Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HANA Integration
Uploaded by
harikiran1729Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HANA Integration
Uploaded by
harikiran1729Copyright:
Available Formats
1 HANA Integration
HANA (High Performance Analytical Appliance) is a product based on New DB that allows the implementation of analytical application that processes a huge amount of data in real time. The Gateway HANA integration exposes HANA content as OData services. For this a generic Minimal Gateway application has been developed on the Gateway Hub, i.e. a local MGW application. The application is a prototype only. Additionally references between other Gateway content and HANA content are possible. Therefore the prototype allows federation between HANA content and Minimal Gateway Content. Gateway retrieves the data from HANA via ABAP Database Connectivity (ADBC). ADBC is an object-based ABAP API for programming relational database accesses, which in its class and model structure follows the JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) diction. For some of the following discussion the different table types in HANA should be known Replicated tables like for example the MM material table MARA Analytic Views are like cube model where Transaction Data is connected to attribute view o o They can have multiple dimensions Data can be sliced and diced (e.g. Grouped by attributes)
Calculation View are based on analytic views enriched with custom functions and calculations o They can be used to define a two dimensional list from a Analytic View
1.1 Prototype
A prototype has been developed in system U3F.
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.1.1 Overview
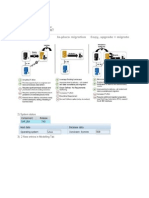
Figure 1 - Gateway HANA Integration
The HANA integration is based on the SAP Data Channel (Minimal Gateway) for local applications. It is developed on the Gateway hub against interfaces not exposed to stakeholders. The main building blocks are "HANA Model Provider" (Class ZHANA_CL_HANA_MODEL_ADP) "HANA Business Data Provider" (Class ZHANA_CL_HANA_MGW_RUNTIME) HANA Database Connector (Class ZHANA_CL_HANA_DATABASE_READER)
1.1.2 HANA Model Provider
The HANA Model Provider extracts metadata out the HANA repository via the HANA Database Connector and adapts it to the SAP Data Channel representation. It implements BADI /IWFND/BD_MED_MDL_MODEL_LOAD and is triggered via the BADI filter EXTERNAL_MODEL_TYPE.
1.1.3 HANA Business Data Provider
The HANA Business Data Provider delegates requests to HANA via the HANA Database Connector. Only read scenarios are supported. The Business Data Provider supports the common set of SAP Data query functionality (e.g. filter, sorting). It implements BADI /IWFND/BD_MGW_RUNTIME and is triggered via the BADI filter SERVICE_DOCUMENT_NAME.
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 2 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.1.4 HANA Database Connector
The HANA Database Connector executes queries against the HANA database and provides the corresponding metadata.
1.1.4.1 Connection to HANA
To execute queries against HANA class CL_SQL_STATEMENT of package SDB_ADBC (part of BASIS) is used. The corresponding connection has been defined in table DBCON. HANA supports user based authority checks. These authority checks are filters that are merged to an executed query. However this requires user based connectivity between Gateway and HANA. This is currently not available.
1.1.4.2 Additional query information
To execute the queries additional information is needed during runtime. This is stored in table ZHANA_DBTAB_NAME. This table has the following fields MODEL_IDENTIFIER SCHEMA_NAME TABLE_NAME CON_NAME IS_ACTIVE COLUMNS_USED KEY_FIELDS MGW Model Identifier (key) HANA Database Schema HANA Database (View) name Logical name for a database connection Indicates that the GSDO Group is Active Names of the columns used from the HANA database Names of the columns that are key fields
1.1.4.3 Metadata
The metadata (entity description) is derived from the corresponding HANA metadata. More precisely it is read from a query result. A query requesting only one entry from the database is executed and the metadata of the result set is read. This information is merged with the data stored in table ZHANA_DBTAB_NAME and then adapted to the corresponding MGW format.
1.1.4.4 Feeds
To retrieve a feed an ADBC query statement matching the OData request is composed and executed.
1.1.4.5 Entities
To retrieve an entity an ADBC query statement is composed and executed requesting only one entry.
1.1.5 Gateway Objects
Several Gateway objects need to be created during design time:
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 3 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
One Service Group One Object Model per HANA database table. The following tables need to be maintained o /IWFND/I_MED_OHD o Defines the model identifier and set active
/IWFND/I_MED_EMM Specifies the external model identifier (used at metadata document)
/IWFND/I_MED_INH Object inheritance information
All models are assigned to the same Service Group. This is done via table o /IWFND/I_MED_SRG Maps models to service groups
While the routing is not done via System Aliases still a GSDO Group is needed to which the Service Group is assigned.
1.1.6 HANA specific meta-data on the Gateway
No additional content specific metadata shall be maintained at Gateway to avoid Lifecycle dependencies between HANA content and Gateway content. As the HANA metadata does currently not support semantic groups of entities that could be translated to SAP Data Service Groups, additions to the current HANA repository are required: SAP Data Service Groups Language Dependent Column Labels
1.2 Conclusions
1.2.1 Limitations / Requirements
The following limitations and requirements have been identified.
1.2.1.1 ADCB
ADCB is the one big question mark for this integration approach. 1.2.1.1.1 Authorization
HANA supports user based authority checks. These authority checks are filters that are merged to an executed query. However this requires user based connectivity between Gateway and HANA. This is currently not available. 1.2.1.1.2 Tools
Connections are created by creating an entry in table DBCON via SE16. 1.2.1.1.3 Scalability
Only a limited fixed numbers (20?) of ADBC connections can be open in parallel from a SAP system. Currently no connection pooling is available.
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 4 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.2.1.1.4
SAP Server Operation System
The Gateway retrieves the data from HANA via ADBC. HANA currently only supports Linux (and Windows?), but not for example Solaris for ADBC. Hence the Gateway ABAP server needs to be running on Linux (or Windows?). 1.2.1.1.5 Future
(To the author of this document) The future support and development of ADBC is not clear. 1.2.1.1.6 Features needed from BASIS
The limitations listed above need to be overcome o o o o User based authorization Tool for connection setup ADBC scalability Supported operation systems (This is rather a limitation of the new DB database driver than ADBC)
1.2.1.2 Renaming of fields
The MGW metadata is created generically from HANA metadata. Hence MGW properties are called as the HANA database table columns. But as there are limitations on the MGW property naming (e.g. no / is allowed) certain columns cannot be used. 1.2.1.2.1 Features needed on Gateway
A method to calculate a MGW (OData) compatible name from a String A possibility for an admin to enhance the generically created transient model
1.2.1.3 Hiding (showing) of fields
The MGW metadata is created generically from HANA metadata. Hence all HANA database table columns are exposed as Gateway properties. 1.2.1.3.1 Features needed on Gateway
A possibility for an admin to enhance the generically created transient model o o Hide certain fields Define a white-list of fields to be exposed. All other fields are not exposed
1.2.1.4 Labels
The metadata retrieved from HANA does not contain label information. It might be possible to read a descriptive XML from a HANA database table which contains label information. But even if that is possible no translation would be available. 1.2.1.4.1 Features needed on Gateway
A possibility for an admin to enhance the generically created transient model
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 5 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.2.1.5 Key Fields
HANA database tables do not support key fields. 1.2.1.5.1 Workaround
Two workarounds seem reasonable: The prototype uses database table ZHANA_DBTAB_NAME on the Gateway to store for each model (i.e. each HANA database tables) the fields which shall be exposed as key fields Flag all characteristics as key. o o Attributes (Characteristics) are descriptions of key figures, such as Customer ID, Material Number, Sales Representative ID, Unit of Measure, and Transaction Date. Measures (Key figures) are numeric values or quantities, such as Per Unit Sales Price, Quantity Sold, and Sales Revenue.
1.2.1.6 READ Entity
HANA database tables do not support key fields. Hence it is not possible to uniquely identify a table entry for a select single. 1.2.1.6.1 Workaround
To retrieve an entity an ADBC query statement is composed and executed requesting only one entry. If the correct characteristics are supplied this is sufficient.
1.2.1.7 HANA Metadata
There are currently 3 options how to retrieve metadata for a HANA database table There is one specific table which contains column information for tables. o o This is only filled for replicated tables. No information can be read for analytic and calculation views. No field labels are available
There is one specific table which contains a metadata XML tables and views. o o No library is available retrieve this metadata. A Gateway application would have to parse this XML itself. It needs to be checked if field labels are available
The ADBC libraries return for every Query result also the corresponding metadata. o o o No field labels are available It needs to be checked if this returns metadata if the query did not find any record This can be fairly slow way when only the metadata is needed
1.2.1.8 Field length in ADBC libraries
The ADBC libraries can only handle field (column) names with a length up to 30 characters. HANA allows longer field names. Corresponding problems are very likely.
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 6 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.2.1.9 Dynamic Object Model assignment
It is not possible on the Gateway to assign Object Models to Service Groups during runtime. Models are assigned to Service Groups during design time via SE80 (or SE16 as in the prototype). 1.2.1.9.1 Features needed on Gateway
It should be possible to assign Object Models to Service Groups during runtime via APIs. A related requirement for many generic Integration scenarios would be some kind of WhiteList. HANA as well as Enterprise Search or Analytics (BW) will most likely host hundreds of potential data sources. Once these can be loaded into Gateway dynamically some selection / registration mechanism is needed allowing an administrator to expose any of these data sources individually.
1.2.1.10 Composition
The following iPhone application has been built for a Sapphire demo based on the prototype Search for customers (Entity Customer) o Based on a specific customer MGW application
Display for a selected customer a list of the 5 products with the highest revenue (Entity Revenue) o Based on a model of the generic HANA application
Display some detail information for a selected product (Entity Product) o Based on a specific product MGW application
To link the HANA model to the Product Details the generically generated Object Model description needs to be enriched with the association information (define the link). To achieve this a new Model Provider class was needed. This class inherits from the original HANA Model Provider class to access the coding describing the Revenue Entity. Specific coding describes the two other entities. A similar concept was needed for the Business Data Provider. 1.2.1.10.1 Features needed on Gateway It should be possible to assign different models from different sources to one Service Group. It should be possible to define associations (links) between models on a Service Group level, i.e. within one Service Group (and for that Service Group only). It should be checked, if it is needed to allow the definition of associations (links) between models on a model level.
1.2.1.11 External Model Type
Not surprisingly the Gateway has no External Model Type for HANA. For the prototype the value B was used as it was available. For a productive coding a specific model type is needed. 1.2.1.11.1 Features needed on Gateway External Model Type should not be based on a domain but rather be customizing with a customer namespace.
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 7 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.2.1.12 Analytic Views
An analytic view describes data in multiple dimensions. An OData response and realistically also a mobile device can only handle 2 dimensional lists. To retrieve such a list from an analytic view grouping information needs to be added to the SQL (ADBC) statement. This could be provided from the client. o It needs to be checked if this is supported by OData or can be added
This could be added by the Gateway. o This would need some additional configuration on the Gateway
This can be overcome by defining corresponding simplified Calculation Views on HANA. o This has been done for the prototype.
1.2.2 Other ideas
Following is a list of some ideas collected before the prototype was designed Use HANA as accelerator for QUERY operation on GW objects (for that matter the HANA object would need to have similar or identical structure compared to the GW object) o o o o This could be done in case the models are identical. In case models are not identical this needs a rather extensive application logic or a even more complex mapping The HANA Business Data Provider would be made available for specific MGW applications. The idea of the prototype is to only provide a generic framework allowing a customer to easily expose HANA database tables which have o Been shipped with a different life cycle Have been created by the customer
But this merging of HANA and none HANA data is not trivial and hence rather a task for SAP development. It would need to be checked if and how this could be developed and shipped
Use HANA as provider to particular GW object's properties (HANA can deliver KPI information based on analytical information to a Gateway object) o The idea of the prototype is to only provide a generic framework allowing a customer to easily expose HANA database tables which have o Been shipped with a different life cycle Have been created by the customer
But this merging of HANA and none HANA data is not trivial and hence rather a task for SAP development. It would need to be checked if and how this could be developed and shipped
Use HANA (or more precisely the underlying newDB) may serve as offlining capability for GW caching o Simple two dimensional data (which is all what is needed for any reasonable Gateway caching) can be read from normal SAP database tables with at least similar speed as from a HANA database. HANA has been designed for multi dimensional mass data analysis, which of course is not needed for Gateway caching.
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 8 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
Use HANA ideally also exposes itself via SAPDATA to allow homogenous access to all data sources of SAP and allow a consistent way for GW to access the information accordingly were needed/reasonable o The Prototype and this document are about the question how to expose HANA data via the Gateway. The question what could be done on HANA has not been addressed.
1.2.3 Design aspects
One service group for all exposed HANA database tables has been created on the Gateway. This is needed for example for the authority check. For every exposed HANA database table one model has been defined. An alternative would be to have one model containing all exposed tables as entities.
1.2.3.1 Gateway Software Component Layer Assignment
The current analytics functionality is a part of IW_CBS. Consequently the integration of High Performance Analytical Appliance should be assigned to the same layer. This allows us to deliver the integration with a later Gateway content pack as well. (Decision pending)
1.3 Summary
From a design perspective the generic integration of HANA as described in the document is a very good fit for the MGW (OData Channel). The current questions around ADBC are the one major obstacles to develop a Gateway quality product based on the ideas of the prototype Developing a generic tool to retrieve a SQL statement for an OData request would be a major part but can be accomplished fairly easy. The major lesson learned from the prototype for the Gateway is that following aspects should become more flexible or should be double checked: o o o The use of Service Groups (e.g. should this be a repository object?) The definition of Object Models (E.g. it should be possible to create and assign them to Service Groups during runtime) Composition and configuration
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 9 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.4 Alternative
There is at least one reasonable alternative architectural approach to integrate HANA. Instead of accessing HANA directly via ADBC rather integrate the Gateway with HANA implicitly by integrating with Analytics. HANA 1.5 will support Analytics. Advantages ADBC will not be used Tool support like for example the Query Designer Analytics shall be integrated into Gateway anyway. So with this one stone 2 birds would be killed.
1.5 Appendix
1.5.1 Links
Hana Input
1.5.1.1 Links to Prototype
1.5.1.1.1 Metadata
http://ldai1u3f.wdf.sap.corp:50050/sap/opu/sdata/sap/ZHANA/$metadata?sapclient=100&$format=xml MARA
1.5.1.1.2
Feed http://ldai1u3f.wdf.sap.corp:50050/sap/opu/sdata/sap/ZHANA/MARACollection?sapclient=100&$format=xml&$filter=substringof(matnr,'AND') Entry http://ldai1u3f.wdf.sap.corp:50050/sap/opu/sdata/sap/ZHANA/MARACollection(mandt='800' ,matnr='APO-FG')?sap-client=100&$format=xml Products per customer
1.5.1.1.3
Feed http://ldai1u3f.wdf.sap.corp:50050/sap/opu/sdata/sap/ZHANA/COPA__ACT_PLCollec tion?sap-client=100&$format=xml&$filter=gjahr%20eq%202010%20and%20kunnr%20eq %20'0000002140'%20&%20&$orderby=revenue%20desc Costing Sheet http://ldai1u3f.wdf.sap.corp:50050/sap/opu/sdata/sap/ZHANAEXT/COPA__ACT_PLCollecti on(gjahr='1996',kunnr='0000001360',matnr='M08',matkl='002',werks='1000')/CopaCostingSheet?sap-client=100&$format=xml
1.5.1.2
Classes in U3F(100)
ZHANA_CL_HANA_MODEL_ADP o Class for BAdI Impl.: ZHANA_BI_HANA_MODEL_ADP o MWG Adapter providing the metadata (Model descriptions) ZHANA_CL_HANA_MGW_RUNTIME o Class for BAdI Impl.: ZHANA_BI_HANA_MGW_RUNTIME o MGW Adapter providing the runtime data(O-Data requests) ZHANA_CL_HANA_DATABASE_READER o Retrieves data and meta-data from HANA database
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 10 of 11
Architecture Concept for <Program/Project/Topic/Integration Scenario>
1.5.2 Gateway Objects
Service Group ZHANA_SG_ALL_MODELS_0001 o Generic Hana Service Group - GW / Hana Integration Prototyping Object Models o ZHANA_OM_MARA_0001_BE o Creation / Assigment for new models /IWFND/I_MED_OHD Define the model indentifier and set active /IWFND/I_MED_EMM Specify the external model identifier (used at metadata document) /IWFND/I_MED_INH Object inheritance table not require -> dummy record BASE_MDL_IDENT = space /IWFND/I_MED_SRG Maps service to models SRV_IDENTIFIER = ZHANA_SG_ALL_MODELS_0001 ZHANA_DBTAB_NAME map model id to hana schema and table name GSDO Group o ZHANA_ALL_OBJECT
Copyright SAP AG 2010
Internal/Confidential
Page 11 of 11
You might also like
- Cool Features 7.4Document10 pagesCool Features 7.4Aparajit BanikNo ratings yet
- Sap InterviewDocument11 pagesSap InterviewFaizan FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c - Second EditionFrom EverandOracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- E - Hanaaw - 16 All in OneDocument43 pagesE - Hanaaw - 16 All in OneCPI Training0% (1)
- Sap Hana: Sudha PaluruDocument56 pagesSap Hana: Sudha PaluruKarthick S NairNo ratings yet
- Features in BI 7Document11 pagesFeatures in BI 7Shane CooperNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Migration Custom Code AdjustmentDocument9 pagesSAP HANA Migration Custom Code AdjustmentRajathi Durai0% (1)
- Optimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalDocument58 pagesOptimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalMani KandanNo ratings yet
- 1310 Success Stories and Lessons Learned Implementing SAP HANA SolutionsDocument24 pages1310 Success Stories and Lessons Learned Implementing SAP HANA SolutionsRahul MaddikuntaNo ratings yet
- A Lower Value Than On A Traditional, Row-Store Only Based DatabaseDocument28 pagesA Lower Value Than On A Traditional, Row-Store Only Based DatabaseMosi DebbieNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandSAP HANA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- BW Best PracticesDocument8 pagesBW Best Practicesjay normousNo ratings yet
- Useful T-Codes and Programs Related IDOC Processing and IDOC DevelopmentDocument5 pagesUseful T-Codes and Programs Related IDOC Processing and IDOC DevelopmentObul Reddy SegireddyNo ratings yet
- HANA Security TechleapDocument23 pagesHANA Security TechleapMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate C - C - TS4CO - 2020 - SAP Certified Application Associate - SAP S/4HANA For Management Accounting (SAP S/4HANA 2020)Document2 pagesThe Ultimate C - C - TS4CO - 2020 - SAP Certified Application Associate - SAP S/4HANA For Management Accounting (SAP S/4HANA 2020)KirstingNo ratings yet
- What Is Sap Hana?: General QuestionsDocument13 pagesWhat Is Sap Hana?: General QuestionsMadhuMichelNo ratings yet
- Create Custom Metrics For HANA Monitoring: With SAP Solution Manager 7.1Document33 pagesCreate Custom Metrics For HANA Monitoring: With SAP Solution Manager 7.1DJ CastleNo ratings yet
- SAP BW On HANADocument13 pagesSAP BW On HANARaman KumarNo ratings yet
- DUMPSDocument54 pagesDUMPSpulkit_khandelwal21No ratings yet
- Sap Hana Course ContentDocument2 pagesSap Hana Course ContentDeepaNarendraNo ratings yet
- Hana View As External View in Abap PDFDocument17 pagesHana View As External View in Abap PDFSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- S03 Native HANA Modeling Part2Document14 pagesS03 Native HANA Modeling Part2solankikavitaNo ratings yet
- In-Line Declarations CDS Views View On View Concept ALV Using IDA (Integrated Data Access) Data Modelling (Attribute, Analytic & Calculation Views)Document23 pagesIn-Line Declarations CDS Views View On View Concept ALV Using IDA (Integrated Data Access) Data Modelling (Attribute, Analytic & Calculation Views)Hemanth Kumar PanagamNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Interview QuestionsDocument47 pagesSAP ABAP Interview QuestionsManish Shankar100% (6)
- BW 7.4 Features: 1) Implementation MethodologyDocument11 pagesBW 7.4 Features: 1) Implementation MethodologykksrisriNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate C - C - SEN - 2005 - SAP Certified Application Associate - SAP Enable NowDocument2 pagesThe Ultimate C - C - SEN - 2005 - SAP Certified Application Associate - SAP Enable NowTeresaNo ratings yet
- Faq in Sap - AbapDocument4 pagesFaq in Sap - AbapSripriya GunaNo ratings yet
- BW Glossary, Definitions & Explanations: A AggregateDocument11 pagesBW Glossary, Definitions & Explanations: A AggregateztanauliNo ratings yet
- SAP - ABAP CDS Development User GuideDocument150 pagesSAP - ABAP CDS Development User GuideC.S.Dinakara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between BW, BW On HANA and Native HANADocument2 pagesDifference Between BW, BW On HANA and Native HANASourabhNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument49 pagesInterview QuestionJoy DeyNo ratings yet
- BW 74 Powered by SAP HANA Use It To Your Advantage V1Document26 pagesBW 74 Powered by SAP HANA Use It To Your Advantage V1vinayrbedre7019No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SAP HANA The BeginingDocument59 pagesFundamentals of SAP HANA The Beginingsaphari76No ratings yet
- ABAP Interview QuestionsDocument48 pagesABAP Interview Questionscharanreddy_1979No ratings yet
- Things To Know ABAP CodingDocument17 pagesThings To Know ABAP CodingJoyNo ratings yet
- He 1-GB Dataset Limitation Does Not Apply To Direct QueryDocument4 pagesHe 1-GB Dataset Limitation Does Not Apply To Direct QuerygayatriNo ratings yet
- 2 e - Hanaaw - 14-1Document11 pages2 e - Hanaaw - 14-1Sampath DasarathiNo ratings yet
- ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesABAP Interview Questions and AnswersSenthil Kumar.SNo ratings yet
- Imp FAQs1Document94 pagesImp FAQs1Govardhan AgamaNo ratings yet
- From A CDS View To An OData Service For AnalyticsDocument18 pagesFrom A CDS View To An OData Service For AnalyticsParesh GanganiNo ratings yet
- SAP BW 7.5 On HANA Online TrainingDocument6 pagesSAP BW 7.5 On HANA Online TrainingAnonymous Z9Mbp4XZNo ratings yet
- IDQ LearningDocument33 pagesIDQ LearningabcNo ratings yet
- BW4HANADocument4 pagesBW4HANAGaurav TipnisNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument15 pagesInterview Question125diptiNo ratings yet
- 2ºestudiarDocument12 pages2ºestudiarlgmNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide To Implement Modeling Scenarios in SAP BW 7.4 On HANADocument24 pagesStep by Step Guide To Implement Modeling Scenarios in SAP BW 7.4 On HANAEcio FerreiraNo ratings yet
- IDQ LearningDocument36 pagesIDQ LearningabcNo ratings yet
- Board SapDocument2 pagesBoard SapArvind YadavNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About Universal Journal (ACDOCA) - SAP S4 HANA (2020)Document16 pagesAll You Need To Know About Universal Journal (ACDOCA) - SAP S4 HANA (2020)gounazerty6No ratings yet
- ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesABAP Interview Questions and Answersvenkat_vantipalliNo ratings yet
- ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesABAP Interview Questions and AnswersGoutam MahatoNo ratings yet
- Overview of SAP BI ArchitectureDocument6 pagesOverview of SAP BI ArchitectureThuNo ratings yet
- Internal Table OperationsDocument75 pagesInternal Table Operationsbhuvan9032No ratings yet
- Universe Designer & WEB IntelligenceDocument27 pagesUniverse Designer & WEB IntelligenceSrujan KumarNo ratings yet
- STORM Startup Focus Program - Hana Solution Validation - ChecklistDocument10 pagesSTORM Startup Focus Program - Hana Solution Validation - ChecklistSeang Hok YievNo ratings yet
- The SAP HANA Database - An Architecture OverviewDocument6 pagesThe SAP HANA Database - An Architecture OverviewloroowNo ratings yet
- Abap InterviewDocument25 pagesAbap InterviewDinesh Reddy VootkuriNo ratings yet
- TREX Architecture and FunctionalityDocument33 pagesTREX Architecture and Functionalityharikiran1729No ratings yet
- E2e Hana Hadoop Technical DemoDocument12 pagesE2e Hana Hadoop Technical Demoharikiran1729No ratings yet
- Process ChainDocument11 pagesProcess Chainfelix_pereira_5No ratings yet
- BIDocument17 pagesBIharikiran1729No ratings yet
- BODS Support Handover Document V0.1Document7 pagesBODS Support Handover Document V0.1harikiran1729No ratings yet
- BI Content 7.0Document3 pagesBI Content 7.0harikiran1729No ratings yet
- Preboard IP (265) MOCK TEST Paper 2Document6 pagesPreboard IP (265) MOCK TEST Paper 2Abhay KunduNo ratings yet
- Creating A Turing Machine in Python - Part 1 - CodeProjectDocument3 pagesCreating A Turing Machine in Python - Part 1 - CodeProjectGabriel GomesNo ratings yet
- SystemVerilogAssertionHandbook FullDocument361 pagesSystemVerilogAssertionHandbook FullAjay GunjiNo ratings yet
- Making Audio Plugins Part 1 - Introduction - Martin Finke's BlogDocument4 pagesMaking Audio Plugins Part 1 - Introduction - Martin Finke's BlogSemih YavuzNo ratings yet
- Unit No. 8Document24 pagesUnit No. 8vishal phuleNo ratings yet
- Vector QuantizationDocument6 pagesVector QuantizationnavyaraviNo ratings yet
- QTP Data Table Methods: Add SheetDocument5 pagesQTP Data Table Methods: Add SheetSeshu VenkatNo ratings yet
- Bca 302 PDFDocument4 pagesBca 302 PDFTapamalya SanyalNo ratings yet
- Code To Solve Set of ProblemsDocument17 pagesCode To Solve Set of ProblemsMamta DoliyaNo ratings yet
- NVENC VideoEncoder API ProgGuide.9.0Document42 pagesNVENC VideoEncoder API ProgGuide.9.0iscrbdi100% (2)
- DNUDocument7 pagesDNUapi-3726332No ratings yet
- Cs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 36 - Function in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimDocument22 pagesCs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 36 - Function in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimGhazan AqeelNo ratings yet
- Visual Foxpro 6.0 Seminar: Presented by Jim BoothDocument68 pagesVisual Foxpro 6.0 Seminar: Presented by Jim BoothViraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern Python Standard Library CookbookDocument356 pagesModern Python Standard Library CookbookJorge FarinhaNo ratings yet
- Warner Cmputer NotesDocument18 pagesWarner Cmputer Notesapi-302957676No ratings yet
- CorejavanotesDocument438 pagesCorejavanotesAnuja Reddy MeedimalaNo ratings yet
- String in JavaDocument3 pagesString in JavaamanNo ratings yet
- Assignment#2Document3 pagesAssignment#2Malika MulkNo ratings yet
- DP ExamplesDocument37 pagesDP ExamplesnadeeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Problem Solving and SearchDocument8 pagesLecture 2: Problem Solving and SearchZerihun BekeleNo ratings yet
- IBM Integration Bus Transformation OptionsDocument56 pagesIBM Integration Bus Transformation OptionsAjaibabu ChagantiNo ratings yet
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 6-1: Practice Activities: Introduction To Explicit CursorsDocument5 pagesDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 6-1: Practice Activities: Introduction To Explicit CursorsMohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Desktop AnalysisDocument4 pagesDesktop AnalysismatthewsheeranNo ratings yet
- AngularjsDocument70 pagesAngularjsAnh Đinh VươngNo ratings yet
- Geektrust Problems5Document13 pagesGeektrust Problems5Dilip Dhanush0% (1)
- Fanuc 30i Data Input OutputDocument10 pagesFanuc 30i Data Input OutputShahzad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Shallow and Deep Copy of A Class: Start Your Coding Journey Now!Document6 pagesDifference Between Shallow and Deep Copy of A Class: Start Your Coding Journey Now!vinayNo ratings yet
- Data-Parallel Architectures andDocument27 pagesData-Parallel Architectures andAmeed UddinNo ratings yet
- The Cloud OSDocument43 pagesThe Cloud OSAkshay 'Jughead' ElaviaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Course Structure BTech CSEDocument32 pages2013 Course Structure BTech CSEMankush JainNo ratings yet