Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distance Versus Directed Distance and Displacement
Uploaded by
Shameem XsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Distance Versus Directed Distance and Displacement
Uploaded by
Shameem XsCopyright:
Available Formats
Distance versus directed distance and displacement[edit
source | editbeta]
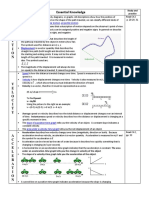
Distance along a path compared with displacement
Distance cannot be negative and distance travelled never decreases. Distance is a scalarquantity or a magnitude, whereas displacement is a vector quantity with both magnitude anddirection. The distance covered by a vehicle (for example as recorded by an odometer), person, animal, or object along a curved path from a point A to a point B should be distinguished from the straight line distance from A to B. For example whatever the distance covered during a round trip from A to B and back to A, the displacement is zero as start and end points coincide. In general the straight line distance does not equal distance travelled, except for journeys in a straight line.
Directed distance[edit
source | editbeta]
Directed distances are distances with a direction or sense. They can be determined along straight lines and along curved lines. A directed distance along a straight line from A to B is a vector joining any two points in a n-dimensional Euclidean vector space. A directed distance along a curved line is not a vector and is represented by a segment of that curved line defined by endpoints A and B, with some specific information indicating the sense (or direction) of an ideal or real motion from one endpoint of the segment to the other (see figure). For instance, just labelling the two endpoints as A and B can indicate the sense, if the ordered sequence (A, B) is assumed, which implies that A is the starting point. A displacement (see above) is a special kind of directed distance defined in mechanics. A directed distance is called displacement when it is the distance along a straight line (minimum distance) from A and B, and when A and B are positions occupied by the same particle at two different instants of time. This implies motion of the particle. displace is a vector quantity. Another kind of directed distance is that between two different particles or point masses at a given time. For instance, the distance from the center of gravity of the Earth A and the center of gravity of the Moon B (which does not strictly imply motion from A to B).Shortest path length may be equal to displacement or may not be equal to.Distance from starting point is always equal to magnitude of displacement. For same particle distance travelled is always greater than or equal to magnitude of displacement. Shortest path length is not necessary always displacement. Displacement may increase or decrease but distance travelled never decreases.
You might also like
- Vector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsFrom EverandVector and Tensor Analysis with ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Chapter 2 - Lecture Notes - MotionDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Lecture Notes - MotionLara LañohanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Pos Vel AccDocument1 pageUnit 2 - Pos Vel Accapi-323795755No ratings yet
- Lec 1 ADocument18 pagesLec 1 ASaad AhmadNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument60 pagesPhysicsNodiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer FinalDocument28 pagesPhysics Reviewer FinalTERESA MATEONo ratings yet
- Kinematics IN One DirectionDocument12 pagesKinematics IN One DirectionEdgar UbaldeNo ratings yet
- 01 - Kinematics of A Particle 1Document26 pages01 - Kinematics of A Particle 1MPRajNo ratings yet
- KinamaticsDocument10 pagesKinamaticsChathur ChandrasooryaNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 3 Review SheetDocument4 pagesScience Quarter 3 Review SheetEljohn MarquezNo ratings yet
- Motion NotesDocument5 pagesMotion NotesmallikaNo ratings yet
- G 9 PhyDocument3 pagesG 9 PhyAhmed Mohammed KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument15 pagesForces and Motionankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Understanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity TimeDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity Timeimran siddiquiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSexyDocument5 pagesPHYSICSexyjeloelydacumosNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line CH3Document49 pagesMotion in A Straight Line CH3Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Motion in PlaneDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Motion in Planearyanbajaj35No ratings yet
- Kinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothyDocument16 pagesKinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothytonyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics Lecture 3Document30 pagesEngineering Dynamics Lecture 3Anokha LadlaNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsSonia OmapersaudNo ratings yet
- Physics 1e Module 2Document14 pagesPhysics 1e Module 2Rian John PedrosaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsE.LOKESH NAIKNo ratings yet
- VelocityDocument5 pagesVelocityRajesh TipnisNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-20 at 11.11.15Document17 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-20 at 11.11.158wgt27gxkgNo ratings yet
- Dynamic LecturesDocument29 pagesDynamic Lectureseid ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument6 pagesKinematics in One DimensionSalahAL-HakimiNo ratings yet
- Class IX Physics NotesDocument163 pagesClass IX Physics Notesmuthu samyNo ratings yet
- Class - 9 Concise Physics Solutions Chapter-Exercise 2 A: Motion in One DimensionDocument7 pagesClass - 9 Concise Physics Solutions Chapter-Exercise 2 A: Motion in One DimensionNobodyNo ratings yet
- Motion and Its Description: Motion. in These Examples, Motion Is Easily Visible To Us. But in Some Cases, Motion Is NotDocument18 pagesMotion and Its Description: Motion. in These Examples, Motion Is Easily Visible To Us. But in Some Cases, Motion Is NotrashidNo ratings yet
- Maimoona: SUBMITTED BY: Adroiterz Hafsa Iqbal 136 Anam Maqsood 134 Aisha Fareed 135Document27 pagesMaimoona: SUBMITTED BY: Adroiterz Hafsa Iqbal 136 Anam Maqsood 134 Aisha Fareed 135Hafsa IqbalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument16 pagesKinematics in One DimensionApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Kelas XIDocument5 pagesKelas XIChristina Natalia PuspitaNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument21 pagesMotionAshutoshBaruaNo ratings yet
- Physics Motion in Straight LineDocument45 pagesPhysics Motion in Straight LineNeeraj MisraNo ratings yet
- Samplenote Motion in One Dimension 1443779794 560e54d200387 161252Document29 pagesSamplenote Motion in One Dimension 1443779794 560e54d200387 161252shivamNo ratings yet
- 2 Motion in 2&3 DimensionsDocument26 pages2 Motion in 2&3 Dimensionsumer iqbalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Curvilinear MotionDocument43 pagesDynamics - Curvilinear Motionawethaf9876No ratings yet
- MotionDocument37 pagesMotionSAMRAT CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Sl. No. Differentiating Property Distance DisplacementDocument8 pagesSl. No. Differentiating Property Distance DisplacementmandarNo ratings yet
- With The Accelerated Motion of A Body. The Subject Dynamics Will Be Presented Into Two PartsDocument7 pagesWith The Accelerated Motion of A Body. The Subject Dynamics Will Be Presented Into Two PartsJayvee ColiaoNo ratings yet
- What Is Motion?Document11 pagesWhat Is Motion?Prisha SinglaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Displacement and Velocity: DynamicsDocument5 pagesKinematics: Displacement and Velocity: DynamicsDoctora NourhanNo ratings yet
- 2020 06 18 IX Physics 0Document18 pages2020 06 18 IX Physics 0ahanafdoNo ratings yet
- HL Study Guide 2Document17 pagesHL Study Guide 2api-323795755No ratings yet
- 02 Robotics PDFDocument29 pages02 Robotics PDFKumaresan.s Kumaresan.sNo ratings yet
- Acceleration: Acceleration, in Physics, Is The Rate ofDocument31 pagesAcceleration: Acceleration, in Physics, Is The Rate ofstallone21No ratings yet
- Physics PrelimDocument5 pagesPhysics PrelimShaheen LontocNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementDocument7 pagesKinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementTorettoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesDocument24 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesBriti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Answers 1dkinematics PacketDocument28 pagesAnswers 1dkinematics PacketAbdalla MhrzNo ratings yet
- Ipc Describing Motion Verbally With Distance and Displacement Study NotesDocument20 pagesIpc Describing Motion Verbally With Distance and Displacement Study NotesGrantNo ratings yet
- 10+1 Physics Book-2 (Motion in A Straight Line) 2021Document101 pages10+1 Physics Book-2 (Motion in A Straight Line) 2021Kalin BhayiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Kinematics PDFDocument19 pagesUNIT 3 Kinematics PDFparveezNo ratings yet
- Motion: Introduction of Motion MotionDocument19 pagesMotion: Introduction of Motion MotionSampat AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Vector AdditionDocument5 pagesVectors and Vector AdditionJamesdomingoNo ratings yet
- SIM!!!Document15 pagesSIM!!!Clarence Sanchez AntoninoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics (Theory) FinalDocument35 pagesKinematics (Theory) FinalAbhishekha Chandra DubeyNo ratings yet
- Open Source FrameworksDocument1 pageOpen Source FrameworksShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Example For Agglomerative ClusteringDocument2 pagesExample For Agglomerative ClusteringShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Cluster DissimilarityDocument1 pageCluster DissimilarityShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Linkage CriteriaDocument1 pageLinkage CriteriaShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Edit Source Edit: Standalone ImplementationsDocument1 pageEdit Source Edit: Standalone ImplementationsShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Edit Source Edit: Goodness-Of-FitDocument1 pageEdit Source Edit: Goodness-Of-FitShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Cluster Analysis HierarchyDocument1 pageData Mining Cluster Analysis HierarchyShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Edit Source Edit: Energy StatisticsDocument1 pageEdit Source Edit: Energy StatisticsShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Distances Between Sets and Between A Point and A SetDocument1 pageDistances Between Sets and Between A Point and A SetShameem XsNo ratings yet
- General Case - DistanceDocument1 pageGeneral Case - DistanceShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Generalization To Metric SpacesDocument1 pageGeneralization To Metric SpacesShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Statistical Distance Probability Distributions Cumulative Distribution FunctionsDocument1 pageStatistical Distance Probability Distributions Cumulative Distribution FunctionsShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Generalization To Higher-Dimensional Objects: ManifoldsDocument1 pageGeneralization To Higher-Dimensional Objects: ManifoldsShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Algebraic DistanceDocument1 pageAlgebraic DistanceShameem XsNo ratings yet
- In Popular Culture: The Many Loves of Dobie GillisDocument1 pageIn Popular Culture: The Many Loves of Dobie GillisShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Variational Formulation of DistanceDocument1 pageVariational Formulation of DistanceShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Distance in Euclidean SpaceDocument1 pageDistance in Euclidean SpaceShameem XsNo ratings yet
- DistanceDocument1 pageDistanceShameem XsNo ratings yet
- Automap 3 User GuideDocument23 pagesAutomap 3 User GuidemammmaxNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Latin Interpersonal Attraction Proximity Similarity Like-Attracts-Like Jeremy Bentham Utilitarian Pleasure Felicific CalculusDocument1 pageSocial Psychology Latin Interpersonal Attraction Proximity Similarity Like-Attracts-Like Jeremy Bentham Utilitarian Pleasure Felicific CalculusShameem XsNo ratings yet
- The Propinquity EffectDocument1 pageThe Propinquity EffectShameem XsNo ratings yet
- BERNAYS ManipulatingPublicOpinionDocument15 pagesBERNAYS ManipulatingPublicOpinionClaireFitzpatrickNo ratings yet
- 4K410 - Exercises 2014-2015Document17 pages4K410 - Exercises 2014-2015Abhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nebular Theory WsDocument5 pagesNebular Theory WsSheila MaliitNo ratings yet
- Brain Teasers - Consig ContiDocument5 pagesBrain Teasers - Consig ContiAakanksha MishraNo ratings yet
- MSE 2103 - Lec 02Document9 pagesMSE 2103 - Lec 02swagy tanjimNo ratings yet
- Scanner Cobra en 201507Document2 pagesScanner Cobra en 201507Shahbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Hoyle J W.Bulbous Bow Design M.1986.TRANS PDFDocument26 pagesHoyle J W.Bulbous Bow Design M.1986.TRANS PDFThanos Niotis100% (1)
- CHP 27 Gassian Laser Beam PDFDocument25 pagesCHP 27 Gassian Laser Beam PDFWeiyong ZhangNo ratings yet
- An Overview of NACA 6-Digit Airfoil Series Characteristics PDFDocument13 pagesAn Overview of NACA 6-Digit Airfoil Series Characteristics PDFBala ChandarNo ratings yet
- 4bak 4siz PeruDocument8 pages4bak 4siz PeruAnonymous cgKtuWzNo ratings yet
- IDP Project DefinationDocument9 pagesIDP Project DefinationDipak KardaniNo ratings yet
- Study of New Type Elliptical Cross Trainer With Symmetrical Driving MechanismDocument9 pagesStudy of New Type Elliptical Cross Trainer With Symmetrical Driving MechanismAbhishekRajNo ratings yet
- The Purpose of The Euler Number in Vedic PhysicsDocument12 pagesThe Purpose of The Euler Number in Vedic PhysicsRiki SaputraNo ratings yet
- 4 Bending of PlatesDocument16 pages4 Bending of PlatessudarshanNo ratings yet
- Liquefaction ThesisDocument208 pagesLiquefaction ThesisRahul Yadav100% (2)
- Sections 4.6 - 4.7 Momentum Equation For Control Volume With Arbitrary Acceleration 4.7 The Angular-Momentum PrincipleDocument10 pagesSections 4.6 - 4.7 Momentum Equation For Control Volume With Arbitrary Acceleration 4.7 The Angular-Momentum Principlepackman465100% (1)
- Lelm 504Document11 pagesLelm 504Vaibhav Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Imbibition PressureDocument11 pagesImbibition PressureMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsAnonymous wTQriXbYt9No ratings yet
- 78903567-Garga by GargacharyaDocument55 pages78903567-Garga by GargacharyaGirish BegoorNo ratings yet
- (Fundamental and Applied Catalysis) R. A. Van Santen, J. W. Niemantsverdriet (Auth.) - Chemical Kinetics and Catalysis-Springer US (1995) PDFDocument290 pages(Fundamental and Applied Catalysis) R. A. Van Santen, J. W. Niemantsverdriet (Auth.) - Chemical Kinetics and Catalysis-Springer US (1995) PDFShafqat HussainNo ratings yet
- 51 Industrial CrystallizationDocument23 pages51 Industrial CrystallizationBoris DiazNo ratings yet
- Novel Separations TechniquesDocument2 pagesNovel Separations TechniquesSP ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Sealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsDocument13 pagesSealed SKF Spherical Roller BearingsMohamed Abdou100% (1)
- Five Types of Same Level FallsDocument1 pageFive Types of Same Level FallsNORMAN ANDRE LOPEZ BECERRANo ratings yet
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Ethanol From Aqueous SolutionsDocument11 pagesSupercritical Fluid Extraction of Ethanol From Aqueous SolutionsPedro LisboaNo ratings yet
- GPH 201Document158 pagesGPH 201ضوسرNo ratings yet
- Flyer ChameleoBoost ConsolDocument26 pagesFlyer ChameleoBoost ConsolAnchita MitraNo ratings yet
- Scalar Energy - A Completely New World Is Possible - Bill MorganDocument4 pagesScalar Energy - A Completely New World Is Possible - Bill MorganEverest DnmsNo ratings yet
- CVSMDocument2 pagesCVSMMou Lali0% (1)