Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)
Uploaded by
Leoni HerreraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)
Uploaded by
Leoni HerreraCopyright:
Available Formats
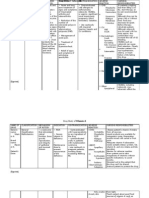
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action Required for nucleoprotein synthesis and maintenance of normal erythropoiesis.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions LOCAL: Pain and discomfort at injection site
Nursing Considerations
Generic: Folic acid (folate) Brand : Folvite
Folic acid Vitamin supplement
Treatment of megaloblastic anemias due to sprue, nutritional deficiency, pregnancy, infancy, and childhood
-Contraindicated with allergy to folic acid preparations; pernicious, aplastic, normolytic anemias
- Administer orally if at all possible. With severe GI malabsorption or very sever disease, give IM, or subcuetaneously
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action Elevates the serum iron concentration, and is then converted to Hgb or trapped in the reticuloendothelial cells for storage and eventual conversion to a usable form of iron.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects -CNS: CNS toxicity, acidosis, coma and death with overdose -GI: GI upset, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, dark stools, temporary staining of teeth (liquid preparations)
Nursing Considerations
Generic: ferrous sulfate Brand : Apo-Ferrous Sulfate (CAN) Feosol Fer-gen-sol Fer-in-sol
Iron preparation
-Prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemias -Dietary supplement for iron -Unlabeled use: Supplemental use during epoetin therapy to ensure proper hematologic response to epoetin
-Contarindicated with allergy to any ingredient; sulfite allergy; hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hemolytic anemias. -Use cautiously with normal iron balance; peptic ulcer, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis
-Confirm that patient does have iron deficiency anemia before treatment. -Give drug with meals (avoiding milk, eggs, coffee ,and tea) if GI discomfort is severe; slowly increase to build up tolerance. -Administer liquid preparations in water or juice to mask the taste and prevent staining -Warn patient that stool may be dark or green
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action Selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to specific tissue receptors found in the vascular smooth muscle and adrenal gland; this action blocks the vasoconstriction effect of the reninangiotensin system as well as the release of aldosterone leading to decreased BP.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects -CNS: Headache, dizziness, syncope, insomnia -CV: Hypertension
Nursing Considerations
Generic: Losartan potassium Brand : Cozaar
Antihypertensive
-Treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensives -Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with an elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria in patients with type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes and a history of hypertension
-Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to losartan -Use cautiously with hepatic or renal impairment, hypovolemia, history of angioedema.
- Administer without regard to meals -Report fever, chills
-Dermatologic: Rash, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin -GI: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, dry mouth
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action Renin, synthesized by the kidneys, is released into the circulation where it acts on a plasma precursor to produce angiotensin I, which is converted by ACE to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that also causes release of aldosterone from the adrenals; both of these actions increase BP. Enalapril blocks the conversion of angiotensin II, decreasing BP, decreasing aldosterone secretion, slightly increasing serum K+ levels, and causing Na+ and fluid loss; increased prostaglandin synthesis also may involved in the antihypertensive action.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects CNS: Headache, dizziness, fatigue CV: Syncope, chest pain, palpitations, hypotension in salts-or in volumedepleted patients
Nursing Considerations
Generic: enalapril maleate Brand : Vasotec
ACE inhibitor Antihypertensive
Oral -Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives, especially thiazidetype diuretics Parenteral -Treatment of hypertension when oral therapy is not possible
-Contraindicated with allergy to enalapril
- Monitor patients on diuretic therapy for excessive hypotension after the first few doses of enalapril. -Monitor patient closely in any situation that may lead to a drop in BP secondary to reduced fluid volume (excessive perspiration and dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea) because excessive hypotension may occur. -Arranged for reduce dosage in patients with impaired renal function.
-Use cautiously with impaired renal function; salt or volume depletion(hypoten sion may occur) GI: Gastric irritation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain GU: Renal insufficiency, renal failure, polyuria, oliguria, urinary frequency Hematologic: Decreased Hct and Hgb
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the cholesterol synthesis pathway, resulting in a decrease in serum cholesterol, serum LDLs, and either an increase or no change in serum HDLs.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects CNS: Headache, sleep disturbances GI: Flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, heartburn, liver failure
Nursing Considerations
Generic: simvastatin Brand : Apo-Simvastatin (CAN) CO Simvastatin (CAN) Gen-Simvastatin (CAN) Novo-Simvastatin (CAN)
Antihyperlipidemic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
-Adjunct to diet in the treatment of elevated total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol with primary hypercholesterolemi a (types IIa and IIb) in those unresponsive to dietary restriction of saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures -Treatment of patients with isolated hypertriglyceridemi a.
-Contraindicated with allergy to simvastatin, active liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevations of serum transaminases -Use cautiously with impaired hepatic and renal functions, cataracts
- Ensure that patient has tried a cholesterol-lowering diet regimen for 3-6mos before beginning therapy. -Give in the evening; highest rates of cholesterol synthesis are between midnight and 5am. -Arrange for regular followup during long-term therapy. Consider reducing dose if cholesterol falls below target.
Drug Name
Classification
Mechanism of Action A natural glycoprotein produced in the kidneys, which stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
Indication
Contraindication
Side/Adverse effects CNS: Headache, seizure, CVA, TIA CV: Hypertension, edema, chest pain GI: Nausea, vomiting
Nursing Considerations
Generic: epoetin alfa Brand : Epogen Eprex (CAN) Procrit
Recombinant human erythropoietin
-Treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal failure, including patients older than 1 mo on dialysis -Treatment of anemia related to therapy with azidothymidine (AZT) in HIVinfected patients -Reduction of allogenic blood transfusions in surgical patients
-Contraindicated with uncontrolled hypertension
-Confirm chronic, renal nature of anemia; not intended as a treatment of severe anemia or substitute for emergency transfusion. -Patients with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis should receive the drug IV, not by subcutaneous injection, to decrease the risk of developing antierythropoietin antibodies - Gently mix; do not shake, shaking may denature the glycoprotein. Use only one dose per vial; do not reenter the vial. Discard unused portions. -Do not give with any other drug solution. -Administer dose three times per week. If administered independent of dialysis, administer into venous access line. If patients on dialysis, administer IV or subcutaneously. -Monitor access line of clotting. -Institute seizure precautions.
You might also like
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Oral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsDocument15 pagesOral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument11 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Drug laxative reduces ammonia lactuloseDocument6 pagesDrug laxative reduces ammonia lactuloseRj MagalingNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsLovely Saad TubañaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indication Action Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nsg. ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Indication Action Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nsg. ResponsibilitiesMia Pascua MangrobangNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- DS Bernie Evan Doku FinnishDocument10 pagesDS Bernie Evan Doku FinnishBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesKhim CaronanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideDocument8 pagesPotassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideJoy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesBenazepril Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drug Index Updated2Document113 pagesDrug Index Updated2tam meiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameDocument12 pagesMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127No ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocument9 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭No ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDocument5 pagesACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SUMMARYDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY SUMMARYEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocument5 pagesAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Memantine, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Rivastigmine, Losartan, Aspirin, ClopidogrelDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Memantine, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Rivastigmine, Losartan, Aspirin, ClopidogrelCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib drug guideDocument10 pagesCelecoxib drug guidejessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilapi-3797941No ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilapi-3797941100% (1)
- Medications on Med Test: Metoprolol, Lisinopril, Furosemide, Warfarin, Insulin, Metformin, Lispro, Docusate Sodium, HydrochlorothiazideDocument8 pagesMedications on Med Test: Metoprolol, Lisinopril, Furosemide, Warfarin, Insulin, Metformin, Lispro, Docusate Sodium, Hydrochlorothiazidetina100% (1)
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseDocument1 pageNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- BAENA, Nicole - Compilation of PharmacardsDocument11 pagesBAENA, Nicole - Compilation of PharmacardsnicoletbaenaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Classification Dosage Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Omeprazole CnsDocument7 pagesGeneric Name Classification Dosage Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Omeprazole CnsJose Matthew AmperNo ratings yet
- Ify Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesIfy Drug StudiesifyNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Treatment For Diabetic Foot UlcersDocument11 pagesTreatment For Diabetic Foot UlcersAnisa SafutriNo ratings yet
- Central Line Removal ProtocolDocument1 pageCentral Line Removal Protocolmathurarun2000No ratings yet
- Knee PainDocument2 pagesKnee PainKKNo ratings yet
- Gold Standards in Medical FieldDocument8 pagesGold Standards in Medical FieldJyothisankar Radhakrishnan100% (2)
- Marginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicDocument2 pagesMarginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicwwxxmmNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in ChildrenDocument7 pagesRheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in ChildrenSurya MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A ReviewDocument8 pagesComplications of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A ReviewIrsanti SasmitaNo ratings yet
- Vulvar and Vaginal Benign LesionsDocument8 pagesVulvar and Vaginal Benign LesionsKristine VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Globemed FormDocument4 pagesGlobemed Formangeloriondo1217No ratings yet
- CPT Coding Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesCPT Coding Practice QuestionsTannu SamadNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Practice Exam For Pharmacology - Musculoskeletal Medications - RNpediaDocument8 pagesNCLEX Practice Exam For Pharmacology - Musculoskeletal Medications - RNpediaKristine SingsonNo ratings yet
- CIDI-based Screening Scale For Bipolar Spectrum Disorders - : Clinical UtilityDocument4 pagesCIDI-based Screening Scale For Bipolar Spectrum Disorders - : Clinical UtilityJagdishVankarNo ratings yet
- Stroke Risk Scorecard 2018Document2 pagesStroke Risk Scorecard 2018wahyu satriaNo ratings yet
- BIO K 211 TDS (EN) Fasciola Hepatica SeroDocument4 pagesBIO K 211 TDS (EN) Fasciola Hepatica SeroPia Loreto Cid TroncosoNo ratings yet
- AHA Vs ERC GuidelinesDocument39 pagesAHA Vs ERC GuidelinesYoel Harianto100% (2)
- PSA and Psoriasis Exam ChecklistDocument2 pagesPSA and Psoriasis Exam ChecklistChaken ManiyanNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument1 pageAcute Myeloid LeukemiaAlleah Salbo KepusNo ratings yet
- PDF Tablet Lepas LambatDocument13 pagesPDF Tablet Lepas Lambatannisya bubblesNo ratings yet
- Resurgence of TB linked to increased pneumothoraxDocument5 pagesResurgence of TB linked to increased pneumothoraxM Tata SuhartaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanJide Manuel100% (1)
- Bacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersDocument15 pagesBacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersNadya AbigailNo ratings yet
- Intranasal Steroids in PediatricsDocument39 pagesIntranasal Steroids in PediatricsKishore ChandkiNo ratings yet
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVHDocument5 pagesCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVHJàson Vòrhees100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Failure For StudentDocument41 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure For Studentapi-379952350% (4)
- PNSS Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPNSS Drug Studyrain peregrinoNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- Suppurative Lung DiseasesDocument39 pagesSuppurative Lung Diseasesmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- 2-Physiotherapy For FracturesDocument17 pages2-Physiotherapy For FracturesJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINo ratings yet
- Acne (Causes and Symptoms)Document4 pagesAcne (Causes and Symptoms)Siddharth ChoudheryNo ratings yet
- Guia Idsa Pie Diabetico PDFDocument42 pagesGuia Idsa Pie Diabetico PDFAliciaNo ratings yet