Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Refers To A Specific Set of Renal Diseases in Which An Immunologic
Uploaded by
Adrian MallarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Refers To A Specific Set of Renal Diseases in Which An Immunologic
Uploaded by
Adrian MallarCopyright:
Available Formats
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS refers to a specific set of renal diseases in which an immunologic mechanism triggers inflammation and proliferation of glomerular
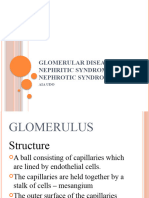
tissue that can result in damage to the basement membrane, mesangium, or capillary endothelium. Acute nephritic syndrome is a group of disorders that cause inflammation of the internal kidney structures (specifically, the glomeruli). In acute glomerulonephritis, the kidneys are normal in size or enlarged and edematous, and the surface of the kidney may show punctate hemorrhages. With the development of the microscope, Langhans was later able to describe these pathophysiologic glomerular changes. Acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) is active inflammation in the glomeruli. Each kidney is composed of about 1 million microscopic filtering "screens" known as glomeruli that selectively remove uremic waste products. The inflammatory process usually begins with an infection or injury (e.g., burn, trauma), then the protective immune system fights off the infection, scar tissue forms, and the process is complete. There are many diseases that cause an active inflammation within the glomeruli. Some of these diseases are systemic (i.e., other parts of the body are involved at the same time) and some occur solely in the glomeruli. When there is active inflammation within the kidney, scar tissue may replace normal, functional kidney tissue and cause irreversible renal impairment. The severity and extent of glomerular damage focal (confined) or diffuse (widespread) determines how the disease is manifested. Glomerular damage can appear as subacute renal failure, progressive chronic renal failure (CRF); or simply a urinary abnormality such as hematuria (blood in the urine) or proteinuria (excess protein in the urine).
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: G.U System Oliguria Hematuria Proteinuria Albuminuria G.I System Vomiting Abdominal pain Anorexia Musculoskeletal System Back pain Weakness Fatigue Respiratory System Tachypnea Dyspnea
Circulatory System RBC Potassium Sodium Cardiovascular System heart rate blood pressure Integumentary System Skin flushing Edema Diaphoresis CNS
Nausea Headache
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING
In partial fulfillment Of the course requirement In Competency Appraisal I
SUBMITTED BY: JOANA D. ELEGADO BSN 4A
SUBMITTED TO: MS. THELMA AGDA INSTRUCTOR
PATHOGENESIS:
Streptococcal Infection Microorganism circulate in the blood stream Deposition of antigen-antibody complex glomerulus Acute inflammation and damage within the nephrons including the glomerulus Proliferation of the endothelial cell lining of the glomerular capillary Leukocytes infiltration of the glomerulus Thickening of the glomerular filtration membrane Scarring and loss of glomerular filtration membrane Decrease glomerular filtration rate
You might also like
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) OverviewDocument8 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) OverviewRalph Wwarren ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nephritic Syndrome - Armando HasudunganDocument14 pagesNephritic Syndrome - Armando HasudunganzahraaNo ratings yet
- C C C C: CC CC CCCC CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCC C CC C CCCCC CCC CC C C CCCC CDocument1 pageC C C C: CC CC CCCC CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCC C CC C CCCCC CCC CC C C CCCC CGabriel Rosales RM RNNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Renal Diseases For Medical Students - GNDocument10 pagesLecture Note On Renal Diseases For Medical Students - GNEsayas KebedeNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases IDocument17 pagesRenal Diseases IPoojaNo ratings yet
- TB, Review, PathoDocument4 pagesTB, Review, PathoKrizzia LaturnasNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-05 at 15.41.06Document122 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-05 at 15.41.06Senuri ManthripalaNo ratings yet
- Glomerular DiseasesDocument92 pagesGlomerular Diseasesfrankozed1No ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument92 pagesGlomerulonephritisNita Hasan80% (5)
- Glomerular DiseasesDocument31 pagesGlomerular DiseasesLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- What Is Glomerulonephritis?Document7 pagesWhat Is Glomerulonephritis?SSNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritislamu123No ratings yet
- ACUTE GlomerulonephritisDocument3 pagesACUTE GlomerulonephritisJohn RayNo ratings yet
- Renal PathologyDocument34 pagesRenal PathologykamaluNo ratings yet
- GLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Document8 pagesGLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Anjitha K. JNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis-Post Streptoccocal GN: MBCHB ViDocument31 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis-Post Streptoccocal GN: MBCHB ViENOCK BENDERENo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis: Lecturer Prof. Yu.R. KovalevDocument39 pagesGlomerulonephritis: Lecturer Prof. Yu.R. Kovalevalfaz lakhani100% (1)
- Causes of Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument8 pagesCauses of Acute GlomerulonephritisShielah YacubNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)Document5 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)smashayielNo ratings yet
- Glomerular DsDocument18 pagesGlomerular Dsnathan asfahaNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology'Riku' Pratiwie TunaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndDocument21 pagesNephrotic Synd238439904No ratings yet
- C C C CC C: Adiong, Joanne Ignacio, Dianne Grace Julian, MarivicDocument9 pagesC C C CC C: Adiong, Joanne Ignacio, Dianne Grace Julian, MarivicufrieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (1of3) - Nephritic SyndromeDocument45 pagesLecture 4 (1of3) - Nephritic SyndromeAliye BaramNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Nephrotic Syndrome: Medical Surgical NursingDocument15 pagesSeminar On Nephrotic Syndrome: Medical Surgical NursingGargi MP100% (1)
- 14 Kidney Diseases PDFDocument128 pages14 Kidney Diseases PDFMayur WakchaureNo ratings yet
- Chronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsDocument8 pagesChronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Document58 pagesGlomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Rahmailla Khanza Diana FebriliantriNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument59 pagesGlomerulonephritistressNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NephritisDocument35 pagesPediatric NephritisLubinda SitaliNo ratings yet
- NEPHRITISDocument37 pagesNEPHRITISJay RathvaNo ratings yet
- What Causes Glomerular DiseaseDocument5 pagesWhat Causes Glomerular DiseaseAswin AgusNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument24 pagesNephritic SyndromeMuhamed Al Rohani100% (1)
- Nepro GNDocument6 pagesNepro GNHajime NakaegawaNo ratings yet
- AUBF Group 1 Chapter 8Document12 pagesAUBF Group 1 Chapter 8Gerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Kidney Cross Section: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocument7 pagesKidney Cross Section: by Mayo Clinic StaffReavin FuentesNo ratings yet
- Immunologic Disorder of The Renal and Renal FailureDocument25 pagesImmunologic Disorder of The Renal and Renal Failureraydan antojadoNo ratings yet
- Robinson Pathology Chapter 20 KidneyDocument11 pagesRobinson Pathology Chapter 20 KidneyElina Drits100% (1)
- UTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseDocument58 pagesUTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseLiana Ika SuwandyNo ratings yet
- 3&4 Glomerular Diseases and Nephrotic SyndromeDocument46 pages3&4 Glomerular Diseases and Nephrotic SyndromeTor Koang ThorNo ratings yet
- Gus156 Slide Ginjal Dan Saluran KemihDocument128 pagesGus156 Slide Ginjal Dan Saluran KemihRina ChairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Rapidly Progressive GlomerulonephritisDocument17 pagesRapidly Progressive GlomerulonephritisEasyOrientDNo ratings yet
- Lecturio Granulomatosis With PolyangitisDocument6 pagesLecturio Granulomatosis With PolyangitisPranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- Nephritis by Triveni SidhaDocument23 pagesNephritis by Triveni SidhaTriveni SidhaNo ratings yet
- Children/adolescents: Nephritic Syndrome Is ADocument2 pagesChildren/adolescents: Nephritic Syndrome Is Arubie ann tillorNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonefritis Akut Dan Kronis: DR - Hasan Basri, Sppd-Kgh-FinasimDocument53 pagesGlomerulonefritis Akut Dan Kronis: DR - Hasan Basri, Sppd-Kgh-FinasimnadddNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Primary Glomerulonephritis UG LectureDocument50 pagesPrimary Glomerulonephritis UG LectureMalik Mohammad AzharuddinNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute Glomerulonephritis?: Acute Glomerulonephritis (GN) Comprises A Specific Set of Renal Diseases inDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acute Glomerulonephritis?: Acute Glomerulonephritis (GN) Comprises A Specific Set of Renal Diseases inAnnapoorna SHNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument5 pagesNephrotic SyndromeAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument12 pagesNephrotic SyndromePutra Fatkhul Rizqi QoroidNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis: Nameesha Natasha Naidu 20130105Document26 pagesGlomerulonephritis: Nameesha Natasha Naidu 20130105AliMalikNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument8 pagesNephrotic SyndromeKanmani AniNo ratings yet
- Sindroma NefrotikDocument57 pagesSindroma NefrotikAstria Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Glomerular Disease: Naifah Luthfiyah Putri 1510211009Document41 pagesGlomerular Disease: Naifah Luthfiyah Putri 1510211009NaifahLuthfiyahPutriNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument36 pagesRenalDumitru BrînzaNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument58 pagesGlomerulonephritisJosa Anggi Pratama0% (1)
- GlomerulonephritisDocument85 pagesGlomerulonephritisCostina GrozaNo ratings yet
- Casestudy FractureDocument22 pagesCasestudy FractureAdrian Mallar0% (1)
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Flail Chest (Tayug)Document25 pagesFlail Chest (Tayug)Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocument1 pageNCP Deficient KnowledgeAdrian Mallar67% (3)
- Community Health Nursing p.31-55Document25 pagesCommunity Health Nursing p.31-55Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byDocument7 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument15 pagesPsychiatric NursingAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument16 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Case StudyDocument8 pagesOrthopedic Case StudyAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- Case Study On SchizophreniaDocument21 pagesCase Study On SchizophreniaAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument12 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Case in Herniorraphy BESTCASEDocument23 pagesCase in Herniorraphy BESTCASEAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Stab Wound Case StudyDocument33 pagesStab Wound Case StudyAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Opti-Cal TPS1200 Terminal Mode QuickguideDocument4 pagesOpti-Cal TPS1200 Terminal Mode QuickguideClaudiu OvidiuNo ratings yet
- MariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Document12 pagesMariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Jateen SoniNo ratings yet
- Animal Instinct (Em, Original) Acordes GuitarraDocument2 pagesAnimal Instinct (Em, Original) Acordes GuitarraGustavoNo ratings yet
- CE-401CE 2.0 Network Diagrams 2015Document83 pagesCE-401CE 2.0 Network Diagrams 2015Shubham BansalNo ratings yet
- Unidajump2019,+5 +31-42+JP+9 (1) +April+2018+AminullahDocument12 pagesUnidajump2019,+5 +31-42+JP+9 (1) +April+2018+AminullahSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Defeat Cancer NaturallyDocument94 pagesDefeat Cancer NaturallyRknuviprasys Low100% (3)
- Features and Highlights - : CapableDocument2 pagesFeatures and Highlights - : CapableaarianNo ratings yet
- ISO 13920 - Tolerâncias para Juntas SoldadasDocument7 pagesISO 13920 - Tolerâncias para Juntas SoldadasRicardo RicardoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 7 English Part 1 PDFDocument157 pagesNCERT Class 7 English Part 1 PDFVvs SadanNo ratings yet
- The Singapore Engineer - September 2018 IssueDocument27 pagesThe Singapore Engineer - September 2018 Issuekrpt0tytNo ratings yet
- CPower Product Training.09.2016.EnDocument70 pagesCPower Product Training.09.2016.Enerdinc100% (1)
- The Book of Paradise - Volume IIDocument964 pagesThe Book of Paradise - Volume IItriamazikamno100% (3)
- Automatic Door Opener With PIC12C508 CircuitDocument3 pagesAutomatic Door Opener With PIC12C508 CircuitLingaraj BeharaNo ratings yet
- Our School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsDocument7 pagesOur School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsprinceNo ratings yet
- Underground-Sprayed Concrete BrochureDocument12 pagesUnderground-Sprayed Concrete BrochureEngTamerNo ratings yet
- Routes of Medication AdministrationDocument2 pagesRoutes of Medication AdministrationTracy100% (6)
- LP 1st ObservationDocument6 pagesLP 1st ObservationMichael AnoraNo ratings yet
- Roger Ghanem, David Higdon, Houman Owhadi (Eds.) - Handbook of Uncertainty Quantification-Springer International Publishing (2017)Document2,035 pagesRoger Ghanem, David Higdon, Houman Owhadi (Eds.) - Handbook of Uncertainty Quantification-Springer International Publishing (2017)Jaime Andres Cerda Garrido100% (1)
- Comsol ProfileDocument4 pagesComsol ProfilePrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic-Regulations, Research & Marketing Challenges and Global Compliance: An OverviewDocument19 pagesCosmetic-Regulations, Research & Marketing Challenges and Global Compliance: An Overviewmaria sepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Testing and OTDR Basics: Brett Isley Terriitory Sales ManagerDocument54 pagesFiber Testing and OTDR Basics: Brett Isley Terriitory Sales ManagerTuppiNo ratings yet
- Digital DividesDocument25 pagesDigital DividesKumaraswamy ChannabasaiahNo ratings yet
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocument12 pagesJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitNguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- Amenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Document284 pagesAmenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Javier100% (1)
- Kyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsDocument6 pagesKyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsJaime RiosNo ratings yet
- Bruce Lyon - Occult CosmologyDocument55 pagesBruce Lyon - Occult Cosmologyeponymos100% (1)
- Alum Rosin SizingDocument9 pagesAlum Rosin SizingAnkit JainNo ratings yet
- Transes - Male & Female GenitaliaDocument10 pagesTranses - Male & Female GenitaliacamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- MV Lec PDFDocument102 pagesMV Lec PDFJonas Datu100% (1)
- April262019 Airline Economic Analysis 2018-2019vfwebDocument62 pagesApril262019 Airline Economic Analysis 2018-2019vfwebapi-548139140No ratings yet