Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MPLS Terms: (Label Stacking)
Uploaded by
Makaran PatilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MPLS Terms: (Label Stacking)
Uploaded by
Makaran PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
MPLS Terms: (Label Stacking) POP Tag: Removes the top label in the MPLS label stack and
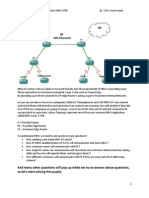
propagates the remaining payload as either labeled packet or as an unlabeled packet. SWAP Tag: Replaces the top label in the MPLS label stack with another value. PUSH Tag: Replaces the top label in the MPLS label stack with a set of labels. AGGREGATE: Removes the top label in the MPLS label stack and does a layer 3 lookup on an underlying IP packet. The removed label is the bottom label in the MPLS label stack. Otherwise datagram discarded. UNTAG: Removes the top label in the MPLS label stack and forward IP packet to the specified IP next-hop. What 1. 2. 3. are advantages of MPLS? Traffic Engineering and QoS Reservation of bandwidth. Label swapping.
Why MPLS is fast? 1) MPLS label swapping is faster because 4. It is exact match unlike IP longest prefix match. 5. LFIB is much smaller as compare long original IP look up table. LDP establisted process? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. router that have highest ip address initiate tcp session with the others. hello packet sent by mpls enable interface on multicast ip address 224.0.0.2 other router mpls enable interface established tcp session. then the source ip address send initialization message to others. others also send initialization message to highest ip address router. lowest one also send Keepalive message to highest ip address router. After received first Keepalive, session is ready to exchange labels.
What is difference between Frame-relay and MPLS? 1. What are the company's WAN objectives? o Does company simply need to connect remote offices to a central location for server resource access? o Are there any critical applications such as voice that must run across the WAN? 2. Is cost a primary decision factor? 3. How much bandwidth do I really need? Frame Relay: 1. You require a private network but do not want to pay for dedicated private links to each location, you may consider Frame Relay. 2. Frame Relay is a cost effective technology when cost is a factor, you can pay for a lower rate of bandwidth than with a dedicated point to point link. 3. Frame Relay has no quality of service (QoS). MPLS: 1. If you have Quality of Service (QoS) sensitive applications running across your WAN then you should consider MPLS. 2. The primary difference with MPLS is that you can purchase quality of service for applications across your WAN. 3. During the provisioning process the carrier will order to determine which applications are important to your business, they will then build a QoS template to service these applications on your WAN. These applications will be given priority over all other traffic in times of peak load.
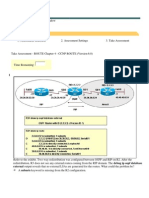
How packets travel in MPLS between two CE routers?
1. When packet arrive from customer end router at ingress point of the MPLS domain, a. FIB table on edge LSR router A contains the entry for the destination network X that is mapped to the IP next hop address. b. At this time next hop label not available, so all packets are forwarded in traditional IP fashion. Routing Table of Edge LSR RA Network Next-Hop X B 2. LSR Router-B generates a locally unique label 25 and assigned to network X. a. When a label is assigned to an IP prefix it is stored in two tables. i. LIB: Used to maintain mapping between IP prefix (network X) and local label (25), and the next hop label (Not yet available). ii. LFIB: Modified to contain the local label mapped to the POP action. POP is used until the next hop label is received from the down stream router (router C). Routing Table of LSR RB Network Next-Hop X C LIB on LSR Router B Network LSR Label X Local 25 LFIB on LSR Router B Label Action Next Hop 25 POP C b. LSR Router (B) propagates this label 25 to all adjacent neighbors, where this label can be used as a next hop. LIB on Router A & C Network LSR Label X B 25 c. Label 25 found in the FIB table of edge LSR Router A is used to label packets. FIB On Router A Network Next Hop Label X B 25 d. LSR Router B must remove the label because LSR B not yet received any next-hop label (the action is POP).
3.
4. 5. 6. LIB:
e. LSR Router B performs label switching in which Label is removed and normal IP packet is sent out of LSR Router B. Edge Router C advertise label 47for the network X and it sent to all adjacent routers, including LSR Router B. LIB on Edge Router C Network LSR Label X B 25 Local 47 LFIB on Edge Router C Label Action Next Hop 47 POP D LIB on LSR Router B Network LSR Label X Local 25 C 47 FIB on LSR Router B Network Next Hop Label X C 47 LFIB on LSR Router B Label Action Next Hop 25 47 C Edge LSR Router C still no next hop label. Label 47 is therefore still mapped to the POP action. Edge LSR Router C removes the label on the egress MPLS domain and forwards the packet to router D (Using LFIB table). Network X is directly connected on Customer end Router. IP to label FIB CE to PE CEF Switching Ingress Routers. Packet to Packet LFIB PE to PE Label Switching (By using LFIB Table). Label to IP LFIB PE to CE Egress Routers.
LDP & TDP in the control plane exchange labels & store them into the LIB. This information is then used in data plane to provide MPLS function. LFIB: FIB: Used to forward receive IP packet to IP packet and labeled IP packets. Used to forward packets based on the labels.
DSCP: Differentiated Service Code Point
Traffic classes are identified by the value of the DSCP value. VSNL Backbone QoS Policy Policing Bandwidth Configured 75000 6750 119250 60750 38250 300000 Total POS BW Queuing B/w in % Priority 3 53 27 17 100 Total POS BW in % Class Class Real Time Control Multimedia Business default Marking Precedence 5 6 4 3 2 1 0 Dropping Queue Limit Min Max
5000 4167 4167 3333 2500
7500 6667 6667 5833 5000
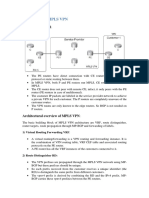
RD: Route Distingutier: RD is used to transform nonunique 32-bit customer ip address IPv4 addresses into unique 96-bit VPNv4 addresses. RT: Route target: RTs are attributes that are attached to VPNv4 BGP route to indicate its VPN membership. The extended BGP community of a routing is used to carry RT of that update, thus identifying which VPN the update belongs to. MPBGP: VPNv4 addresses are exchanged between PEs routers only. BGP between PE routers must support IPv4 and VPNv4. A BGP session PE routers is called MPBGP session.
OSPF Super Backbone: The MPLS VPN architecture extends the OSPF by introducing another backbone called Super backbone. The OSPF super backbone is implemented with
MPBGP between PE routers, its completely transparent to the OSPF routers. The Super backbone allows disjoint OSPF backbone areas (area 0) at MPLS VPN customer sites. 1. Super backbone shall not use standard OSPF-BGP redistribution. 2. Internal OSPF routes must remain internal OSPF routes. 3. External OSPF routes must remain external OSPF routes. 4. OSPF metrics and metric types (external 1 or external 2) have to be preserved. 5. PE routers set down bit when redistributing routes from MPBGP to OSPF. Business VPN Classifications: 1. Intra-organization (intranet) 2. Communication with other organization (extranet) 3. VPDN Types of VPN network topologies: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Hub-and-spoke Partial-or-Full mesh Hybrid Simple extranet Central service VPDN Network Managed Network
OSPF PE CE Config / redistribute BGP router ospf 250 vrf V798:DHL-VPN log-adjacency-changes
redistribute bgp 4755 subnets network 10.70.3.132 0.0.0.3 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.70.3.136 0.0.0.3 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.70.3.156 0.0.0.3 area 0.0.0.1 address-family ipv4 vrf V798:DHL-VPN redistribute connected redistribute static redistribute ospf 250 vrf V798:DHL-VPN metric 1 match internal external 1 external 2 no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family BGP PE CE Config Config. address-family ipv4 vrf V3099:DHL-TCS-EXT-etc redistribute connected neighbor 10.70.3.26 remote-as 65500 neighbor 10.70.3.26 activate neighbor 10.70.3.26 send-community neighbor 10.70.3.26 as-override neighbor 10.70.3.26 route-map setLP in no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family ip vrf V3099:DHL-TCS-EXT-etc rd 4755:13062 export map grey_mgmt_vpn_TATA_VSNL_BROADBAND_V3099:DHL-TCS-EXT-etc route-target export 4755:10153 route-target export 4755:10475 route-target import 4755:10011 route-target import 4755:10153 route-target import 4755:10475 ! ip vrf V634:DHL-VPN rd 4755:10614 export map grey_mgmt_vpn_TATA_VSNL_BROADBAND_V634:DHL-VPN route-target export 4755:10153 route-target import 4755:10011 route-target import 4755:10153 !
Label Distribution Parameters 1. Label Space options:
a. b. 2. Label a. b. 3. Label a. b. 4. Label a. b.
Per interface label space where labels must be unique for the interface. Per platform label space where label must unique for entire platform. generation and distribution Unsolicited downstream distribution labels is used in frame-mode MPLS where all routers are generate local label and propagate those label to all adjacent routers. (Ex. Frame-mode) Down steam on demand distribution of labels is used cell mode MPLS where ATM LSR have to request a label for destination found in the IP routing table. allocations: Frame mode MPLS uses independent control mode where all routers can start propagating labels independently to others. Cell mode MPLS requires LSR to ready have the next hop label if they want to propagate the label to others and this is called ordered control mode. distribution Frame mode MPLS may receive multiple labels but only one is used. Others are kept in LIB. This is called Liberal label retention mode. Cell mode only keeps label that are requested. This is called conservative label retention mode.
You might also like
- MPLSDocument15 pagesMPLSnaveen.anjeriNo ratings yet
- Mpls VPN: Nguyen Hoang Minh Chiem Thach PhatDocument38 pagesMpls VPN: Nguyen Hoang Minh Chiem Thach PhatLala NguyenNo ratings yet
- Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) : Manoj Wadhwa 18 Oct 2008Document52 pagesMulti Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) : Manoj Wadhwa 18 Oct 2008Bon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Multiprotocol Label SwitchingDocument13 pagesMultiprotocol Label SwitchingAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Mpls Lab 2 - Mpls VRF VpnsDocument13 pagesMpls Lab 2 - Mpls VRF VpnsSo ManiNo ratings yet
- CCIE SP Notes For LabDocument252 pagesCCIE SP Notes For LabAsif DarveshNo ratings yet
- Mpls InertviewDocument22 pagesMpls InertviewAbu FadilahNo ratings yet
- Yasser Auda Cciev5 Mpls Guide (LDP, VRF Lite, Mpls VPN)Document65 pagesYasser Auda Cciev5 Mpls Guide (LDP, VRF Lite, Mpls VPN)Muhammad Ali100% (2)
- ROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document12 pagesROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (5)
- MPLS & MPLS VPN10Document35 pagesMPLS & MPLS VPN10Kunio KunNo ratings yet
- OSPF Routing in MikroTik PDFDocument48 pagesOSPF Routing in MikroTik PDFAung Myo TunNo ratings yet
- Introducing MPLS Networks: Implementation of Frame Mode MPLSDocument100 pagesIntroducing MPLS Networks: Implementation of Frame Mode MPLSrajkumarlodhNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument751 pagesNotesusertestNo ratings yet
- Established? One Session Forward The Traffic of Customers or Not?Document16 pagesEstablished? One Session Forward The Traffic of Customers or Not?ntrimcevicNo ratings yet
- Network Virtualization LISP, OMP, and BGP EVPN Operation and Interaction Toni PasanenDocument122 pagesNetwork Virtualization LISP, OMP, and BGP EVPN Operation and Interaction Toni PasanenÅlex TurciosNo ratings yet
- MPLS - Unicast IP ForwardingDocument9 pagesMPLS - Unicast IP ForwardingMohamed Oussema DerradjiNo ratings yet
- MPLS TermsDocument8 pagesMPLS Termsgbabar121No ratings yet
- Ab - MPLS VPNDocument41 pagesAb - MPLS VPNarbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Label SwitchingDocument9 pagesLabel SwitchingAYENEWNo ratings yet
- MPLS JuniperDocument37 pagesMPLS JunipersiddharthNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MPLS - BRKMPL-1100Document78 pagesIntroduction To MPLS - BRKMPL-1100innovativekalu100% (1)
- Assignment 2 MasetwalDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 MasetwalEstifanos EndalewNo ratings yet
- Intra-AS and Inter-AS Routing: GatewaysDocument31 pagesIntra-AS and Inter-AS Routing: GatewaysCristian RamosNo ratings yet
- CCNA Practice Final PDFDocument21 pagesCCNA Practice Final PDFBachi BachiNo ratings yet
- Nokia Practice Exam For Nokia Multiprotocol Label Switching (4A0 103) Document ENDocument16 pagesNokia Practice Exam For Nokia Multiprotocol Label Switching (4A0 103) Document ENPadawan ingéNo ratings yet
- 20111110 - CHT - TL - 教育訓練 Day5Document58 pages20111110 - CHT - TL - 教育訓練 Day5劉博仁No ratings yet
- Basic Routing Lab: Topology of Module 1Document9 pagesBasic Routing Lab: Topology of Module 1NwankwoNo ratings yet
- CCNP Bsci Final PDFDocument18 pagesCCNP Bsci Final PDFAngel Mauricio Mercado AguirreNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networking & SecurityDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking & SecurityAhmed Hamed BadrNo ratings yet
- 16 - Cisco IOS XR MPLS Operation and Implementation - Student Learning Guide v5.0 - Word-DPDocument50 pages16 - Cisco IOS XR MPLS Operation and Implementation - Student Learning Guide v5.0 - Word-DPDúber PérezNo ratings yet
- MPLS Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute - Link Protection: Feature OverviewDocument24 pagesMPLS Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute - Link Protection: Feature OverviewilialisseNo ratings yet
- Practice CCNA 200-120Document22 pagesPractice CCNA 200-120vadmanhNo ratings yet
- Prod Presentation0900aecd8031204cDocument173 pagesProd Presentation0900aecd8031204c1philipsNo ratings yet
- CCIE Boothcamp MPLS Peter MesjarDocument44 pagesCCIE Boothcamp MPLS Peter MesjardwthomasNo ratings yet
- MPLS OverviewDocument61 pagesMPLS OverviewprodigynaveenNo ratings yet
- CCNA ICND2 CheatsheetDocument10 pagesCCNA ICND2 CheatsheetLulzim BruçajNo ratings yet
- Multi-Protocol Label Switch (MPLS) : Overview and Short TutorialDocument30 pagesMulti-Protocol Label Switch (MPLS) : Overview and Short TutorialMuhammad Daniyal Ahmed BaigNo ratings yet
- 12 - MPLSDocument30 pages12 - MPLSMuhammad Daniyal Ahmed BaigNo ratings yet
- MPLS Fundamentals and MPLS L2/L3 VPN Concepts.: AgendaDocument10 pagesMPLS Fundamentals and MPLS L2/L3 VPN Concepts.: AgendaRitesh Kumar TripathiNo ratings yet
- MPLS PDFDocument127 pagesMPLS PDFLarbi DoubajiNo ratings yet
- CCIE RS Quick Review KitDocument63 pagesCCIE RS Quick Review KitJaime LuqueNo ratings yet
- Lab - Mpls Te With Per VRFDocument16 pagesLab - Mpls Te With Per VRFRuben VillafaniNo ratings yet
- BRKMPL 3124Document129 pagesBRKMPL 3124abc123No ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSFrom EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- MarginDocument5 pagesMarginMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- 4th History MarDocument140 pages4th History MarMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Yojana March 2014Document56 pagesYojana March 2014Vedadnya AghorNo ratings yet
- BER Analysis of Wavelet Based OFDM Using Different Modulation TechniquesDocument5 pagesBER Analysis of Wavelet Based OFDM Using Different Modulation TechniquesMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Makaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Aicte Parakh - Students - Registration Process - User ManualDocument7 pagesAicte Parakh - Students - Registration Process - User ManualMakaran Patil100% (1)
- Analysis of Bit Error Rate For OFDM in LTEDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Bit Error Rate For OFDM in LTEMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Yojana March 2014Document56 pagesYojana March 2014Vedadnya AghorNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Delay and Slew: Subject: System On Chip Presented by Makarand PatilDocument12 pagesFactors Affecting Delay and Slew: Subject: System On Chip Presented by Makarand PatilMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Web InterconnectsDocument60 pagesWeb InterconnectsThee TeeNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing in Wireless Communication Systems: A ReviewDocument5 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing in Wireless Communication Systems: A ReviewmonuchaudhariNo ratings yet
- Yojana August15Document42 pagesYojana August15Makaran PatilNo ratings yet
- MCX Daily MarginDocument3 pagesMCX Daily MarginMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Interview Answer.Document2 pagesInterview Answer.Makaran Patil0% (2)
- F Y B A G 1 NotesDocument9 pagesF Y B A G 1 NotesMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- MCX Margin ReportDocument3 pagesMCX Margin ReportMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- MPSC Books ListDocument9 pagesMPSC Books ListPravin Salunkhe100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentCristina Aida MusatNo ratings yet
- Steve Nison Japanese Candlestick Charting TechniquesDocument316 pagesSteve Nison Japanese Candlestick Charting TechniquesDPFL_Invest96% (84)
- Mcx-Currency Margin ReportDocument1 pageMcx-Currency Margin ReportMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- F Y B A Functional English NotesDocument18 pagesF Y B A Functional English NotesMakaran Patil100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Speeder JohnNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management System VBDocument22 pagesHospital Management System VBkumarvj15No ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument7 pagesSwitchingMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- Net AdminDocument9 pagesNet AdminMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- OSPFDocument9 pagesOSPFMakaran PatilNo ratings yet
- UCS-4785 - UCS Fast Facts (2012 San Diego) - 1 Hour - OKDocument89 pagesUCS-4785 - UCS Fast Facts (2012 San Diego) - 1 Hour - OKaaajjj jjjaaaNo ratings yet
- Common Network Attacks: David J. MarchetteDocument107 pagesCommon Network Attacks: David J. MarchetteJorge López FernándezNo ratings yet
- Transceiver Data SheetDocument19 pagesTransceiver Data Sheethb2938943No ratings yet
- IEEE 1904.1 (SIEPON) Architecture and Model: Marek Hajduczenia ZTE CorporationDocument15 pagesIEEE 1904.1 (SIEPON) Architecture and Model: Marek Hajduczenia ZTE CorporationAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- Palo Alto Global ProtectDocument3 pagesPalo Alto Global ProtectPepeNo ratings yet
- Open ZR+ MSA Technical Specification: Rev No. Date DescriptionDocument74 pagesOpen ZR+ MSA Technical Specification: Rev No. Date DescriptionSai Krishna SNo ratings yet
- J Jncip-Sp Lab-Subject 160218 00Document4 pagesJ Jncip-Sp Lab-Subject 160218 00Meklati YounessNo ratings yet
- Linux Shell Script Entire EbookDocument574 pagesLinux Shell Script Entire EbookMichael AriganNo ratings yet
- RouterOs - Mikrotik Configuration PDFDocument533 pagesRouterOs - Mikrotik Configuration PDFMtangoNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork TopologyJason CuarentaNo ratings yet
- Example Corrosion Coupon Report PDFDocument423 pagesExample Corrosion Coupon Report PDFLeonardo Fabián Arboleda Mosquera67% (3)
- Esmpro Customer PresentationDocument65 pagesEsmpro Customer PresentationSerge StasovNo ratings yet
- Acteon PSPIX BrochureDocument12 pagesActeon PSPIX BrochureJTDentalGroupNo ratings yet
- Configuring SDH Cross-ConnectsDocument15 pagesConfiguring SDH Cross-Connectslatinocomm2009No ratings yet
- Installation Guide For R and RStudioDocument4 pagesInstallation Guide For R and RStudioPrerna SinghNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesAbstract:: Disadvantagesprabhujaya97893No ratings yet
- BGP Synchronization Rule & WhyDocument7 pagesBGP Synchronization Rule & WhyMd. Jahid Bin HossainNo ratings yet
- Small InternetworksDocument26 pagesSmall InternetworksSrinivasReddyNo ratings yet
- ScaN Skills Assess - EIGRP - Student TRNG - ExamDocument16 pagesScaN Skills Assess - EIGRP - Student TRNG - Examchristian318_810% (10)
- Ultima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureDocument15 pagesUltima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureVarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Online Reservation SystemDocument5 pagesOnline Reservation SystemSara AliNo ratings yet
- Dark Hotel APTDocument21 pagesDark Hotel APTAnupam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Exaopc GSDocument34 pagesExaopc GSAyman AL-SheryaniNo ratings yet
- 56 Computer Tricks (AMAZING SECRETS & Hacks) : o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument29 pages56 Computer Tricks (AMAZING SECRETS & Hacks) : o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oABDOULIENo ratings yet
- ARDF RadioMobile Instruction Manual V1Document17 pagesARDF RadioMobile Instruction Manual V1Mathew Santiago AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Cryptography MCQDocument4 pagesCryptography MCQShesh Narayan MishraNo ratings yet
- HPUG UA08 V05.04 Preliminary ExtDocument639 pagesHPUG UA08 V05.04 Preliminary ExtAlselawi AhmadNo ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument32 pagesChangelogEduardo LemosNo ratings yet
- Usart Coding MethodDocument22 pagesUsart Coding MethodSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- Direct Coupled AmpsDocument8 pagesDirect Coupled Ampsronga38No ratings yet