Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ankylosing Leafletfa
Uploaded by
Aaron NelsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ankylosing Leafletfa
Uploaded by
Aaron NelsonCopyright:
Available Formats
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an arthritic condition that affects the joints of the spine, causing inammation, severe pain and stiffness in the back. As the condition progresses, the inammation of the spinal joints may cause the entire spine to fuse together, causing severe immobility and deformity (i.e the spine is locked in a bent position). In some patients the peripheral joints like the hips and knees can also be affected. The cause of ankylosing spondylitis is still unknown, although there is a strong linkage to a gene called HLA-B27.
Who gets affected?
Generally, ankylosing spondylitis affects 1 in 1000 people, mainly young people from the age of 15 to 35. Men are 10 times more prone to develop the condition than women.
is made. Very often, in active disease, inammatory markers like the ESR and CRP are raised. In majority of AS patients the gene HLA-B27 is present. X-rays of the spine and MRI are often helpful in conrming the diagnosis
Depending on the severity and progression of the condition, DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) like sulphasalazine may also be prescribed to reduce the inammation of the spine and peripheral joints. A new group of drugs known as biologic agents like Enbrel, Remicade and Humira can be used in resistant cases. These drugs have to be injected regularly and are very expensive. Your doctor is the best judge to decide on the type of drugs you need.
At a sedentary job, it is important to practise safe ergonomics. You should adjust your seat to the proper height so that you do not stoop over the table or workbench, and its easier to keep your posture with a high-back chair.
Complications of ankylosing spondylitis What are the risk factors for ankylosing spondylitis?
While the exact cause of the condition is unknown, it is linked to genetic factors associated with the immune system. In other words, a family history of ankylosing spondylitis is a risk factor. There is about a 15% chance for a child to develop ankylosing spondylitis when a parent has the condition. Ankylosing spondylitis has a variable course. In some patients the disease is mild and limited to the lower back or spine. In others the whole of the spine can be involved including many of the larger joints like the hips and knees. In advanced stage the following complications can develop:A stooped posture Restricted expansion of the chest leading to breathlessness, cough, frequent lung infection b. Exercise A daily regimen of specially-designed exercise or physiotherapy is often recommended. Exercise helps reduce stiffness of the spine, and strengthens the back muscles.
d. Rest During the active stage of ankylosing spondylitis, a period of rest at home or in the hospital may be needed due to the chronic pain and stiffness. It is important to lie at in bed alternating on the back and in the prone position on a rm surface.
What happens to the joints in ankylosing spondylitis?
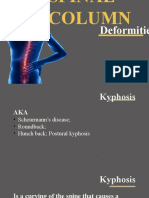
The human spine is POSTURE CHANGE IN ANKYLOSING made up of 24 vertebrae SPONDYLITIS or bone blocks and it connects the skull to the pelvis, and helps us to stand upright, bend forward and move vertebrae fused sideways. The spine together and its vertebrae can be divided into three main segments: the Normal posture Posture in some people with ankylosing spondylitis cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), and lumbar (back). Below the lumbar segment of the spine is the triangular bone called the sacrum, which connects the spine to the pelvis (the sacroiliac joint). Ankylosing spondylitis often affects the sacroiliac joints and lumbar segments rst although occasionally the neck and thoracic segments can also be affected. As the condition progresses, the inammation will cause fusion of the spine and in extreme cases the entire spine may become fused resulting in complete rigidity of the spine, a condition known as bamboo spine.
What are the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis?
The rst signs of ankylosing spondylitis are pain and stiffness in the lower back. This is especially bad in the morning on getting up. This is quite different from back strain which is better after rest. Occasionally this may be associated with pain in the hips and knees. As the condition progresses, the pain and stiffness can affect the entire spine and last the whole day. This causes difculty in walking, getting out of bed, bending forward and other activities of daily living. Patients with active AS often experience fatigue, poor appetite and weight loss. The eyes can also be affected in AS and the symptoms include redness of the eyes, increased sensitivity to light and blurred vision.
Eye inammation Bowel inammation Heart complications
The Final Word
Ankylosing spondylitis is a life-long illness but despite the potential complications most people are able to live productive lives. The most important measure is early diagnosis - therefore one must not neglect any backache or back stiffness lasting for more than three months especially in a young male. Typically this backache or stiffness is worse in the morning on getting up and improves during the day. If you have ankylosing spondylitis you can help yourself by doing regular exercises like swimming and stretching, adopting a healthy life-style, taking your medicine regularly as advised by your doctor, joining a support group or learning more about your disease.
How is ankylosing spondylitis treated?
There is currently no cure for ankylosing spondylitis but the condition is not beyond help. Treatment strategies centre on alleviating the symptoms and managing the progression of the condition to regain mobility of the spine.
In general, swimming is recommended for all forms of arthritis. Other physical therapies must be recommended and approved by a rheumatologist in consultation with a physiotherapist. In order to be effective, all exercises need to be done regularly and on a long term basis.
a. Medication Most medications prescribed treat only the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis. NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inammatory drugs) like indomethacin, diclofenac acid (Voltaren) and the newer COX-2 inhibitors like Celebrex and Arcoxia are often prescribed to reduce inammation, pain and stiffness of the spine. Other pain relieving drugs like panadol, tramadol and Ultracet are also used.
How is ankylosing spondylitis diagnosed?
Ankylosing spondylitis is diagnosed by taking a careful history, reviewing the family history and careful examination of the spine. There is no direct test for ankylosing spondylitis and it may take several visits to the doctor and accurate reporting of symptoms, over a period of time before a denitive diagnosis
c. Posture Posture management is very important for patients living with ankylosing spondylitis. As they are in danger of developing spinal curvatures and bent hips as the joints of the spine and hips fuse, it is necessary to keep a good posture during your waking hours.
Back ache in ankylosing spondylitis
Singapore Ankylosing Spondylitis Club Tel: 1800 227 9726 Fax: 6220 2116 Email: info@arthritis.org.sg National Ankylosing Spondylitis Society (UK) www.nass.co.uk Spondylitis Association of Amercia www.spondylitis.org
You might also like
- AFT ManualDocument58 pagesAFT ManualHodaya Ben Shachar50% (2)
- Common General Practice Consultations - Notes For OSCEsDocument54 pagesCommon General Practice Consultations - Notes For OSCEshaydenfarquhar89% (9)
- Chakra HandoutDocument2 pagesChakra Handoutmecardxviii100% (10)
- 2007 SaeDocument20 pages2007 Saelila1284No ratings yet
- Japanese Meridian Therapy in The Community Acupuncture ModelDocument4 pagesJapanese Meridian Therapy in The Community Acupuncture ModelkeirakuNo ratings yet
- DX TX Iliocostal Friction Syndrome PDFDocument6 pagesDX TX Iliocostal Friction Syndrome PDFMohammad GhaniNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spine - Mechanical Diagnosis TherapyDocument178 pagesLumbar Spine - Mechanical Diagnosis Therapyjimitkapadia91% (11)
- Lec4 Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument25 pagesLec4 Ankylosing Spondylitissana mumtazNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument29 pagesAnkylosing SpondylitisKrisna ajiNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondilytisDocument4 pagesAnkylosing Spondilytisandreas kevinNo ratings yet
- Apyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiDocument131 pagesApyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiFathimathNo ratings yet
- Four Myths About Spondylitis: Clinician's GuideDocument2 pagesFour Myths About Spondylitis: Clinician's GuideAmy YoungNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument6 pagesAnkylosing SpondylitisAnonymous VzFhQ3iNo ratings yet
- How To Cure Cervical Spondylosis Permanently? - Rela HospitalDocument4 pagesHow To Cure Cervical Spondylosis Permanently? - Rela Hospitaldd2officeNo ratings yet
- Types of Spine Curvature DisordersDocument7 pagesTypes of Spine Curvature DisordersNicu MacariNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpodylitisDocument13 pagesAnkylosing SpodylitisMuzlifah Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spine CurvaturesDocument7 pagesAbnormal Spine CurvaturesMartin SageNo ratings yet
- A Positive Response To Ankylosing Spondylitis: Guidebook For PatientsDocument18 pagesA Positive Response To Ankylosing Spondylitis: Guidebook For PatientsdipanshuroyNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Submitted by Safeer Mohammed S 302 General Medicine Submitted To Dr. Marietta DavidianDocument20 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitis: Submitted by Safeer Mohammed S 302 General Medicine Submitted To Dr. Marietta DavidianSafeer VarkalaNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylarthritis PDFDocument3 pagesAnkylosing Spondylarthritis PDFMa OlayaNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis - Symptoms - Causes - TreatmentDocument5 pagesKyphosis - Symptoms - Causes - TreatmentMara ColegiuNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondilitis Latest 25 SepDocument12 pagesAnkylosing Spondilitis Latest 25 Sepsyafiqa abdullahNo ratings yet
- Bamboo SpineDocument1 pageBamboo Spinecitihomes2009No ratings yet
- Patient - Info/doctor/ankylosing Spondylitis ProDocument8 pagesPatient - Info/doctor/ankylosing Spondylitis ProJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument16 pagesUntitled PresentationtasneemsofiNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis, A Simple Guide To The Disease, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKyphosis, A Simple Guide To The Disease, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pinal Stenosis TreatmentDocument10 pagesPinal Stenosis Treatmentravideva84No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument21 pagesLecture 4 - Ankylosing SpondylitissharmeenNo ratings yet
- Guidebook Guidebook: Answers and Practical Advice Answers and Practical AdviceDocument34 pagesGuidebook Guidebook: Answers and Practical Advice Answers and Practical AdviceluckymaanNo ratings yet
- Types of ScoliosisDocument5 pagesTypes of ScoliosisDimple Castañeto CalloNo ratings yet
- SP SkoliosisDocument19 pagesSP SkoliosisSantosa OkaNo ratings yet
- Congenital ScoliosisDocument21 pagesCongenital ScoliosisSarmiento, Jovenal B.No ratings yet
- Scolio SIS: Submitted ToDocument10 pagesScolio SIS: Submitted Tojean thereseNo ratings yet
- S Pondy Lols Ys ThesisDocument35 pagesS Pondy Lols Ys ThesisSal LieNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument4 pagesScoliosisDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- LBP 2Document12 pagesLBP 2Attika DiniNo ratings yet
- KYPHOSISDocument18 pagesKYPHOSISminangsung minangnengNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Disease OverviewDocument7 pagesScoliosis Disease OverviewReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAnkylosing Spondylitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- What Is Cervical SpondylosisDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cervical SpondylosisBibhash MishraNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Kagal KolhapurDocument27 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Kagal KolhapurSujay NirmaleNo ratings yet
- Fatima Sehar-699Document6 pagesFatima Sehar-699Fatima SeharNo ratings yet
- ArthritiscomplicationsDocument2 pagesArthritiscomplicationsSai Krishna SeethamrajuNo ratings yet
- Share 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Document105 pagesShare 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Hunaid 1000No ratings yet
- Scoliosis, Lordosis, and KyphosisDocument40 pagesScoliosis, Lordosis, and KyphosisRati W. PaneseNo ratings yet
- Back Pain: Back Pain Treatment: Back Pain Relief: How To Heal Back ProblemsFrom EverandBack Pain: Back Pain Treatment: Back Pain Relief: How To Heal Back ProblemsNo ratings yet
- IntroSPINAL CORD INJURYDocument6 pagesIntroSPINAL CORD INJURYAmie GarduqueNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisDocument22 pagesKyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisTheeya Quigao100% (1)
- Spinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesFrom EverandSpinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesNo ratings yet
- Lec3 DiscDocument50 pagesLec3 Discsana mumtazNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ScoliosisDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ScoliosisKhrizjan RebloraNo ratings yet
- N N N N N: ©2014 UptodateDocument7 pagesN N N N N: ©2014 UptodateDayron TorresNo ratings yet
- Handout On Health: Back PainDocument16 pagesHandout On Health: Back Painpkkumar1209No ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument7 pagesSpinal Cord CompressionDashNo ratings yet
- Ergo Experiment 2Document15 pagesErgo Experiment 2John Paul Espineli FeranilNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- NCP ScoliosisDocument4 pagesNCP ScoliosisCharley DegamoNo ratings yet
- Spondylosis Information LeafletDocument3 pagesSpondylosis Information LeafletAnis Azizah MogilNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Biology Investigatory Project by Rajni PriyaDocument25 pagesVdocuments - MX - Biology Investigatory Project by Rajni PriyaRoshan AbbasNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosisTracy100% (1)
- Postural DeformitiesDocument37 pagesPostural DeformitiesBalram Jha80% (5)
- About:: Birth Defects Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy Marfan's DiseaseDocument4 pagesAbout:: Birth Defects Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy Marfan's DiseaseAbie BeyNo ratings yet
- Essentials of D I Agnosis: 3. Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument8 pagesEssentials of D I Agnosis: 3. Ankylosing SpondylitisNau HasNo ratings yet
- LimpDocument7 pagesLimpRakesh DudiNo ratings yet
- Adult Scoliosis: A Beginner's 2-Week Quick Start Guide on Managing Adult Scoliosis Through Diet and Other Natural Methods, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandAdult Scoliosis: A Beginner's 2-Week Quick Start Guide on Managing Adult Scoliosis Through Diet and Other Natural Methods, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- The Danger of AnkylosingDocument4 pagesThe Danger of AnkylosingZeeshan IslamNo ratings yet
- Chestionar SanatateDocument4 pagesChestionar SanatateEugenNo ratings yet
- 170110Document8 pages170110XYZ ABCNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Treatment in Conservative Management of Paraplegia Due To Tuberculosis of Spine - A Case StudyDocument1 pageAyurvedic Treatment in Conservative Management of Paraplegia Due To Tuberculosis of Spine - A Case StudyK. KNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of A Low Back Pain ClassificationDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of A Low Back Pain ClassificationLuis cabezas mirandaNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain - A Call For ActionDocument5 pagesLow Back Pain - A Call For ActionRobertoNo ratings yet
- Group Name/Channel IndicationsDocument2 pagesGroup Name/Channel IndicationsRanga NathanNo ratings yet
- Emedica Stage2 Study GuideDocument39 pagesEmedica Stage2 Study GuideDulau LarisaNo ratings yet
- Hypokinetic DiseasesDocument5 pagesHypokinetic DiseasesMartha BelayNo ratings yet
- Etiologies of Failed Back Surgery SyndroDocument15 pagesEtiologies of Failed Back Surgery SyndrowladjaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Back PainDocument26 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Back PainKristy Besarab100% (1)
- Presentation Lower Back PainDocument86 pagesPresentation Lower Back PainSten SchaperNo ratings yet
- Medula ContinumDocument252 pagesMedula ContinumRafaelNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain in Elderly AgeingDocument29 pagesLow Back Pain in Elderly AgeingJane ChaterineNo ratings yet
- Red FlagsDocument2 pagesRed FlagsHeidiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Sciatica2Document6 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Sciatica2Hayyu F RachmadhanNo ratings yet
- Feldenkrais Method Empowers Adults With Chronic.4Document13 pagesFeldenkrais Method Empowers Adults With Chronic.4Yvette M Reyes100% (1)
- HWF30203 Final Assessment (Exam)Document9 pagesHWF30203 Final Assessment (Exam)Nurul NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Williams Flexion ExercisesDocument2 pagesWilliams Flexion ExercisesSyeda Abida Hussain SheraziNo ratings yet
- Yoga For Low Back PainDocument97 pagesYoga For Low Back PainEllen PaeroaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Visceral Osteopathic Manual Therapy Applications On PainDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Visceral Osteopathic Manual Therapy Applications On PainCarlos PaisNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Management in Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome - A Single Case StudyDocument5 pagesPhysiotherapy Management in Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome - A Single Case StudyCambriaChicoNo ratings yet
- LBPDocument27 pagesLBPAnonymous 7jKR9XbNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Management of Acute Musculoskeletal Pain 2Document259 pagesEvidence Based Management of Acute Musculoskeletal Pain 2api-26227671100% (4)