny Theo, MBBS, (DNB)The Telugu DoctorNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemAlloiBialbaNo ratings yet
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease)Document12 pagesThromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease)Sheila AzelyaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing: OxygenationDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Nursing: OxygenationFEVIE ANNE BANATAONo ratings yet
- 1.acute PharyngitisDocument88 pages1.acute PharyngitisIhsan Hanif0% (1)
- Tetanus: HistoryDocument15 pagesTetanus: HistorydanielleNo ratings yet
- Seminar Asthma PDFDocument39 pagesSeminar Asthma PDFAriff Mahdzub0% (1)
- Pneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument28 pagesPneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology Division COPD GuideDocument59 pagesPulmonology Division COPD GuideKarenmedicalNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument59 pagesDiabetesshiv gautamNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument23 pagesBroncho Pneumoniaanon-84769398% (43)
- Asthma (Reactive Airway Disease)Document33 pagesAsthma (Reactive Airway Disease)anwar jabariNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument10 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndromealina abu rumiNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument73 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsankitaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DisordersDocument9 pagesRespiratory System Disordersasop06No ratings yet
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cavite State University: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCavite State University: I. ObjectivesChamy CruzNo ratings yet
- Types of InhalersDocument23 pagesTypes of Inhalersshamie1110No ratings yet
- PTBDocument71 pagesPTBAnonymous 9fLDcZrNo ratings yet
- Key Facts About Chronic BronchitisDocument3 pagesKey Facts About Chronic BronchitiskvishwanathNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- BronchitisDocument9 pagesBronchitisMS AntikaNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH Mom OliveDocument9 pagesMAKALAH Mom Olivemaragantigaming04officialNo ratings yet
- 11 Core CompetenciesDocument10 pages11 Core CompetenciesMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MicroscopeDocument1 pageChemistry MicroscopeMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thyroid Gland For You and For Me!Document2 pagesAnatomy of The Thyroid Gland For You and For Me!Melvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- What Is Bronchitis? Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageWhat Is Bronchitis? Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Injury Skin Trauma Contusion Pathology DermisDocument2 pagesInjury Skin Trauma Contusion Pathology DermisMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument2 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Patellar Fracture 1Document2 pagesPatellar Fracture 1Melvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- PotassiumDocument2 pagesPotassiumMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Pq-Unocal Csms '03Document15 pagesPq-Unocal Csms '03Ismail Hamzah Azmatkhan Al-husainiNo ratings yet
- Non-Steroid Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergy DrugsDocument217 pagesNon-Steroid Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergy DrugsAstri DesmayantiNo ratings yet
- Girl, Interrupted Film Analysis Diana Fox Molloy CollegeDocument5 pagesGirl, Interrupted Film Analysis Diana Fox Molloy CollegeDiana Fox100% (1)
- Mole Airlines, Emp. Form. ExcerciseDocument2 pagesMole Airlines, Emp. Form. ExcerciseKamariah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Douglas Crucey, A043 446 797 (BIA June 12, 2017)Document20 pagesDouglas Crucey, A043 446 797 (BIA June 12, 2017)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCNo ratings yet
- USMLE High YieldDocument8 pagesUSMLE High YieldNajia ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapists in Private Practice During PandemicsDocument15 pagesPsychotherapists in Private Practice During PandemicsAnup AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities in Preventive and Social MedicineDocument3 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Preventive and Social MedicineIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- AMEE 2023 Final Programme OverviewDocument2 pagesAMEE 2023 Final Programme OverviewMohamed IshagNo ratings yet
- Aiapget 2020 QPDocument29 pagesAiapget 2020 QPGanesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Alvarez 2015Document18 pagesAlvarez 2015Clara RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Changes in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidDocument3 pagesChanges in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidHanh HoangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Health LectureDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Health LectureJudy OuNo ratings yet
- Buku Koding 1Document74 pagesBuku Koding 1indra_igrNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological Water Analysis of Hostel's WaterDocument12 pagesBacteriological Water Analysis of Hostel's Waterapi-3705267No ratings yet
- Verification of Conformity Safety Consideration For Radio Equipment DirectiveDocument1 pageVerification of Conformity Safety Consideration For Radio Equipment DirectiveThắng CòiNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PhobiaDocument2 pagesIntroduction of PhobiawoodenskyNo ratings yet
- D A Up To 2 YearDocument7 pagesD A Up To 2 YearNischitha G CNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies of Athletes for Competitive AnxietyDocument13 pagesCoping Strategies of Athletes for Competitive AnxietyHONEY JEAN ESPENORIONo ratings yet
- Ar-Afff 3 MSDS LCFDocument5 pagesAr-Afff 3 MSDS LCFMark YeNo ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFBuloy ReggieNo ratings yet
- SWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanDocument1 pageSWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanHassan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- OD-PRO-HSE-032 Safety To Work at Height - Rev.01Document31 pagesOD-PRO-HSE-032 Safety To Work at Height - Rev.01aymenmoataz100% (1)
- Understanding The Self Module 4Document13 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 4Jovet QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument41 pagesWater QualityPaschal MazikuNo ratings yet
- All India Aakash Test Series (AIATS) 12th Class Test Schedule for NEET/AIIMS 2019Document2 pagesAll India Aakash Test Series (AIATS) 12th Class Test Schedule for NEET/AIIMS 2019Chirasree Laha100% (1)
- 16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsDocument3 pages16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsSyed Murtuza BakshiNo ratings yet
- The ABO Blood Groups: Phenotypes GenotypesDocument2 pagesThe ABO Blood Groups: Phenotypes GenotypesSheila Mae CabahugNo ratings yet
- MedEx FAQDocument2 pagesMedEx FAQJee CHIUN CHENNo ratings yet