Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prepared by G.PREMKUMAR, SDE, RTTC, TVM.: Question Bank On
Uploaded by
Mohammad AslamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prepared by G.PREMKUMAR, SDE, RTTC, TVM.: Question Bank On
Uploaded by
Mohammad AslamCopyright:
Available Formats
1
QUESTION BANK on GSM
Prepared by G.PREMKUMAR, SDE,RTTC,TVM.
The following 111 questions are prepared for the benefit of those who are preparing for SDE Competitive Examination 2007.Please study the topic well and try to answer the following questions . Wish you a grand success !!!
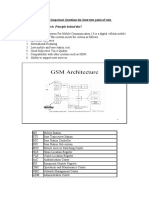
I. Fill in the blanks with suitable answer:1. The SIM inserted mobile equipment is called ------------- . 2. The interface connecting MS and BTS is ----------- . 3. The standard based on which GSM functions is ---------- . 4. The access method used in GSM is ------------ . 5. The RF channel spacing in GSM is -----------. 6. The number of chnls per carrier in GSM is ------------. 7. The voice coding algorithm used in GSM is -----------. 8. The modulation method used in GSM is --------------. 9. The voice coding rate used in GSM is -----------. 10.The uplink frequency used in GSM 900 is -------------. 11.The downlink frequency used in GSM- 900 is -------------. 12. The duplexing method used in GSM is --------------. 13. The duplex separation used in GSM-900 is --------------. 14.The uplink frequency used in GSM -1800 is -------------. 15. The downlink frequency used in GSM-1800 is -------------. 16. The duplex separation used in GSM-1800 is --------------. 17. Transcoding is the function of ----------------- . 18. The MSC used to interconnect external network is called ---------. 19. Intra BSC handover is a function of ----------. 20. Billing is associated with ---------- element of NSS. 21. BTS and BSC are elements of --------- subsystem. 22. MSC is an element of ------------- subsystem. 23. -------- element stores the subscriber parameters permanently.
2 24.The data stored in HLR which can be changed only by MMC is called ------------. 25. -------------- reduces the number of queries to HLR. 26. ------------- assigns TMSI to the mobile customer. 27. IMSI Attach and Detach operations are functions of --------------. 28. A base station with a number of RF chnls is called a -----------. 29. A group of cells where the frequency reuse is not done is called. 30. The interference offered to a cell from a cell of same frequency is called ---------------. 31. As cluster size increases the co channel interference -------------. 32. ------------ channels are divided into traffic channels and control channels. 33. BCCH channels operates only in ----------- links. 34. The duration of a time slot in GSM air interface is -------------. 35. The duration of a TDMA frame in GSM is --------------. 36. The different types of Multiframes are -------- and -----------. 37. The duration of a super frame is ------------------. 38. One hyperframe is equal to -------------- number of super frames. 39. The technique used to improve C/I ratio by utilizing many frequency chnls is called --------------------. 40. The most commonly used propagation model for macro cell coverage is ----------------. 41. The most commonly used propagation model for micro cell coverage is ----------------. 42.The feature that controls the power of transmission when the mobile is in silent mode is -------------------. 43. A mobile equipment is identified by -----------------. 44. The international identity used to identify a mobile customer within the network is called ------------------. 45.A number assigned to the mobile subscriber which is used by the calling party to dial is ------------------. 46. The identity which guaranties the integrity of mobile subscriber on the radio interface is ----------------. 47.The temporary number used for routing call to MS IS -------------. 48.The structure of MSRN is the same as that of ------------------ . 49.The max: length of LAC is --------------. 50.The algorithm used for authentication purpose is -----------------.
3 51. RAND, SRE, Kc are together called --------------. 52. RAND signal is of ---------------- bit length. 53. GSM belongs to ----------------- generation mobile communication standard. 54. The inputs of A3 algorithm are ----------. 55. The output of A3 algorithm is ----------. 56. -------------- carries authentication check. 57. VLR provides ------------ to BTS for encryption the radio path. 58. The inputs of A8 algorithm are ----------. 59. The output of A8 algorithm is ----------. 60. An action taken by MSC/VLR set the subscriber status to present is -------------. 61. The output of A5 algorithm is -----------------. 62. The action taken by MSC/VLR to set the subscriber status to absent when the mobile station has not achieved radio contact for a certain period of time is -------------. 63. The action taken by MSC/VLR to set the subscriber status to absent is -------------. 64. The procedure invoked when MS moves from one LA to another LA is ------------------ . 65. The MS distinguishes between cells using -------- code. 66. GPRS uses --------------- modulation method. 67. The support nodes used in GPRS are ------------ and --------------- . 68. In GPRS , HLR querying is done by ------------ . 69 .In GPRS , ------------ is used to interface to protocol data network (PDN). 70. In GPRS, the procedure that handle the mobility of user is called ---------. 71. In GPRS, the procedure that handle the user connection to external networks is called ---------. 72. In GPRS, the phase of connecting the GPRS terminal to the network is called ------------. 73. In GPRS, the phase of connecting the GPRS terminal to the external network is called ------------. 74. The two types of OMC used are ----------- and ---------------. 75. The cell size can be reduced by reducing the -------------- and -----------of the antenna.
4 II. Write whether TRUE/ FALSE. If FALSE correct the underlined word/words:76. EIR is the network element responsible for storing IMEIs of mobile handsets. 77. XCDR is an element of BSS. 78. Transcoding and rate adaptation functionality is available in BTS. 79. Frequency hopping is a function of BTS. 80. In GSM, basic switching is the function of MSC. 81.HLR is an element of BSS. 82. One PLMN contains only one HLR. 83.IMSI is a temporary dta in HLR. 84.VLR address is temporary data in HLR. 85.One VLR may be in charge of one or more LA. 86. VLR is updated by HLR on entry of MS in its area. 87. Frequency reuse introduces interference. 88.Co chnl interference is a function of Q where Q= D/R. 89.Q = Square root of 3N where N is the cluster size.
90.The low frequency unit of BTS is responsible for Digital Signal Processing. 91. The high frequency unit of BTS is responsible for GMSK. 92.Voice Activity Detection is used in Discontinuous Transmission (DTX). 93. IMSI is stored in EIR. 94.TMSI is used only over radio path. 95.Reallocation of IMSI is possible. 96.A3,A5,A8 Algorithms are available in SIM card. 97.A3 and A8 can be different for different networks. 98.There can be many MSC/VLR in one PLMN area . 99. There are many location areas in one MSC/VLR area. 100. GPRS belongs to 3G standard. 101.In GPRS combination of time slots is allowed . 102.There are four types of coding schemes used in GPRS.
103. SGSN delivers packets to mobile packets to mobile stations within its service area. 104.The existing BSS must be enhanced to make it GPRS compatible. 105. The HLR must be enhanced to make it GPRS compatible. 106. When GPRS terminal is powered on it sends an attach message to the network. 107. Phase establishing a connection to an external data network is called PDP Context Activation. 108. GPRS uses packet switching. 109. CCCH operates in both U/L and D/L. 110. MSRN is used in GMSC to set up connection to visited MSC/VLR. 111. For analysis purpose a cell is represented by a hexagon shape. ------0--------
You might also like
- NMC Test 2013Document4 pagesNMC Test 2013محمد أحمد عبدالوهاب محمدNo ratings yet
- GSM - Network Aspects: Handover Location Updating and Call Authentication and SecurityDocument5 pagesGSM - Network Aspects: Handover Location Updating and Call Authentication and Securityabhineetkumar100% (1)
- GSM QuestionBank 1Document2 pagesGSM QuestionBank 1girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- GSM Principles ComDocument67 pagesGSM Principles Compsychomantis1No ratings yet
- Tech ExamDocument3 pagesTech Examمحمد أحمد عبدالوهاب محمدNo ratings yet
- Luc BitsDocument2 pagesLuc BitslucysmileyNo ratings yet
- MOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICDocument89 pagesMOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICAli MurtazaNo ratings yet
- CM E2 E3 Question BankDocument60 pagesCM E2 E3 Question BankAnkit Ranjan82% (11)
- Chapter 7Document52 pagesChapter 7Henok EshetuNo ratings yet
- GSM System OverviewDocument79 pagesGSM System OverviewChee Leong100% (1)
- CMCDocument17 pagesCMCManasa ManuNo ratings yet
- NT MCQDocument25 pagesNT MCQShripad Joshi0% (1)
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Document52 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Manisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Wireless 5Document38 pagesWireless 5Varun TomarNo ratings yet
- GSM Theories, Network Analayzation & Microwave TransmissionDocument57 pagesGSM Theories, Network Analayzation & Microwave TransmissionGavinda LakmalNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument25 pagesQuestion Bankmokara borisNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Discontinuous Reception and Discontinuous TransmissionDocument2 pages1.8 Discontinuous Reception and Discontinuous Transmissionnaveedraza4213No ratings yet
- GSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaDocument32 pagesGSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaAnjnay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Revised MCQsDocument5 pagesMobile Computing Revised MCQsJunaid Jan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- An Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByDocument43 pagesAn Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByLet's Go TlmNo ratings yet
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Document23 pagesSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshNo ratings yet
- TD-SCDMA Network Planning and Optimization: Jianhua Zhang and Guangyi LiuDocument40 pagesTD-SCDMA Network Planning and Optimization: Jianhua Zhang and Guangyi LiuIgor MalianovNo ratings yet
- GSM Fundamentals RFDocument65 pagesGSM Fundamentals RFPuneet YadavNo ratings yet
- GSM Basics 1 PDFDocument21 pagesGSM Basics 1 PDFSimba MakenziNo ratings yet
- 1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1Document11 pages1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1edwinNo ratings yet
- Ik1330lab2 (KTH)Document7 pagesIk1330lab2 (KTH)Mehdi RabbaniNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEWDocument79 pagesOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document6 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)RobertoNo ratings yet
- Project: GPRS: Wireless Systems (Tsks03)Document12 pagesProject: GPRS: Wireless Systems (Tsks03)VinayakNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oDocument34 pagesBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithNo ratings yet
- GSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgeDocument11 pagesGSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgealonindNo ratings yet
- MC Maritime RadioDocument8 pagesMC Maritime RadioJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölDocument47 pagesCellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölChibueze Ezeokafor100% (1)
- WMC MCQs 3Document64 pagesWMC MCQs 3Zeeshan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- GSM Air InterfaceDocument10 pagesGSM Air InterfacebhathiyaengNo ratings yet
- GSM, GPRS and UMTS OverviewDocument56 pagesGSM, GPRS and UMTS Overviewambika_sNo ratings yet
- E5-E6 - Text - Chapter 3. Overview of Mobile CommunicationDocument46 pagesE5-E6 - Text - Chapter 3. Overview of Mobile Communicationsumit15sksNo ratings yet
- PUE 3123 - Telecommunication Network Design and Planning - 06Document55 pagesPUE 3123 - Telecommunication Network Design and Planning - 06Solomon Teshome100% (1)
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Machindra GaikarNo ratings yet
- Architecture of The GSM NetworkDocument17 pagesArchitecture of The GSM NetworkOmFaNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLDocument46 pagesBasic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document11 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Teja MylavarapuNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLDocument46 pagesBasic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLSachin SonkusareNo ratings yet
- GSM Overview UpdatedDocument131 pagesGSM Overview UpdatedSandip DasNo ratings yet
- GSM Principles Com 4Document67 pagesGSM Principles Com 4someoneniceNo ratings yet
- MCW MCQDocument15 pagesMCW MCQPriti Patil100% (1)
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument8 pagesGSM Network ArchitectureAvanish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Overview of GSM Cellular Network and Operations: Ujjwal JainDocument90 pagesOverview of GSM Cellular Network and Operations: Ujjwal JainroobowNo ratings yet
- 1 GSM Protocol Stack 4 Location Update 7Document46 pages1 GSM Protocol Stack 4 Location Update 7kvsreddiNo ratings yet
- Overview of GSM Cellular Network and OperationsDocument90 pagesOverview of GSM Cellular Network and OperationsscribdmithunNo ratings yet
- Présentation Sur GSMDocument60 pagesPrésentation Sur GSMSarahHattanNo ratings yet
- MCN Unit 4.1Document18 pagesMCN Unit 4.1venkatNo ratings yet
- Cellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölDocument47 pagesCellular Network: Özge Bengür Merih Miran S.Burak SarıgölAnmol KhanNo ratings yet
- Bss-Bts Overview BaniDocument79 pagesBss-Bts Overview Baniseth_awuah28No ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document17 pagesGlobal System For Mobile (GSM)Barhav SarbastNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SNOC - CM - MOP - GUFTL Removing Insufficient Space On CC Board - ZTE - V1.0Document12 pagesSNOC - CM - MOP - GUFTL Removing Insufficient Space On CC Board - ZTE - V1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- GU - NetNumen U31 R18 V12.18 Test Guide - Distributed - R1.0Document300 pagesGU - NetNumen U31 R18 V12.18 Test Guide - Distributed - R1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Migration of GSM Site Using ICMDocument27 pagesMigration of GSM Site Using ICMMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Netnumen™ U31 R50: Unified Element Management SystemDocument35 pagesNetnumen™ U31 R50: Unified Element Management SystemMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- DSCP Addition and Change MOPDocument4 pagesDSCP Addition and Change MOPMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Snoc CM Mop 4g Enodeb Software Upgrade Zte v1.0Document12 pagesSnoc CM Mop 4g Enodeb Software Upgrade Zte v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- SNOC CM MOP 3G NodeB Rehoming Via TransferSiteTool ZTE v1.0Document25 pagesSNOC CM MOP 3G NodeB Rehoming Via TransferSiteTool ZTE v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- SNOC - CM - MOP - 3G - NODEB - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Document12 pagesSNOC - CM - MOP - 3G - NODEB - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- SNOC - CM - MOP - 4G - eNodeB - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Document9 pagesSNOC - CM - MOP - 4G - eNodeB - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Snoc CM Mop 2g Bts Vlan Change Zte v1.0Document10 pagesSnoc CM Mop 2g Bts Vlan Change Zte v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- S.No Site Id Site 3G ID Site NameDocument5 pagesS.No Site Id Site 3G ID Site NameMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- SNOC - CM - MOP - 2G - BTS - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Document10 pagesSNOC - CM - MOP - 2G - BTS - VLAN Change - ZTE - v1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- LTE Principle: - UMTS Radio Network Planning & Optimization DeptDocument48 pagesLTE Principle: - UMTS Radio Network Planning & Optimization DeptMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- G - TM - ZXUR 9000 GSM OMM Commissioning - R1.0Document26 pagesG - TM - ZXUR 9000 GSM OMM Commissioning - R1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Short Test 11b: Unit 11Document1 pageShort Test 11b: Unit 11Ксения ДауроваNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plasma Physics: Plasma Types and DefinitionsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Plasma Physics: Plasma Types and DefinitionsNelly Milagros Esperilla LupoNo ratings yet
- Partita1 Bach ViolinDocument13 pagesPartita1 Bach Violinjesseka.jasmine8550No ratings yet
- Brainwave FrequenciesDocument13 pagesBrainwave Frequenciesdhop__100% (4)
- 1756-IF16 WiringDocument24 pages1756-IF16 WiringjfeyesNo ratings yet
- Pueblo Bonito Flute Replicas: by Jonathan WalpoleDocument9 pagesPueblo Bonito Flute Replicas: by Jonathan WalpoleHerbert RiveraNo ratings yet
- WE FOXES Full Vocal Score Pace ReadingDocument372 pagesWE FOXES Full Vocal Score Pace ReadingPatrickNo ratings yet
- Saxo TenorDocument1 pageSaxo TenorTenorioNo ratings yet
- 3 RD PartyDocument2 pages3 RD PartyNonso NwankwoNo ratings yet
- Alto Chart PDFDocument1 pageAlto Chart PDF谢重霄No ratings yet
- DR Robert Bass CNN 1985 DEW60GHzDocument6 pagesDR Robert Bass CNN 1985 DEW60GHz3adrianNo ratings yet
- Music of The Classical PeriodDocument42 pagesMusic of The Classical PeriodKristhel-b Lapitan100% (2)
- 125 Transistor Projects Rufus TurnerDocument100 pages125 Transistor Projects Rufus TurnerIldefonso ArevaloNo ratings yet
- The Strange and Beautiful Sorrows of Ava Lavender Chapter SamplerDocument32 pagesThe Strange and Beautiful Sorrows of Ava Lavender Chapter SamplerCandlewick Press0% (2)
- Grammar-EXTRA NI 3 Unit 6 Past Simple PassiveDocument1 pageGrammar-EXTRA NI 3 Unit 6 Past Simple PassiveMariNo ratings yet
- HW8.4-AP Harmonics and Doppler-SOLNSDocument6 pagesHW8.4-AP Harmonics and Doppler-SOLNSMaher TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Valse FavoriteDocument2 pagesValse FavoriteArtur Costa100% (1)
- Contemporary Dance ResearchDocument3 pagesContemporary Dance ResearchMicah ErguizaNo ratings yet
- Chassis CX-A21FB CY-8895C Manual de ServicioDocument20 pagesChassis CX-A21FB CY-8895C Manual de ServicioLuis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Manual Placa Base ASUS p6x58dDocument126 pagesManual Placa Base ASUS p6x58dAitor Carrión AmorinNo ratings yet
- Link Budget Calculation: Training Materials For Wireless TrainersDocument28 pagesLink Budget Calculation: Training Materials For Wireless TrainersusmanNo ratings yet
- Music Perception and Cognition: Development, Neural Basis, and Rehabilitative Use of MusicDocument11 pagesMusic Perception and Cognition: Development, Neural Basis, and Rehabilitative Use of MusicAutes AG100% (1)
- 50 Dramatic TermsDocument3 pages50 Dramatic TermsAlvina IlukeNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Complete The Sentences APRIL (SEND!)Document3 pagesPresent Simple Complete The Sentences APRIL (SEND!)Irene Zabiela CobasNo ratings yet
- KPOP Fans Should KnowDocument6 pagesKPOP Fans Should KnowmelissaNo ratings yet
- Nte996 CA3080 EQUIVALENTEDocument3 pagesNte996 CA3080 EQUIVALENTERobert GabrielNo ratings yet
- Pare Mahal Mo Raw Ako PianoDocument6 pagesPare Mahal Mo Raw Ako PianojordzNo ratings yet
- Helix Traveling Wave TubeDocument18 pagesHelix Traveling Wave Tubeamvarman100% (1)
- Konstantin Saradzev BellsDocument3 pagesKonstantin Saradzev BellsAleksandar TamindžićNo ratings yet
- Total Telecom Soluction For Soul Space.Document10 pagesTotal Telecom Soluction For Soul Space.Mark HernandezNo ratings yet