Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction
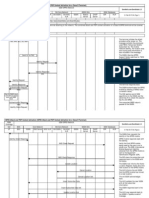
This article covers mobile terminated call flow between Mobile(UE) and network. It covers messages exchanged between Layer 3 entities(RR,MM,CC) at both side. It include channels(PCH,RACH,AGCH,SDCCH,FACCH,TCH) used at layer 1 to carry these messages over the air. This article assumes that initial frequency and time synchronization is done between UE and Network as described in GSM tutorial in tutorial section.
As described in the figure, PCH will be sent by network to alert mobile with ring tone if someone dials. This is called mobile terminated call. After PCH is received, mobile will transmit RACH and obtain SDCCH and other resources for further process. As described in GSM protocol stack, messages flow between both mobile and network at various layers(layer 3,layer 2,layer 1(physical layer). The message flow is self explanatory to establish the circuit switched mobile terminated(MT) call in GSM.
Mobile Terminated Call Release
The figure above mentions messages exchanged between mobile and network for call release.
This article covers mobile originated call flow between Mobile(UE) and network. It covers messages exchanged between Layer 3 entities(RR,MM,CC) at both side. It include channels(RACH,AGCH,SDCCH,FACCH,TCH) used at layer 1 to carry these messages over the air. This article assumes that initial frequency and time synchronization is done between UE and Network as described in GSM tutorial in tutorial section.
As described in the figure, before RACH is sent by mobile(UE) mobile is synchronized with network(BTS) both time and frequency wise. It means it has tuned frequency as per FCCH and time as per SCH burst. It has received and decoded SIs as per BCCH. Once BCCH is decoded mobile station comes to know where it has to transmit CCCH(RACH) and where it has to listen for CCCH(carrying PCH,AGCH). RACH is used in mobile originated call while PCH is used in mobile terminated call at the start. As described in GSM protocol stack, messages flow between both mobile and network at various layers(layer 3,layer 2,layer 1(physical layer). The message flow is self explanatory to establish the circuit switched mobile originated(MO) call in GSM.
Mobile Originated Call Release
The figure above mentions messages exchanged between mobile and network for call release.
GSM mobile phone network entry procedure or Power ON procedure
Fig.6 GSM Call Setup, it depicts basic flow of logical frames between BTS and MS to establish voice/data connection. Following steps are followed at GSM Mobile phone before you actually start talking or using it for data operations. These are called initial mobile phone procedures when you power ON the phone. Step-1 : Mobile phone scans for carriers and determine RSSI of all and pass them to upper layer, upper layer decide which carrier/channel has the highest RSSI and mobile will lock on to that carrier. There are two modes here first mode where mobile has prior knowledge of broadcast carriers and the other mode where mobile has no prior knowledge. In the second case mobile has to search for entire band while in the first case as mobile has broadcast carriers known and it will determine RSSI of those carriers only, hence it will complete cell search operation in less time. Step-2: Once carrier is known it will detect FB(Frequency correction Burst) on that carrier/channel which is a pure sine wave as mentioned above of value 67.7 KHz. Any deviation from this value is
determined and this much frequency offset is corrected on LO module by controlling through VCTCXO/VCO/OCXO used in the handset design. Step-3: After correcting for Frequency offset, now mobile need to lock on to particular time slot on that carrier frequency in the the GSM time domain frame structure. This is done using SB decoding. 25 bits of decoded data of SCH gives reduced frame number(19 bits) and BSIC(6 bits). Reduced frame number will provide very useful information of mobile's physical slot in the entire hyperframe. BSIC is made of BCC(Base Station Color code- 3 bits) and NCC(Network Color code-3 bits). BCC field directly provide training sequence details(26 bits in size).The correlation is performed with known training sequence to determine peak and hence timing offset is determined on the received frame. channel estimation is also performed using this training sequence. Remember SB comes on the same time slot as FB but after 8 time slots duration. This means time multiplexing of logical channels(FB,SB,BCCH,CCCH...) is used on the dedicated physical time slot(TS0 at Broadcast Freq). Step-4: Once SB is decoded now BCCH will appear on the same allocated physical time slot but after 8 time slot duration. BCCH is decoded which gives useful system informations(SI). Now mobile is camped on the network and it is ready to use voice services by exchanging useful frames/channels based on mobile initiated or mobile terminated call. If GPRS is enabled on the mobile phone, it can use data services provided by operator.
Fig.4 GSM Physical Layer These modules are speech coding, channel coding, interleaving, ciphering, burst assembly, modulation. Speech coding block uses 13kbps RELP (Residually Excited Linear Predictive coder). Channel coding block uses convolution coding of rate 1/2 with constraint length of 5. Interleaving block does diagonal interleaving, after 456 encoded bits in 20ms duration are broken into 57 bits sub-blocks. There will be about total 8 sub blocks of 57 bits each. Ciphering block uses A3 and A5 encryption algorithms. Encryption is changed call by call to enhance privacy. Burst assembly block frames the burst as required by GSM frame structure. The same is modulated and Gaussian filtered. Modulation block minimizes the occupied BW using GMSK modulation with BT of 0.3. For more details on GSM Physical layer refer our page in articles section.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Demo DLPDocument7 pagesDemo DLPRed Labrador ColegadoNo ratings yet
- STARBUCKSDocument12 pagesSTARBUCKSLeesaa88No ratings yet
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya Computer DetailsDocument1 pageChinmaya Vidyalaya Computer DetailsManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture: Submitted by (1110046)Document58 pagesGSM Architecture: Submitted by (1110046)Mukesh BhakarNo ratings yet
- CdkeyDocument1 pageCdkeyAnam Chaerul DamaiNo ratings yet
- All Computers Details - UpdatedDocument21 pagesAll Computers Details - UpdatedManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document13 pagesWireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- GSM Message FlowsDocument13 pagesGSM Message FlowsSharath Kumar100% (1)
- All Old & New Computers Counting DetailsDocument1 pageAll Old & New Computers Counting DetailsManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- C V, K, B - 34 I N D: Hinmaya Idyalaya Oramangala Angalore Ntercom Umbers EtailsDocument2 pagesC V, K, B - 34 I N D: Hinmaya Idyalaya Oramangala Angalore Ntercom Umbers EtailsManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- 3g Call FlowDocument28 pages3g Call FlowNiyojit RoyNo ratings yet
- Handoff FreedmanDocument30 pagesHandoff FreedmanKafayat AheerNo ratings yet
- UMTS Physical LayerDocument59 pagesUMTS Physical LayercristianneacsuNo ratings yet
- Gprs Attach PDP Sequence DiagramDocument4 pagesGprs Attach PDP Sequence Diagramapi-3838344100% (1)
- Ueintroductionul1 120605033509 Phpapp01Document25 pagesUeintroductionul1 120605033509 Phpapp01Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- PrachDocument7 pagesPrachManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document13 pagesWireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- MKDocument7 pagesMKManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Ts 121133v040100pDocument27 pagesTs 121133v040100pManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Access by GSMDocument18 pagesAccess by GSMManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- MKDocument7 pagesMKManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- GSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessDocument2 pagesGSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Sentence Fragments, Elliptical Clause, and Run On SentenceDocument9 pagesSentence Fragments, Elliptical Clause, and Run On SentenceLorendel SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Linux-Insides Interrupts Linux-Interrupts Part 4Document4 pagesLinux-Insides Interrupts Linux-Interrupts Part 4Avinash PalNo ratings yet
- Run-Ons Comma Splices & FragmentsDocument3 pagesRun-Ons Comma Splices & Fragments2484688644wuboyuanNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 (2ND gRADING MODULE)Document5 pagesGRADE 8 (2ND gRADING MODULE)rica jean barroquilloNo ratings yet
- JSGrammar2e 2B U18 AnsDocument10 pagesJSGrammar2e 2B U18 AnsTimmy SzeNo ratings yet
- Flarenet Data Import From ExcelDocument15 pagesFlarenet Data Import From ExcelAbhay BhoirNo ratings yet
- EViews 11 Getting StartedDocument69 pagesEViews 11 Getting StartedJesus Fernando Salazar RojasNo ratings yet
- Ovrdbf 1. What Exactly The OVRDBF Does?: 'HSTATUS "C" & HCUST 08177' 'HCUST 08177'Document13 pagesOvrdbf 1. What Exactly The OVRDBF Does?: 'HSTATUS "C" & HCUST 08177' 'HCUST 08177'venkateswarlu mNo ratings yet
- Instruction Booklet For Creating A Custom Kakejiku (Wall Scroll)Document10 pagesInstruction Booklet For Creating A Custom Kakejiku (Wall Scroll)Claudio OyarzunNo ratings yet
- The Happy Linguist by 3 Minute LanguagesDocument921 pagesThe Happy Linguist by 3 Minute LanguagesAlexandre KrulNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of RizalDocument9 pagesLife and Works of RizalMazmaveth CabreraNo ratings yet
- Install Visual Basic 6Document3 pagesInstall Visual Basic 6avijit babuNo ratings yet
- DBF Java JDBCDocument105 pagesDBF Java JDBCchato_orosNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark The Jogger Interactive WorksheetDocument1 page1 Mark The Jogger Interactive WorksheetHuma RiazNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Checklist 284 PDF 2023 by Parul GeraDocument25 pagesReasoning Checklist 284 PDF 2023 by Parul GeraManvendra FauzdarNo ratings yet
- Koi Desh PunjaboN Sohna NaDocument12 pagesKoi Desh PunjaboN Sohna Nahirdaypallsingh2241No ratings yet
- Baudelaire - TranslationDocument5 pagesBaudelaire - Translationapi-357156106No ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflectionaliffnajmieNo ratings yet
- A Popular History of Russia, Earliest Times To 1880, VOL 3 of 3 - Alfred RambaudDocument299 pagesA Popular History of Russia, Earliest Times To 1880, VOL 3 of 3 - Alfred RambaudWaterwind100% (2)
- Chapter 3Document91 pagesChapter 3minhddhe180032No ratings yet
- SummarizingDocument2 pagesSummarizingJuan Felipe VasquezNo ratings yet
- Manage inbound and outbound routesDocument25 pagesManage inbound and outbound routesJavier FreiriaNo ratings yet
- Namespace: "Application.H" "Staticfunctions.H"Document6 pagesNamespace: "Application.H" "Staticfunctions.H"iDenisNo ratings yet
- A Letter To Kawabata Yasunari From Osamu DazaiDocument2 pagesA Letter To Kawabata Yasunari From Osamu DazaiKunotamashi KanakacheroNo ratings yet
- A History of Eclecticism in Greek PhilosophyDocument396 pagesA History of Eclecticism in Greek PhilosophyFaris MarukicNo ratings yet
- 101 ReactDocument221 pages101 ReactrupeshNo ratings yet
- Why Pymel?: The Nature of The BeastDocument4 pagesWhy Pymel?: The Nature of The BeastOzgur YildirimNo ratings yet
- Coherence Cohesion 1 1Document36 pagesCoherence Cohesion 1 1Shaine MalunjaoNo ratings yet