Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQ Thermodynamics Compressible Flow
Uploaded by
Tochi Krishna AbhishekOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCQ Thermodynamics Compressible Flow
Uploaded by
Tochi Krishna AbhishekCopyright:
Available Formats
m cq-e ngine e ring.blo gspo t .
in
http://mcq-engineering.blo gspo t.in/2012/11/thermo dynamics-co mpressible-flo w.html
Thermodynamics (Compressible Flow)
1. All real f luids are (a) incompressible (b) compressible to some extent (c) compressible to any extent (d) none of the above. 2. A change in the state of a system at constant volume is called (a) isobaric process (b) isochoric process (c) isothermal process (d) adiabatic process. 3. A process during which no heat is transf erred to or f rom the gas is called an (a) isochoric process (b) isobaric process (c) adiabatic process (d) isothermal process. 4. T he sonic velocity is largest in which of the f ollowing ? (a) Water (b) Steel (c) Kerosene (d) Air. 5. An isentropic f low is one which is (a) isothermal (b) adiabatic (c) adiabatic and irreversible (d) adiabatic and reversible. 6. Indica upto what Mach number can a f luid f low be considered incompressible ? (a) 0.1 (b) 0.3 (c) 0.8 (d) 1.0. 7. Which of the f ollowing is the basic equation of compressible f luid f low ? (a) Continuity equation (b) Momentum equation (c) Energy equation (d) Equation of state (e) All of the above. 8. T he velocity of disturbance in case of f luids is ...... the velocity of the disturbance in solids. (a) less than (b) equal to (c) more than (d) none of the above. 9. Sonic velocity (C) f or adiabatic process is given as
(a) C = RT 3 (b) C = RT (c) C = 2RT (d) C = RT. where = ratio of specif ic heats, R = gas constant, T = temperature. 10. T he f low is said to be subsonic when Mach number is (a) equal to unity (b) less than unity (c) greater than unity (d) none of the above. 11. T he region outside the Mach cone is called (a) zone of action (b) zone of silence (c) control volume (d) none of the above. 12. A stagnation point is the point on the immersed body where the magnitude of velocity is (a) small (b) large (c) zero (d) none of the above. 13. A convergent-divergent nozzle is used when the discharge pressure is (a) less than the critical pressure (b) equal to the critical pressure (c) more than the critical pressure (d) none of the above. 14. At critical pressure ratio, the velocity at the throat of a nozzle is (a) equal to the sonic speed (b) less than the sonic speed (c) more than the sonic speed (d) none of the above. 15. Laval nozzle is a (a) convergent nozzle (b) divergent nozzle (c) convergent-divergent nozzle (d) any of the above. 16. A shock wave is produced when (a) a subsonic f low changes to sonic f low (b) a sonic f low changes to supersonic f low (c) a supersonic f low changes to subsonic f low (d) none of the above. 17. T he sonic velocity in a f luid medium is directly proportional to (a) Mach number (b) pressure (c) square root of temperature (d) none of the above. 18. T he stagnation pressure (ps) and temperature (Ts) are (a) less than their ambient counterparts
(b) more than their ambient counterparts (c) the same as in ambient f low (d) none of the above. 19. Across a normal shock (a) the entropy remains constant (b) the pressure and temperature rise (c) the velocity and pressure decrease (d) the density and temperature decrease. 20. A normal shock wave (a) is reversible (b) is irreversible (c) is isentropic (d) occurs when approaching f low is supersonic. 21. T he sonic speed in an ideal gas varies (a) inversely as bulk modulus (b) directly as the absolute pressure (c) inversely as the absolute temperature (d) none of the above. 22. In a supersonic f low, a dif f user is a conduit having (a) gradually decreasing area (b) converging-diverging passage (c) constant area throughout its length (d) none of the above. 23. Choking of a nozzle f itted to a pressure tank containing gas implies (a) sonic velocity at the throat (b) increase of the mass f low rate (c) obstruction of f low (d) all of the above. 24. A shock wave which occurs in a supersonic f low represents a region in which (a) a zone of silence exists (b) there is no change in pressure, temperature and density (c) there is sudden change in pressure, temperature and density (d) velocity is zero. 25. Which of the f ollowing statements regarding a normal shock is correct ? (a) It occurs when an abrupt change takes place f rom supersonic into subsonic f low condition (b) It causes a disruption and reversal of f low pattern (c) It may occur in sonic or supersonic f low (d) None of the above. 26. Which of the f ollowing statements is incorrect ? (a) A shock wave occurs in divergent section of a nozzle when the compressible f low changes abruptly f rom supersonic to subsonic state (b) A plane moving at supersonic state is not heard by the stationary observer on the ground until it passes him because zone of disturbance in Mach cone trails behind the plane (c) A divergent section is added to a convergent nozzle to obtain supersonic velocity at the throat (d) none of the above. Answer
1. (b) 2. (b) 3. (c) 4. (b) 5. (d) 6. (b) 7. (e) 8. (a) 9. (b) 10. (b) 11. (b) 12. (c) 13. (a) 14. (a) 15. (c) 16. (c) 17. (c) 18. (b) 19. (b) 20. (d) 21. (d) 22. (a) 23. (d) 24. (c) 25. (a) 26. (c)
You might also like
- FM & FM Lab MCQDocument11 pagesFM & FM Lab MCQrajmehaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Objective Questions For Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics Objective Questions For Mechanical Engineeringrashik072No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering-Compressors, Gas Turbines and Jet Engines Important MCQDocument28 pagesMechanical Engineering-Compressors, Gas Turbines and Jet Engines Important MCQavantgarde bwoyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering MCQDocument32 pagesThermal Engineering MCQsanthisree100% (1)
- Ad1 MCQDocument11 pagesAd1 MCQYashwanth Srinivasa100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Fluid Mechanics 1Document8 pagesMechanical Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Fluid Mechanics 1kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- 255 TOP FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument38 pages255 TOP FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Fluid FlowDocument4 pagesMCQs On Fluid FlowRavi KantNo ratings yet
- 136 TOP Engineering Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument21 pages136 TOP Engineering Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsNagaraj Muniyandi50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics 2 MCQDocument109 pagesFluid Mechanics 2 MCQRCNo ratings yet
- Thyristor MCQDocument6 pagesThyristor MCQnandhakumarme0% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics MCQ - Part OneDocument17 pagesFluid Mechanics MCQ - Part OneMohamed Salah Yassin100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics MCQDocument30 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQjasonmani90100% (1)
- Geometric Modeling: MCQ No - 2Document20 pagesGeometric Modeling: MCQ No - 2ashish100% (1)
- Hydraulic Machines MCQs PDFDocument13 pagesHydraulic Machines MCQs PDFSk Saravana100% (1)
- 138 Top Machine Design Question and AnswersDocument16 pages138 Top Machine Design Question and AnswersIlhariri Muhammad IrlisNo ratings yet
- 2nd MCQ AUTOMATION IN MANUFACTURINGDocument10 pages2nd MCQ AUTOMATION IN MANUFACTURINGGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Fluid PowerDocument12 pagesMCQ On Fluid Powerraj kunduNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Multiple Choice QuestionsGnana Subramanian Arumugam67% (3)
- 132 TOP Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument1 page132 TOP Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFengineeringmcqs100% (4)
- Fluid Mechanics MCQ - Bundle 1 - SampleDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics MCQ - Bundle 1 - SampleMohamed Salah Yassin100% (1)
- Bme MCQ QuestionDocument6 pagesBme MCQ QuestionAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- 250 TOP Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers List - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument24 pages250 TOP Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers List - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsNagaraj Muniyandi60% (10)
- Hydraulic Machines - MCQDocument8 pagesHydraulic Machines - MCQsudheer92No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine MCQDocument6 pagesGas Turbine MCQnimymech100% (1)
- ME8694 Hydraulics and Pneumatics MCQDocument19 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and Pneumatics MCQaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 3Document10 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 3kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On State Variable Analysis and DesignDocument23 pagesQuestions & Answers On State Variable Analysis and Designkibrom atsbha100% (1)
- MCQ Electrical Induction MotorDocument44 pagesMCQ Electrical Induction MotorEng Mohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- ROBOTICS (MEB-465) : Quiz QuestionsDocument21 pagesROBOTICS (MEB-465) : Quiz QuestionsVishal Dhiman100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Objective Type QuestionsDocument223 pagesFluid Mechanics Objective Type Questionshello17No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery Objective Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesDynamics of Machinery Objective Question and Answerskumar km67% (9)
- M & M MCQ QPDocument34 pagesM & M MCQ QPtamilselvan n100% (2)
- DTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Document6 pagesDTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Mannam Sarath Sarath100% (2)
- Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageHydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsengineeringmcqsNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Multiple Choice Questions For EngineersDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Multiple Choice Questions For EngineersGerry Lou Quiles80% (5)
- MCQ GDJPDocument5 pagesMCQ GDJPrajapurushoth7227660% (5)
- Electrical Vehicle MCQ - Unit 1 & 2Document15 pagesElectrical Vehicle MCQ - Unit 1 & 2Rocky RuleNo ratings yet
- Copyjjjj of Viva Voice QuestionDocument6 pagesCopyjjjj of Viva Voice QuestionVigy BossNo ratings yet
- MidTermExam CADCAM2019 FFDocument6 pagesMidTermExam CADCAM2019 FFkhalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Objective2 CADCAM 2019-20Document1 pageObjective2 CADCAM 2019-20Rajyalakshmi MNo ratings yet
- Tom MCQ VISemDocument5 pagesTom MCQ VISempurukumar32250% (2)
- Control System MCQDocument4 pagesControl System MCQPriyankNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - MCQsDocument25 pagesThermodynamics - MCQsmujtabahassan100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics McqsDocument19 pagesEngineering Mechanics McqsArunKumar50% (2)
- Synchro Reviewer (Multiple Choice)Document5 pagesSynchro Reviewer (Multiple Choice)Denaiya Watton LeehNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics MCQs PDFDocument22 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQs PDFvimalNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 2Document10 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering MCQ PDF Part 2kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (MCQ)Document17 pagesFluid Mechanics (MCQ)John WilmarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics MCQSDocument46 pagesFluid Mechanics MCQSyaseenNo ratings yet
- Viva VoiceDocument6 pagesViva VoiceRakesh Kumar Shukla KECNo ratings yet
- DTE Unit 2 MCQs (Belt, Chain and Rope Drives)Document8 pagesDTE Unit 2 MCQs (Belt, Chain and Rope Drives)Mannam Sarath SarathNo ratings yet
- Important Mcq-Automatic Control SystemsDocument21 pagesImportant Mcq-Automatic Control Systemsarijitlgsp50% (2)
- 250 TOP Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers List - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument22 pages250 TOP Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers List - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsKhairy Elsayed100% (1)
- Engineering Materials 74 Important MCQDocument10 pagesEngineering Materials 74 Important MCQaditya100% (4)
- Multiple Choice Questions:: FLUID POWER (665 (S) ) Third Year, Second Semester (6 Sem) 70Document3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions:: FLUID POWER (665 (S) ) Third Year, Second Semester (6 Sem) 70dipsankar chatterjee100% (1)
- MM All Units MCQDocument38 pagesMM All Units MCQkrishnabr100% (2)
- Shaft WorkDocument20 pagesShaft WorkEdward MorganNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument5 pagesMCQsebrahem khalidNo ratings yet
- Brexit: Regaining Sovereignty?: - An Political Science ProjectDocument19 pagesBrexit: Regaining Sovereignty?: - An Political Science ProjectTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Digital Marketing Checklist PDFDocument6 pagesThe Ultimate Digital Marketing Checklist PDFAdnanNo ratings yet
- Product Labelling RequirementsDocument13 pagesProduct Labelling RequirementsTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- StepsDocument2 pagesStepsFajri IsnantoNo ratings yet
- The Security Council: Membership, Structures, FunctionsDocument17 pagesThe Security Council: Membership, Structures, FunctionsTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Digital Marketing Checklist PDFDocument6 pagesThe Ultimate Digital Marketing Checklist PDFAdnanNo ratings yet
- This Critique and Literary Analysis of The Drama "Silence! The Court Is in Session" by Vijay Tendulkar Focuses OnDocument6 pagesThis Critique and Literary Analysis of The Drama "Silence! The Court Is in Session" by Vijay Tendulkar Focuses OnTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Mis Tutorial 3 (NOT MY PROPERTY)Document77 pagesMis Tutorial 3 (NOT MY PROPERTY)Pat ZednetneNo ratings yet
- Abandoned Cart Emails: A Data-Driven Guide To Recovering Lost SalesDocument37 pagesAbandoned Cart Emails: A Data-Driven Guide To Recovering Lost SalesTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Booklet - Children in India and Their RightsDocument77 pagesBooklet - Children in India and Their RightsTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Provisions .FullDocument8 pagesConstitutional Provisions .FullTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Facebook Ad Checklist by DeepakDocument1 pageFacebook Ad Checklist by DeepakTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- All About Deep Cycle BatteriesDocument15 pagesAll About Deep Cycle BatteriesTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor ListDocument15 pagesExhibitor ListTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument1 pageHTTPTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Detailedad GATE2015Document8 pagesDetailedad GATE2015Ramanareddy AnathapurNo ratings yet
- Cozi Car PresentationDocument24 pagesCozi Car PresentationTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (1)
- 10 Chapter 6Document41 pages10 Chapter 6Tochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- K - 301Document4 pagesK - 301Tochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Interview TipsDocument23 pagesInterview TipsTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
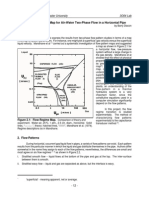
- Slug Flow Two Phase FlowDocument15 pagesSlug Flow Two Phase FlowTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (1)
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries09Document2 pagesMinistry of Food Processing Industries09Tochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cold Chain in IndiaDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Cold Chain in IndiaTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of CCGT Power Plant Using MATLAB Simulink Based SimulationDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of CCGT Power Plant Using MATLAB Simulink Based SimulationTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (1)
- Ruby TutorialDocument42 pagesRuby TutorialRadu PavelcoNo ratings yet
- List of Consuer Groups TRAI 16july13Document3 pagesList of Consuer Groups TRAI 16july13Tochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Ruby TutorialDocument11 pagesRuby TutorialTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- LAB #2 Flow Regime Map For Air-Water Two-Phase Flow in A Horizontal PipeDocument4 pagesLAB #2 Flow Regime Map For Air-Water Two-Phase Flow in A Horizontal PipeTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 3rdrail Data SheetDocument2 pages3rdrail Data SheetNarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Major Project TitleDocument1 pageMajor Project TitleTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Ready To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaDocument25 pagesReady To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaKABERA RENENo ratings yet
- 9702 w22 QP 36 PDFDocument16 pages9702 w22 QP 36 PDFsangdeepNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: June 2018Document12 pagesMark Scheme: June 2018BethanyNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Radiology: Bachtiar MurtalaDocument75 pagesBasic Principles of Radiology: Bachtiar MurtalaMargaretha SonoNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter SchemeDocument226 pagesMultilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter Schemejuancho2222No ratings yet
- Badminton Sport: Submitted By: Manav Lakdawala Institution:l.p Savani International SchoolDocument35 pagesBadminton Sport: Submitted By: Manav Lakdawala Institution:l.p Savani International SchoolManav LakdawalaNo ratings yet
- Mwakican Joint Examination: 232/3 PhysicsDocument3 pagesMwakican Joint Examination: 232/3 Physicsandy gideonNo ratings yet
- Us 20060145019Document11 pagesUs 20060145019Raymond100% (4)
- Click125 82K60H30Y 0Document169 pagesClick125 82K60H30Y 0yeoj manaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Design ProjectDocument3 pagesControl Systems Design ProjectHasan ÇalışkanNo ratings yet
- Programming Exercise 2Document2 pagesProgramming Exercise 2hamidahrazakNo ratings yet
- Maths - 2B Imp QuestionsDocument93 pagesMaths - 2B Imp QuestionsBandaru Chiranjeevi100% (1)
- Ambit ManiforlDocument6 pagesAmbit Maniforlmd_taheriNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications-Notes PDFDocument110 pagesAnalog Communications-Notes PDFjyothimunjam100% (1)
- Power Amplifiers: Ranjith Office Level 4 - Building 193 - EEE BuildingDocument19 pagesPower Amplifiers: Ranjith Office Level 4 - Building 193 - EEE BuildingArambya Ankit KallurayaNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten-DLL Week 1 (June 3-7, 2019)Document7 pagesKindergarten-DLL Week 1 (June 3-7, 2019)Ma. Cristina DumallagNo ratings yet
- Chem 152 Lab ReportDocument21 pagesChem 152 Lab Reportapi-643022375No ratings yet
- The Chemistry Maths Book: Erich SteinerDocument16 pagesThe Chemistry Maths Book: Erich SteinerDewi MariyamNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Solid State Fermentation Over Submerged FermentationDocument32 pagesAdvantages of Solid State Fermentation Over Submerged Fermentationtelangsachin12No ratings yet
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFDocument99 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFRaj Shekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirDocument14 pagesLiquid Solutions: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirSunnyNo ratings yet
- FG Wilson AtsDocument5 pagesFG Wilson AtsErwan Shidiq FathoniNo ratings yet
- On The Coupling of Mechanics With Bioelectricity and Its Role in MorphogenesisDocument12 pagesOn The Coupling of Mechanics With Bioelectricity and Its Role in MorphogenesisVishvendraNo ratings yet
- Training Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionDocument46 pagesTraining Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionHansraj Kayda100% (1)
- Activities InterventionDocument2 pagesActivities InterventionDonabel Villasaya CariosNo ratings yet
- API TutorialDocument22 pagesAPI TutorialKomarudinNo ratings yet
- ALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuDocument67 pagesALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuMeghaNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipeline Decommissioning Scale and ContextDocument4 pagesOffshore Pipeline Decommissioning Scale and ContextHieu Le TrungNo ratings yet
- Iconnect v3.1 User ManualDocument105 pagesIconnect v3.1 User Manualcjamiz2006No ratings yet
- Chem 105 Lab Manual 08 EKIM 1Document42 pagesChem 105 Lab Manual 08 EKIM 1hooraNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)