Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Discussion
Uploaded by
Vijay RohillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Discussion
Uploaded by
Vijay RohillaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1 1) GROUP DISCUSSION A) The mineral nutrients for plants. How are these replenished in the soil?
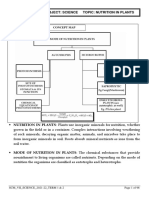
Answer- The 13 mineral nutrients, which come from the soil, are dissolved in water and absorbed through a plant's roots. There are not always enough of these nutrients in the soil for a plant to grow healthy. This is why many farmers and gardeners use fertilizers to add the nutrients to the soil. The mineral nutrients are divided into two groups: macronutrients and micronutrients. 2) GROUP ACTIVITY
A) Visit a zoo. list the animals present there. Find out the food they eat and classify
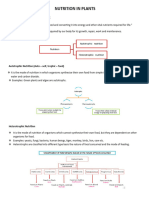
them on the basis of the mode of nutrition. Answer-list of animals: (a) Herbivorous-they eat only grass,plants. E.g-elephant,camal (b) Carnivorous-they eat only meat.e.g-lion,tiger (c) Omnivorous-they eat both plants and meat. E.g-crow,dog Classification: Modes of nutrition Organism have different modes of nutrition. They are classified into two major groups on the basis of mode of their taking food. 1. Autotrophic nutrition: Auto means self and trophein means to nourish. In this mode of nutrition, organism synthesize their own food in their own bodies from simpler inorganic substances. Such organism are known as autotrophs. Autotrophic nutrition is further classified into two types depending on the source of energy used. (i) Photoautotrophic nutrition: All green plants, certain protists and photosynthesis bacteria have this mode of nutrition. They can directly use the solar
energy in the presence of chlorophyll to make their organic food from simpler inorganic substances,i.e., water and carbon dioxide. The green pigment present in them is oftrapping the solar energy . This energy is used for synthesis of food from raw materials- carbon dioxide, water and some minerals. These organisms are known as photoautotrophs. (ii) Chemoautotrophic nutrition or chemosynthesis: certain bacteria can make organic food from simpler organic substances without using an solar energy. They use energy produced by the breakdown of these inorganic substances. This process is known as chemosynthesis and their mode of nutrition as chemoautotrophic nutrition. These organism are known as chemoautotrophs. For examples, sulphur bacteria and iron bacteria. 2. Heterotrophic nutrition: Hetro a greek word means different. In this mode of nutrition, the nutritions are taken from others. All, animals, fungi, many bacteria and some non-organic plants cannot make their own food. Such organisms are known as heterotrophs. Thus, heterotrophs nutrition may be defined as a type nutrition in which energy is obtained from the digestion of organic matter, of plant and animal source. In this mode of nutrition, first organic is digestion of organic matter, of plants and animals sources. b) Perform any experimental activity given in thechapter. The Leaf A beautiful green summer leaf. Warm summer days. The sun is shining. The leaves are just hanging there, doing nothing but looking pretty and wiggling in the wind. Wrong! It looks peaceful, but those leaves are busy. At speeds almost beyond our comprehension, thousands of chemical reactions and processes are occuring every second, inside thousands of cells. Busy, busy, busy, making stuff - carbohydrates that will be the building blocks to make more plant cells and the energy source for all the plant cell processes. This is photosynthesis. Where does all this "photosynthesizing" take place? Do all the leaf cells do it? Do they have to go to school to learn how? Naw, not all the leaf cells do it; and somehow, like most other living things, they just know how to do what they do without going to school. (In the case of plant cells, it's more like being programmed than "knowing".)
Keep scrolling down to get an overview of the places and parts in a typical leaf where photosynthesis gets done. Then keep scrolling down, or click on the specific words if you are the skipping type, to get a more detailed look at the leaf parts and names and processes involved with turning solar energy, water, and carbon dioxide, into food. 3) SEMINAR: a) collect information about a plant called Rafflesia found in Sumatra. Answer: Several species of Rafflesia grow in the jungles of Southeast Asia,all of them threatened or endangered. Raffesia arnoldii is the largest; its blossom attains a diameter of nearly a meter and can weigh up to 11 Kg. Not only is it the worlds largest flower, it is one of the most bizarre and improbable organisms on the planet. It produces no leaves, steams or roots but lives as a parssite on the Tetrastigmavine, which grows oniy in primary (undisturbed) rainforest. Only the flower or bud can be seen; the rest of the plant exists only as filaments within its unfortunate host. The blossom is pollinated by flies attracted by its scent,which resembles that of carrion. The Rafflesia is rare and fairly hard to locate. It is especially difficult to see in bloom;the buds take many months to develop and the blossom lasts for just a few days. How many of these strange plants still survive is unknown,but the last of them can be expectedto vanish as the remaining primary forests of Borneo and Sumatra are burned.ud can be seen; the rest of the plant exists only as filaments within its unfortunate host. The blossom is pollinated by flies attracted by its scent, which resembles that of carrion. PICTURE:
You might also like
- Nutrition in Plants ExplainedDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants ExplainedAmos JosephatNo ratings yet
- The Living World - Class7Document32 pagesThe Living World - Class7EsolNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Nutrition in PlantsDocument10 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Nutrition in PlantsKalpavriksha1974No ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 1Document5 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 1Yash ArdeshnaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument12 pagesNutrition in Plantsdvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Class 7 SCIENCE CH 1Document20 pagesClass 7 SCIENCE CH 1Saurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Awetan BasahDocument13 pagesLaporan Awetan BasahAni NurHidayantiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plantsgtbit.cse.aashishNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument7 pagesNutrition in PlantsSonuSharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument20 pagesCh1 Nutrition in Plantsshyam123gNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants or Nutrients in Plants For Class 7 CBSE Science PDFDocument8 pagesNutrition in Plants or Nutrients in Plants For Class 7 CBSE Science PDFAtanu Ghosh100% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument4 pagesBiology NotesAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- How Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandHow Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument44 pagesNutrition in Plantsgeorgy shibuNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following:: Ls.1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument3 pagesAnswer The Following:: Ls.1 Nutrition in PlantsAravind MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument4 pagesNutrition in PlantsAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- What Is A Plant?Document35 pagesWhat Is A Plant?Precious UdoadaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesDocument4 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesshravandownloadNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument21 pagesNutrition in PlantsRavinder Sutari100% (1)
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School - Bopal, Ahmedabad (2021-22) : Class: VII Subject: Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Study NotesDocument10 pagesDelhi Public School - Bopal, Ahmedabad (2021-22) : Class: VII Subject: Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Study Notesbhargav guptaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument3 pagesNutrition in Plantsridhamjain860No ratings yet
- Class 8 21thDocument9 pagesClass 8 21thAbdulmonir MominyarNo ratings yet
- The Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Producers, Consumers and Decomposers in an EcosystemDocument2 pagesProducers, Consumers and Decomposers in an Ecosystemmilf hunterNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPradip KumarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledArnav SNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Components and RelationshipsDocument8 pagesEcosystem Components and RelationshipsArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument10 pagesNutritionJerwin GarnaceNo ratings yet
- Focus Questions: Week 1Document5 pagesFocus Questions: Week 1api-238747348No ratings yet
- Grdae VII-Biology - Nutrition in Plants - NotesDocument6 pagesGrdae VII-Biology - Nutrition in Plants - NotesDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- Do Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandDo Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Green plants nutrition notesDocument6 pagesGreen plants nutrition notesSeema Singh SengarNo ratings yet
- Life Processes TutionDocument37 pagesLife Processes Tutionmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- NutritionnquestionsDocument4 pagesNutritionnquestionsRUPANo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument53 pagesPlant KingdomAashutosh GujareNo ratings yet
- Makalah Animal and PlantDocument17 pagesMakalah Animal and PlantMuhammad FuadiNo ratings yet
- The First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3From EverandThe First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument13 pagesChapter-1 Nutrition in PlantsRitu RajNo ratings yet
- plant Nutritions: I.Q TestDocument15 pagesplant Nutritions: I.Q TestXX OniiSan XXNo ratings yet
- Early Plant Life and AdaptationsDocument7 pagesEarly Plant Life and Adaptationsklavier10244379No ratings yet
- How Do We Classify The Living WorldDocument5 pagesHow Do We Classify The Living WorldAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Science SCMDocument98 pagesScience SCMKoustavi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument93 pagesPlantsnehmiryll sumaletNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants NotesDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Class7 - Nutrition in Plants-1Document6 pagesClass7 - Nutrition in Plants-17A04Aditya Mayank100% (1)
- Clasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesDocument16 pagesClasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesPamelaMelissaManriqueGraosNo ratings yet
- CLASS 7-Notes-CH 1-Nurition in PlantsDocument5 pagesCLASS 7-Notes-CH 1-Nurition in PlantsAKHILA SURESH PNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Fungi and PlantsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Fungi and PlantsAgrimonyNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Bio Heterotrophic Nutrition in Plants Part B New 1624717471Document5 pagesClass 7 Bio Heterotrophic Nutrition in Plants Part B New 1624717471Darshan PadmapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Plants and Charactertics Natsci NotesDocument11 pagesLesson 1 - Plants and Charactertics Natsci NotesKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- W7 NotesDocument21 pagesW7 NotesAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- What Is An AlgaeDocument4 pagesWhat Is An AlgaeKirk BacsainNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examinations for 7th Semester EEEDocument123 pagesScheme of Examinations for 7th Semester EEEVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- 4final Syllabus IT 3rd Semester4,5,6,7,8Document104 pages4final Syllabus IT 3rd Semester4,5,6,7,8ridamNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document1 pageBook 2Vijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1Vijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- GAS Power PlantDocument7 pagesGAS Power PlantVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument3 pagesIntrinsic Extrinsic SemiconductorsJohn Dolph FacundoNo ratings yet
- Telephone Numbers of Offices OP' Circle, Sonipat, UHBVNDocument1 pageTelephone Numbers of Offices OP' Circle, Sonipat, UHBVNParmod Ranga0% (1)
- Ntexmevl 27654Document10 pagesNtexmevl 27654Abhinav MadanNo ratings yet
- EEE Department Vision, Mission & ObjectivesDocument3 pagesEEE Department Vision, Mission & ObjectivesVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- SBI Life - EWealth Insurance 300415 V2Document16 pagesSBI Life - EWealth Insurance 300415 V2Tejas JasaniNo ratings yet
- Maruti Wagon R Brochure PDFDocument6 pagesMaruti Wagon R Brochure PDFVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- India Energy Statistics 2013Document102 pagesIndia Energy Statistics 2013zikapasiNo ratings yet
- Cele Rio BrochureDocument6 pagesCele Rio BrochureKiran KoraddiNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument6 pagesBrochureVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- SSVEP Channel Selection Using Adaptive Filtering: Presented By:-Vijay RohillaDocument14 pagesSSVEP Channel Selection Using Adaptive Filtering: Presented By:-Vijay RohillaVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- SSVEP Channel Selection Using Adaptive Filtering: Presented By:-Vijay RohillaDocument14 pagesSSVEP Channel Selection Using Adaptive Filtering: Presented By:-Vijay RohillaVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Power OscillationsDocument54 pagesPower OscillationsVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Preventive, Emergency and Restorative Control ActionsDocument4 pagesModule 6: Preventive, Emergency and Restorative Control ActionsVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Series Compensation BenefitsDocument10 pagesSeries Compensation BenefitsVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Article 3: What Is Reactive Power?Document8 pagesArticle 3: What Is Reactive Power?MAT JIBRUDNo ratings yet
- GunuDocument1 pageGunuVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Concept of LoadabilityDocument12 pagesConcept of LoadabilityVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Compensation Technologies, State-of-the-Art ReviewDocument21 pagesReactive Power Compensation Technologies, State-of-the-Art ReviewsharptrNo ratings yet
- Economic Load Dispatch Using Bacterial Foraging TechniqueDocument8 pagesEconomic Load Dispatch Using Bacterial Foraging TechniqueVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- New Arranged REFERENCESDocument1 pageNew Arranged REFERENCESVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Energy Markets & Technologies-Revised1Document14 pagesEnergy Markets & Technologies-Revised1Jasim FarooqNo ratings yet
- Nikon India Private LimitedDocument1 pageNikon India Private LimitedVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Comparison of Thermal-Thermal System in Three GencosDocument8 pages8.3 Comparison of Thermal-Thermal System in Three GencosVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Guide4BankExams English GrammarDocument11 pagesGuide4BankExams English GrammarShiv Ram Krishna100% (3)
- Assignment2-9509Document5 pagesAssignment2-9509ritadhikarycseNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell SizeDocument3 pagesModal Analysis of Honeycomb Structure With Variation of Cell Sizeprateekg92No ratings yet
- Space Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFDocument841 pagesSpace Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFNita NabanitaNo ratings yet
- DELA PENA - Transcultural Nursing Title ProposalDocument20 pagesDELA PENA - Transcultural Nursing Title Proposalrnrmmanphd0% (1)
- PSPO I Question AnswerDocument11 pagesPSPO I Question AnswerAurélie ROUENo ratings yet
- Structural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaDocument10 pagesStructural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaCarlos AcnNo ratings yet
- Rhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 07Document14 pagesRhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 07maildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- NMIMS MBA Midterm Decision Analysis and Modeling ExamDocument2 pagesNMIMS MBA Midterm Decision Analysis and Modeling ExamSachi SurbhiNo ratings yet
- Philippine Development Plan (Optimized)Document413 pagesPhilippine Development Plan (Optimized)herbertjohn24No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFTiên Nguyễn100% (1)
- Reich Web ADocument34 pagesReich Web Ak1nj3No ratings yet
- Paaralan Tungo Sa Magandang Kinabukasan" The Campaign Kicked Off in All The PublicDocument7 pagesPaaralan Tungo Sa Magandang Kinabukasan" The Campaign Kicked Off in All The PublicJOHN FRANCIS OCTAVIANONo ratings yet
- Sublime QR CodeDocument6 pagesSublime QR Codejeff_sauserNo ratings yet
- Moment Baseplate DesignDocument10 pagesMoment Baseplate DesignNeil JonesNo ratings yet
- Failure Reporting, Analysis, and Corrective Action SystemDocument46 pagesFailure Reporting, Analysis, and Corrective Action Systemjwpaprk1No ratings yet
- Mosek UserguideDocument81 pagesMosek UserguideadethroNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Mapjebzkiah productionNo ratings yet
- Es E100091 Pi PDFDocument1 pageEs E100091 Pi PDFCarlos Humbeto Portillo MendezNo ratings yet
- 62046PSYCHICSDocument1 page62046PSYCHICSs0hpokc310No ratings yet
- SMK ST GabrielDocument39 pagesSMK ST Gabrielzanariah1911No ratings yet
- HAU Theology 103 Group Goal Commitment ReportDocument6 pagesHAU Theology 103 Group Goal Commitment ReportEM SagunNo ratings yet
- Tutor Marked Assignment (TMA) SR Secondary 2018 19Document98 pagesTutor Marked Assignment (TMA) SR Secondary 2018 19kanna2750% (1)
- Growing Up Psychic by Chip Coffey - ExcerptDocument48 pagesGrowing Up Psychic by Chip Coffey - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group100% (1)
- IS BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITECTURE A NEW STYLE OF DESIGNDocument5 pagesIS BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITECTURE A NEW STYLE OF DESIGNJorge DávilaNo ratings yet
- CIPP ModelDocument36 pagesCIPP ModelIghfir Rijal TaufiqyNo ratings yet
- Companies DatabaseDocument2 pagesCompanies DatabaseNIRAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- © Call Centre Helper: 171 Factorial #VALUE! This Will Cause Errors in Your CalculationsDocument19 pages© Call Centre Helper: 171 Factorial #VALUE! This Will Cause Errors in Your CalculationswircexdjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Matrices Form 5Document22 pagesChapter 4 Matrices Form 5CHONG GEOK CHUAN100% (2)
- Digital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustDocument16 pagesDigital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustAtifMinhasNo ratings yet
- Develop Your Kuji In Ability in Body and MindDocument7 pagesDevelop Your Kuji In Ability in Body and MindLenjivac100% (3)