Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control and Coordination
Uploaded by
anjupalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Control and Coordination
Uploaded by
anjupalCopyright:
Available Formats
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.
com by - Anju Pal
Control and Coordination
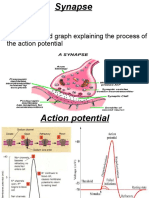
Control and coordination are the functions of the nervous system and hormones in our bodies. The responses of the nervous system can be classified as reflex action, voluntary action or involuntary action All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells ( Reseptors). Ear- hearing Nose (olfactory receptors) - detect smell Tongue (gustatory receptors) detect taste Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialised for conducting information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another. A general scheme of how nervous impulses travel in the body. a) Information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell , sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. b) This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. c) At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. d) These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. Test your self Identify the parts of a neuron (i) Where information is acquired__________, (ii) Through which information travels as an electrical impulse___________, and (iii) Where this impulse must be converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission___________.
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Nerve fibres
Sensory
Motor
( afferent)
(efferent)
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Reflex action Reflex Action is Autonomous, Sudden and Involuntary action immediate response of spinal cord. The pathway taken by nerve impulses in a reflex action is called the Reflex Arc.
Reflex arc
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM
HUMAN BRAIN
The brain sits inside a bony box (Cranium). Inside the box, the brain is contained in a fluid-filled (Cerebrospinal fluid) balloon which provides further shock absorption. The vertebral column or backbone protects the spinal cord.
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Human Brain
Fore brain
Mid brain
Hind brain
Two Hemi cerebrum
Pons
Medulla
Cerebellum
Frontal loab
parietal loab
Temporal loab
Occipitl loab
Fore brain- main thinking part
Hind brain : a ) Medulla- involuntary actions including blood pressure, salivation and vomiting b) Cerebellum- precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and balance of the body
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
How does the Nervous Tissue cause Action?
When a nerve impulse reaches the muscle, the muscle fibre move. Muscle cells have special proteins that change both their shape and their arrangement in the cell in response to nervous electrical impulses.
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Peripheral Nervous System
10
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal Hormones in Animals
11
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal Coordination in plants
Movement in Plants
Turgor movement
Tropic movement
Positive tropic movements
Turgour / Nastic movements Induced by stimuli like heat, light, touch etc Dependent on growth Independent of direction of the stimulus
Negative tropic movements
Mimosa pudica ( Sensitive plant)
Plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking, and therefore in changing shapes. Tropic Movement Movement is related to the direction of stimulus known as Tropism. Tropism can be Positive or Negative Independent of growth Types of Tropism Phototropism- stem Geotropism- root Hydrotropism-root
12
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Chemotropism- pollen tube Thigmotropism- tendril
13
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Tendril in contact of support shows less growth ( less auxin at the side of contact) More growth on other side ( more auxin on side away from the support)
PHYTOHORMONES- Plant hormones Plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. They are synthesized at places away from where they act and simply diffuse to the area of action.
Phytohormones
Growth promoters
Growth inhibitors
Auxin
Cytokinin
Gibberellin
Ethylene
Abscisic acid
14
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
15
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
Limitations of Nervous coordination They will reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue. once an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and transmitted, the cell will take some time to reset Its mechanisms before it can generate and transmit a new impulse Advantages of Chemical coordination Hormones diffuse all around the original cell. If other cells around have the means to detect this compound using special molecules on their surfaces, then they would be able to recognise information, and even transmit it. It can be done steadily and persistently A feedback mechanism The timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanisms.
16
Blog: Scienceworkplace.blogspot.com by - Anju Pal
For example, if the sugar levels in blood rise, they are detected by the cells of the pancreas which respond by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
17
You might also like
- Control and Coordination Class NotesDocument13 pagesControl and Coordination Class NotesTripura Neelima100% (2)
- Our Environment Notes Class XDocument7 pagesOur Environment Notes Class XMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: The CellDocument25 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: The CellAnisha PanditNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination MCQDocument6 pagesControl and Coordination MCQSameekshaKashyap80% (5)
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument137 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeSudarshan S KNo ratings yet
- X Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter Notes AugDocument18 pagesX Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter Notes AugAyush Pateria33% (3)
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesMd AurangjebNo ratings yet
- Life Process Class 10 Science NotesDocument19 pagesLife Process Class 10 Science NotesPranav PatilNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- Delhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesDocument54 pagesDelhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesAnin BertNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - CBSE Class 10 BiologyDocument7 pagesLife Processes - CBSE Class 10 BiologyGurukul24x775% (8)
- Lecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesLecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsaditya100% (3)
- 7. HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION: Mendel's Contributions and Laws of InheritanceDocument15 pages7. HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION: Mendel's Contributions and Laws of InheritanceAtharv AggarwalNo ratings yet
- International Chemistry Olympiads PDFDocument38 pagesInternational Chemistry Olympiads PDFReden Jay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination NotesDocument21 pagesControl and Coordination NotesShivraj singhNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument61 pagesCell-The Fundamental Unit of Liferitik100% (1)
- Life Processes - AssignmentDocument3 pagesLife Processes - Assignmentmanol sahooNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Science: Life ProcessesDocument94 pagesScience: Life ProcessesNandhaKumarSNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesleenaapNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFDocument5 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- VASISHTHA GENESIS SCHOOL MCQ ON CELLSDocument6 pagesVASISHTHA GENESIS SCHOOL MCQ ON CELLSprachi pundhirNo ratings yet
- The Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermDocument2 pagesThe Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermJhangir Awan33% (3)
- X-7-Control and CoordinationDocument30 pagesX-7-Control and CoordinationArohan BuddyNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeShivansh Shrivastava100% (1)
- 10th CBSE - Our EnvironmentDocument5 pages10th CBSE - Our EnvironmentAshwin KokilNo ratings yet
- Cell WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell WorksheetSRNo ratings yet
- Puberty Changes in Boys and GirlsDocument47 pagesPuberty Changes in Boys and GirlsAvi :DNo ratings yet
- Grade+10+ +Biology+Revision+Question+ +part+2Document20 pagesGrade+10+ +Biology+Revision+Question+ +part+2MoghanNo ratings yet
- Mineral and Energy ResourcesDocument14 pagesMineral and Energy Resourcesthinkiit100% (1)
- 9th Biology - Chapter 1 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument38 pages9th Biology - Chapter 1 The Fundamental Unit of LifeAbhaya RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11: Force and PressureDocument15 pagesChapter - 11: Force and PressurePraveen MaramNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument28 pagesTransport in PlantsGautam Dayal100% (1)
- Presentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Document13 pagesPresentation Fundamental Unit of Life 1536577024 21871Keerthana RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cell BiologyDocument124 pagesFundamentals of Cell BiologyMadhu SatapathyNo ratings yet
- 1st Term s3 BiologyDocument35 pages1st Term s3 BiologyAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Life Process Chapter QuestionsDocument11 pagesLife Process Chapter QuestionsAdwaith TsNo ratings yet
- Esson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument12 pagesEsson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Class X Biology: Life Processes Chapter NotesDocument18 pagesClass X Biology: Life Processes Chapter NotesSuresh Raghav50% (2)
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsSyed Nazir AhammedNo ratings yet
- Biology Practice TestDocument8 pagesBiology Practice TestSir Jerome NatividadNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue PDFDocument63 pagesPlant Tissue PDFJitendra Kumar100% (1)
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Force And Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes Revision NotesDocument19 pagesForce And Laws Of Motion Class 9 CBSE Notes Revision Notesagain Kumar bisoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes - Our Environment - Class 10 Science - PANTOMATHDocument9 pagesChapter Notes - Our Environment - Class 10 Science - PANTOMATHsourav9823No ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Life ProcessDocument11 pagesClass 10 Life ProcessShubham Tiwari100% (2)
- Diversity in The Living WorldDocument17 pagesDiversity in The Living WorldRiya Singh100% (1)
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument17 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsGaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life WorksheetThe Shikshak100% (1)
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocument16 pagesLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMSDocument13 pagesComprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMSPranjal ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Short ConceptsDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesis Short Conceptsauguste noe100% (2)
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesDocument34 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesAnubhav MamgainNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument39 pagesBiology NotesdarakhshanNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table and ElementsDocument54 pagesThe Periodic Table and Elementsapi-326727127No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Transport in MammalsDocument119 pagesChapter 8 - Transport in Mammalsapi-3728508100% (1)
- Reproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8Document8 pagesReproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8anjupalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination - Class XDocument7 pagesControl & Coordination - Class XanjupalNo ratings yet
- Science Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFDocument13 pagesScience Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFanjupalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFanjupal80% (5)
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument16 pagesHeredity and EvolutionanjupalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Human BeingsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Human BeingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy - Class XDocument9 pagesSources of Energy - Class XanjupalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Improvement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind MappingDocument12 pagesImprovement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind Mappinganjupal83% (6)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plantsanjupal100% (2)
- HeatDocument11 pagesHeatanjupalNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint - Vivek - X-ADocument33 pagesCarbon Footprint - Vivek - X-AanjupalNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument11 pagesImprovement in Food Resourcesanjupal100% (2)
- Force and Laws of MotionDocument20 pagesForce and Laws of MotionanjupalNo ratings yet
- Cell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesCell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeanjupalNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesanjupalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument19 pagesNutrition in AnimalsanjupalNo ratings yet
- L-8 Motion: List of ConceptsDocument11 pagesL-8 Motion: List of ConceptsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument8 pagesNutrition in PlantsanjupalNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument28 pagesLife Processesanjupal100% (1)
- Yuval T Plos 2007 PDFDocument14 pagesYuval T Plos 2007 PDFVasanthan RajuNo ratings yet
- Bacterial StainingDocument11 pagesBacterial StainingSanju mishraNo ratings yet
- JKJKJKJDocument3 pagesJKJKJKJPaolo DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Sex - How Genes and Gender Influence Our Relationships (1997) by David P. Barash & Judith Eve LiptonDocument244 pagesMaking Sense of Sex - How Genes and Gender Influence Our Relationships (1997) by David P. Barash & Judith Eve LiptonGoosvieNo ratings yet
- Laminine - The Symbol of Life and RenewalDocument44 pagesLaminine - The Symbol of Life and RenewalNoel NievesNo ratings yet
- Biology Ia IbdpDocument10 pagesBiology Ia Ibdpzain ahmedNo ratings yet
- Biology ObjectivesDocument12 pagesBiology ObjectivesDerek CastroNo ratings yet
- Course List For The Bachelor of Pharmacy (Honours) - My - UQ - The University of Queensland, AustraliaDocument2 pagesCourse List For The Bachelor of Pharmacy (Honours) - My - UQ - The University of Queensland, AustraliaLy Huyen TranNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Baptist Hospital: Laboratory ResultsDocument3 pagesBangalore Baptist Hospital: Laboratory ResultskavyaksNo ratings yet
- Synapse Structure and Function ExplainedDocument11 pagesSynapse Structure and Function ExplainedMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Deciphering The Diversity and History of New Worldnightjars (Aves Caprimulgidae) Usingmolecular PhylogeneticsDocument40 pagesDeciphering The Diversity and History of New Worldnightjars (Aves Caprimulgidae) Usingmolecular PhylogeneticsDavid RDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BotanyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To BotanyJulianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document5 pagesChapter 5 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20prat.medbooksNo ratings yet
- WARRIER-Some Important Medicinal Plants of The Western Ghats, India, A Profile (2001) PDFDocument408 pagesWARRIER-Some Important Medicinal Plants of The Western Ghats, India, A Profile (2001) PDFJuanManuelAmaroLuisNo ratings yet
- Biuret Test for ProteinsDocument2 pagesBiuret Test for ProteinsEmily Nowak73% (11)
- Deng Et Al., 2021-Compressed-1Document17 pagesDeng Et Al., 2021-Compressed-1Dacheng LiangNo ratings yet
- The Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in HumansDocument4 pagesThe Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in HumansTrashun LacailladeNo ratings yet
- RNA Therapeutics: How Far Have We Gone?: Maria Francisca Coutinho, Liliana Matos, Juliana Inês Santos, and Sandra AlvesDocument45 pagesRNA Therapeutics: How Far Have We Gone?: Maria Francisca Coutinho, Liliana Matos, Juliana Inês Santos, and Sandra AlvesIgor BatistaNo ratings yet
- Super 20 Ch-7 Control & Coordination Class 10 Science (2) YeahhhhhDocument2 pagesSuper 20 Ch-7 Control & Coordination Class 10 Science (2) Yeahhhhhkamalkandpal4848No ratings yet
- Principle: An Atom Is Most Stable When Its Outermost: CELL BIOLOGY © Gerald Karp, John Wiley and Sons - Chapter 1Document7 pagesPrinciple: An Atom Is Most Stable When Its Outermost: CELL BIOLOGY © Gerald Karp, John Wiley and Sons - Chapter 1Jasper PanosoNo ratings yet
- LSM4225-1 CytogeneticsDocument63 pagesLSM4225-1 CytogeneticseveNo ratings yet
- Major Catalogue Complet PDFDocument237 pagesMajor Catalogue Complet PDFHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- P4 EnzymeDocument44 pagesP4 EnzymeJames Allen100% (1)
- Human Impact On The Microbiological Water Quality of The RiversDocument6 pagesHuman Impact On The Microbiological Water Quality of The Riversaddisu maruNo ratings yet
- Torres Guzmán Moncayo Year 8Document18 pagesTorres Guzmán Moncayo Year 8John OsborneNo ratings yet
- Cissus Populnea (Guill & Perr)Document4 pagesCissus Populnea (Guill & Perr)Oladipupo Adejumobi LawalNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Made By: Roll No.: ClassDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: Made By: Roll No.: ClassChiranjiv KarkeraNo ratings yet
- Nano Today: Marcel Alexander Heinrich, Byron Martina, Jai PrakashDocument21 pagesNano Today: Marcel Alexander Heinrich, Byron Martina, Jai Prakashvishal makadiaNo ratings yet
- Bioplastic A Bettter Alternative For Sustanable FutureDocument72 pagesBioplastic A Bettter Alternative For Sustanable FutureShanaiah Charice GanasNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Environmental Monitoring by Settle Plate MethodDocument2 pagesProcedure For Environmental Monitoring by Settle Plate Methodejazmaqsood100% (1)