Professional Documents
Culture Documents
College of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time Allowed
Uploaded by
Mohd RashdanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
College of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time Allowed
Uploaded by
Mohd RashdanCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1
College of Engineering
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Midterm Test Answer
SEMESTER 1, ACADEMIC YEAR 2010/2011
Subject Code : EEEB273
Course Title : Electronics Analysis & Design II
Date : 21 August 2010
Time Allowed : 2 hours
Page 2
Question 1 [40 marks]
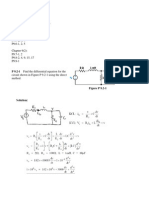
(a) Consider the circuit in Figure 1a, the bias voltages are V
+
=5V, V
=-5V. Let
I
S1
=I
S2
=5x10
-15
A, V
T
=0.026 V, I
REF
=200A and I
o
=50A. Assume V
A
= and neglect
base currents.
i. Calculate V
BE1
and V
BE2
.
[6 marks]
ii. Design the circuit that provides the bias current (I
o
) and the reference current (I
REF
).
[6 marks]
iii. List the advantages of a Widlar current source as compared to a basic two-transistor
current source.
[2 marks]
Figure 1a
1
2
/
/
1 15
2 15
200
ln( ) (0.026) ln 0.6347
5 10
50
ln( ) (0.026) ln 0.5987
5 10
BE T
BE T
V V
REF S
V V
O S
REF
BE T
S
O
BE T
S
I I e
I I e
I
V V V
I
I
V V V
I
=
=
= = =
= = =
1
1
2
2
1 2
1 2
1
1
0.6347 0.5987
720
50
(5) ( 5) 0.6347
46.826
200
BE BE o E
BE BE
E
o
REF BE
BE
REF
V V I R
V V
R
I
I R V V V
V V V
R k
I
+
+
=
= = =
+ =
= = =
1
2
1
2
The advantage of a Widlar current source is that:
It requires small resistance values to produce the
desired bias currents
A difference in V
BE
voltages of the two transistors can
produce a large magnitude difference between I
REF
and I
o
.
1
1
Page S
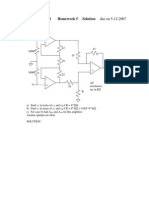
(b) Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1b, derive the equations that gives the relationship
between I
o
and I
REF
. Assume all transistors are identical and >>1.
[6 marks]
Figure 1b
(c) In the NMOS cascode current source as shown in Figure 1c, I
REF
=0.1mA. All transistors
are matched with parameters V
TN
=0.5V, K
n
=100A/V
2
and =0.02V
-1
.
i. Draw the ac equivalent circuit if the gates voltages of all transistors are constant.
[3 marks]
Grounds 1 mark
M2 and M4 correctly connected 1 marks
Labels 1 mark
Figure 1c
) ln(
) ln(
2
1
/
2
/
1
2
1
S
O
T BE
S
REF
T BE
V V
S C O
V V
S C REF
I
I
V V
I
I
V V
e I I I
e I I I
T BE
T BE
=
=
= =
=
) ln(
) ln(
1 1 2
1 2
REF
O
T E REF
E REF E E BE BE
REF
O
T BE BE
I
I
V R I
R I R I V V
I
I
V V V
=
=
=
Label
1
1
1
1
1
1
Page 4
ii. Draw the small-signal equivalent circuit for the circuit obtained in part i.
[5 marks]
Each transistor - 1mark = 2marks
r
o2
connection 1 mark
Node labels 2 marks.
iii. Calculate the V
GS
of each transistors and the output resistance R
o
looking into M
4
.
[10 marks]
iv. Calculate the changes on the output current if V
D4
changes from -2V to +2V.
[2 marks]
1
1
( 2 ( 2 ) 8 0
5 0
o o
o
o
d I d V
R
d I n A
M
=
= =
Matched transistors:
( )
V V V
I I
V V V
K
I
V V
V V K I
GS GS
REF o
GS GS
n
REF
TN GS
TN GS n REF
5 . 1
5 . 1
1 . 0
1 . 0
5 . 0
2 4
2 1 3
2
3
= =
=
= = = + = + =
=
( ) [ ]
= = =
= + + = + + =
= = = =
= =
= = = =
M k k m r r g R
or
M k m k k r g r r R
V mA m I K I K g
k r r
k
m I I
r
o o m o
o m o o O
REF n o n m
o o
REF o
o
50 ) 500 )( 500 )( 2 . 0 (
51 ) 500 )( 2 . 0 ( 1 500 500 1
/ 2 . 0 ) 1 . 0 )( 100 ( 2 2 2
500
500
) 1 . 0 )( 02 . 0 (
1 1 1
4 2
4 2 4
2 4
2
1
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
1
Page S
Question 2 [30 marks]
(a) Sketch the equivalent AC circuit of a BJT differential amplifier with differential-mode
input signal.
[5 marks]
Ac circuit equivalent with (a) two-sided output and (b) one-sided output
(b) With aid of circuit diagram, Design a BJT differential amplifier with a three-transistor
current source to establish the desired bias current I
Q
=0.2 mA. The supply voltages are
V
+
=10 V and V
-
=-10 V. The transistor parameters for the BJT diff-amp pair are =100,
V
A
=, V
O2
=8 V, V
T
=26 mV and A
cm
=0.5. The circuit parameters of the current source are
V
BE(on)
=0.7 V, V
A
=, and =150. Neglect the base currents and consider one-side output.
i. Draw the designed circuit. Label the circuit clearly.
[5 marks]
Any circuit (a) or (b) is correct
1
0.5
0.5
1
1
0.5
0.5
1
0.5
0.5
1
1
0.5
0.5
Page 6
ii. Determine the value of R
C
and R
ref
.
[6 marks]
2
0.2
0.1 ,
2 2
10 8
20 ,
0.1
Q
o
I
Ic mA
V v
Rc k
Ic mA
+
= = =
= = =
3 1
0.2
10 1.4 10
93
0.2
REF
BE BE
REF
REF
I Io mA
V V V V
R k
I mA
+
=
+
= = =
iii. Determine the differential voltage gain (A
d
) and the CMRR.
[6 marks]
3
3 3
2
0.1
3.846 10
26
3.846 10 20 10
38.4615
2
38.4615
76.923
0.5
20 (76.923) 37.72
m C
d
CQ
m
T
d
d
cm
dB
g R
A
I
mA
g
V mV
A
A
CMRR
A
CMRR Log
=
= = =
= =
= = =
= =
iv. Determine the differential-mode input resistance (R
id
).
[4 marks]
3
2
2
2 100 0.026
52
0.1 10 ^
id
CQ
id
VT
R r
I
R K
= =
= =
v. Find the output voltage of the differential amplifier when a differential-mode input
voltage of v
d
=0.3 sin t V is applied.
[4 marks]
,
38.461 0.3 11.538
o d d
o
V A V
V Sin t Sin t V
=
= =
1
2
1
2
1
1
2
1
1
2
2
2
2
Page 7
Question 3 [30 marks]
Figure 2 shows a MOSFET differential amplifier biased using a MOSFET current source. M
1
and M
2
are always in saturation. Study Figure 2 carefully. Transistor parameters are V
TN
= 2 V,
K
n
= 0.25 mA/V
2
, and = 0. Given that V
GS3
is 3.16 V. Show all your calculations clearly
when answering the following questions.
(a) Find I
1
, I
Q
, and I
D1
.
[12 marks]
Figure 2
(b) Determine V
GS1
, V
DS1
, and V
DS4
.
[9 marks]
I
1
= (V
+
- V
GS3
- V
-
) / (R
1
) [2]
= (10 - 3.16 - (-10))/(50k) [2]
= 0.337 mA
I
Q
= I
REF
[2]
= 0.337 mA [2]
I
D1
= I
Q
/ 2 [2]
= 0.168 mA [2]
I
D1
= K
n
(V
GS1
V
TN
)
2
[1]
0.168m = (0.25m)(V
GS1
2)
2
[1]
V
GS1
= 2.821 V [1]
V
DS1
= V
D1
- V
S1
[1]
= (V
+
I
D1
R
D
) (V
G1
V
GS1
) [1]
= (10 (0.168m)(24k)) (0 2.82) [1]
= 8.779 V
V
DS4
= V
S1
V
-
[1]
= (V
G1
V
GS1
) (V
-
) [1]
= (0 2.82) (-10) [1]
= 7.179 V
Page 8
(c) What is the output resistance (R
O
) of the current source if for M
4
is 0.01 V
-1
?
[3 marks]
(d) A one-sided output voltage at the drain of M
2
can be derived using small-signal equivalent
circuit to produce
{1}
R
O
is the output resistance of the current source. Using Equation {1} above, find the
differential-mode voltage gain (A
d
), the common-mode voltage gain (A
cm
), and the common
mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of the MOSFET differential amplifier in Figure 2. Use the
output resistance value obtained from question (c) above.
[6 marks]
-End of questions paper-
cm
o m
D m
d
D m
o
V
R g
R g
V
R g
V
2 1 2 +
=
R
O
= r
O4
[1]
= 1 / ( I
Q
) [1]
= 1 / (0.01)(0.337m) [1]
= 296.9 k
A
d
= (g
m
R
D
) / 2
= R
D
SQRT(K
n
I
Q
/ 2) [1]
= (24k) SQRT((0.25m)(0.337m)
/2) [1]
= 4.92
A
cm
= (-g
m
R
D
) / (1+2g
m
R
o
)
= (-R
D
SQRT(2K
n
I
Q
)) / (1+2R
o
SQRT(2K
n
I
Q
))
{i.e. Equation 11.82(b) in textbook} [1]
= {Put in all relevant values} [1]
= -0.04
CMRR = | A
d
/ A
cm
| [1]
= |4.92 / 0.04| [1]
= 122.34
CMRR
dB
= 20 log
10
| A
d
/ A
cm
|
= 41.75 dB
You might also like
- Jntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Document18 pagesJntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Krishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Sem1 1314 SolutionDocument16 pagesSem1 1314 SolutionThinesh StNo ratings yet
- 5 Two Port NetworksDocument14 pages5 Two Port NetworksNitinNo ratings yet
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbNo ratings yet
- Sem1 1213 SolutionDocument17 pagesSem1 1213 SolutionThinesh StNo ratings yet
- IIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Document8 pagesIIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Ridhwan Asri100% (1)
- Homework Assignment 8 SolutionDocument8 pagesHomework Assignment 8 SolutionKL Chiang100% (1)
- Solns 29Document102 pagesSolns 29ramprakash_rampelliNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- JNTU Electrical Circuits Exam SolutionsDocument19 pagesJNTU Electrical Circuits Exam SolutionsnbprNo ratings yet
- Darlington and CascodeDocument7 pagesDarlington and CascodeArjay Cajes0% (1)
- ECE-438 MOS Transistor Circuit AnalysisDocument10 pagesECE-438 MOS Transistor Circuit Analysisneeno2013No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2DrGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- ANU ENGN 2211 BJT CE Amplifier CircuitsDocument9 pagesANU ENGN 2211 BJT CE Amplifier CircuitsAristotle Atijera AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (2)
- Mohit Jetani 1270404 0Document32 pagesMohit Jetani 1270404 0ronajoj120No ratings yet
- Electronics design II amplifier calculationsDocument14 pagesElectronics design II amplifier calculationsbhanuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Modified)Document8 pagesExperiment 5 (Modified)Mark Sangalang100% (1)
- AP PGECET 2015 EC Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadDocument16 pagesAP PGECET 2015 EC Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadpavaniNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaNo ratings yet
- UOM Electrical Engineering ExamDocument7 pagesUOM Electrical Engineering ExamchetsNo ratings yet
- Floyd ED9 Part1 SolutionsDocument162 pagesFloyd ED9 Part1 SolutionsEngin Yiğit75% (44)
- Class-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StageDocument23 pagesClass-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StagelaksologinNo ratings yet
- Ycmou Ast MQP T34 S04Document22 pagesYcmou Ast MQP T34 S04sujitkadam90No ratings yet
- Solns 2cmosDocument18 pagesSolns 2cmosramprakash_rampelliNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument18 pagesAnalog CircuitsSAMIT KARMAKARNo ratings yet
- Gain the Edge with High-Accuracy Sensor CircuitsDocument10 pagesGain the Edge with High-Accuracy Sensor CircuitsKalaiNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 Solution Circuit AnalysisDocument10 pagesHomework 5 Solution Circuit AnalysisUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- Isolated Zeta Converter: Principle of Operation and Design in Continuous Conduction ModeDocument10 pagesIsolated Zeta Converter: Principle of Operation and Design in Continuous Conduction ModejhntfghkmNo ratings yet
- X L W C: Motor Shaft CapacitiveDocument14 pagesX L W C: Motor Shaft CapacitiveMuhamadFirdaus0% (1)
- Skema QuizDocument5 pagesSkema Quizmuhammad_mmdNo ratings yet
- Electronic 2 Solved ProblemDocument8 pagesElectronic 2 Solved ProblemAbdullah S OthmanNo ratings yet
- TITLEElectronic Circuits Tutorial SolutionsDocument9 pagesTITLEElectronic Circuits Tutorial SolutionsKemproof100% (3)
- B. Tech: Roll NoDocument5 pagesB. Tech: Roll NoRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED LEVEL PHYSICS PROBLEMS SOLUTIONSDocument10 pagesADVANCED LEVEL PHYSICS PROBLEMS SOLUTIONSManan SharmaNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator Full DerivationDocument12 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator Full DerivationPranav Itraj0% (1)
- ZZ - Electricity & MagnetismDocument137 pagesZZ - Electricity & Magnetismvenkyrocker777750% (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits 2-1 N-D-12Document15 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits 2-1 N-D-12nbprNo ratings yet
- Bistable Multivibrator Design PDFDocument20 pagesBistable Multivibrator Design PDFOmkar Thakur100% (1)
- Electronics Analysis & Design I Test Paper SummaryDocument4 pagesElectronics Analysis & Design I Test Paper SummaryzawirNo ratings yet
- Eee 334 Lab 1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsDocument18 pagesEee 334 Lab 1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsplaystationNo ratings yet
- Irg 4 PF 50 WDocument8 pagesIrg 4 PF 50 WQuickerManNo ratings yet
- Gate by RK KanodiaDocument440 pagesGate by RK KanodiaAfshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Document66 pagesTransistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Adri Muhaimin AfifNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument43 pagesUncontrolled RectifiersAbhijeet Singh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Jntu Hyd 2 2ece Eca Set 2Document18 pagesJntu Hyd 2 2ece Eca Set 2Travis BennettNo ratings yet
- NUS EE2005 Homework Solution for Current Mirror CircuitDocument7 pagesNUS EE2005 Homework Solution for Current Mirror CircuitKL ChiangNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- MajedDocument12 pagesMajedMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document63 pagesCH 03trebeheiramNo ratings yet
- BMS2024 Kruskal Wallis 2013Document13 pagesBMS2024 Kruskal Wallis 2013Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Zain KSA ProspectusDocument249 pagesZain KSA ProspectusMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- V V V V: Tutorial 1 ( Questions 4, 5 and 6 Are From Past Year Final Exams)Document3 pagesV V V V: Tutorial 1 ( Questions 4, 5 and 6 Are From Past Year Final Exams)Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Matlab NotehisDocument38 pagesMatlab NotehisMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- PdfMESB 33hi3 Chapter 2x1Document19 pagesPdfMESB 33hi3 Chapter 2x1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part 1 Real FunctionsDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Part 1 Real FunctionsMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- 22159Document8 pages22159Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- WLANDocument6 pagesWLANMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Chap 012Document42 pagesChap 012Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- UNITEN ICEE 2006 Prospects For Ocean Energy in MalaysiaDocument7 pagesUNITEN ICEE 2006 Prospects For Ocean Energy in MalaysiaMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Q3Document4 pagesQ3Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram ReductionDocument21 pagesBlock Diagram ReductionAzeem AliNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design (CSNB 163) (Due Date: Monday 26 August 2013) AssignmentDocument1 pageDigital Logic Design (CSNB 163) (Due Date: Monday 26 August 2013) AssignmentMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Thrmo 2Document1 pageThrmo 2Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1Document1 pageBusiness 1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Dutch Lady - Annual Report 2005Document87 pagesDutch Lady - Annual Report 2005Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1Document1 pageBusiness 1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1Document1 pageBusiness 1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- 1Document58 pages1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1design The Most Economical Truss That Will Support The Loading. The Members Cost $7.50/m, and The Gusset Plates Cost $8.00 EachDocument1 pageBusiness 1design The Most Economical Truss That Will Support The Loading. The Members Cost $7.50/m, and The Gusset Plates Cost $8.00 EachMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1Document1 pageBusiness 1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument4 pagesSolarMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Business 1Document1 pageBusiness 1Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- La PlaceDocument7 pagesLa PlaceMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.0 - Block DiagramDocument37 pagesChapter 3.0 - Block DiagramAzyan Wafiqah AzmiNo ratings yet
- XP6-C (A) : Six Circuit Supervised Control Module and SYNC-1 Accessory CardDocument2 pagesXP6-C (A) : Six Circuit Supervised Control Module and SYNC-1 Accessory CardLogan Marquez AguayoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Ed Boylestad Chapter 9 141002064028 Phpapp02Document32 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Ed Boylestad Chapter 9 141002064028 Phpapp02Phoebe FaithNo ratings yet
- A New Trans-Admittance Mode Biquad Filter Using MO-VDTADocument11 pagesA New Trans-Admittance Mode Biquad Filter Using MO-VDTAtritranNo ratings yet
- BE ECE Regular SyllabusDocument71 pagesBE ECE Regular SyllabusGanesh RamNo ratings yet
- DBX 786 Mic PreDocument8 pagesDBX 786 Mic PreSimon WalkerNo ratings yet
- 1.0SMB SeriesDocument6 pages1.0SMB SeriesPablo AllosiaNo ratings yet
- Electret Amplifier Application NoteDocument14 pagesElectret Amplifier Application NoterobkosaNo ratings yet
- Single transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACDocument7 pagesSingle transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACyr48No ratings yet
- Feedback: 8.1 General ConsiderationsDocument45 pagesFeedback: 8.1 General ConsiderationsthanhvinhegnNo ratings yet
- 1000 Series: Established Leaders in Actuation TechnologyDocument8 pages1000 Series: Established Leaders in Actuation TechnologymahamvhNo ratings yet
- Electricidad y Magnetismo PDFDocument110 pagesElectricidad y Magnetismo PDFlast730No ratings yet
- FM3 Release NotesDocument17 pagesFM3 Release NotesIan MannNo ratings yet
- Applications of Radars in MilitaryDocument8 pagesApplications of Radars in MilitaryPrabhu EaswarNo ratings yet
- PL515M4-HG102633v5 15iDocument235 pagesPL515M4-HG102633v5 15iHerry SusiloNo ratings yet
- Parts list for PT amplifiersDocument2 pagesParts list for PT amplifiersPepe NavaNo ratings yet
- Optical Pickup Specifications for DVD-ROM Drive Model HOP-1200WDocument27 pagesOptical Pickup Specifications for DVD-ROM Drive Model HOP-1200WPaul Neufeld100% (1)
- I888Document42 pagesI888ejmelchiorsNo ratings yet
- 13.8v Power Supply PS HighCurrentDocument17 pages13.8v Power Supply PS HighCurrentMadumathi BulumullaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Practice QuestionsDocument25 pagesMaintenance Practice QuestionsDanish israilNo ratings yet
- Ifr 1000a Service Notes1Document11 pagesIfr 1000a Service Notes1marioNo ratings yet
- BTESA Video-Audio Generator Distribution ModulesDocument2 pagesBTESA Video-Audio Generator Distribution ModulesEdgardo RadaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tutorial3Document3 pagesLaboratory Tutorial3Tal HaNo ratings yet
- Qx2442usb Qx2222usb Qx1832usb Qx1622usb M enDocument26 pagesQx2442usb Qx2222usb Qx1832usb Qx1622usb M enLAVINIA VIORICA POPANo ratings yet
- Hi-Fi PC Speaker SystemDocument11 pagesHi-Fi PC Speaker SystemMohsen IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 10A 1-30V Variable Power Supply With LM317Document4 pages10A 1-30V Variable Power Supply With LM317Antonio José Montaña Pérez de CristoNo ratings yet
- TM-11-5820-477-30 Control Radio Gra 39Document99 pagesTM-11-5820-477-30 Control Radio Gra 39Thoukididis ThoukididouNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTOR BIASING AND STABILIZATIONDocument57 pagesTRANSISTOR BIASING AND STABILIZATIONNaseer Mohammed100% (1)
- Bipolar Stepper Motor Control CircuitDocument3 pagesBipolar Stepper Motor Control CircuitArda AkberkNo ratings yet
- Lm568e 6 (1) .BDocument2 pagesLm568e 6 (1) .Bcinematic3006No ratings yet


















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)