Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis of Gravity Dam - Advance Engineering Mathematics Review
Uploaded by
imrancenakkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Gravity Dam - Advance Engineering Mathematics Review
Uploaded by
imrancenakkCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Gravity Dam
Tags: eccentricity righting moment overturning moment foundation pressure hydrostatic force factor of safety factor of safety against overturning Factor of safety against sliding friction hydrostatic uplift sliding
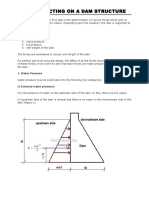
Dams are structures whose purpose is to raise the water level on the upstream side of river, stream, or other waterway. The rising water will cause hydrostatic force which will tend the dam to slide horizontally and overturn about its downstream edge or toe. The raised water level on the upstream edge or heel will also cause the water to seep under the dam. The pressure due to this seepage is commonly called hydrostatic uplift and will reduce the stability of the dam against sliding and against overturning.
Gravity Dam Analysis
The weight of gravity dam will cause a moment opposite to the overturning moment and the friction on the base will prevent the dam from sliding. The dam may also be prevented from sliding by keying its base into the bedrock.
Step 1 Consider 1 unit length (1 m length) of dam perpendicular to the cross section. Step 2 Determine all the forces acting: 1. Vertical forces = Weight of dam = Weight of water in the upstream side (if any) = Hydrostatic uplift Weight of permanent structures on the dam 2. Horizontal forces = Horizontal component of total hydrostatic force Wind pressure, wave action, floating bodies, earthquake load, etc.
Step 3
Solve for the reaction 1. Horizontal component of the reaction 2. Vertical component of the reaction
Step 4 Moment about the toe 1. Righting moment, = Sum of all rotation towards the upstream side 2. Overturning moment, = Sum of all rotation towards the downstream side
Step 5 Location of
as measured from the toe
Factors of Safety Factor of safety against sliding,
Factor of safety against overturning,
Where
= coefficient of friction between the base of the dam and the foundation.
Foundation Pressure Eccentricity,
If
is within the middle third and the foundation pressure is trapezoidal (triangular if
is exactly
) acting from heel to toe.
For the sign of , use (+) at point where is nearest. From the diagram above, use (+) for and (-) for . A negative indicates compressive stress and a positive indicates tensile stress. A positive will occur when . In foundation design, soil is not allowed to carry tensile stress, thus, any will be neglected in the analysis. If , is outside the middle third and the foundation pressure is triangular.
Submitted by Romel Verterra on December 11, 2012 - 2:10pm
SPONSORED LINKS
Fluid Mechanics Foundation Engineering Soil
You might also like
- Solutions for Biot's Poroelastic Theory in Key Engineering Fields: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandSolutions for Biot's Poroelastic Theory in Key Engineering Fields: Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument5 pagesDamsMark Anthony CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure On SurfacesDocument23 pagesHydrostatic Pressure On SurfacesJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Principal and Shear StressesDocument5 pagesPrincipal and Shear Stressesgsmrbharath_91100% (1)
- Water Resources Engineering Lecture Notes on Gravity DamsDocument18 pagesWater Resources Engineering Lecture Notes on Gravity Damssyed tabNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structure Pe 701cDocument57 pagesHydraulic Structure Pe 701cmdrajkumar410No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures-15CV832 Module - Gravity Dams ForcesDocument85 pagesHydraulic Structures-15CV832 Module - Gravity Dams ForcesSiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Total Hydrostatic Force on SurfacesDocument10 pagesTotal Hydrostatic Force on SurfacesZam DresNo ratings yet
- 3 2 PDFDocument10 pages3 2 PDFJohn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Gravity DamskerbyreyesmanaloNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamsDocument17 pagesGravity DamsParikshith PrasadNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On A Dam StructureDocument10 pagesForces Acting On A Dam StructureSantosh Rai100% (1)
- 9.2 Dams Mark Ferrater TTHDocument8 pages9.2 Dams Mark Ferrater TTHRubelyn AlabadoNo ratings yet
- Axis of Dam: Axis of A Gravity Dam Is The Line of The Upstream Edge of The Top (Crown) ofDocument10 pagesAxis of Dam: Axis of A Gravity Dam Is The Line of The Upstream Edge of The Top (Crown) ofCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES ON CONCRETE GRAVITY DAMSDocument31 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON CONCRETE GRAVITY DAMSkavinNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On A Dam StructureDocument7 pagesForces Acting On A Dam StructureChaminda Rathnayaka100% (1)
- Forces Acting On A Dam StructureDocument7 pagesForces Acting On A Dam StructureSantosh RaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DamsDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Damsace pedroNo ratings yet
- documents_null-Forces+Acting+on+Gravity+Dams+-+Nagendra+SirDocument6 pagesdocuments_null-Forces+Acting+on+Gravity+Dams+-+Nagendra+SirArarsa FayisaNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument23 pagesDamsMeggy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On Gravity DamsDocument6 pagesForces Acting On Gravity DamsRama Sagar Naik100% (2)
- Gravity Dam1Document56 pagesGravity Dam1Mary Elizabeth AltaNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamDocument89 pagesGravity DamartiNo ratings yet
- HS CH2Document98 pagesHS CH2Baysa CamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Slope StabilityDocument54 pagesChapter 10 Slope Stabilityhare krishna90% (10)
- Analysis of Forces Acting on Gravity DamsDocument27 pagesAnalysis of Forces Acting on Gravity DamsEleazar Tami-ingNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam (An Overview) : AbstractDocument10 pagesStability Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam (An Overview) : AbstractSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Large Check Dam or PondDocument27 pagesLarge Check Dam or Pondinam.emadi2No ratings yet
- Gravity Dams Unit-IIDocument44 pagesGravity Dams Unit-IIvixivi6780No ratings yet
- Design of Concrete Gravity Dam SectionsDocument23 pagesDesign of Concrete Gravity Dam SectionsManan ParikhNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam StabilityDocument14 pagesGravity Dam StabilityHarilal Kishan67% (3)
- Gravity Dam Engineering: Design, Forces, Stability Analysis & Failure ModesDocument43 pagesGravity Dam Engineering: Design, Forces, Stability Analysis & Failure ModesMadan Mohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Gravity DamDocument22 pagesPresentation On Gravity DamSarvesh Bhairampalli100% (2)
- 𝑐 𝑥 𝐴 (𝑊 cos 𝛽−𝑈−𝑉 sin 𝛽+𝑇 sin (𝜃+𝛽) ) tan Ф+𝑇 cos (𝜃+𝛽) 𝑊 sin 𝛽+𝑉 cos 𝛽Document2 pages𝑐 𝑥 𝐴 (𝑊 cos 𝛽−𝑈−𝑉 sin 𝛽+𝑇 sin (𝜃+𝛽) ) tan Ф+𝑇 cos (𝜃+𝛽) 𝑊 sin 𝛽+𝑉 cos 𝛽Nicole DuránNo ratings yet
- Topc 2 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE - StudentDocument36 pagesTopc 2 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE - StudentMuhammad AzarulNo ratings yet
- 7 28 MizutaniDocument8 pages7 28 MizutaniRamadhani SatyaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Types of Dams and Analysis of Gravity DamDocument8 pagesModule 4 Types of Dams and Analysis of Gravity DamAragones, Trisha Marie CNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force CalculationDocument2 pagesHydrostatic Force CalculationMavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesLecture 10 - HydrodynamicsPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamDocument50 pagesGravity DamSajid Nazir100% (5)
- CEL351 GravityDamForces Lect3Document46 pagesCEL351 GravityDamForces Lect3Fajrin HernataNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsDocument152 pagesHydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsAbduljebar HussienNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Wave Force Acting On Horizontal Plate Above Still Water LevelDocument12 pagesPrediction of Wave Force Acting On Horizontal Plate Above Still Water LevelSwamy ManiNo ratings yet
- A. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaDocument20 pagesA. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaKim Kelley AngNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam 1Document69 pagesGravity Dam 1DHANUSHREE K CVE20ANo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument33 pagesSlopeMuhammadImranShahzadNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering II DamsDocument86 pagesWater Resources Engineering II DamsAdyasha Swayamsiddha AmantaNo ratings yet
- Stress N Rock MassesDocument57 pagesStress N Rock MassesAmy AckerNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Theory Important QuestionsDocument7 pagesBoundary Layer Theory Important Questionskonetinarendra67% (3)
- CEL351 GravityDam StabilityAnalysisDocument41 pagesCEL351 GravityDam StabilityAnalysisJulio Humberto Díaz RondánNo ratings yet
- Wave-In-Deck Forces On Jetties and Related StructuresDocument8 pagesWave-In-Deck Forces On Jetties and Related Structuresvasanthk81No ratings yet
- Shear Stress: Name: Wael Atiah Dhedan Bardi Grad:First Stage Subject: MechanicalDocument7 pagesShear Stress: Name: Wael Atiah Dhedan Bardi Grad:First Stage Subject: MechanicalSara Alyousif100% (1)
- Swedge TheoryDocument16 pagesSwedge TheoryPedro HrnNo ratings yet
- Bending and Shear StressDocument5 pagesBending and Shear StressAtish KumarNo ratings yet
- Stability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurDocument89 pagesStability of Rock Slopes: Dr. R.S.Banshtu Associate Professor Civil Engineering Department NIT HamirpurAastha SoniNo ratings yet
- 1979-C.L。Kirk and E.UDocument11 pages1979-C.L。Kirk and E.UShuai MengNo ratings yet
- Design of Gravity DamDocument26 pagesDesign of Gravity Damrakshansh jainNo ratings yet
- 10 Secrets To A Great BodyDocument16 pages10 Secrets To A Great BodyimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- The Self-Taught ProgrammerDocument299 pagesThe Self-Taught Programmerimrancenakk100% (1)
- Design Calculations For AgitatorsDocument5 pagesDesign Calculations For AgitatorsimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Agitator Vessel (Design&Costing)Document34 pagesAgitator Vessel (Design&Costing)imrancenakk100% (2)
- Sample design calculation for skirt support of vertical columnDocument8 pagesSample design calculation for skirt support of vertical columnimrancenakk100% (2)
- Valves & Fittings Catalog 2015Document20 pagesValves & Fittings Catalog 2015imrancenakkNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- NSPM 12 Guidelines Guidelines For Assessment, Audit and Accreditation of Fumigation Agencies For Undertaking Methyl Bromide FumigationDocument46 pagesNSPM 12 Guidelines Guidelines For Assessment, Audit and Accreditation of Fumigation Agencies For Undertaking Methyl Bromide FumigationimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Lug Support DesignDocument11 pagesLug Support Designimrancenakk100% (6)
- Shaft DeflectionDocument15 pagesShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesNo ratings yet
- NSK CAT E1102m B304-325Document11 pagesNSK CAT E1102m B304-325dassoumennNo ratings yet
- Castor Wheel CatalogueDocument12 pagesCastor Wheel CatalogueimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Solitons in Elastic SolidsDocument9 pagesSolitons in Elastic SolidsimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- A Thermo-Viscoelastic-Viscoplastic-Viscodamage Constitutive Model Forasphaltic MaterialsDocument17 pagesA Thermo-Viscoelastic-Viscoplastic-Viscodamage Constitutive Model Forasphaltic MaterialsimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Towards Optimization of Patch Shape On The Performance of Bonded Composite Repair Using FEMDocument11 pagesTowards Optimization of Patch Shape On The Performance of Bonded Composite Repair Using FEMimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Local Strain Field in Adhesive Layer of An Unsymmetrically Repaired CFRP Panel Using Digital Image CorrelationDocument13 pagesAssessment of Local Strain Field in Adhesive Layer of An Unsymmetrically Repaired CFRP Panel Using Digital Image CorrelationimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- A Continuum Damage Mechanics Framework For Modeling Micro-Damage HealingDocument22 pagesA Continuum Damage Mechanics Framework For Modeling Micro-Damage HealingimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Problem 04 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument1 pageProblem 04 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Problem 04 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesProblem 04 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Translation - Moving Vessel - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesRectilinear Translation - Moving Vessel - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Problem 03 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesProblem 03 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Manometers - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesManometers - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Energy and Head - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument4 pagesEnergy and Head - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Relative Equilibrium of Liquids - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument1 pageRelative Equilibrium of Liquids - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- 02 Pressure On The Face of A Dam - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument1 page02 Pressure On The Face of A Dam - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Discharge - Flow Rate - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesDischarge - Flow Rate - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- 05 Depth of Water in Which Pressure Is 200 Kpa - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument1 page05 Depth of Water in Which Pressure Is 200 Kpa - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- 03 Pressure Below The Surface of The Ocean - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument1 page03 Pressure Below The Surface of The Ocean - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis in Structural ElementsDocument20 pagesStress Analysis in Structural ElementsLong Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Zero thickness interface elements for soil-structure analysisDocument20 pagesZero thickness interface elements for soil-structure analysissajanmalviya30No ratings yet
- FACADE MODELING Structural AnalysisDocument39 pagesFACADE MODELING Structural AnalysisGodino Christian100% (3)
- Measuring Bulk Density Values of Powders and Other Bulk Solids As Function of Compressive StressDocument5 pagesMeasuring Bulk Density Values of Powders and Other Bulk Solids As Function of Compressive StressДмитрий ШленсковойNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Key WordsDocument6 pagesAs Level Physics Key Words林仁超No ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Soil-Foundation Interaction under a Bridge PierDocument7 pagesSeismic Analysis of Soil-Foundation Interaction under a Bridge PierAngga Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report Entuple Technologies Week 4: by Ritesh KumarDocument12 pagesSummer Internship Report Entuple Technologies Week 4: by Ritesh KumarriteshNo ratings yet
- Floor ManualDocument35 pagesFloor ManualGihan ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Thickness of Shell Courses For Storage Tanks Using One Foot MethodDocument5 pagesDetermination of Thickness of Shell Courses For Storage Tanks Using One Foot MethodJatin Rambo100% (1)
- MILD STEEL Properties and UsesDocument12 pagesMILD STEEL Properties and UsesMohtisham JuttNo ratings yet
- DESIGN OF FLOOR SLAB (0.15m Thick)Document9 pagesDESIGN OF FLOOR SLAB (0.15m Thick)Living Life100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2nurulselangorNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Mechanic of Materials SEM 2 20132014Document65 pagesLab Manual Mechanic of Materials SEM 2 20132014saruwatari michiyo100% (1)
- Stiffner Design For Beam Column ConnectionsDocument84 pagesStiffner Design For Beam Column ConnectionsfabnameNo ratings yet
- Basics of Reinforced Concrete Design: OutlineDocument10 pagesBasics of Reinforced Concrete Design: OutlineariNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature Variation and Shrinkage On Circular TanksDocument12 pagesEffect of Temperature Variation and Shrinkage On Circular TanksGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- N4 Engineering Science August 2022 Question PaperDocument8 pagesN4 Engineering Science August 2022 Question PaperProffesor BhenguNo ratings yet
- Crushable Foam Plasticity ModelsDocument11 pagesCrushable Foam Plasticity ModelsNayanaNo ratings yet
- 4 Control of Deflection in Concrete StructuresDocument76 pages4 Control of Deflection in Concrete Structureshakim2020No ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesResearch MethodologyAkshay KhamarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsKailash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- r05321403 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pagesr05321403 Principles of Machine DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Investigation on Roll-Over Crashworthiness of an Intercity CoachDocument18 pagesInvestigation on Roll-Over Crashworthiness of an Intercity CoachsibieNo ratings yet
- Forming Technologies IncDocument29 pagesForming Technologies InctuấnNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING REPORT DETAILSDocument18 pagesENGINEERING REPORT DETAILSvinujohnpanickerNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesMechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualPatrick Stephens100% (34)
- Astm d5311m 13 CyclicDocument11 pagesAstm d5311m 13 CyclicSiwadol Dejphumee100% (1)
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Taller3 Modeling Concepts in Buried Pipe AnalysisDocument29 pagesTaller3 Modeling Concepts in Buried Pipe AnalysisFSAAVEDRAF100% (1)