Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Erp From Aim-Oum
Uploaded by
redroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Erp From Aim-Oum
Uploaded by
redroCopyright:
Available Formats
ERP From AIM (RICE) To OUM (CEMLI)
Recently i am confused with terms "Customization", "Extension" and "Personalization", so i serached in google find so many definitions. Here is the Details AIM (Applications Implementation Methodology) OUM (Oracle Unified Method) OUM is Oracle's Method Integration Strategy. It supports methods currently being used by Oracle customers including - Compass, AIM, ABF, Siebel. OUM has been developed as a single, integrated method to support the entire Oracle ecosystem and across the complete suite of Oracle products. The aim is to decommission all legacy methods as every Oracle product group transitions to OUM. OUM is product and technology agnostic. Oracle is evolving the Oracle Unified Method (OUM) to achieve the vision of supporting the entire Enterprise IT Lifecycle, including support for the successful implementation of every Oracle product. OUM replaces Legacy Methods, such as AIM Advantage, AIM for Business Flows, EMM Advantage, PeopleSoft's Compass, and Siebel's Results Roadmap. OUM provides an implementation approach that is rapid, broadly adaptive, and business-focused. OUM includes a comprehensive project and program management framework and materials to support Oracle's growing focus on enterprise-level IT strategy, architecture, and governance. While implementing an Oracle ERP system to a client, to meet the client requirements a consultant needs to make changes to original Vanila system (Unchanged Oracle ERP Implemented system). The changes made to Original Oracle ERP comes under RICE components. RICE During an implementation, development of RICE components involves: 1. Creation of Reports that are not available as standard reports in the oracle apps modules. 2. Creation of the Interfaces to external systems. 3. Creation of Conversion programs to transfer data from a legacy system to the new system. 4. Enhancements (or extensions) to the existing system to add additional functionality to existing system without disturbing the core software functionality of the system. RICE terminology has been introduced by Oracle Corporation and later some Oracle consultants has added their own flavor and introduced some other terminologies like FRICE and RICEW. FRICE stands for Forms, Reports, Interfaces, Conversions and Enhancements / Extensions
RICEW stands for Reports, Interfaces, Conversions, Enhancements / Extensions and Workflows Documenting terminology for RICE components AIM (Applications Implementation Methodology) is documenting structure introduced by Oracle Corporation which is used through out the life cycle of a RICE component object. Process in AIM methodology includes approval to develop, functional design specification, technical design specification, coding, testing and implementation. CEMLI later in 2007, in Release 12 Oracle corporation has extended the RICE components and introduced a new terminology called CEMLI components. CEMLI is an ERP software extension framework provided in Oracle Applications by Oracle Corporation. CEMLI Stands for Configurations/Customization, Extension, Modification, Localization, and Integration. "Oracle defined the CEMLI Framework, which translates into 20 classes of extensions that customers can add to their Oracle systems." The framework was established by Oracle On Demand to categorize customizations, meaning software that had to be added by the customer or implementer to the Oracle applications. Configurations : Configure the existing, pre-built application features according to your clients requirement.Changing setups and profile values can be the example of configurations. Customization : Customization means altering/changing the standard objects or creation of custom object to meet clients business need. It may be Extensions or Modifications. Extensions : Extension means creating custom code from scratch, existing objects (views, packages and java classes etc) can be used. It is having different behaviour from seeded one. Modifications : Modifications is enhancing/changing the existing code to meet the clients requirements. It is the modification of seeded behaviour. Localization : It is to define the different legislative support provided by oracle Applications based on country/region/language requirements. Integration : It can be Data Integration or Application Integration, options for these two are Open Interface tables, APIs, EAI(Enterprise Application Integration Tools), BPEL, AQ, EDI etc.
OUM (Oracle Unified Method) which is introduced by Oracle corporation after 2007 to standardize the documentation process for almost all products from oracle which includes Business Intelligence (BI) and Enterprise Performance Management (EPM), WebCenter, Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), Application Integration Architecture (AIA), Business Process Management (BPM), Enterprise Integration and Custom Software.
OUM Project Phases : The Workflows within an OUM project are categorized into five phases: Inception, Elaboration, Construction, Transition, and Production. These phases are described below: (A) Phase I: Inception :As the first phases in the project life cycle.Major goal of this phase is to achieve concurrence among all stakeholders on the lifecycle objectives for the project. Kick off's, review , high-level business requirements along with initial project plan is being targeted in this phase only. (B) Phase II: Elaboration :This is the second phases in the project life cycle, where major focus would be to develop the detailed requirements models, partition the solution, develop functional prototyping, and baseline the architecture of the system. (C) Phase III: Construction :As the third phases in the project life cycle, Construction focuses on design, implementation, and testing of functions to develop a complete system. (D) Phase IV: Transition :This typically consist from installation onto the production system through the UAT and launch of the live application, open and ready for business. (E) Phase V: Production : The goal of the Production phase is to operate the newly developed system, assess the success of the system, and support the users. This includes: monitoring the system; acting appropriately to ensure continued operation; measuring system performance; operating and maintaining supporting systems; responding to help requests, error reports and feature requests by users; and managing the applicable change control process so that defects and new features are prioritized and assigned to future releases.
ID
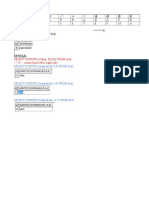
RD.001 RD.005 RD.011 RD.030
Work Product Objectives Detail Business and System Business and System Objectives Objectives Document Requirements Create System Context Diagram System Context Diagram Develop Future Process Model Future Process Model Develop Current Business Process Model Current Process Model
Task
Template Business and System Objectives System Context Diagram Future Process Model Current Process Model
RD.045 RD.065 RA.023 RA.024
Prioritize Requirements (MoSCoW) Develop Domain Model (Business Entities) Develop Use Case Model Develop Use Case Details
MoSCoW List Domain Model
MoSCoW List-Excel, MoSCoW List-Word, Generic Workshop Notes, Generic Workshop Schedule, and Workshop Preparation Notes Domain Model Use Case Model, Visio Template and Stencil Use Case Specification Validated Functional Prototype Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Validated Functional Prototype Business Data Structure Setups Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Application Setup Documents Analysis Model Refer to the Task Overview for guidance.
Use Case Model Use Case Specification Map Requirements Mapped Business Requirements Application Extension Definition and Estimates Gap Resolutions Functional Prototype Validated Functional Prototype Configure Business Data Structure Setups Business Data Structures
AN.010 AN.020 AN.030 IM.010 RA.085 DS.010 RA.040 DS.030 AN.050 AN.060
Map Business Requirements Define and Estimate Application Extensions Define Gap Resolutions Develop Functional Prototype Validate Functional Prototype
Define Business Data Structure Setups Define Business Data Structures
Define Application Setups Application Setup Documents Analyze and Design Components Analyze Data Data Analysis Analyze Behavior Behavior Analysis
AN.090 DS.080 DS.090 DS.100 DS.130 DS.150
Analyze User Interface Design Software Components Design Data Design Behavior Component Design User Interface Develop Database Design
User Interface Analysis Software Component Design Component Data Design Behavior Design
User Interface Design Logical Database Design Implement Components Conceptual Prototype Implemented Database Implemented Components Assembled Components Integrate Integrated Services Test Unit-Tested Components Test Integration-Tested Components System-Tested Applications Integration-Tested System
Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Logical Database Design Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Physical Database Design Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Refer to the Task Overview for guidance. Integration Test Results System Test Results Systems Integration Test Results
IM.005 IM.040 IM.050 IM.070
Develop Conceptual Prototype Implement Database Implement Components Assemble Components
IM.080
Integrate Services
TE.030 TE.040 TE.070 TE.100
Perform Unit Test Perform Integration Perform System Test Perform Systems Integration Test
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- B2PLUS UNIT 6 Test Answer Key HighDocument2 pagesB2PLUS UNIT 6 Test Answer Key HighАндрій НікітінNo ratings yet
- YSUUSYs NiCd Battery RepairDocument6 pagesYSUUSYs NiCd Battery Repairrwesseldyk50% (2)
- Canna DispensariesDocument35 pagesCanna DispensariesWaf Etano100% (1)
- Mahmoud Muhammad Elasry: EducationDocument5 pagesMahmoud Muhammad Elasry: EducationredroNo ratings yet
- What Are The Interfaces in Oracle Project Costing andDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Interfaces in Oracle Project Costing andredroNo ratings yet
- Sales TaxDocument2 pagesSales TaxredroNo ratings yet
- M OrgDocument13 pagesM OrgpolimersubbuNo ratings yet
- 11 - 10 - 9 - 8 - 7 - 6 - 5 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 1 J A Y A P R A K A S H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 L R SELECT 'Jayaprakash' FROM DualDocument1 page11 - 10 - 9 - 8 - 7 - 6 - 5 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 1 J A Y A P R A K A S H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 L R SELECT 'Jayaprakash' FROM DualredroNo ratings yet
- Flexfields in Oracle HRMSDocument6 pagesFlexfields in Oracle HRMSredroNo ratings yet
- Top CommandDocument1 pageTop CommandredroNo ratings yet
- Apps Modules RelationDocument1 pageApps Modules RelationredroNo ratings yet
- Shipping Transactions Form Action Bar Greyed OutDocument1 pageShipping Transactions Form Action Bar Greyed OutredroNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Programs CollectionDocument7 pagesPLSQL Programs CollectionredroNo ratings yet
- Advanced PLSQL - UpdatedDocument81 pagesAdvanced PLSQL - UpdatedredroNo ratings yet
- Preface in This Book I Have Explained About A Complete Beginners Guide For Oracle Apps. Hope This Will Be A Great Start For BeginnersDocument209 pagesPreface in This Book I Have Explained About A Complete Beginners Guide For Oracle Apps. Hope This Will Be A Great Start For BeginnersredroNo ratings yet
- System Administration User GuideDocument472 pagesSystem Administration User GuideRizwan233No ratings yet
- Course Topics v1.2Document3 pagesCourse Topics v1.2redroNo ratings yet
- InterfacesDocument4 pagesInterfacesredroNo ratings yet
- InterfacesDocument4 pagesInterfacesredroNo ratings yet
- H.V.S.Vara Prasad Email: Mobile: 8688330479Document2 pagesH.V.S.Vara Prasad Email: Mobile: 8688330479redroNo ratings yet
- Oracle Projects Is Suite of Modules Which CombinesDocument8 pagesOracle Projects Is Suite of Modules Which CombinesredroNo ratings yet
- Room 1 Innovinit (To Everyone) : Room 1 Innovinit (To Everyone) : Nanda (To Everyone)Document1 pageRoom 1 Innovinit (To Everyone) : Room 1 Innovinit (To Everyone) : Nanda (To Everyone)redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-03-22 03 53Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-03-22 03 53redroNo ratings yet
- Start MenuDocument6 pagesStart MenuredroNo ratings yet
- Room2 Innovin (To Everyone) : Room2 Innovin (To Everyone) :: Best-Practices/ Manufacturing?next - Slideshow 1Document1 pageRoom2 Innovin (To Everyone) : Room2 Innovin (To Everyone) :: Best-Practices/ Manufacturing?next - Slideshow 1redroNo ratings yet
- Start MenuDocument1 pageStart MenuredroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-03 23 45Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-03 23 45redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-09 23 52Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-09 23 52redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-18 23 54Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-18 23 54redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-10 23 47Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-10 23 47redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-18 23 54Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-18 23 54redroNo ratings yet
- ChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-17 23 58Document1 pageChatLog 1750 Oracle SCM Prakash Teja 7 00am IST 2018-04-17 23 58redroNo ratings yet
- PL/SQL Runtime Engine: Without Bulk Bind Oracle ServerDocument2 pagesPL/SQL Runtime Engine: Without Bulk Bind Oracle ServerredroNo ratings yet
- Ce125-2500 Open FrameDocument48 pagesCe125-2500 Open FrameRomão OliveiraNo ratings yet
- History shapes Philippine societyDocument4 pagesHistory shapes Philippine societyMarvin GwapoNo ratings yet
- Socio-cultural influences on educationDocument4 pagesSocio-cultural influences on educationofelia acostaNo ratings yet
- Turabian Sample PaperDocument9 pagesTurabian Sample Paperemme_lopez908133% (3)
- Soft StarterDocument6 pagesSoft StarterEric Maglinte TolosaNo ratings yet
- Historical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentDocument5 pagesHistorical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentMark Saldie RoncesvallesNo ratings yet
- Marketing Budget: Expenses Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Totals Budget %Document20 pagesMarketing Budget: Expenses Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Totals Budget %Miaow MiaowNo ratings yet
- Occupant Load CalculationsDocument60 pagesOccupant Load CalculationsKAIVALYA TIWATNENo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past SimpleDocument11 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past Simplealmastar officeNo ratings yet
- Ifatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesIfatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFCondor GuatonNo ratings yet
- Technology & Livelihood Education: WEEK 6-7Document28 pagesTechnology & Livelihood Education: WEEK 6-7my musicNo ratings yet
- BBRC4103 - Research MethodologyDocument14 pagesBBRC4103 - Research MethodologySimon RajNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6Document226 pagesManual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6rsp filmes100% (1)
- Management and Breeding of Game BirdsDocument18 pagesManagement and Breeding of Game BirdsAgustinNachoAnzóateguiNo ratings yet
- Mini Centre CatalogDocument26 pagesMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyNo ratings yet
- Business Plan1Document38 pagesBusiness Plan1Gwendolyn PansoyNo ratings yet
- Health Information SystemDocument11 pagesHealth Information SystemVineeta Jose100% (1)
- Psalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFDocument129 pagesPsalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFirrrs100% (1)
- Teaching Support Untuk Managemen HRDocument102 pagesTeaching Support Untuk Managemen HRFernando FmchpNo ratings yet
- Amna Hameed: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesAmna Hameed: ObjectiveSabrina GandapurNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing & IdentityDocument218 pagesAcademic Writing & IdentityGustavo RegesNo ratings yet
- Clustering Social Network GraphsDocument12 pagesClustering Social Network GraphsRáhùl SréédhãrNo ratings yet
- Connection Between Academic and Professional IntegrityDocument3 pagesConnection Between Academic and Professional IntegrityJoshua NyabindaNo ratings yet
- Manual EDocument12 pagesManual EKrum KashavarovNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenic Basis of Malaria: InsightDocument7 pagesThe Pathogenic Basis of Malaria: InsightRaena SepryanaNo ratings yet
- Financial Services : An OverviewDocument15 pagesFinancial Services : An OverviewAnirudh JainNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument23 pagesANAPHYYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet