Professional Documents
Culture Documents
European Central Bank
Uploaded by
nairpranavOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
European Central Bank
Uploaded by
nairpranavCopyright:
Available Formats
European Central Bank
The ECB is the central bank for Europe's single currency, the euro. The ECBs main task is to maintain the euro's purchasing power and thus price stability in the euro area. It administers the monetary policy of the 17 EU member states which constitute the Eurozone, one of the largest currency areas in the world. Basic tasks to be carried out through the Euro system are: The definition and implementation of monetary policy for the Eurozone: 1. Main focusa. On Price Stability i.e. to maintain inflation rates at levels below, but close to, 2%, recognizing relative change in prices, avoiding inflation risk, etc. 2. Strategya. By setting short-term interest rates, monetary policy influences the economy, and ultimately the price level. b. How? :- Two pillar approach- Economic Analysis for assessing the short to medium-term determinants of price developments influenced largely by the interplay of supply and demand in the goods, services and factor markets. Monetary Analysis focuses on credit and liquidity conditions in the economy and their consequences in terms of risks to price stability. 3. Monetary Policy Instrumentsa. Deposit Facilities b. Marginal lending Facilities c. Open market operations like long term financing d. Reserve requirements like reserve base, reserve ratio, etc.
The conduct of foreign exchange operations: The holding and management of the official foreign reserves of the euro area countries (portfolio management): The ECBs foreign reserves ensure that the ECB has sufficient liquidity to conduct foreign exchange operations. The ECBs foreign reserves portfolio consists of US dollars, Japanese yen, g old and special drawing rights. The promotion of the smooth operation of payment systems (TARGET2). Further tasks Banknotes: The ECB has the exclusive right to authorize the issuance of banknotes within the euro area. Financial stability and supervision: The Euro system contributes to the smooth conduct of policies by the competent authorities as regards the prudential supervision of credit institutions and the stability of the financial system. International and European cooperation: The ECB maintains working relations with relevant institutions both within the EU and at the global level, in respect of the tasks entrusted to the Euro system. ECBs response to subprime mortgage crisis: -Aug 2007: Provided overnight liquidity to the interbank money markets to reduce short-term interest rate volatility and to contain the risk that tensions in the financial markets -Dec 2007: The ECB started, in cooperation with the Federal Reserve System, to provide dollar funding to euro area banks to address shortages of dollar liquidity.
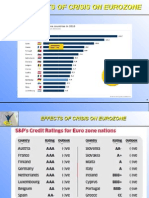
-Oct 2008: Euro zone banks were able to get unlimited liquidity from the ECB at the main refinancing rate provided they offered adequate collateral. -Jun 2009: Announces covered bond purchase programme. Its purpose was to help revive the market in covered bonds. -May 2010: Introduce the (now terminated) Securities Markets Programme so that ECB and the national central banks of the euro zone could intervene in certain debt securities markets, mostly government bond markets. -Dec 2011: Conducted 2 long term refinancing operations, decided to increase the availability of collateral by reducing the rating threshold for certain asset-backed securities, reduce the reserve ratio to 1% (from 2%).
Euro Convertible Bonds
A
You might also like
- Paper Presentation EcbDocument3 pagesPaper Presentation EcberikaNo ratings yet
- The European Central Bank: Monetary Policy of EU Member States. The ECB ControlsDocument1 pageThe European Central Bank: Monetary Policy of EU Member States. The ECB ControlsSusan MihaiNo ratings yet
- Invesment Bank PaperDocument3 pagesInvesment Bank PaperWidya AstutiNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy in ItalyDocument4 pagesMonetary Policy in Italygshah_20No ratings yet
- European Central BankDocument4 pagesEuropean Central BankANDREA LEI VILLA SANTANo ratings yet
- ECB European Central BankDocument12 pagesECB European Central BankHiral SoniNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy IndicatorsDocument6 pagesMonetary Policy IndicatorsHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Monetary Policy in The EUDocument3 pagesTask 2 Monetary Policy in The EUekateryna249No ratings yet
- Central BanksDocument9 pagesCentral BanksTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- EU Politics and EconomicsDocument4 pagesEU Politics and Economicscondesemma7No ratings yet
- With Good Page Num DocumentDocument24 pagesWith Good Page Num Documenttanwir13No ratings yet
- The European Central BankDocument3 pagesThe European Central Bankmesteru_alexandraNo ratings yet
- ECBDocument6 pagesECBalex nikifarovNo ratings yet
- A House Built On Sand? The ECB and The Hidden Cost of Saving The EuroDocument20 pagesA House Built On Sand? The ECB and The Hidden Cost of Saving The EuroAzhar HeetunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Central BanksDocument21 pagesChapter 9 Central BanksJay Ann DomeNo ratings yet
- Towards A Banking Union: Uropean OmmissionDocument6 pagesTowards A Banking Union: Uropean OmmissionMolnár LeventeNo ratings yet
- EU Emergency MeasuresDocument6 pagesEU Emergency MeasuresA paulNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument77 pagesThesisAngates1No ratings yet
- Eu Vision For Closer UnionDocument52 pagesEu Vision For Closer UnionEKAI CenterNo ratings yet
- 3 The Central Bank: Mission and BehaviorDocument5 pages3 The Central Bank: Mission and BehaviorDelise LimNo ratings yet
- 2: European Central Bank and Monetary System (Monetary Policy Objectives and Targets)Document3 pages2: European Central Bank and Monetary System (Monetary Policy Objectives and Targets)Akshat KediaNo ratings yet
- European Central Bank Master ThesisDocument6 pagesEuropean Central Bank Master Thesisvxjtklxff100% (1)
- Monetary and Foreign Currency Policy of The European Central BankDocument9 pagesMonetary and Foreign Currency Policy of The European Central BankJasmina HrvattNo ratings yet
- PC 2014 14 PDFDocument11 pagesPC 2014 14 PDFBruegelNo ratings yet
- Banking Regulation and SupervisionDocument2 pagesBanking Regulation and SupervisionRomina BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Econ MonDocument28 pagesEcon MoncarolorhurNo ratings yet
- What Is The 'European Monetary System - EMS'Document5 pagesWhat Is The 'European Monetary System - EMS'Swathi JampalaNo ratings yet
- Central and Monetary BankDocument14 pagesCentral and Monetary BankDEVERLYN SAQUIDONo ratings yet
- Main Functions: The Maintenance of Price StabilityDocument16 pagesMain Functions: The Maintenance of Price StabilityMariana PopaNo ratings yet
- List of Acronyms Associated With The Eurozone CrisisDocument8 pagesList of Acronyms Associated With The Eurozone Crisisjosh321No ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Reserves and Operations of The Eurosystem: 1 Introduction: The Institutional FrameworkDocument7 pagesForeign Exchange Reserves and Operations of The Eurosystem: 1 Introduction: The Institutional FrameworkaldhibahNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 11Document6 pagesNotes Chapter 11Amaia MartinicorenaNo ratings yet
- Banking On Bonds - The New Links Between States and MarketsDocument19 pagesBanking On Bonds - The New Links Between States and MarketsAdrian SanduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - International Finance by Krugman 11th EditionDocument20 pagesLecture 10 - International Finance by Krugman 11th EditionWuZiFankoalaNo ratings yet
- Role of National Governments: Single MarketDocument6 pagesRole of National Governments: Single MarketZharmineNo ratings yet
- European Banking SystemDocument5 pagesEuropean Banking SystemRidhima PangotraNo ratings yet
- Central BanksDocument63 pagesCentral BanksAmir Abdalla IbrahimNo ratings yet
- European Moneytary System - LapDocument13 pagesEuropean Moneytary System - LapThanh phong HồNo ratings yet
- EURODocument11 pagesEUROalishaanejaNo ratings yet
- The Role and Importance of Ecb'S Monetary Policy in The Global Economic CrisisDocument11 pagesThe Role and Importance of Ecb'S Monetary Policy in The Global Economic CrisisJasmina HrvattNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction Central Banks T2 2020-21Document31 pagesLecture 1 Introduction Central Banks T2 2020-21Jean KwokNo ratings yet
- Memo 14 244 - enDocument10 pagesMemo 14 244 - enopreanioan01No ratings yet
- Monetary Policy 2011 enDocument161 pagesMonetary Policy 2011 enDavidNo ratings yet
- The Euro and Its Consequences: What Makes A Currency Strong?Document17 pagesThe Euro and Its Consequences: What Makes A Currency Strong?Kritika_Gupta_3748No ratings yet
- The European Union and The Global Financial CrisisDocument37 pagesThe European Union and The Global Financial CrisisHamza AbbasiNo ratings yet
- History of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldDocument7 pagesHistory of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldZahin SarwarNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document1 pageCase 1Maria del Pilar Arango MauryNo ratings yet
- Central BankDocument9 pagesCentral BanksakibNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Paper Cassola Durre HolthausenDocument64 pagesSession 5 Paper Cassola Durre HolthausenAyu LestariNo ratings yet
- European Central BankDocument7 pagesEuropean Central BankTudor SusanuNo ratings yet
- European Central BankDocument24 pagesEuropean Central Bankchhadwaharshit50% (2)
- Term Paper of FM&INSDocument13 pagesTerm Paper of FM&INSKetema AsfawNo ratings yet
- National Bank of Romania Versus European Central Bank: Popescu IonuțDocument9 pagesNational Bank of Romania Versus European Central Bank: Popescu IonuțAdina Cosmina PopescuNo ratings yet
- European Central Bank: Project 3Document15 pagesEuropean Central Bank: Project 3mhildbrand7034No ratings yet
- Euro Crisis PPT by AnkitDocument15 pagesEuro Crisis PPT by AnkitShailesh KumarNo ratings yet
- International Financial MarketsDocument3 pagesInternational Financial MarketsDung Le ThuyNo ratings yet
- IftmDocument6 pagesIftmrawatamit1985No ratings yet
- CH 16Document7 pagesCH 16cddaniel910411No ratings yet
- Euro ZoneDocument14 pagesEuro ZoneNidhi GargNo ratings yet
- NRO Vs NREDocument3 pagesNRO Vs NREsushantNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Public Debt Upon Economic Growth: Gheorghita DINCĂ - Corresponding AuthorDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Public Debt Upon Economic Growth: Gheorghita DINCĂ - Corresponding AuthorfarahNo ratings yet
- Paragraf Siklus BisnisDocument2 pagesParagraf Siklus BisnisMaryaNo ratings yet
- Financial and Physical Performance Report FORMATDocument9 pagesFinancial and Physical Performance Report FORMATJeremiah TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 2010 Economic Report On Indonesia: ISSN 0522-2572Document26 pages2010 Economic Report On Indonesia: ISSN 0522-2572tanjq87No ratings yet
- TM - PGDM - 103 - MeDocument39 pagesTM - PGDM - 103 - Mebitunmou100% (1)
- The Labor Market, Unemployment, and Inflation: Fernando & Yvonn QuijanoDocument31 pagesThe Labor Market, Unemployment, and Inflation: Fernando & Yvonn QuijanoCharles Reginald K. HwangNo ratings yet
- Unemployment Introduction Unemployment or Joblessness IsDocument1 pageUnemployment Introduction Unemployment or Joblessness IsNitesh KotianNo ratings yet
- Crowding OutDocument2 pagesCrowding OutAkanksha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- FM 1004 Monetary Policy and Central Banking Course Syllabus 1Document3 pagesFM 1004 Monetary Policy and Central Banking Course Syllabus 1Cielo ObriqueNo ratings yet
- Pestel Analysis - Mms and MbaDocument7 pagesPestel Analysis - Mms and MbarsvmarketingNo ratings yet
- Liberian Daily Observer 11/20/2013Document24 pagesLiberian Daily Observer 11/20/2013Liberian Daily Observer NewspaperNo ratings yet
- 1 IB Nature & ScopeDocument19 pages1 IB Nature & ScopePanav MohindraNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Money Supply PDFDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Money Supply PDFhahaNo ratings yet
- Tripticio - Cajamarca en InglesDocument2 pagesTripticio - Cajamarca en InglesMargot Milagro Cuzcano Campos0% (1)
- Press Release 2013: Imagine Musa Tabling A RM40 Billion 2014 Sabah Budget 13 Nov 2013Document2 pagesPress Release 2013: Imagine Musa Tabling A RM40 Billion 2014 Sabah Budget 13 Nov 2013Daniel John JambunNo ratings yet
- Manmgt3 1 PDFDocument29 pagesManmgt3 1 PDFWilsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Business Environment Assignment 3Document18 pagesUnit 4 Business Environment Assignment 3stoneage98990% (10)
- TTL GSTDocument2 pagesTTL GSTchetankumarmrbt01No ratings yet
- Trade Wars: Then and NowDocument34 pagesTrade Wars: Then and NowShreyes A. JayaramNo ratings yet
- VAT Solving Exercise (TAX2)Document3 pagesVAT Solving Exercise (TAX2)Peter Paul Enero PerezNo ratings yet
- Central BankDocument5 pagesCentral BankMohammad JamilNo ratings yet
- Argument Paper FDDocument7 pagesArgument Paper FDapi-312461507No ratings yet
- Macro Fiscal Policy and Money SupplyDocument136 pagesMacro Fiscal Policy and Money SupplyJia QiNo ratings yet
- Assignment MGT 340Document13 pagesAssignment MGT 340Hanis RamliNo ratings yet
- Yukon HuangDocument22 pagesYukon HuangMalcolm RiddellNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Costs of Tax ComplianceDocument21 pagesThe Hidden Costs of Tax ComplianceMercatus Center at George Mason UniversityNo ratings yet
- New 5Document5 pagesNew 5nikosNo ratings yet
- ECO372 Week 1 Discussion QuestionsDocument4 pagesECO372 Week 1 Discussion QuestionsWellThisIsDifferentNo ratings yet
- MbaDocument4 pagesMbaB RaoNo ratings yet