Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crane Design and Calculation
Uploaded by
odim73Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crane Design and Calculation
Uploaded by
odim73Copyright:
Available Formats
Haider Crane Co.
1 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Single Girder
Haider Crane Co.
2 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Single Girder
Haider Crane Co.
3 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Single Girder
Haider Crane Co.
4 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Double Girder
Haider Crane Co.
5 12/25/07
H
o
i
s
t
C
r
a
n
e
D
o
u
b
l
e
G
i
r
d
e
r
Haider Crane Co.
6 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Single Girder Gantry crane
Haider Crane Co.
7 12/25/07
H
o
i
s
t
C
r
a
n
e
S
i
n
g
l
e
G
i
r
d
e
r
G
a
n
t
r
y
c
r
a
n
e
Haider Crane Co.
8 12/25/07
Hoist Crane Gantry crane
Haider Crane Co.
9 12/25/07
H
o
i
s
t
C
r
a
n
e
G
a
n
t
r
y
c
r
a
n
e
Haider Crane Co.
10 12/25/07
Suspension Crane
Haider Crane Co.
11 12/25/07
Haider Crane Co.
12 12/25/07
Suspension Crane
Haider Crane Co.
13 12/25/07
Jib Crane
Haider Crane Co.
14 12/25/07
C
a
r
g
o
L
i
f
t
Haider Crane Co.
15 12/25/07
Setting Crane Girder
Haider Crane Co.
16 12/25/07
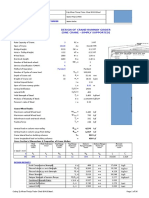
Crane Design Basics
Haider Crane Co.
17 12/25/07
Span
P
Dead Load Bending
Max Moment =
el Pl
2
8 4
+
P = Center drive + Controls
w = Footwalk + Beam + Lineshaft
Dynamic Mx = Max Moment x factor
Dynamic My = Max Moment x factor
Span
P1 P2
x
y
Live Load Bending
L = Span
Jika P1=P2, pakai point-41, jika P1P2 pakai
point-42. Hitung juga moment maksimum
memakai rumus PL/4. Dengan kata lain
gunakan nilai terbesar yang diperoleh.
Compute Moments
Haider Crane Co.
18 12/25/07
Compute Stress
a
b
DL Dead load, LL = Live Load, Fy = Yield normally @ 36 ksi for A36 material, Fb = Allowable Stress
Dynamic Mx = LL Mx + DL Mx
My = LL My + DL My
f
M
S
F
b
x
bott
y
x
T
= s 06 .
f
M
S
f
M
S
f
F
f
F
b
x
Top
b
y
Top
b
b
b
y
x
C
y
C
x
C
x
y
C
=
=
+ s
0 6
10
.
.
Girder Beam
Fabricated/Box Beam
Available to 60 ft max. length
L/h should not exceed 25
L/b should not exceed 65
h
b
Haider Crane Co.
19 12/25/07
Compute Deflection
A
A
=
=
5
384
48
4
3
wl
EI
Pl
EI
For Uniform Load
For Conc. Load
For Trolley:
| |
P
LL TW
Pa
EI
l a
=
+
=
2
24
3 4
2 2
A
Haider Crane Co.
20 12/25/07
=
12000
L
d
A
f
= 06 . o
y
Allowable Compressive Stress Fb per CMAA 74
1/600
1/888
Use when the flanges
are not welded on the
top and bottom
Haider Crane Co.
21 12/25/07
Allowable Compressive Stress
y b
f
b
t
b
y
t
y
b
y t t
F
CMAA per
A
d
L
F
r
L
F Otherwise
F
r
L
F
F
F r
L
and
y
F r
L
o 6 . 0
) (
12000
170000
,
1530000 3
2
,
510000 102000
1
3
2
2
2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
(
(
(
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
= s >
Select Allowable Stress which is the Greatest of all.
Then check for the following:
1
6 . 0
6 . 0
< +
<
y
y
comp
b
x
comp
y tensile
f o
o
o
o o
Haider Crane Co.
22 12/25/07
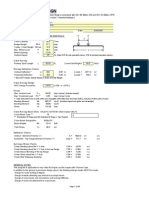
Lower Flange loading per CMAA 74
For a crane where the trolley is running on the bottom flange, it is necessary to check the local bending of
flange due to the wheel load. The flange must be OK before a beam selection is made.
This is a empirical formula
Haider Crane Co.
23 12/25/07
Lower Flange loading per CMAA 74
Haider Crane Co.
24 12/25/07
Lower Flange loading per CMAA 74
Haider Crane Co.
25 12/25/07
Lower Flange loading - Alternate procedure I
Flens bagian bawah dari balok crane harus diperiksa terhadap :
1) Tension in the web. 2) Bending of the bottom flange.
Panjang daerah perlawanan diambil 3,5 k (k = jarak yang diukur pada kemiringan 30
0
dari titik
beban crane). Dengan asumsi 4 roda (2 set) pada setiap ujung crane, setiap roda bekerja P/4
yang akan disalurkan ke-perletakan balok crane. Beban as roda sebesar P/2, mengakibatkan
tarik pada web.
Tegangan tarik pada web sebesar :
( )
f
P
A
P
t
P
t
t
w w
= = =
2 2 35 7 .
30 deg
P/2
3.5k
tf
k
Bottom Flange
e
e
Point of Load
tw
e
k1
P/4
tf
Lentur pada flens tergantung posisi roda
dengan reaksi web balok (e = jarak dari titik
beban ke bagian tepi web). Beban roda
sebesar P/4. Panjang arah longitudinal flens
yang ikut menahan lentur sebesar 2e.
Tegangan lentur sebesar ;
f
M
S
Pe
bd
Pe
et
P
t
b
f f
= = = =
4
6
4
6
2
075
2 2 2
.
Refer to Engineering Journal, 4
th
quarter, 1982, Tips for avoiding Crane Runway Problems by David T. Ricker
Haider Crane Co.
26 12/25/07
Lower Flange loading - Alternate procedure II
Now, the angle is changed from 30 degree to 45 degrees.
tw
e
k1
P/4
tf
45 deg
b=2e
Load
Capacity = 6000 lb (daya angkut crane)
Hoist, W
t
= 1000 lb (berat crane)
Load = 6000 +1000 = 7000 lb
Wheel load = 7000/4 = 1750 lb
With 15% impact = 1750(1.15) = 2013 lb
Lebar flens, b =11.5 inc, sehingga e = b/2 = 5.75 inc
Tebal flens, t
f
= 0.875 inc
Momen pada flens, M = 2013 (5.75) = 11574.75 lb-inc
Teg arah-y,
y
= M/S
y
= 11574.75. (6)/(11.5)(0.875)
2
= 7890.15 lb/in
2
Moment = 7000(1.15)(30)(12)/4 + 110 (12x30)
2
/(8 x12) = 873.000 lb-in
30 ft crane
Span
110 lb/ft
Teg arah-x,
x
= M/S
x
= 873.000/280 = 3117.8 lb/in
2
( ) 15 , 7890 8 , 3117
2
15 , 7890
2
8 , 3117
2 2
+ + = + + =
y x y x
o o o o o
= 9.827 << 0.6
y
= 21.600 lb/in
2
OK
Haider Crane Co.
27 12/25/07
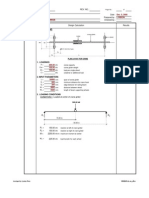
EXAMPLE Simple Approach
Capacity: 2 Ton (=4000 lb), Span: 20 Ft (=240 in)
Hoist Wt: 200 lb, Hoist W.B: 12 in
Vertical Impact factor = 15%, Hor. Impact = 10%
Solution:
in
L
in
E E
EI
a L
Pa
EI
wL
in lb
S
M
in lb
S
M
in lb Mx
a
L
L
P wL
Mx
y
y
x
x
x
x
4 . 0
600
237 . 0
218 24
) 114 4 240 3 (
114 15 . 1 2100
218 12 384
240 ) 8 . 31 ( 5
24
) 4 3 (
384
5
/ 5 . 3039
15 . 1 27 . 9
1 . 0 1 . 1 1 . 294571
/ 6 . 8092
4 . 36
1 . 294571
1 . 294571
2
12
240
240 2
15 . 1 2100
8
240
12
8 . 31
2 2 8
2 2 4
2 2 4
2
2
2
2
2
2
= < =
+
=
+ =
=
= =
= = =
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
o
o
o
o
o
240
P1 P2
114
12 P=2100lb
OK
Say, for example, we select a A36, S beam
S-12x31x8, Ix=218 in
4
, Iy=37.1 in
4
,
Sx=36.4 in
3
, Sy=9.27 in
3
, d/Af=4.41
P=2100 lb, w = (31.8/12) lb/in
.
2
2 1
2
2
2
1
2
/ 8 . 337 . 11 , min_
/ 8 . 337 . 11
41 . 4 240
12000 12000
/ 000 . 216 36 6 . 0 6 . 0
/ 1 . 132 . 11 5 . 3039 6 . 8092
all comb
all all all
f
all
y all
comb
in lb of
in lb
A
d
L
in lb
in lb
o o
o o o
o
o o
o
<
= =
=
=
= = =
= + =
OK
Beam must be checked for
Lower flange load, if the
trolley is under running
Haider Crane Co.
28 12/25/07
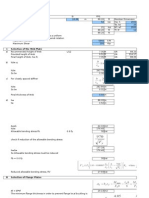
EXAMPLE Conservative Approach
11 105
2000
12 . .
.
. s + s
Br speed
015 0005 05 . . ( ) . s s HoistSpeed
0078 0025 . ( _ .) . Bridge acc s
( ) ( )
C T WB X X
T WB
HLF
T Wt
DLF
2 2
1 2
_
_
_
(
+
(
P P M
P P
L
X X
L WB P
P P
OR M
PL
1 2
1 2 2 2
1 2
05
4
> =
+
=
+
(
= ,
( )
, . , ,
wL PL
2
8 4
+
o =
Mx
Sx
b
DLF =
HLF =
IFD =
Wheel Ld (P1/P2) =
= 1.10
= 1.15
= 0.39
= 2410
240
P1 P2
114
12 P=2100lb
Moment A = HLF x M (whichever is greater) =
= 166290
Moment B = IFD x M (whichever is greater) =56394
Static Moment = = 19080
Moment C = DLF x Static Moment
Moment D = IFD x Static Moment
= 20988
= 7441.2
Moment Mx = A+C = 187278
Moment My = B+D = 63835.2
Tensile Stress = = 5.15 < 0.6(36) OK
Comp. Stress X =
o =
Mx
Sx
t
= 5.15
= 17.07 Comp. Stress Y =
o =
My
Sy
C
f
C
F
x
b
y
y
+ <
06
1
.
= + = >
515
216
17 07
216
103 1
.
.
.
.
. ERR
d
wL
EI
1
5
384
00181
4
= = .
d
PL
EI
2
3
0
3
= =
( ) | |
d
P P
a
L a
EI
3
2
3 4
24
02188
1 2
2 2
=
+
= .
d
PL
EI
4
48
01098
1
3
= = .
Total Deflection = d1+d2+(Greater of d3 and d4)
Deflection = 0.0181+0+0.2188 = 0.2369 in
Deflection 0.2369 < L/600 (0.4) OK
Above calculation is for S12x31.8 Beam
Beam must be
checked for
Lower flange
load, if the trolley
is under running
You might also like
- Jib Crane Design SellDocument13 pagesJib Crane Design Selljafary100% (3)
- Manual Crane CalculationDocument98 pagesManual Crane CalculationLarry Bea67% (15)
- Design Gantry Girder Industrial Building CraneDocument28 pagesDesign Gantry Girder Industrial Building Cranes_bharathkumar75% (12)
- Crane Runway Girder DesignDocument27 pagesCrane Runway Girder Designyeemonzolo100% (6)
- Crane DesignDocument18 pagesCrane DesignSina Enteshari100% (4)
- Crane Girder DesignDocument6 pagesCrane Girder DesignAya Montes100% (3)
- Crane Girder DesignDocument6 pagesCrane Girder Designarzu50% (2)
- Crane Beam DesignDocument4 pagesCrane Beam DesignPat Baker100% (1)
- Gantry CraneDocument18 pagesGantry Craneamirthraj7494% (16)
- Crane BeamDocument8 pagesCrane BeamastorNo ratings yet
- Design of Gantry Girders 1Document10 pagesDesign of Gantry Girders 1Abhishek Agarwal100% (2)
- Design Analysis-Jib CraneDocument22 pagesDesign Analysis-Jib Cranesainal100% (3)
- Crane Girder Design Sheet - ASD 2005Document36 pagesCrane Girder Design Sheet - ASD 2005Panha Menh100% (3)
- Jib Crane HandbookDocument10 pagesJib Crane Handbookprp_a100% (3)
- Calculate Design Beam Jib CraneDocument25 pagesCalculate Design Beam Jib Cranejafary100% (14)
- Crane Girder Design-5T-5.7m SpanDocument32 pagesCrane Girder Design-5T-5.7m SpanKyatoor SantoshNo ratings yet
- CraneBeam v1 1Document44 pagesCraneBeam v1 1harry_1981No ratings yet
- Jib Crane Example ProblemDocument7 pagesJib Crane Example Problemearthboy2u100% (1)
- Crane Girder Design ProcedureDocument18 pagesCrane Girder Design ProcedureBhadresh Shah0% (1)
- Crane LoadingsDocument2 pagesCrane Loadingsmoseslugtu632470% (10)
- Structural Calculation EOTDocument9 pagesStructural Calculation EOTswatantar17100% (6)
- Ravindu: VS Consulting 1Document5 pagesRavindu: VS Consulting 1Ravindu JayalathNo ratings yet
- Crane Runway Beam Design - Crane Load Calculation-1Document5 pagesCrane Runway Beam Design - Crane Load Calculation-1sergiooiNo ratings yet
- Crane Buffer ForcesDocument243 pagesCrane Buffer ForcesFourHorsemenNo ratings yet
- 1984Document46 pages1984Praveen Kumar85% (13)
- Design Concept For Jib CraneDocument12 pagesDesign Concept For Jib Cranevish5610100% (3)
- Bridge Crane Load CalculationDocument20 pagesBridge Crane Load Calculationcadsultan100% (2)
- CRANE BEAM DESIGN CHECKSDocument38 pagesCRANE BEAM DESIGN CHECKSyercNo ratings yet
- Jib CraneDocument16 pagesJib Cranesuperman3k100% (2)
- 5Tx5m JIB & STRUCTURE CAL (R0)Document3 pages5Tx5m JIB & STRUCTURE CAL (R0)Kishan Panchal100% (1)
- Crane BeamDocument20 pagesCrane BeamPreyash Shah100% (1)
- 11 Crane Frame StructuresDocument6 pages11 Crane Frame StructuresYonas YGNo ratings yet
- Double Girder Box Type Eot Crane Design v2.0Document64 pagesDouble Girder Box Type Eot Crane Design v2.0deua2004100% (1)
- Crane Gantry Girder (BS5950 - Part1 - 2000)Document6 pagesCrane Gantry Girder (BS5950 - Part1 - 2000)sayed100% (1)
- Crane Design Basics Webpage Provides IntroductionDocument13 pagesCrane Design Basics Webpage Provides IntroductionAnandh PsNo ratings yet
- Section 12Document14 pagesSection 12herrerafaridNo ratings yet
- Basic Environmental Technology Water Supply Waste Management and Pollution Control 6th Edition Nathanson Test Bank 1Document36 pagesBasic Environmental Technology Water Supply Waste Management and Pollution Control 6th Edition Nathanson Test Bank 1brandijameskfgxardmjy100% (23)
- Rotating Axle Application - 115326-18-1100Document16 pagesRotating Axle Application - 115326-18-1100Erc Nunez VNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Propeller MT AFDAL MAMMARDocument17 pagesPerhitungan Propeller MT AFDAL MAMMARMuhamad Rifki AfanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Spreader Beam Design Calculations As Per DNV 5th VerDocument29 pagesMathcad - Spreader Beam Design Calculations As Per DNV 5th VerAbderraoufAffes100% (3)
- Sab4323 Ocw Topic 2Document39 pagesSab4323 Ocw Topic 2Eduardo Millas100% (1)
- Design of Balanced Cantilever BridgeDocument32 pagesDesign of Balanced Cantilever BridgeMorsed Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Design Z Section PurlinDocument9 pagesDesign Z Section PurlinSudipta HuiNo ratings yet
- Deep FoundationsDocument47 pagesDeep Foundationsipman99No ratings yet
- Skin PlateDocument12 pagesSkin Platerupesh dangolNo ratings yet
- Universidad Alas Peruanas - Filial Huancayo: Diseño de Losa de 4 TramosDocument28 pagesUniversidad Alas Peruanas - Filial Huancayo: Diseño de Losa de 4 TramosMilagros NatyNo ratings yet
- Whiteboard-Shifter (2) Final Print (Repaired)Document19 pagesWhiteboard-Shifter (2) Final Print (Repaired)Aklesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Steady Pipe Flows: Single and Branched Lines: M.S. Ghidaoui (Spring 2006)Document16 pagesSteady Pipe Flows: Single and Branched Lines: M.S. Ghidaoui (Spring 2006)khalidh20100% (1)
- L12 Bolt Connection 2Document17 pagesL12 Bolt Connection 2Kidus KidaneNo ratings yet
- Access Scaffoding DesignDocument10 pagesAccess Scaffoding DesignSyed Munawar Ali100% (5)
- Machine DesignDocument76 pagesMachine DesignTerenz Calangi67% (3)
- Design Verification CalculationsDocument15 pagesDesign Verification CalculationsKarthik KrNo ratings yet
- Transmission Tower Foundation DesignDocument26 pagesTransmission Tower Foundation DesignSara Nuon86% (7)
- Determine Material Property (PSG Data Book Page No 1.9 & 1.5)Document28 pagesDetermine Material Property (PSG Data Book Page No 1.9 & 1.5)Sagarias Albus100% (1)
- Belt conveyor design and specificationsDocument24 pagesBelt conveyor design and specificationsEnrique100% (1)
- Examples On Curved BeamsDocument12 pagesExamples On Curved BeamsJob ManNo ratings yet
- PROJECT: Proposed Formation of Housing Layout at Raichur Growth Center, Raichur CityDocument8 pagesPROJECT: Proposed Formation of Housing Layout at Raichur Growth Center, Raichur CityANIL KUMAR H CNo ratings yet
- Potable Water Pumps: Lamah EstDocument18 pagesPotable Water Pumps: Lamah Estفتحى أحمدNo ratings yet
- Potable Water Tank CalculationDocument37 pagesPotable Water Tank Calculationcamycax0% (1)
- ASTM D1037-12 - Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel MaterialsDocument16 pagesASTM D1037-12 - Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel MaterialsDiego De Castro Sales100% (1)
- Coiled Tubing Unit: ApplicationsDocument24 pagesCoiled Tubing Unit: Applicationswill castellanosNo ratings yet
- Egypt Code Design-MainDocument11 pagesEgypt Code Design-Mainmoganna73100% (1)
- Ceramics Term PaperDocument7 pagesCeramics Term PaperJerad AmesNo ratings yet
- Wood-Based Structural Panels in Compression: Standard Test Methods ForDocument6 pagesWood-Based Structural Panels in Compression: Standard Test Methods ForAnvit GadkarNo ratings yet
- Critical Remarks On The Application of The Yield Line Method On MasonryDocument13 pagesCritical Remarks On The Application of The Yield Line Method On MasonryRadekNo ratings yet
- REACTION SYSTEM Theory vs Experience From Load TestsDocument8 pagesREACTION SYSTEM Theory vs Experience From Load TestshenryLYDNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Module 1 STM & Problems DR - Ajitha PHY1701Document15 pagesClass 9 Module 1 STM & Problems DR - Ajitha PHY1701Abhijit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cswip 3 1-300 - Multiple Choice QuestionDocument43 pagesCswip 3 1-300 - Multiple Choice QuestionTrương Ngọc SơnNo ratings yet
- Constant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxDocument33 pagesConstant Mesh Manual Transmission Gear BoxBirhanu AsfawNo ratings yet
- Terms VidDocument15 pagesTerms VidThea Audrey DeritNo ratings yet
- FRP Strengthening of Concrete Structures - DesignDocument15 pagesFRP Strengthening of Concrete Structures - Designshafiullah100% (1)
- Use of epoxy adhesives in FiatDocument7 pagesUse of epoxy adhesives in FiatDiego Santana BragançaNo ratings yet
- ASME VIII-1 Low Temperature Operation Impact Test ExemptionsDocument10 pagesASME VIII-1 Low Temperature Operation Impact Test Exemptionschuckhsu1248No ratings yet
- Plate 6Document3 pagesPlate 6XDXDXDNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Lattice Structured MaterialsDocument13 pagesMechanical Properties of Lattice Structured MaterialsHadiNo ratings yet
- L5 Junction in Friction - Junction Growth - 2021Document7 pagesL5 Junction in Friction - Junction Growth - 2021Gonzalo SanzNo ratings yet
- Technical guide to corrugated web steel beamsDocument141 pagesTechnical guide to corrugated web steel beamsIvan KlyuchkaNo ratings yet
- Iso 15733 2015 en PDFDocument6 pagesIso 15733 2015 en PDFponorNo ratings yet
- Pile/Conductor stick-up calculations API RP2A specificationsDocument5 pagesPile/Conductor stick-up calculations API RP2A specificationsSamsul Imran BahromNo ratings yet
- Shell Stress and ForcesDocument57 pagesShell Stress and ForcesFiras DiknashNo ratings yet
- DEFLECTION Using Simplified Method of IsDocument8 pagesDEFLECTION Using Simplified Method of IsWHITE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- The Marsh Cone As A Viscometer Theoretical AnalysiDocument7 pagesThe Marsh Cone As A Viscometer Theoretical Analysisonny nebbiNo ratings yet
- Ch-6 Compatibility ModeDocument32 pagesCh-6 Compatibility Modedreamgurl9011No ratings yet
- Heavy Weight DrillPipe PDFDocument10 pagesHeavy Weight DrillPipe PDFDanielStiglitzNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Tutorial-Crack ProblemDocument8 pagesANSYS Tutorial-Crack ProblemMahdi100% (3)
- Strength of Materials AdvancedDocument21 pagesStrength of Materials AdvancedJoe OlsenNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy: Unit - 9Document24 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy: Unit - 9Vivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Nucleating Agents For High-Density Polyethylene-A ReviewDocument14 pagesNucleating Agents For High-Density Polyethylene-A ReviewCao TúNo ratings yet
- Tabeshpour A 10 57 1 77f3196Document9 pagesTabeshpour A 10 57 1 77f3196Irfan KhanNo ratings yet