Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LMMEC220
Uploaded by
Katon KUNCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LMMEC220
Uploaded by
Katon KUNCopyright:
Available Formats
LABORATORY MANUAL MEC220
SOLID MECHANICS LABORATORY
LMMEC220
Page 1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
S. No. 1. 2.
Title of the Experiment To perform tensile test on a specimen material using universal testing machine (UTM) Verification of the bending equation and determination of flexural rigidity and elastic modulus for a given beam To perform torsion test on a specimen and find the modulus of rigidity of the material To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Brinell's hardness test. To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Rockwell hardness test To determine the stiffness of spring, modulus of rigidity of the spring wire and the maximum strain energy stored To perform the compression test on a specimen material and find the compression strength
Page No. 3-5 6-8
3. 4. 5. 6.
9-11 12-13 14-15 16-18
7.
19-21
8.
To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Charpy's test; To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Izod test To perform shear test on a specimen material using universal testing machine To find the fatigue strength of a specimen material by performing the fatigue test
22-24
9. 10.
25-26 27-29
LMMEC220
Page 2
Experiment: 1 Experiment: To perform tensile test on a specimen material using universal testing machine (UTM) Equipment Required: Universal Testing Machine, Scale, Vernier calliper Material Required: Specimen of MS & CI Learning Objectives: Understanding of stress - strain diagrams, tensile strength of a material, significance of Young's modulus Outline of the Procedure: Measure the original length and diameter of the specimen. The length may either be length of gauge section which is marked on the specimen with a preset punch or the local length of the specimen. Insert the specimen into test machine. Begin the load application and record load Vs elongation data. Measure elongation values with the help of dividers and a ruler. Continue the test till fracture occurs. Measure the final length and diameter of specimen. Required Results: Parameters: A) Original dimensions: Length= ---------------------Diameter= ---------------------Area= ---------------------B) Final Dimensions: Length= ----------------------Diameter= ----------------------Area= -----------------------Average breaking Stress = Ultimate Stress = Average Percentage Elongation = Relationships to be determined: Relationship between stress and strain Graphs/Plots: Stress vs strain plot and identify yield point, ultimate tensile strength and E and % elongation and % reduction in area. Error Analysis: Cautions: If the strain measuring device is an extensometer it should be removed before necking begins. Measure deflection on scale carefully and accurately.
LMMEC220
Page 3
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To perform tensile test on a specimen material using universal testing machine (UTM)
Observations:
S. No.
Load(N)
Original Gauge length
Extension (mm)
Stress (N/mm2)
Strain
Calculations:
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 4
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 5
Experiment: 2 Experiment: Verification of the bending equation and determination of flexural rigidity and elastic modulus for a given beam Equipment Required: Bending of beams apparatus, pan, weights, beam of different crosssections Learning Objectives: To practically visualize the bending of beams for different support reactions, understand the importance of flexural rigidity and elastic modulus of beam Outline of the Procedure: Adjust cast- iron block along the bed so that they are symmetrical with respect to the length of the bed. Place the beam on the knife edges on the block so as to project equally beyond each knife edge. See that the load is applied at the centre of the beam. Note the initial reading of vernier scale. Add a weight of 20N (say) and again note the reading of the vernier scale. Go on taking readings adding 20N (say) each time till you have minimum six readings. Find the deflection () in each case by subtracting the initial reading of vernier scale. Draw a graph between load (W) and deflection () . On the graph choose any two convenient points and between these points find the corresponding values of W and . Calculate the value of E and the bending stresses for different loads. Required Results: Parameters: 1. The youngs modulus for steel beam is found to be----- N/mm2. 2. The youngs modulus for wooden beam is found to be----- N/mm2 Graphs/Plots: Graph between load (W) and deflection (). Error Analysis: Cautions: 1. Make sure that beam and load are placed a proper position. 2. The cross- section of the beam should be large. 3. Note down the readings of the vernier scale carefully
LMMEC220
Page 6
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: Verification of the bending equation and determination of flexural rigidity and elastic modulus for a given beam Observations:
S. No.
Load
Bending moment
Bending stress
Deflection
Youngs Modulus
Calculations:
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 7
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 8
Experiment: 3 Experiment: To perform torsion test on a specimen and find the modulus of rigidity of the material Equipment Required: A torsion testing machine, twist meter for measuring angles of twist, steel rule and Vernier caliper or micrometer. Learning Objectives: To understand the concept of torsion, twist angle and torsional rigidity Outline of the Procedure: Select the driving dogs to suit the size of the specimen and clamp it in the machine by adjusting the length of the specimen by means of a sliding spindle. Measure the diameter at about three places and take the average value. Choose the appropriate range by capacity change lever. Set the maximum load pointer to zero. Set the protector to zero for convenience and clamp it by means of knurled screw. Carry out straining by rotating the handweel in either direction. Load the machine in suitable increments. Then load out to failure as to cause equal increments of strain reading. Plot a torque- twist (T- ) graph. Read off co-ordinates of a convenient point from the straight line portion of the torque twist (T- ) graph and calculate the value of C by using relation Required Results: Parameters: i) Modulus of rigidity of mild steel rod is ------------- N/mm2 ii) Modulus of rigidity of Aluminum rod is ------------- N/mm2 Graphs/Plots: Torque- twist (T- ) graph. Error Analysis: Cautions: 1) Measure the dimensions of the specimen carefully. 2) Measure the Angle of twist accurately for the corresponding value of Torque.
LMMEC220
Page 9
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To perform torsion test on a specimen and find the modulus of rigidity of the material Observations: Gauge length of the specimen, l = Diameter of the specimen, d = Polar moment of inertia =
Torque 1 (T) Angle of twist()in radians Modulus of rigidity (C) N/mm2 Calculations:
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 10
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 11
Experiment: 4 Experiment: To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Brinell's hardness test. Equipment Required: Brinell's hardness testing machine, Brinell Microscope.
Material Required: Soft and hard mild steel specimens, brass, aluminum etc. Learning Objectives: To understand the concept of hardness and the various hardness numbers Outline of the Procedure: Specimen is placed on the anvil. The hand wheel is rotated so that the specimen along with the anvil moves up and contact with the ball. The desired load is applied mechanically (by gear driven screw) and the ball presses into the specimen. The diameter of the indentation made in the specimen by the pressed ball is measured by the use of a micrometer microscope, having transparent engraved scale in the field of view. The indentation diameter is measured at two places at right angles to each other, and the average of two readings is taken. The Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) which is the pressure per unit surface area of the indentation is noted down. Required Results: Parameters: The hardness of the material is found to be Specimen 1 = Specimen 2 = Specimen 3 = Error Analysis: Cautions: 1. Brinell test should be performed on smooth, flat specimens from which dirt and scale have been cleaned. 2. The test should not be made on specimens so thin that the impression shows through the metal, nor should impressions be made too close to the edge of the specimen.
LMMEC220
Page 12
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Brinell's hardness test. Observations: Material
Load
S. No.
Diameter Of the Indenter in mm
Diameter of indentation in mm 1 2 3
the Brinell Hardness Number(BHN)
Calculations:
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 13
Experiment: 5 Experiment: To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Rockwell hardness test Equipment Required: Rockwell hardness testing machine Material Required: Soft and hard mild steel specimens, brass, aluminum etc. Learning Objectives: To understand the concept of hardness and the various hardness numbers Outline of the Procedure: Place the specimen securely upon the anvil. Elevate the specimen so that it come into contact with the penetrator and put the specimen under a preliminary or minor load of 100+2N without shock. Apply the major load 900N by loading lever. Watch the pointer until it comes to rest. Remove the major load. Read the Rockwell hardness number or hardness scale. Required Results: Parameters: The hardness of the material is found to be Specimen 1 = Specimen 2 = Specimen 3 = Error Analysis: Cautions: 1. Hardness test should be performed on smooth, flat specimens from which dirt and scale have been cleaned. 2. The test should not be made on specimens so thin that the impression shows through the metal, nor should impression be made too close to the edge of a specimen.
LMMEC220
Page 14
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To determine the hardness of a specimen material using Rockwell hardness test Observation Table: S. no. Material HRC reading 1 2
Mean 3
Calculations:
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 15
Experiment: 6 Experiment: To determine the stiffness of spring, modulus of rigidity of the spring wire and the maximum strain energy stored Equipment Required: Spring testing machine, Vernier caliper, Scale, Micrometer. Material Required: Spring Learning Objectives: To understand the behaviour of springs subjected to loads, significance of stiffness of spring, modulus of rigidity and the maximum strain energy stored Outline of the Procedure: Measure the diameter of the wire of the spring by using the micrometer. Measure the diameter of spring coils by using the vernier calliper. Count the number of turns. Insert the spring in the spring testing machine and load the spring by a suitable weight and note the corresponding axial deflection in tension or compression. Increase the load and take the corresponding axial deflection readings. Plot a curve between load and deflection. The shape of the curve gives the stiffness of the spring. Required Results: Parameters: The value of spring constant k of closely coiled helical spring is found to be------------ N / mm Graphs/Plots: Graph between load and deflection. Error Analysis: Cautions: 1)The dimension of spring is to be measured accurately. 2) Deflection obtained in spring is measured accurately.
LMMEC220
Page 16
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To determine the stiffness of spring, modulus of rigidity of the spring wire and the maximum strain energy stored Observations: Least count of micrometer = mm Diameter of the spring wire, d =mm (Mean of three readings) Least count of vernier caliper = mm Diameter of the spring coil, D = mm (Mean of three readings) Mean coil diameter, Dm = D - dmm Number of turns, n =
S.NO
Load(N)
Deflection(mm)
Stiffness(N / mm)
Calculations:
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 17
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 18
Experiment: 7 Experiment: To perform the compression test on a specimen material and find the compression strength Equipment Required: Compression testing machine, Oven, Vernier Caliper, Scale,Etc. Material Required: Bricks Learning Objectives: Understanding of stress strain diagrams, compression strength of a material, significance of Young's modulus Outline of the Procedure: Select some brick with uniform shape and size. Measure its all dimensions. (LXBXH) Now fill the frog of the brick with fine sand. And Place the brick on the lower platform of compression testing machine and lower the spindle till the upper motion of ram is offered by a specimen the oil pressure start increasing the pointer start returning to zero leaving the drug pointer that is maximum reading which can be noted down. Required Results: Parameters: The average compressive strength of new brick sample is found to be . Kg/sq.cm. Error Analysis: Cautions: 1) Measure the dimensions of Brick accurately. 2) Specimen should be placed as for as possible in the of lower plate. 3) The range of the gauge fitted on the machine should not be more than double the breaking load of specimen for reliable results.
LMMEC220
Page 19
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To perform the compression test on a specimen material and find the compression strength Observations:
S.No
L X B XH (Cm3)
Area (Cm2)
Load (N)
Compressive Strength (N/mm2)
Average Compressive Strength (N/mm2)
Calculations:
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 20
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 21
Experiment: 8 Experiment: To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Charpy's test; To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Izod test Equipment Required: Charpy's test apparatus, Izod test apparatus Material Required: Specimen of MS & CI Learning Objectives: To understand the concept of impact strength and the difference between the two methods of determination of impact strength Outline of the Procedure: (a) lzod test With the striking hammer (pendulum) in safe test position, firmly hold the steel specimen in impact testing machines vice in such a way that the notch face the hammer and is half inside and half above the top surface of the vice. Bring the striking hammer to its top most striking position unless it is already there, and lock it at that position. Bring indicator of the machine to zero, or follow the instructions of the operating manual supplied with the machine. Release the hammer. It will fall due to gravity and break the specimen through its momentum, the total energy is not absorbed by the specimen. Then it continues to swing. At its topmost height after breaking the specimen, the indicator stops moving, while the pendulum falls back. Note the indicator at that topmost final position. Again bring back the hammer to its idle position and back ( b) Charpy Test With the striking hammer (pendulum) in safe test position, firmly hold the steel specimen in impact testing machines vice in such a way that the notch faces s the hammer and is half inside and half above the top surface of the vice. Bring the striking hammer to its top most striking position unless it is already there, and lock it at that position. Bring indicator of the machine to zero, or follow the instructions of the operating manual supplied with the machine. Release the hammer. It will fall due to gravity and break the specimen through its momentum, the total energy is not absorbed by the specimen. Then it continues to swing. At its topmost height after breaking the specimen, the indicator stops moving, while the pendulum falls back. Note the indicator at that topmost final position. The specimen is placed on supports or anvil so that the blow of hammer is opposite to the notch. Required Results: Parameters: The impact strength for the given material is _________ J/mm2 Error Analysis:
Cautions: 1. Measure the dimensions of the specimen carefully. 2. Hold the specimen (lzod test) firmly. 3. Locate the specimen (Charpy test) in such a way that the hammer, strikes it at the middle. 4. Note down readings carefully.
LMMEC220
Page 22
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Charpy's test To determine the impact strength of a specimen material using Izod test Observations: Area of cross section of the given material:
(a) Charpy test S. Material No. Used
Energy absorbed by force (A) J
Energy spent to break the specimen (B) J
Energy Impact absorbed Strength by the J/mm2 specimen (A-B) J
(b) Izod test S. Material No. Used
Energy absorbed by force (A) J
Energy spent to break the specimen (B) J
Energy Impact absorbed Strength by the J/mm2 specimen (A-B) J
Calculations:
LMMEC220
Page 23
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 24
Experiment: 9 Experiment: To perform shear test on a specimen material using universal testing machine Equipment Required: Universal Testing Machine, Scale, Vernier calliper, shear testing attachment Material Required: Specimen of MS & CI Learning Objectives: Understanding of stress strain diagrams, shear strength of a material, significance of modulus of rigidity Outline of the Procedure: Insert the specimen in position and grip one end of the attachment in the upper portion and one end in the lower portion. Switch on the main switch of universal testing machine. The drag indicator in contact with the main indicator. Select the suitable range of loads and space the corresponding weight in the pendulum and balance it if necessary with the help of small balancing weights. Operate (push) buttons for driving the motor to drive the pump. Gradually move the head control level in left-hand direction till the specimen shears. Down the load at which the specimen shears. Stop the machine and remove the specimen Repeat the experiment with other specimens. Required Results: Parameters: The Shear strength of mild steel specimen is found to be = N/mm2 Error Analysis: Cautions: 1 The measuring range should not be changed at any stage during the test. 2. The inner diameter of the hole in the shear stress attachment should be slightly greater than that of the specimen. 3. Measure the diameter of the specimen accurately.
LMMEC220
Page 25
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To perform shear test on a specimen material using universal testing machine Observation Table: Diameter of the Rod, D = . mm Cross-section area of the Rod (in double shear) = 2x /4x d2 =. mm2 Load taken by the Specimen at the time of failure , W = .N
Calculations:
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 26
Experiment: 10 Experiment: To find the fatigue strength of a specimen material by performing the fatigue test Equipment Required: Fatigue testing machine, Set of weights, Scale, Vernier calliper, Pencil / chalk. Material Required: Fatigue testing specimen Learning Objectives: To understand the behaviour of a material subjected to repeated or continuous loads with respect to time, fatigue strength of a material Outline of the Procedure: Measure the overall (L), gauge length (Ig) and diameter at the middle portion (d) of the given specimen. Mark the centre of the specimen using pencil / chalk and fix the specimen in the machine properly. Place a suitable weight (W) say, 50kg in the weight in the weight hanger of the machine and release the cam so as to apply the weight / load to the specimen. Measure the distance between centre of the specimen and centre of the weight hanger (l). Calculate the bending stress, which will develop in the specimen. Set the electrical counter of the machine to zero position and start the motor of the machine. Record the number indicated on the electrical counter after the specimen failure. Calculate the actual number of revolutions (N) under gone by the specimen during the test by multiplying the number indicated on the electrical counter with constant of multiplication (i.e. 20) given by the manufacture. Fix another specimen of same material, size and shape in the machine. Repeat the steps from 3 to 8 with 20% decrease in weight at each time. Conduct at least 5 tests for a given material with specimen of same material, size and shape. Plot a graph between log Vs log N by taking log along Y axis and log N along x axis. Read the value of stress corresponding to the knee of N curve, which will be the endurance limit stress for the given specimen. Required Results: Parameters: The endurance limit stress for the given material of the specimen -------------------N/mm2 Graphs/Plots: Plot a graph between log Vs log N Error Analysis: Cautions: 1 The measuring range should not be changed at any stage during the test. 2. Measure the lengths of the specimen accurately.
LMMEC220
Page 27
Date of Performance
Worksheet of the student
Registration Number:
Aim: To find the fatigue strength of a specimen material by performing the fatigue test Observations : 1. Material of the specimen 2. Overall length of the specimen, L 3. Gauge length of the specimen. lg 4. Diameter at the middle portion of the specimen,d 5. Distance between centre of the specimen and centre Of the weight hanger, l
= = = = =
mm mm mm mm
Sl.No. Weight (W) in kg N
Moment (M) In Nmm (w x l)
Bending stress In N/mm2 ( = MY / I)
Indication in the counter (P)
Actual No. of Log revolutions (N) ( p X 20)
Log N
Calculations:
Graphs attached:
LMMEC220 Page 28
Result and Discussion:
Error Analysis:
Learning Outcomes:
To be filled in by Faculty: S.No Parameter Marks obtained . 1 Understanding of the student about the procedure/apparatus. 2 Observations and analysis including learning outcomes 3 Completion* of experiment, Discipline and Cleanliness Signature of Faculty Total marks obtained
LMMEC220
Max. Marks 20 20 10
Page 29
You might also like
- Valid Civil III PDFDocument19 pagesValid Civil III PDFKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- BLR DIB: TICKET - ConfirmedDocument2 pagesBLR DIB: TICKET - ConfirmedKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- Valid Civil IIIDocument19 pagesValid Civil IIIKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- Valid Civil I Firms Arunachal Pradesh 2019Document11 pagesValid Civil I Firms Arunachal Pradesh 2019Katon KUNNo ratings yet
- Passport Application Form Government of INDIA, Ministry of External AffairsDocument1 pagePassport Application Form Government of INDIA, Ministry of External AffairsKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- Valid Civil IIDocument8 pagesValid Civil IIKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- 5 Aug Manu Mehta Assignment - rs1Document2 pages5 Aug Manu Mehta Assignment - rs1Katon KUNNo ratings yet
- Time Table 3rdsemesterDocument2 pagesTime Table 3rdsemesterKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification: Making A Hash of It?Document25 pagesDrug Classification: Making A Hash of It?Katon KUNNo ratings yet
- Special Request Form: To, Date: . / / . CSODocument1 pageSpecial Request Form: To, Date: . / / . CSOKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- List of Death Metal Bands, !-K - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesList of Death Metal Bands, !-K - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaKaton KUNNo ratings yet
- Diploma 09Document83 pagesDiploma 09Katon KUNNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Head Coverings BookDocument86 pagesHead Coverings BookRichu RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pidsdps 2106Document174 pagesPidsdps 2106Steven Claude TanangunanNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Journal - Absorption RefrigerationDocument11 pagesASHRAE Journal - Absorption Refrigerationhonisme0% (1)
- India TeenagersDocument3 pagesIndia TeenagersPaul Babu ThundathilNo ratings yet
- JIS G 3141: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet and StripDocument6 pagesJIS G 3141: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet and StripHari0% (2)
- SachinDocument3 pagesSachinMahendraNo ratings yet
- SSP 237 d1Document32 pagesSSP 237 d1leullNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Mortality - A Community ApproachDocument13 pagesNeonatal Mortality - A Community ApproachJalam Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument10 pagesPityriasis Versicolorketty putriNo ratings yet
- Module 2 MANA ECON PDFDocument5 pagesModule 2 MANA ECON PDFMeian De JesusNo ratings yet
- YIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTDocument63 pagesYIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTMebre WelduNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Principles of Economics 7th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Principles of Economics 7th Edition Frank Solutions Manual PDFmirthafoucault100% (8)
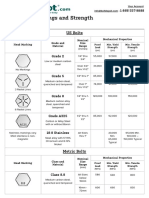
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDocument2 pagesBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffNo ratings yet
- HatfieldDocument33 pagesHatfieldAlex ForrestNo ratings yet
- WarringFleets Complete PDFDocument26 pagesWarringFleets Complete PDFlingshu8100% (1)
- Buried PipelinesDocument93 pagesBuried PipelinesVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Biblical World ViewDocument15 pagesBiblical World ViewHARI KRISHAN PALNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechRizal rindawunaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralMaharani UtamiNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics 2Document8 pagesApplied Economics 2Sayra HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Applications SeawaterDocument23 pagesApplications SeawaterQatar home RentNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab Midterm Study GuideDocument15 pagesMicro Lab Midterm Study GuideYvette Salomé NievesNo ratings yet
- ChatGpt PDFDocument19 pagesChatGpt PDFsanx2014100% (1)
- 16783Document51 pages16783uddinnadeemNo ratings yet
- ELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1Document10 pagesELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1vigneshNo ratings yet
- Journal of Biology EducationDocument13 pagesJournal of Biology EducationFarah ArrumyNo ratings yet
- Apexi Powerfc Instruction ManualDocument15 pagesApexi Powerfc Instruction ManualEminence Imports0% (2)
- Caspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Document255 pagesCaspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Roc SolàNo ratings yet
- MCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFDocument3 pagesMCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFMBBS ABROADNo ratings yet
- Model 255 Aerosol Generator (Metone)Document20 pagesModel 255 Aerosol Generator (Metone)Ali RizviNo ratings yet