Professional Documents
Culture Documents
USB Pinout and Connections at Pinouts
Uploaded by
Bilal TayyabOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
USB Pinout and Connections at Pinouts
Uploaded by
Bilal TayyabCopyright:
Available Formats
3/30/13
USB pinout and connections @ pinouts.ru
USB pinout
Bookmark / Discuss / Edit this page or submit new.
computer bus specification
USB (Universal Serial Bus) designed to connect peripherals such as mice, keyboards, scanners, digital cameras, printers, hard disks, and networking components to PC. It has become the standard connection method for scanners, digital cameras and for some printers. Complete pinout.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a specification to establish communication between
4 pin USB A or USB B plug connector at the peripherals
71
devices and a host controller (usually personal computers). An USB system consists of a host controller and multiple devices connected using special hub devices. Hubs may be cascaded, up to 5 levels. USB can connect computer peripherals such as mice, keyboards, digital cameras, PDA, mobile phones, printers, personal media players, flash drives, GPS, Network Adapters, and external hard drives. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB interface aimed to remove the need for adding expansion cards into the computer's PCI or PCI-Express bus, and improve plug-and-play capabilities by allowing devices to be hot swapped or added to the system without rebooting the computer.
4 pin USB A / USB B / mini-USB jack connector at the controller
See also:
Mini-USB connector of cell phones pinout Micro-USB connector pinout Apple iPhone (1G, 3G, 3GS, 4, 4S) Dock cable connector pinout Micro-USB connector pinout Nokia Micro USB connector and cable pinout Micro-USB mobile phone/smartphone cable connector pinout Mini-USB charging cable pinout HTC ExtUSB charger pinout
Mezza-pede SMT Connector
www.advanced. 1.0mm pitch hi-rel cable-to-board or surface mount board stacking.
The USB Pinout:
Pin 1 2 3 4 Name VCC DD+ GND Cable color Red White Green Black Description +5 VDC Data Data + Ground
Pin x of mini-USB connector may be not connected, connected to GND or used as attachment identification at some portable devices. This pin is numbered x here due to historical reasons.
USB connectors
There are several types of USB connectors. The original USB specification detailed Standard-A and Standard-B plugs and receptacles. Nowdays there are 7 USB connectors known: Standard-A, Standard-B, Mini-A, Mini-B (shown on left), Micro-A, Micro-AB, Micro-B.
USB pinout signals
USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires: two for power (+5v & GND) and two for differential data signals (labelled as D+ and D- in pinout). NRZI (Non Return to Zero Invert) encoding scheme used to send data with a sync field to synchronise the host and receiver clocks. In USB data cable Data+ and Data- signals are transmitted on a twisted pair. No termination needed. Half-duplex differential signaling helps to combat the effects of electromagnetic noise on longer lines. Contrary to popular belief, D+ and D- operate together; they are not separate simplex connections. USB 2.0 provides for a maximum cable length of 5 meters for devices running at Hi Speed.
USB transfer modes
Univeral serial bus supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer modes.
USB interfaces: USB 1.0, USB 2.0, USB 3.0.
There are three USB versions known nowdays:
USB 1.0
released in 1996. Specifies data rates of 1.5 Mbit/s (Low-Bandwidth, is mostly used for Human Input Devices (HID) such as keyboards, mouses, joysticks and often the buttons on higher speed devices such as printers or scanners) and 12 Mbit/s (Full-Bandwidth). nowadays is still used used by some devices that don't need faster data transfer rates.
USB 2.0
released in 2000 in addition to USB 1.0 adds signaling rate of 480 Mbit/s (Hi-Speed) compatible with USB 1.0, but some hardware designed for USB 2.0 may not work with
pinouts.ru/Slots/USB_pinout.shtml
1/3
3/30/13
USB pinout and connections @ pinouts.ru
USB 1.0 host controllers.
USB 3.0
released in 2008 added transmission rates up to 5 Gbit/s (SuperSpeed)
USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 shares same pinout, USB 3.0 pinout features new connectors. A USB device must indicate its speed by pulling either the D+ or D- line high to 3.3 volts. These pull up resistors at the device end will also be used by the host or hub to detect the presence of a device connected to its port. Without a pull up resistor, USB assumes there is nothing connected to the bus. In order to help user to identify maximum speed of device, a USB device often specifies its speed on its cover with one of the USB special marketing logos. When the new device first plugs in, the host enumerates it and loads the device driver necessary to run it. The loading of the appropriate driver is done using a PID/VID (Product ID/Vendor ID) combination supplied by attached hardware. The USB host controllers has their own specifications: UHCI (Universal Host Controller Interface), OHCI (Open Host Controller Interface) with USB 1.1, EHCI (Enhanced Host Controller Interface) is used with USB 2.0.
USB powered devices
The USB connector provides a single 5 volt wire from which connected USB devices may power themselves. A given segment of the bus is specified to deliver up to 500 mA. This is often enough to power several devices, although this budget must be shared among all devices downstream of an unpowered hub. A bus-powered device may use as much of that power as allowed by the port it is plugged into. Bus-powered hubs can continue to distribute the bus provided power to connected devices but the USB specification only allows for a single level of bus-powered devices from a bus-powered hub. This disallows connection of a bus-powered hub to another bus-powered hub. Many hubs include external power supplies which will power devices connected through them without taking power from the bus. Devices that need more than 500 mA or higher than 5 volts must provide their own power. When USB devices (including hubs) are first connected they are interrogated by the host controller, which enquires of each their maximum power requirements. However, seems that any load connected to USB port may be treated by operating system as device. The host operating system typically keeps track of the power requirements of the USB network and may warn the computer's operator when a given segment requires more power than is available and may shut down devices in order to keep power consumption within the available resource.
USB power usage:
Bus-powered hubs: Draw Max 100 mA at power up and 500 mA normally. Self-powered hubs: Draw Max 100 mA, must supply 500 mA to each port. Low power, bus-powered functions: Draw Max 100 mA. High power, bus-powered functions: Self-powered hubs: Draw Max 100 mA, must supply
500 mA to each port.
Self-powered functions: Draw Max 100 mA. Suspended device: Max 0.5 mA Dedicated charger mode:
A simple USB charger should short the 2 data lines together. The device will then not attempt to transmit or receive data, but can draw up to 1.8A, if the supply can provide it.
USB voltage:
Supplied voltage by a host or a powered hub ports is between 4.75 V and 5.25 V. Maximum voltage drop for bus-powered hubs is 0.35 V from its host or hub to the hubs output port. All hubs and functions must be able to send configuration data at 4.4 V, but only low-power functions need to be working at this voltage. Normal operational voltage for functions is minimum 4.75 V.
USB cable shielding:
Shield should only be connected to Ground at the host. No device should connect Shield to Ground.
USB cable wires:
Shielded:
Data: 28 AWG twisted
pinouts.ru/Slots/USB_pinout.shtml
2/3
3/30/13
USB pinout and connections @ pinouts.ru
Power: 28 AWG - 20 AWG non-twisted
Non-shielded:
Data: 28 AWG non-twisted Power: 28 AWG - 20 AWG non-twisted
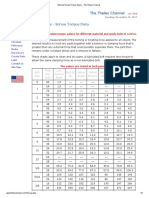
Power Gauge 28 26 24 22 20 Max length 0.81 m 1.31 m 2.08 m 3.33 m 5.00 m
Ads by Google
USB Device
Is this document
USB Network
correct or incorrect?.
USB 2.0 Drivers
USB Serial
There are 134 reports in our database: 118 positive and 10 negative.
Pinouts.ru > Buses and slots connectors > Pinout of USB and layout of 4 pin USB A or USB B plug connector and 4 pin USB A / USB B / mini-USB jack connector Source(s) of this and additional information: USB Implementers Forum USB Specification v1.0 at USB Implementers Forum, wikipedia.org, "USB in a Nutshell", http://www.usb.org/developers/devclass_docs/batt_charging_1_1.zip Last updated 2012-12-18 21:53:39. This page contain parts under Copyright 2000-2012 by pinouts.ru team. No portion of this webpage may be reproduced in any form without providing visible HTML link to Pinouts.ru . Webmaster permission required in any other cases. Efforts have been made to ensure this page is correct, but it is the responsibility of the user to verify the data is correct for their application.
pinouts.ru/Slots/USB_pinout.shtml
3/3
You might also like
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101From EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101No ratings yet
- USB Protocol BasicsDocument34 pagesUSB Protocol BasicsAmitav Shaw100% (2)
- Notes On Sprockets and ChainsDocument6 pagesNotes On Sprockets and ChainsBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Notes On Sprockets and ChainsDocument6 pagesNotes On Sprockets and ChainsBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- USB Tutorial Part 1Document25 pagesUSB Tutorial Part 1EmbeddedCraft100% (2)
- Area, Perimeter & VolumeDocument27 pagesArea, Perimeter & VolumeBilal Tayyab100% (2)
- Area, Perimeter & VolumeDocument27 pagesArea, Perimeter & VolumeBilal Tayyab100% (2)
- UsbDocument34 pagesUsbSantosh Sandy100% (1)
- USB Made Simple - Part 1 PDFDocument5 pagesUSB Made Simple - Part 1 PDFyeniuye100% (1)
- Usb 3.0Document27 pagesUsb 3.0Umar Rahamatullah Shareef100% (1)
- USB GuideDocument38 pagesUSB GuideRamesh Ramasamy100% (1)
- Piping HandbookDocument17 pagesPiping HandbookBilal Tayyab100% (1)
- Usb Pin AssignmentsDocument4 pagesUsb Pin AssignmentsewakxmhrNo ratings yet
- Advanced PIC18 Projects-USB Bus ProjectsDocument66 pagesAdvanced PIC18 Projects-USB Bus ProjectsManu ManuNo ratings yet
- How USB WorksDocument7 pagesHow USB Works123.shalini100% (1)
- USB Background - TOTALPHASEDocument21 pagesUSB Background - TOTALPHASETechnical NoviceNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)Document15 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (USB)rajkumar_jain4855100% (2)
- USB Pinout and WiringDocument4 pagesUSB Pinout and WiringnelsonhooverNo ratings yet
- PortsDocument8 pagesPortsFredrick MugoNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 USB - SCI - PCI BusDocument4 pagesUnit-4 USB - SCI - PCI BusOm DevNo ratings yet
- USB Overview: This Course Serves As An Introduction To USBDocument68 pagesUSB Overview: This Course Serves As An Introduction To USBDien Nguyen100% (1)
- Universal Serial Bus (Usb)Document18 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (Usb)saranaccel1No ratings yet
- Beagle AnalyzerDocument205 pagesBeagle AnalyzerbelzurkurNo ratings yet
- How USB Ports WorkDocument5 pagesHow USB Ports WorkAchilles Aldave100% (1)
- Wireless Usb Full Seminar Report Way2project - inDocument22 pagesWireless Usb Full Seminar Report Way2project - inmanthapan0% (1)
- Usb History ResumDocument7 pagesUsb History ResumjordanvicenteNo ratings yet
- "Universal Serial BUS (USB) ": Presentation OnDocument17 pages"Universal Serial BUS (USB) ": Presentation OnSai LohithNo ratings yet
- CPH Microproject CompleteDocument20 pagesCPH Microproject CompleteVaibhav JadhavNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) Is A Serial Bus Standard To ConnectDocument22 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (USB) Is A Serial Bus Standard To ConnectMahesh Supekar100% (1)
- Universal Serial Bus: 4.1. Overview of USBDocument28 pagesUniversal Serial Bus: 4.1. Overview of USBSaddamNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial Bus (US B) : EE 446 Embedded ArchitectureDocument34 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (US B) : EE 446 Embedded ArchitectureRonabolNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems I/O: Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1Document10 pagesEmbedded Systems I/O: Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1ahamed100% (2)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) : A Seminar Report OnDocument22 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (USB) : A Seminar Report OnAbdulkhadar KitturNo ratings yet
- Compdsp Burk USB FundamentalsDocument81 pagesCompdsp Burk USB FundamentalsDamian Primo100% (2)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) Is A SpecificationDocument4 pagesUniversal Serial Bus (USB) Is A Specificationmirajshah05No ratings yet
- Usb Seminar ReportDocument33 pagesUsb Seminar ReportTuhina Nath100% (1)
- Super Fast Usb 3.0 What Is USB Stands For?Document4 pagesSuper Fast Usb 3.0 What Is USB Stands For?Sumit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial BusDocument11 pagesUniversal Serial BusDileepmk10No ratings yet
- BookDocument29 pagesBookAnonymous yy8In96j0rNo ratings yet
- Es Notes Unit 3Document7 pagesEs Notes Unit 3Sai ReddyNo ratings yet
- Usb 3.0Document36 pagesUsb 3.0ravindra022100% (1)
- Introduction To Superspeed Usb 3.0 Protocol: Ankur Tomar & Edmund Lim - Global Technology CentreDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Superspeed Usb 3.0 Protocol: Ankur Tomar & Edmund Lim - Global Technology Centrejit20088791100% (1)
- Documentation of USB 3.0Document26 pagesDocumentation of USB 3.0srinidhi2allNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial BusDocument12 pagesUniversal Serial BusQazi DaudNo ratings yet
- SNGCE, Kolenchery Dept. of CSEDocument19 pagesSNGCE, Kolenchery Dept. of CSERajeev SndhrNo ratings yet
- History: Compaq DEC IBM Intel Microsoft NEC NortelDocument24 pagesHistory: Compaq DEC IBM Intel Microsoft NEC NortelRajesh MandalNo ratings yet
- USB in A NutshellDocument40 pagesUSB in A Nutshellpraveen_vendraNo ratings yet
- How USB Ports WorkDocument7 pagesHow USB Ports Workima87_daisy100% (1)
- USB - Universal Serial Bus SandeepDocument10 pagesUSB - Universal Serial Bus Sandeepakashsrivastava4530No ratings yet
- Common USB Development Mistakes - Farnell UkDocument7 pagesCommon USB Development Mistakes - Farnell Uklxz5101No ratings yet
- Project Report 2Document62 pagesProject Report 2Alex VPNo ratings yet
- About Usb InterfaceDocument6 pagesAbout Usb InterfaceSantosh Kumar100% (1)
- Usb-3 0Document31 pagesUsb-3 0dhavalbe1272100% (1)
- User Guide: Desktop USB 2.0 7-Port Hub With Audio Pass-ThroughDocument16 pagesUser Guide: Desktop USB 2.0 7-Port Hub With Audio Pass-ThroughTyas Te PyNo ratings yet
- USB in A NutShellDocument35 pagesUSB in A NutShellSandro Jairzinho Carrascal Ayora100% (1)
- Usbserial Adapter: Item Min Typical Max Unit Operating Voltage Work CurrentDocument3 pagesUsbserial Adapter: Item Min Typical Max Unit Operating Voltage Work CurrentMark F. ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Usb Data Interface KNX RMDDocument4 pagesUsb Data Interface KNX RMDmoannaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Rahul Yadav 07EI 438 4/7/2011 4/7/2011Document18 pagesSubmitted By: Rahul Yadav 07EI 438 4/7/2011 4/7/2011Praveen RatheeNo ratings yet
- USB in A NutShellDocument33 pagesUSB in A NutShellNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- USB-Basics 4518wpDocument3 pagesUSB-Basics 4518wpkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit-3Document11 pagesCoa Unit-3singhshiva8082No ratings yet
- USB To RS-232 Converter - User's ManualDocument7 pagesUSB To RS-232 Converter - User's ManualJuan José NihilNo ratings yet
- Stm32 & Usb: Roman LudinDocument33 pagesStm32 & Usb: Roman LudinAnonymous 1OlQQ3cW100% (1)
- Torrent SeedDocument1 pageTorrent SeedJitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Categories of ShareholdersDocument1 pageCategories of ShareholdersBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Asian Mall ListDocument2 pagesAsian Mall ListBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle WorksheetDocument4 pagesMotorcycle WorksheetBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Torrent SeedDocument1 pageTorrent SeedJitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Canon Eos Rebel T7i Ef S 18 55mm Is STM Specifications ChartDocument11 pagesCanon Eos Rebel T7i Ef S 18 55mm Is STM Specifications ChartBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- H5 - Engineerign Management NotesDocument12 pagesH5 - Engineerign Management NotesBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Nomination Form For Basic It Training CourseDocument1 pageNomination Form For Basic It Training CourseBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Categories of ShareholdersDocument1 pageCategories of ShareholdersBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- H6 - Engineering Measurement System NotesDocument24 pagesH6 - Engineering Measurement System NotesBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- P6 - Autometic Controll System NotesDocument36 pagesP6 - Autometic Controll System NotesBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Canon Eos Rebel T7i Ef S 18 55mm Is STM Specifications ChartDocument11 pagesCanon Eos Rebel T7i Ef S 18 55mm Is STM Specifications ChartBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- P6 - Manufacturing Technology NotesDocument14 pagesP6 - Manufacturing Technology NotesBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Helicoil Plus en 0100Document56 pagesHelicoil Plus en 0100Ahmet MetinNo ratings yet
- Problem 21Document1 pageProblem 21Bilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Problem 21Document1 pageProblem 21Bilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Zubair Ahmed CVDocument2 pagesZubair Ahmed CVBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Bolt and Screw Torque SpecsDocument3 pagesBolt and Screw Torque SpecsBilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- PROPERTY TABLES ThermalFluidsEngineeringDocument231 pagesPROPERTY TABLES ThermalFluidsEngineeringAgus SetiyonoNo ratings yet
- E3 10 03 02Document9 pagesE3 10 03 02rikumohanNo ratings yet
- Spur Gear Calculations and FormulasDocument2 pagesSpur Gear Calculations and FormulasBilal Tayyab100% (2)
- Ansys Assignment No. 1Document5 pagesAnsys Assignment No. 1Bilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Private Vihicles POF EtagDocument2 pagesPrivate Vihicles POF EtagBilal Tayyab100% (2)
- Presentation 2Document29 pagesPresentation 2Bilal TayyabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document129 pagesChapter 10Bilal TayyabNo ratings yet