Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uit RGPV First Year Syllabus
Uploaded by
Yasir MujtabaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uit RGPV First Year Syllabus
Uploaded by
Yasir MujtabaCopyright:
Available Formats
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem. Engineering Chemistry Mid Sem. Tests End (Two tests Average) assignment Sem 30 20 30 Quiz, Lab assignment Practical L T P Credits
CH 1001
100
20
Course Contents Unit I WATER AND ITS INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS : Sources, Impurities, Hardness & its units, Industrial water characteristics, softening of water by various methods, Exrernal & Internal treatment, Boiler troubles, causes, effects & remedies, Characteristics of municipal water & its treatment, Numerical problems based on softening methods. Unit II FUELS & COMBUSTION: Fossil fuels & classification, Calorific value, Determination of calorific value by Bomb Calorimeter, Proximate and Ultimate analysis of coal and their significance, calorific value Computation based on ultimate analysis data, Carbonization, Manufacturing of coke & recovery of by products. Knocking, relationship between' knocking & structure of hydrocarbons, improvement of anti knocking characteristics of IC engine fuels, Diesel engine fuels, Cetane number, combustion and it related numerical problems. Unit III A. LUBRICANTS: Introduction, Mechanisms of lubrication, Classification of lubricants, lubricating oils, Numerical problems based on testing methods.
Properties and Testing of
B. CEMENT & REFRACTORIES: Manufacture , IS specifications, Setting and hardening of cement, Plaster of Paris. Refractory : Introduction, classification and properties of refractories . Unit IV HIGH-POLYMER : Introduction, types and classification of polymerization, Reaction Mechanism, Natural & Synthetic Rubber; Vulcanization of Rubber, Preparation,Properties & uses of the following- Polythene, PVC, PMA, PMMA, Teflon, Poly acrylonitrile, PVA, Nylon, Nylon 6:6, Terylene, Phenol formaldehyde, Urea -Formaldehyde Resin, Glyptal, Silicone Resin, Polyurethanes; Butyl Rubber, Neoprene, Buna N, Buna S. Flow sheet manufacturing diagram of Nylon 6:6 & Decoran. Unit V A. INSTRUMENTAL TECHNIQUES IN CHEMICAL ANALYSIS :Introduction, Principle, Instrumentation and applications of IR, NMR,UV, Visible, spectroscopy, Gas Chromatography, Lambert's and Beer's Law B. WATER ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES : Alkalinity, hardness ( Complexo-metric ), Chloride, Free chlorine, DO, BOD and COD, Numerical problems based on above technique
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 1
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
CH 1001Engineering Chemistry
Books: 1. Sawyer, McCarty and Parkin , Chemistry for Environmental Engineering, Mc Graw Hill,International. 2. B.K. Sharma , Engineering Chemistry , Krishna Publications, Meerut. 3. S. S. Dara & A.K. Singh , A Text Book of Engineering Chemistry , S. Chand Publication, New Delhi. 4. O.P. Viramani, A.K. Narula , Applied Chemistry - Theory and Practice, , New Age Publictions,New Delhi 5. Ghosh , Polymer Science, Tata McGraw Hill. New Delhi 6. Jain & jain , Engineering Chemistry , Dhanpat Rai Publications,New Delhi. 7. Shashi Chawla , Engineering Chemistry , Dhanpat Rai Publications, New Delhi. Engineering Chemistry Practical NOTE: At least 10 of the following core experiments must be performed during the session. 1. Water Testing (i) Determination of Total hardness by Complexometric titration method. (ii) Determination of mixed alkalinity (a) OH -& C03- (b) CO3- - & HCO3 (iii) Chloride ion estimation by Argentometric method. 2. Fuels & lubricant testing: (i) Flash & fire points determination by a) Pensky Martin Apparatus, b) Abel's Apparatus, c) Cleveland's open cup Apparatus. d) Calorific value by bomb calorimeter (ii) Viscosity and Viscosity index determination by a) Redwood viscometer No.1 b) Redwood viscometer No.2 (iii) Proximate analysis of coal a) Moisture content b) Ash content c) Volatile matter content c) Carbon residue (iv) Steam emulsification No & Anline point determination (v) Cloud and Pour point determination of lubricating oil 3. Alloy Analysis (i) Determination of percentage of Fe in an iron alloy by redox titration using N-Phenyl anthranilic acid as internal indicator. (ii) Determination of Cu and or Cr in alloys by Iodometric Titration.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 2
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Theory Subject Code Subject End Sem. Mid Sem. Tests Quiz, (Two tests Average) assignment End Sem Lab assignmen t Practical L
Credits
MA 1002
Engineering Mathematics I
100
30
20
Course Contents Unit-I Expansion of functions by Maclaurins and Taylors theorem for one variable; Taylors theorem for function of two variables, Partial differentiation and its application in approximation and errors;; Maxima and minima of two variables; Curvature, Radius of curvature and centre of curvature, Asymptotes, Curve tracing .
Unit-II Definite Integral as limit of a sum and its Application in summation of series, Double and triple integrals, Change of order of integration, Area and Volume using double and triple integral, Beta and Gamma functions , Length of the curves. Unit-III Ordinary differential equations of first order linear and higher degree, Linear higher order differential equations with constant coefficients, Homogeneous linear differential equations, Simultaneous linear differential equations.
Unit-IV Rank of matrix, Solution of simultaneous linear equations by elementary transformation, Consistency of equation, Eigen values and Eigen Vectors, Cayley-Hamilton theorem and its application to find inverse, Vector space, Vector subspace, Linear dependence and independence . Unit-V Algebra of logic, Boolean algebra, Principle of duality, Basic theorems, Boolean expressions and function; Elementary concept of Fuzzy logic : Definition, Union, Intersection and applications, Graph theory: Graphs, Sub graphs, Path, Walk, Tree, Matrix representation of undirected graphs. Books: 1. Ramana: Advance Engg. Mathematics, TMH New Delhi. 2. B.S. Grewal: Higher Engineering Mathematics , Khanna Publication. 3. D.G.Guffy: Advance Engineering Mathematics, C R C Press 4. S.Arumungam: Mathematics for Engineers, SCITECH Publuication. 5. Erwin Kreyszig: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Wiley India.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 3
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem. Communication Skills Mid Sem. Tests (Two tests Average) L Quiz, assignment 20 End Sem 30 Lab assignment 20 4 1 2 T P Practical Credits
HN1003
100
30
Course Contents
Unit I Introduction to communication- Communication, meaning and significance, defining communication objectives, communication situation, process of communication, 7 cs of communication, oral and written communication, barriers to communication and ways to overcome them, Importance of communication for technical students, Achieving success through effective business communication. Unit II Linguistic techniques - Grammar usage and mechanics, Parts of speech, sentence structure, paragraph development, precise writing, prcis writing, punctuation, style, register, word usage, vocabulary, Reading comprehension, Phonetic symbols and pronunciation, dialogue, conversation, telephone conversation, debate, designing and delivery of oral presentation. Unit III Technical communication: writing skills Writing definitions of engineering objects, processes and principles, technical descriptions of engineering objects and processes, technical report writing, objectives, characteristics of a report, structure of a formal report, types of technical reports, short and long report. Report of trouble, project report, laboratory report, progress report. Unit IV Business correspondence- Business letters, parts and layouts of formal letter, writing resume and application letter, calling and sending quotations, orders and complaints. Tenders, memos, electronic mail. Unit V Listening and non-verbal communication- Listening, types of listening, process of listening, active listening, improving listening skills, barriers to listening, non-verbal communication, concept of time and space, cross cultural communication, communicating information through visuals. Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
Krizan and Merrier, Effective business communication, Cengage learning. Shirley Taylor, Communication for business a practical approach , Pearson Education. Francis Soundararaj, Speaking and writing for effective business communication, Macmillan. M Arshaf Rizvi , Effective technical communication ,Tata Mcgraw Hill. R. C. Sharma and Krihna Mohan, Business correspondence and report writing ,Tata Mcgraw Hill . Meenakshi Raman and Sangeeta Sharma, Technical communication: principles and practice, Oxford. Scot Ober, Biztantra Contemporary business communication.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 4
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem. Basic Electrical Engg. Mid Sem. Tests Quiz, (Two tests Average) assignment End Sem Lab assignment L T P Practical Credits
EX1004
100
30
20
30
20
Course Contents Unit I D.C. Circuits- Units and dimensions, Ohms Law, Kirchhoffs Law, Superposition theorem, Thevenins theorm and their application for analysis of series and parallel resistive circuits excited by independent voltage sources, Power & Energy in such circuits. Mesh & nodal analysis, Star Delta circuits. Unit II 1- phase AC Circuits- Generation of sinusoidal AC voltage, definition of average value, R.M.S. value, form factor and peak factor of AC quantity , Concept of phasor, Concept of Power factor, Concept of impedance and admittance, Active, reactive and apparent power, analysis of R-L, R-C, R-L-C series & parallel circuit Unit III 3-phase AC Circuits- Necessity and advantages of three phase systems, Meaning of Phase sequence, balanced and unbalanced supply and loads. Relationship between line and phase values for balanced star and delta connections. Power in balanced & unbalanced three-phase system and their measurements Unit IV Magnetic Circuits- Basic definitions, analogy between electric and magnetic circuits, magnetization characteristics of Ferro magnetic materials, self inductance and mutual inductance, energy in linear magnetic systems, coils connected in series, AC excitation in magnetic circuits, magnetic field produced by current carrying conductor, Force on a current carrying conductor. Induced voltage, laws of electromagnetic Induction, direction of induced E.M.F. single phase transformer- its general construction, working principle, e.m.f. equation, open circuit and short circuit test . Unit V Electrical Machines- . D.C. Motor & D.C. Generator, Three phase Induction motor and Synchronous Machines, their general construction, working principle, emf equation and applications. Types of losses occurring in electrical machines. Books:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Vincent Del Toro, Principles of Electrical Engineering , Prentice Hall, 1987. A.E. Fitzgerald, Higginbotham and Grabel, Basic Electrical Engineering, McGraw Hill. H. Cotton, Electrical Technology, Wheelers Parkar Smith, Problems in Electrical Engineerin CBS HUGHES Electrical Technology , Pearson P.S. Bimbhra Electrical Machinary Khanna Publisher. D.P. Kothari & I.J. Nagrath, Basic Electrical Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill, 1991. C.L. Wadhwa Basic Electrical Engineering. New Age International
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 5
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
EX1004 Basic Electrical Engg.
List of experiments1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Verification of Krichhoffs voltage & current law Verification of Thevenins theorem Verification of superposition theorem Observe various A.C. waveforms and prove relationship between maximum and RMS value for a sine wave. Prove voltage relationship for R-L-C series circuit . Measure inductance and resistance of a choke coil. Measure power & power factor of an AC circuit Verify relation ship between line and phase quantities for star & delta connected circuit Measure Power in a three phase circuit Plot magnetization characteristic for a coil Study of construction of various electrical machines Operation of various electrical machines.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 6
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Subject Code
Maximum Marks Theory Subject End Sem. Engineering Graphics 100 Mid Sem. Tests (Two tests Average) 30 Quiz, End assignment Sem 20 30
Credits Practical Lab assignment 20 L T P
ME1005
Course Contents Unit I Introduction To Engineering Drawing: Principles of Engineering Graphics and their Significance Drawing Instruments and their Use Conventions in Drawing Lettering BIS Conventions. Various types of lines, principal of dimensioning, types of dimensioning . Concept of Engineers Scale, Graphical Scales, Differences and their Construction. Curves used in Engineering Practice & their Constructions Conical curves: Ellipse, parabola, Hyperbola By different methods , Construction of Roulettes Cycloid, Trochoid Inferior and superior , Epicycloid, Epitrochoid Inferior and superior, Hypocycloid Hypotrochoid Inferior and superior, Special conditions, Involutes of different polygons, Drawing of tangents and normal to the above curves. Unit II Computer Aided Drafting (CAD): Introduction of Design and Drafting, Benefit, softwares, Wire frame, Surface and Solid Model, Basic commands of drafting entities like line, circle, polygon, polyhedron, cylinders. Modification and editing commands like offset, Fillet, Chamfer, trim Extend, mirror, array etc. Solution of projection problems on CAD. Principle of projection: Introduction, types of projections, plane of projection, first angle and third angle projection system, Projection of points. Unit III Projection of Lines, Projection of parallel Line, perpendicular line and oblique Line, line placed in two quadrants, line contained by Profile Plane, Traces of lines, methods of determining T.L. and T.I. of oblique line, rotating line method, Trapezoidal method, Real world problems. Projection of planes: Projection of Perpendicular and oblique plane. Traces of plane.
Unit IV Projection of Solids: Classification of Solids, Position of solids with respect to R.P., projection of platonic solids, polyhedrons, Solids of revolution, projection of solids on Auxiliary plane, Projection of Combination of Solids. Section of Solids: Classification of section planes, B.I.S. representation, Section of right solids by normal and inclined planes, Section of platonic solids, True and apparent shape of section, Problems on anti section. Unit V Development of Surfaces: Principle of development of surfaces, methods of development Parallel line and radial line method for right solids, solids with cutouts, Intersection of cylinders. Isometric Projections: Principle of Isometric projection, Isometric scale, Isometric axes, isometric views, methods of drawing isometric projections, Combinations of Solids, Isometric Projection from orthographic drawing. Conversion of Isometric views to Orthographic Views
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 7
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL ME1005 Engineering Graphics
Books 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Bhatt. N.D, Engineering Drawing Venugopal,Engineering Drawing and graphics ,New Age Jeyopoovan. T,Engineering Drawing , Vikas Publication. John K.C, Engineering Graphics for Degree , PHI Agrawal & Agrawal ,Engineering Graphics, TMH. Dhawan RK ,Engineering Drawing,S Chand & Co. A Premier on Computer Aided Engg drawing-Visvesvaraya Technological University (VTU), Belgaum.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 8
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem Work Shop Practice Mid Sem tests (Two tests Average) End assignment Sem 30 Quiz, Lab assignment 20 L Practical
Credits
ME1006
Course Contents Unit I : Introduction : Manufacturing Process and its classification ,Casting ,Machining ,Plastic deformation and metal forming ,Joining Processes ,Heat treatment process ,Assembly process. Powder Metallurgy, Introduction to computers in manufacturing. Black Smithy Shop/Lab.: Use of various smithy tools .Forging operations: Upsetting, Drawing down, Fullering, Swaging, Cutting down, Forge welding, Punching and drafting. Suggested Jobs/Laboratory work: Forging of chisel, Forging of Screw Driver Unit II: Carpentry Shop/Lab.: Timber: Type, Qualities of timber disease, Timber Grains, Structure of timber, Timber Seasoning, Timber preservation .Wood working tools: Wood working machinery, joints & joinery .Various operations of planning using various carpentry planes sawing & marking of various carpentry joints. Suggested Jobs/Laboratory work: Any of the Carpentry joints like mortise of tennon joint. Unit III: Fitting Shop/Lab.: Study and use of Measuring instruments, Engineer steel rule, Surface gauges caliper, Height gauges, feeler gauges, micro meter. Different types of files, File cuts, File grades, Use of surface plate, Surface gauges drilling tapping Fitting operations: Chipping filling, Drilling and tapping. Suggested Jobs/Laboratory work: Preparation of job piece by making use of filling, sawing and chipping, drilling and tapping operations. Unit IV Foundry/Lab.: Pattern Making: Study of Pattern materials, pattern allowances and types of patterns .Core box and core print. Use and care of tools used for making wooden patterns. Moulding/Lab.: Properties of good mould & Core sand, Composition of Green, Dry and Loam sand. Methods used to prepare simple green and bench and pit mould dry sand bench mould using single piece and split patterns. Unit V: Welding : Study and use of tools used for Brazing ,Soldering ,Gas & Arc welding .Preparing Lap & Butt joints using gas and arc welding methods ,Study of TIG & MIG welding processes .Safety precautions. Books: 1. 2. 3. 4.
Bawa,Workshop Practice TMH. Rao P.N.,Manufacturing Technology Vol 1&2, TMH. Hazara Choudhary, Workshop Practice , Vol I & II Chapman, Workshop Technology Vol 1-5
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 9
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem Engineering Physics Mid Sem. tests (Two tests Average) 30 Quiz, assignment 20 End Sem 30 Lab assignment 20 L T P Practical Credits
PH1051
100
Course Contents Unit I Quantum Physics-Group and particle velocities & their relationship. Uncertainty principle with elementary proof and applications ( determination of position of a particle by a microscope, non existence of electron in nucleus, diffraction of an electron beam by a single slit). Compton scattering. Wave function and its properties, energy and momentum operators, time dependent and time independent Schrdinger wave equation. Application of time independent Schrdinger wave equation to particle trapped in a one dimensional square potential well (derivation of energy eigen values and wave function) Unit II Wave Optics Interference: Fresnel's biprism, Interference in thin films (due to reflected and transmitted lght), interference from a wedge shaped thin film, Newtons rings and Michelsons interferometer experiments and their applications. Diffraction at single slit, double slit and n-slits (diffraction grating). Resolving power of grating and prism. Concept of polarized light, Brewster's laws, Double refraction, Nicol prism, quarter & half wave plate. Unit III Nuclear Physics- Nuclear liquid drop model (semi empirical mass formula), nuclear shell model, Linear Particle acceleratos: Cyclotron, general description of Synchrotron, Synchrocyclotron, and Betatron. Geiger- Muller Counter, Motion of charged particles in crossed electric and magnetic fields. Uses of Bainbridge and Auston mass Spectrographs. Unit IV Solid State Physics- Qualitative discussion of Kronig Penny model (no derivation), Effective mass, Fermi-Dirac statistical distribution function, Fermi level for Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductors, Zener diode, tunnel diode, photodiode, solar-cells, Hall effect. Superconductivity: Meissner effect, Type I and Type II superconductors, UNIT V Laser and Fiber Optics- Laser: Stimulated and spontaneous processes, Einsteins A & B Coefficients, transition probabilities, active medium, population inversion, pumping, Optical resonators, characteristics of laser beam. Coherence, directionality and divergence. Principles and working of Ruby, Nd:YAG, He-Ne ,Carbon dioxide Lasers & p-n junction diode laser with energy level diagrams. Fundamental idea about optical fiber, types of fibers, acceptance angle & cone, numerical aperture, V-number, propagation of light through step index fiber (Ray theory) pulse dispersion, attenuation, losses & various uses. Applications of lasers and optical fibers.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 10
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL PH1051 Engineering Physics
Books: 1. Ghatak, Optics , TMH 2. V. S. Yadava, Engineering Physics TMH 3. Optics by Brijlal and Subhraininyan. 4. .N. Avadhanulu and P.G. Kshirsagar, Engineering physics M S. Chand & Co. 5. Brijlal and Subraminiyan. Atomic and Nuclear physics 6. Beiser, Concepts of Modern Physics TMH 7. Kittel Solid State Physics ,Wiley India 8. Halliday, Fundamentals of Physics Wiley India
List of experiments: 1. Biprism, Newton's Rings, Michelsons Interferometer. 2. Resolving Powers Telescope, Microscope, and Grating. 3. G.M. Counter 4. Spectrometers-R.I., Wavelength, using prism and grating 5. Optical polarization based experiments: Brewsters angle, polarimeter etc. 6. Measurements by LASER-Directionality, Numerical aperture, Distance etc. 7. Uses of Potentiometers and Bridges (Electrical).. 8. Experiments connected with diodes and transistor. 9. Measurement of energy band gap of semiconductor. 10. To study Hall effect. 11. Solar cell. 12.To find the width of s single slit by f He-Ne Laser. 13. To determine the numeral aperture (NA) of a Optical Fibre. 14. To determine planks constant. 15. Other conceptual experiments related to theory syllabus.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 11
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Subject Code
Maximum Marks Allotted Theory Subject End Sem 100 Mid Sem. Tests (Two tests Average) End assignment Sem 20 Quiz,
Credits Practical Lab assignment L
05
T P
MA 1052
Engineering Mathematics II
30
Course Contents Unit-I Fourier series: Eulers formula, Fourier series for discontinuous functions, Expansion of odd and even periodic functions, Half range series, Complex form of Fourier Series Parsevals formula, Fourier Transform: Definition of Fourier transform, Fourier Sine and Cosine transform, Fourier Integral theorem, Properties of Fourier transform. Unit-II Laplace Transform: Introduction of Laplace transform, Laplace transform of elementary functions, Properties of Laplace transform, Change of scale property, First and second shifting properties, Laplace transform of derivative and integral. Inverse Laplace transform & its properties, Convolution theorem, Applications of Laplace transforms to solve the ordinary differential equations. Z-transform and its properties. Unit-III Second Order linear differential equation with variable coefficients: Solution by Methods One integral is known, Removal of first derivative, Changing independent variable and variation of parameter.Series solution method, Solutions of Legendre and Bessels equation. Unit-IV Partial Differential Equations: Formulation of partial differential equations ,Linear and non-linear partial differential equations of first order , Linear homogeneous and non homogeneous partial differential equations of second and higher order with constant coefficients. Separation of variable method, Heat equation, Wave equation and Laplaces equations. . Unit-V Vector Calculus: Differentiation of vectors, scalar and vector point function, Gradient, Geometrical meaning of gradient, Directional derivative, Divergence and curl .Line Integral, Surface Integral and Volume Integral, Stokes theorem (Greens theorem as a special case) and Gauss divergence theorem. Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
B.S. Grewal: Higher Engineering Mathematics , Khanna Publication. S S Sastri: Engineering Mathematics, PHI S.Arumungam: Mathematics for Engineers, SCITECH Publuication. Ramana: Advance Engg. Mathematics, TMH New Delhi Babu Ram :Engineering Mathematics, Pearson Erwin Kreyszig: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Wiley India.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 12
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Theory Subject Code Subject End Sem. Basic Mechanical Engineering. Mid Sem. tests (Two tests Average) Quiz, assignment End Sem
Credits Practical Lab assignment L T P
ME1053
100
30
20
30
20
Course Contents Unit I : Materials : Classification of engineering material ,Composition of Cast iron and Carbon steels, alloy steels their applications . Mechanical properties like strength , hardness, toughness , ductility, brittleness , malleability etc. of materials , Tensile test- Stress-strain diagram of ductile and brittle materials ,Hooks law and modulus of elasticity . Hardness and Impact testing of materials Unit II: Measurement: Temperature, pressure, velocity, flow, strain & torque measurement ,concept of measurement error & uncertainty analysis , Micrometer ,Dial gauge, Slip gauge ,Sine-bar and Combination set. Production Engineering : Introduction to Lathe and Drilling machines and their various operations. Unit III : Fluids : Fluid properties pressure, density and viscosity . Types of fluids , Newtons law of viscosity , Pascals law, Pressure variation with depth , Bernoulls equation for incompressible fluids , Introduction to Laminar and Turbulent flow , working principle of Hydraulic machines, pumps, turbines, Reciprocating pumps , Torque Converter . Unit IV: Thermodynamics : Thermodynamic system , properties , state , process , Zeroth, First and second law of thermodynamics, thermodynamic processes at constant pressure ,volume, enthalpy & entropy . Steam Engineering : Classification and working of boilers , mountings and accessories of boilers ,natural and artificial draught , steam properties, use of steam tables, working principle of steam Engine. Unit V: IC Engine : Working of Two stroke & Four stroke Petrol & Diesel Engine, Otto and Diesel cycles ,P-V & T-S diagrams . Refrigeration: Methods of Refrigeration , Reverse Carnot cycle , Working principle of simple vapor Compression Refrigeration System , coefficient of perform (COP), Unit of Refrigeration. Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Kothandaraman & Rudramoorthy, Fluid Mechanics & Machinery, New Age . Nakra & Chaudhary , Instrumentation and Measurements, TMH. Nag P.K, Engineering Thermodynamics , TMH . Ganesan , Internal Combustion Engines, TMH . Agrawal C M, Basic Mechanical Engineering ,Wiley Publication. Achuthan M , , Engineering Thermodynamics ,PHI.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 13
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
ME1053 Basic Mechanical Engineering.
List of Experiments: Theory related Eight to Ten experiments including core experiments as follows : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Tensile testing of standard Mild Steel specimen. Verification of Bernoullis Theorem . Linear and Angular measurement using ,Micrometer , Slip Gauges, Dial Gauge and Sine-bar. Study of different types of Boilers and Mountings . To find COP of a Refrigeration unit . Study of different IC Engines . Study of Lathe & Drilling Machines.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 14
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Theory Subject End Sem. Basic Civil Engg.& Engineering Mechanics Mid Sem. tests (Two tests average) Quiz, End assignment Sem Credits Practical Lab assignment L T P
Subject Code
CE 1054
100
30
20
30
20
Course Contents Unit I Engineering Materials - Stones, Bricks, Cement, Lime, Timber, Mortar and Concrete- types, basic properties, tests & uses. Unit II Building construction- Sub and super structure of a building, Types of Foundations, Types of Brick and Stone masonry, Planning & Orientation of building, Plastering and Pointing, Concept of Green Building. Unit III Surveying & Positioning- Introduction to Surveying- Classification, Fundamental Principles, & Instrument Used, Linear measurement by Chain survey, Angular measurement by Compass survey, Measurement of elevation by levelling, Introduction to Remote Sensing & its applications. Engineering Mechanics Unit IV Forces, Centroid & Moment of Inertia- Composition and resolution of forces, Concurrent, non-concurrent and parallel forces in a plane, Free body diagrams, Moment of a force and Varigon's theorem, Conditions of equilibrium, Polygon of forces , Couple, Moment of a couple, Equivalent couple, Addition of couples, Location of Centroid and Moment of Inertia of plane areas, Perpendicular Axis and Parallel Axis theorems, Unit V Shear Force and Bending Moment: Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagram for Cantilever and Simply supported beam with concentrated load, distributed load and couple. Point of Inflexion/ Contra-flexure, Relationship between bending moment and shear for pure bending. Books: 1. Palanichamy, Basic Civil Engineering , TMH 2. S. Ramamrutam & R. Narayanan: Basic Civil Engineering, Dhanpat Rai Pub, New Delhi. 3. Duggal: Surveying, Tata McGraw Hill New Delhi. 4. S. C. Rangwala: Building Construction, Charotar Publications House, Anand. 5. Sushil Kumar: Building Construction. 6. Shesha Prakash & Mogaveer: Elements of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, PHI Learning Pvt. ltd New Delhi 7. R.K. Rajput : Engineering Mechanics, S. Chand & Co. 8. Dr. K.L. Kumar Engineering Mechanics, Tata Mc Graw Hills New Delhi. 9. Timoshenko TMH: Engineering Mechanics. 10. R S Khurmi : Engineering Mechanics. 11. Jivan Kachnane & Ruchi Shrivastava : Engineering Mechanics, Ane Books. 12. Duggal : Building Materials, New Age International Publishers.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 15
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
CE 1054 Basic Civil Engg. & Engineering Mechanics
List of Experiments: Students are expected to perform minimum ten experiments from the list suggested below by preferably selecting experiments from each unit of syllabus. Basic Civil Engineering 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. To perform Chain survey of a given area for locating existing ground features. To perform Traverse surveying with prismatic compass, check for local attraction and determine corrected bearings To perform Levelling exercise by Height of instrument method and Rise & Fall method. To study the use of Theodolite for determining horizontal and vertical angles To determine the Compressive strength of Bricks. To determine the Compressive strength of Concrete. To determine (a) Normal consistency (b) Initial and Final Setting time of a cement sample.
Engineering Mechanics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. To verify the law of Triangle of Forces and Lamis theorem. To verify the law of parallelogram of forces. To verify law of polygon of forces To find the forces in members of a simple jib crane and to compare them with theoretical values To determine the moment of inertia of fly wheel by falling weight method. To verify the law of moments using a bell crank lever. To determine support reaction and shear force at a given section of a simply Supported beam and verify in analytically using parallel beam apparatus To find out the centroid of plane areas graphically and verify it analytically.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 16
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Allotted Theory Subject Code Subject End Sem. Mid Sem. Tests Quiz, (Two tests Average) assignment End Sem Credits Practical L Lab assignment T
P
CS 1055
Basic Computer Engineering
100
30
20
30
20
Course Contents UNIT I Computer: Definition, Classification, Organization i.e. CPU, register, Bus architecture, Instruction set, Memory & Storage Systems, I/O Devices, System & Application Software. Computing Ethics, Computer Application in eBusiness, Bio-Informatics, health Care, Remote Sensing & GIS, Meteorology and Climatology, Computer Gaming, Multimedia and Animation etc. UNIT II Operating System: Definition, Function, Types, Management of File, Process & Memory.Programming Languages: Generations, Characteristics & Categorization. Introduction to Programming : Procedure Oriented Programming VS object oriented programming, , OOPS Features and Merits. UNIT III C++ : Features, Character, Tokens, Precedence and Associativity, Program Structure, Data Types, Variables, Operators, Expressions, Statements and control structures, I/O operations, Array, Functions, Structures & Unions, Object & Classes, Constructors & Destructors, Overloading Functions & Operators, Derived Classes and Inheritance. UNIT IV Data base Management System : Introduction, File oriented approach and Database approach, Data Models, Architecture of Database System, Data independence, Data dictionary, DBA, Primary Key, Data definition language and Data Manipulation Language UNIT V Computer Networking : Introduction, Goals, ISO-OSI Model, Functions of Different Layers. Internetworking Concepts, Devices, TCP/IP Model. Introduction to Internet, World Wide Web, Network Security & E-commerce, Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. E Balagurusamy, Fundamentals of Computers TMH. V Rajaraman, Fundamentals of Computers PHI Anita Goel, Computer Fundamentals Pearson. Balagurusamy, Peter Norton, Introduction to Computers TMH Object Oriented Programming with C++ :E. TMH Rajesh K.Shukla, Object Oriented Programming in C++ Wiley India Ajoy Kumar Ray & Tinku Acharya Information Technology Principles and Application PHI. Kenneth Hoganson, Concepts in Computing Jones & Bartlett. Silberschatz and Galvin Operating Systems Wiley India Andrew Tananbaum, Computer Networks PHI
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 17
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
CS 1055 Basic Computer Engineering
List of Experiment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. . Study and practice of Internal & External DOS commands. Study and Practice of MS windows Folder related operations, My-Computer, window explorer, Panel, Study and practice of Basic linux Commands ls, cp, mv, rm, chmod, kill, ps etc. Creation and editing of Text files using MS- word. Creation and operating of spreadsheet using MS-Excel. Creation and editing power-point slides using MS- power point Creation and manipulation of database table using SQL in MS-Access. WAP to illustrate Arithmetic expressions. WAP to illustrate Arrays. WAP to illustrate functions. WAP to illustrate constructor & Destructor. WAP to illustrate Object and classes. WAP to illustrate Operator overloading. WAP to illustrate Function overloading. WAP to illustrate Derived classes & Inheritance.
Control
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 18
UIT- RGPV (Autonomous), BHOPAL
Maximum Marks Subject Code Theory Subject End Sem. Mid Sem. Tests Quiz, (Two tests Average) assignment End Sem Practical Lab Assignment L
Credits T P
HN1056
Language lab & Seminars
30
20
Course Contents Course objective: This course intends to impart practical training in the use of English Language for Communicative purposes and aims to develop students personality through Language Lab. Topics to be covered in the Language laboratory sessions: 1. 2. Introducing oneself, family, social roles, personal image design, building relationships, body language, concept of time and space. Public Speaking and oral skills with emphasis on conversational practice, Role plays, extempore speech, JAM (Just a minute sessions), describing objects and situations, giving directions, debate, telephonic etiquette. Reading Comprehension: Intensive reading skills, rapid reading, and reading aloud (Reading material to be selected by the teacher). Translation from English to Hindi and vice versa. Oral Presentation: preparation and delivery (Topic to be selected by the teacher.)
3. 4. 5.
w.e.f. academic session 2010-11 19
You might also like
- RGPV 1st Year (Sy) 1st & 2nd SemDocument17 pagesRGPV 1st Year (Sy) 1st & 2nd Semsaurabhrai160290No ratings yet
- Experimental Methods and Instrumentation for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandExperimental Methods and Instrumentation for Chemical EngineersNo ratings yet
- Vit University SyallabusDocument95 pagesVit University Syallabuspranavateja12399No ratings yet
- Btech Electronics and Communication Engg Semester I To Viii Cbcegs GnduDocument118 pagesBtech Electronics and Communication Engg Semester I To Viii Cbcegs GnduSonakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceNo ratings yet
- ECE SyllabusDocument88 pagesECE SyllabusBrijesh PalNo ratings yet
- Finite Element and Finite Difference Methods in Electromagnetic ScatteringFrom EverandFinite Element and Finite Difference Methods in Electromagnetic ScatteringM.A. MorganNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination & Syllabus OF: Kashmere Gate DELHI 110006Document16 pagesScheme of Examination & Syllabus OF: Kashmere Gate DELHI 110006Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Computational Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Science Using PythonFrom EverandComputational Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Science Using PythonNo ratings yet
- 3rd SemesterDocument13 pages3rd SemesterRed-KanNo ratings yet
- Full-Field Measurements and Identification in Solid MechanicsFrom EverandFull-Field Measurements and Identification in Solid MechanicsMichel GrediacNo ratings yet
- Btech Civil SyllabusDocument44 pagesBtech Civil SyllabusValmik PatelNo ratings yet
- Multiscale Modeling of Additively Manufactured Metals: Application to Laser Powder Bed Fusion ProcessFrom EverandMultiscale Modeling of Additively Manufactured Metals: Application to Laser Powder Bed Fusion ProcessNo ratings yet
- CUSAT B.Tech ECE Syllabus For 2000 AdmissionDocument61 pagesCUSAT B.Tech ECE Syllabus For 2000 Admissionenky4uNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry: Unit V: FUELSDocument8 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Unit V: FUELSABHAY PATELNo ratings yet
- IV Sem EC GradingDocument7 pagesIV Sem EC GradingSneha HerleNo ratings yet
- First YearDocument23 pagesFirst YearsaratknairNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1st & 2ndDocument24 pagesSyllabus 1st & 2ndAbyakta BaurahNo ratings yet
- Vit Ece 1st Year SyllabusDocument13 pagesVit Ece 1st Year Syllabuspranavateja12399100% (1)
- 2 NdsemDocument14 pages2 NdsemAkshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Elective - IDocument33 pagesElective - IMohit RanaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Course FileDocument32 pagesCHEMISTRY Course FileRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- Mech All PDFDocument46 pagesMech All PDFtoshugoNo ratings yet
- Btech - CSE 1999-2000 Syllabus Book JNTUDocument76 pagesBtech - CSE 1999-2000 Syllabus Book JNTUfasi425No ratings yet
- 01 B.Tech CSE Syllabus FinalDocument79 pages01 B.Tech CSE Syllabus FinalSamir KarNo ratings yet
- Btech SyllabusDocument29 pagesBtech Syllabusforgetevil1No ratings yet
- IV B.E. (Chemical Engineering)Document7 pagesIV B.E. (Chemical Engineering)9y9aNo ratings yet
- RGPV BE Syllabus BE-101 Engineering ChemistryDocument2 pagesRGPV BE Syllabus BE-101 Engineering ChemistryDeepak prasadNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BE RevisedDocument40 pagesSyllabus BE RevisedJayesh SawarkarNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology, Raipur (C.G.) : Periods/weekDocument12 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Raipur (C.G.) : Periods/weekMukul GargNo ratings yet
- Uvce 2nd Sem B.e-Mech Syl Copy 2k11Document12 pagesUvce 2nd Sem B.e-Mech Syl Copy 2k11hemanth kumar s gNo ratings yet
- Ganpat University: U.V.Patel College of EngineeringDocument13 pagesGanpat University: U.V.Patel College of EngineeringMalith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Se (Old) SyllabusDocument19 pagesSe (Old) SyllabusAnonymous I13s99No ratings yet
- Cse RGPV SyllabusDocument54 pagesCse RGPV Syllabusnayansharma19485No ratings yet
- Syllabus First Year 2015-16Document7 pagesSyllabus First Year 2015-16Harish kumawatNo ratings yet
- Paul C. Painter Michael M. Coleman Physical Properties of PolymersDocument3 pagesPaul C. Painter Michael M. Coleman Physical Properties of Polymersvivek sarojNo ratings yet
- B.tech in Electrical EngineeringDocument112 pagesB.tech in Electrical EngineeringShravani SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Gtu Be Civil First YearDocument14 pagesGtu Be Civil First YearHR Divya RanaNo ratings yet
- B Tech I Yr Syllabus Civil 291223022748Document54 pagesB Tech I Yr Syllabus Civil 291223022748abhaypal617No ratings yet
- I/Iv B.Tech Common With Six Year Dual Degree Course Ii/Vi (B.Tech.+ M.Tech.)Document13 pagesI/Iv B.Tech Common With Six Year Dual Degree Course Ii/Vi (B.Tech.+ M.Tech.)Harsha Vardhan BaleNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. All Branch Ist Scheme AKTUDocument27 pagesB. Tech. All Branch Ist Scheme AKTUsanjay kumarNo ratings yet
- 10100Document42 pages10100احمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- JNTUK-DAP-Course Structure and Syllabus-B.tech (Petrochemical Engg) - III YEAR-R9 Students - 28!06!2011Document26 pagesJNTUK-DAP-Course Structure and Syllabus-B.tech (Petrochemical Engg) - III YEAR-R9 Students - 28!06!2011Param AddalaNo ratings yet
- R-18 Eee SyllabusDocument47 pagesR-18 Eee SyllabusSwaroopNo ratings yet
- NIT DurgapurDocument115 pagesNIT DurgapurSayak DasNo ratings yet
- B Tech First YearDocument15 pagesB Tech First YearuttamsaxenaNo ratings yet
- Dip Engg To BE Lat SchemeDocument4 pagesDip Engg To BE Lat SchemeJingle MingleNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology (Common For All Branches) Credit-Based (2014-15 Onwards in Phased Manner)Document47 pagesBachelor of Technology (Common For All Branches) Credit-Based (2014-15 Onwards in Phased Manner)Mohit GanwaalNo ratings yet
- National Power Training Institute, Badarpur Syllabus of All SemestersDocument112 pagesNational Power Training Institute, Badarpur Syllabus of All SemestersVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- IET ComputerDocument77 pagesIET ComputerCricket legacyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)Document11 pagesMathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)HhhhNo ratings yet
- Css Mphil 2008Document5 pagesCss Mphil 2008Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Document4 pagesEngineering Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21cat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Study Plan For NITK SurathkalDocument14 pagesStudy Plan For NITK SurathkalSai Deepak BhimarajuNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument40 pagesB.Tech. Electrical Engineering Syllabussaurabh1116No ratings yet
- Nifft B.tech MME Syllabus.Document36 pagesNifft B.tech MME Syllabus.Rajesh0% (1)
- VJTI Syllabus 28-08-2008Document560 pagesVJTI Syllabus 28-08-2008Abhinav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Learning Curve CalculatorDocument7 pagesLearning Curve CalculatorYasir MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Tap Install LocationDocument1 pageTap Install LocationYasir MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Definiciones Conversor A - D NationalDocument2 pagesDefiniciones Conversor A - D NationalelvagojpNo ratings yet
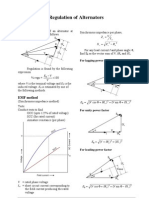
- Regulation of AlternatorsDocument3 pagesRegulation of Alternatorsrakeshkr07No ratings yet
- Creativity MCQDocument17 pagesCreativity MCQAmanVatsNo ratings yet
- APP PinAAcle 900 Elemental Analysis of Beer by FAAS 012049 01Document3 pagesAPP PinAAcle 900 Elemental Analysis of Beer by FAAS 012049 01strubingeraNo ratings yet
- 0404 eDocument80 pages0404 eFrancisco MisleNo ratings yet
- AVT 2217 Module 5 Aiport Lighting SystemDocument15 pagesAVT 2217 Module 5 Aiport Lighting SystemJane PazNo ratings yet
- Excel Tips Tricks e-BookV1.1 PDFDocument20 pagesExcel Tips Tricks e-BookV1.1 PDFSulabhNo ratings yet
- Title DefenseDocument3 pagesTitle DefenseLiezl Sabado100% (1)
- Oracle SQL Developer User GuideDocument194 pagesOracle SQL Developer User Guidesureshreddy_iNo ratings yet
- Implications of PropTechDocument107 pagesImplications of PropTechAnsar FarooqiNo ratings yet
- 2 Mathematics For Social Science-1-1Document58 pages2 Mathematics For Social Science-1-1ሀበሻ EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument6 pagesGeoKanadeTachibana75% (4)
- Chapter Two: Describing DataDocument20 pagesChapter Two: Describing DataJames Alex HabaradasNo ratings yet
- MAS500 2011 Vår Masteroppgave Henrik Engedal Per Magne EgelidDocument130 pagesMAS500 2011 Vår Masteroppgave Henrik Engedal Per Magne EgelidPoppy DanielsNo ratings yet
- ARCO ANDI Wayne PIB Installation and Start Up GuideDocument39 pagesARCO ANDI Wayne PIB Installation and Start Up GuidejotazunigaNo ratings yet
- Rizal and The Theory of NationalismDocument37 pagesRizal and The Theory of NationalismLiza Betua Sotelo78% (58)
- B4 Ethical Problems and Rules of Internet NetiquetteDocument11 pagesB4 Ethical Problems and Rules of Internet NetiquetteTarkan SararNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3.1 Math 10Document2 pagesSummative Test 3.1 Math 10Christian DecenaNo ratings yet
- Soft-Starter: Programming ManualDocument162 pagesSoft-Starter: Programming ManualThaylo PiresNo ratings yet
- Abu Khader Group ProposalDocument5 pagesAbu Khader Group ProposalChristine AghabiNo ratings yet
- UFO and PentagonDocument69 pagesUFO and PentagonNur Agustinus100% (3)
- Mind Surge NewDocument65 pagesMind Surge NewmazzagraNo ratings yet
- Reports On TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROVIDED by The Teachers To The Learners / Learning FacilitatorsDocument2 pagesReports On TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROVIDED by The Teachers To The Learners / Learning FacilitatorsJerv AlferezNo ratings yet
- EPAL TRW EPAL2 2edition Section2 Part2 GBDocument45 pagesEPAL TRW EPAL2 2edition Section2 Part2 GBGabriele AsnaghiNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Gp1200 Owners ManualDocument3 pagesYamaha Gp1200 Owners ManualGregoryNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityShruti BiradarNo ratings yet
- Arts NPSH TutorialDocument3 pagesArts NPSH TutorialDidier SanonNo ratings yet
- X20PS9600-en V1.20Document10 pagesX20PS9600-en V1.20PREVENCIONISTA HUAQUIANNo ratings yet
- Philippine Ecd Checklist Class Summary (Post-Test) SY: 2022-2023Document5 pagesPhilippine Ecd Checklist Class Summary (Post-Test) SY: 2022-2023UltravioletHeartNo ratings yet
- Stas 500-2-80 RDocument4 pagesStas 500-2-80 RSzabolcs KovacsNo ratings yet
- Prompt by NikistDocument4 pagesPrompt by NikistMãnoj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DriveDocument8 pagesVariable Frequency DriveNAYEEM100% (1)
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionFrom EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedFrom EverandThe House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherFrom EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherNo ratings yet
- The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]From EverandThe Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Welcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticFrom EverandWelcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Sex, Drugs, and Cocoa Puffs: A Low Culture ManifestoFrom EverandSex, Drugs, and Cocoa Puffs: A Low Culture ManifestoRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (1428)
- The Comedians in Cars Getting Coffee BookFrom EverandThe Comedians in Cars Getting Coffee BookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Most Forbidden Knowledge: 151 Things NO ONE Should Know How to DoFrom EverandThe Most Forbidden Knowledge: 151 Things NO ONE Should Know How to DoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- 1,001 Facts that Will Scare the S#*t Out of You: The Ultimate Bathroom ReaderFrom Everand1,001 Facts that Will Scare the S#*t Out of You: The Ultimate Bathroom ReaderRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (48)
- The Book of Bad:: Stuff You Should Know Unless You’re a PussyFrom EverandThe Book of Bad:: Stuff You Should Know Unless You’re a PussyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Travel: The Worst-Case Scenario Survival Handbook: How to Survive Runaway Camels, UFO Abductions, High-Rise Hotel Fires, LeechesFrom EverandTravel: The Worst-Case Scenario Survival Handbook: How to Survive Runaway Camels, UFO Abductions, High-Rise Hotel Fires, LeechesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (126)
- Maybe You Should Talk to Someone: the heartfelt, funny memoir by a New York Times bestselling therapistFrom EverandMaybe You Should Talk to Someone: the heartfelt, funny memoir by a New York Times bestselling therapistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (642)
- Cats On The Run: a wickedly funny animal adventureFrom EverandCats On The Run: a wickedly funny animal adventureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)



































































































![The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711420909/198x198/ba98be6b93/1712018618?v=1)




















