Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Loloy
Uploaded by
Archie CuyacotOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Loloy
Uploaded by
Archie CuyacotCopyright:
Available Formats
What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language SQL lets you access and manipulate databases SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard
What Can SQL do? SQL can execute queries against a database SQL can retrieve data from a database SQL can insert records in a database SQL can update records in a database SQL can delete records from a database SQL can create new databases SQL can create new tables in a database SQL can create stored procedures in a database SQL can create views in a database SQL can set permissions on tables, procedures, and views
SQL is a Standard - BUT.... Although SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard, there are different versions of the SQL language. However, to be compliant with the ANSI standard, they all support at least the major commands (such as SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, WHERE) in a similar manner. RDBMS RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS is the basis for SQL, and for all modern database systems such as MS SQL Server, IBM DB2, Oracle, MySQL, and Microsoft Access. The data in RDBMS is stored in database objects called tables. A table is a collection of related data entries and it consists of columns and rows.
Database Tables A database most often contains one or more tables. Each table is identified by a name (e.g. "Customers" or "Orders"). Tables contain records (rows) with data. In this tutorial we will use the well-known Northwind sample database (included in MS Access and MS SQL Server). Below is a selection from the "Customers" table: CustomerID 1 CustomerName Alfreds Futterkiste ContactName Maria Anders Address Obere Str. 57
2 3 4
Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados Antonio Moreno Taquera Around the Horn
Ana Trujillo Antonio Moreno Thomas Hardy
Avda. de la Constitucin 2222 Mataderos 2312 120 Hanover Sq.
Berglunds snabbkp
Christina Berglund
Berguvsvgen 8
The table above contains five records (one for each customer) and seven columns (CustomerID, CustomerName, ContactName, Address, City, PostalCode, and Country).
SQL Statements Most of the actions you need to perform on a database are done with SQL statements. The following SQL statement selects all the records in the "Customers" table: Example SELECT * FROM Customers; SQL is NOT case sensitive: SELECT is the same as select
Semicolon after SQL Statements?
Some database systems require a semicolon at the end of each SQL statement. Semicolon is the standard way to separate each SQL statement in database systems that allow more than one SQL statement to be executed in the same call to the server. In this tutorial, we will use semicolon at the end of each SQL statement.
Some of The Most Important SQL Commands SELECT - extracts data from a database UPDATE - updates data in a database DELETE - deletes data from a database INSERT INTO - inserts new data into a database CREATE DATABASE - creates a new database ALTER DATABASE - modifies a database CREATE TABLE - creates a new table ALTER TABLE - modifies a table DROP TABLE - deletes a table CREATE INDEX - creates an index (search key) DROP INDEX - deletes an index
Demo Database In this tutorial we will use the well-known Northwind sample database. Below is a selection from the "Customers" table: CustomerName Alfreds Futterkiste ContactName Maria Anders Address Obere Str. 57
CustomerID 1
2 3 4
Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados Antonio Moreno Taquera Around the Horn
Ana Trujillo Antonio Moreno Thomas Hardy
Avda. de la Constitucin 2222 Mataderos 2312 120 Hanover Sq.
Berglunds snabbkp
Christina Berglund
Berguvsvgen 8
The SQL SELECT DISTINCT Statement In a table, a column may contain many duplicate values; and sometimes you only want to list the different (distinct) values. The DISTINCT keyword can be used to return only distinct (different) values. SQL SELECT DISTINCT Syntax Operators in The WHERE Clause The following operators can be used in the WHERE clause: Operator = <> > < >= <= BETWEEN LIKE IN Description Equal
Not equal. Note: In some versions of SQL this operator may be written as != Greater than Less than Greater than or equal Less than or equal Between an inclusive range Search for a pattern To specify multiple possible values for a column
The SQL AND & OR Operators The AND operator displays a record if both the first condition AND the second condition are true. The OR operator displays a record if either the first condition OR the second condition is true.
AND Operator Example The following SQL statement selects all customers from the country "Germany" AND the city "Berlin", in the "Customers" table: Example SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Country='Germany' AND City='Berlin'; OR Operator Example The following SQL statement selects all customers from the city "Berlin" OR "Mnchen", in the "Customers" table: Example SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City='Berlin' OR City='Mnchen'; Combining AND & OR You can also combine AND and OR (use parenthesis to form complex expressions). The following SQL statement selects all customers from the country "Germany" AND the city must be equal to "Berlin" OR "Mnchen", in the "Customers" table: The SQL ORDER BY Keyword The ORDER BY keyword is used to sort the result-set by one or more columns. The ORDER BY keyword sorts the records in ascending order by default. To sort the records in a descending order, you can use the DESC keyword.
You might also like
- Humanmetrics Jung Typology TestDocument1 pageHumanmetrics Jung Typology TestArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Post Doc Letters ExamplesDocument2 pagesPost Doc Letters ExamplesPriyance NababanNo ratings yet
- Sample Outlinefor Case Study F'05Document1 pageSample Outlinefor Case Study F'05viji88mbaNo ratings yet
- First Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesFirst Reaction PaperArchie Cuyacot70% (10)
- Network Operating SystemDocument2 pagesNetwork Operating SystemArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramDocument1 pageUse Case DiagramArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Portersgenericcompetitivestrategies 111012204625 Phpapp01Document17 pagesPortersgenericcompetitivestrategies 111012204625 Phpapp01Kawchhar AhammedNo ratings yet
- Tae Kim - Japanese Grammar GuideDocument354 pagesTae Kim - Japanese Grammar GuideAcebo Clau100% (4)
- Article V SuffrageDocument3 pagesArticle V SuffrageArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- FRMDocument1 pageFRMArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- How To Describe DiagramsDocument28 pagesHow To Describe Diagramssurya100% (1)
- Income Statement - 12 Months: Date: 11/18/2014Document1 pageIncome Statement - 12 Months: Date: 11/18/2014Archie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- ScreenDocument4 pagesScreenArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- What Is Accounting ArchDocument1 pageWhat Is Accounting ArchArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Operating System Which Made by MicrosoftDocument2 pagesOperating System Which Made by MicrosoftArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- HumanintDocument24 pagesHumanintArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Cuyacot, Archie Daming, Michael Abao, Jirehnel Abella, Herolyn Daguinsal, Charie Mae Timoteo, JezaDocument1 pageCuyacot, Archie Daming, Michael Abao, Jirehnel Abella, Herolyn Daguinsal, Charie Mae Timoteo, JezaArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Bukidnon State University: Video ChatDocument2 pagesBukidnon State University: Video ChatArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
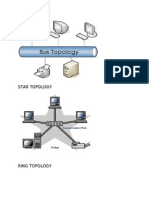
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork Topologykim15mmNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument2 pagesFigure of SpeechArchie Cuyacot100% (1)
- Mga PicturesDocument2 pagesMga PicturesArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Types of Operating SystemsDocument7 pagesTypes of Operating Systemspritika86No ratings yet
- Mga PicturesDocument2 pagesMga PicturesArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Classification of Operating SystemsDocument2 pagesClassification of Operating Systemscrystal_143_2006No ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Coal To Generate ElectricityArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- From The BeginningDocument1 pageFrom The BeginningArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Jaime B. Vallente: I Hereby Certify That The Above Records Are True and CorrectDocument2 pagesJaime B. Vallente: I Hereby Certify That The Above Records Are True and CorrectArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Cuyacot, Archie Daming, Michael Abao, Jirehnel Abella, Herolyn Daguinsal, Charie Mae Timoteo, JezaDocument1 pageCuyacot, Archie Daming, Michael Abao, Jirehnel Abella, Herolyn Daguinsal, Charie Mae Timoteo, JezaArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Three Types of CableDocument1 pageThree Types of CableArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Joins in Report StudioDocument29 pagesJoins in Report StudiocognosNo ratings yet
- TasksDocument3 pagesTasksMohit AkerkarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual 3 PHP Database Programming: Visual Studio Code ManualDocument8 pagesLaboratory Manual 3 PHP Database Programming: Visual Studio Code ManualAbebaw AmareNo ratings yet
- Rebellabs SQL Cheat Sheeasdasdasd55555555Document1 pageRebellabs SQL Cheat Sheeasdasdasd55555555cuevaNo ratings yet
- 1 Database Language DDL, DCL, TCLDocument2 pages1 Database Language DDL, DCL, TCLprerana sheteNo ratings yet
- FCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1Document38 pagesFCUBS Database Practices Db11gr2 Fc12.0.1cuonglunNo ratings yet
- Dataset y DataTable en VISUAL STUDIO 2010 1Document19 pagesDataset y DataTable en VISUAL STUDIO 2010 1carlitosNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 MidtermDocument24 pagesSem 1 MidtermDorin ChioibasNo ratings yet
- PLSQL - 5 - 2 - Brayan Ferney Perez Moreno PDFDocument3 pagesPLSQL - 5 - 2 - Brayan Ferney Perez Moreno PDFBryan Perez100% (2)
- PLSQL s05 l05 TryDocument3 pagesPLSQL s05 l05 TryMadalina MV0% (1)
- M1 LD-Relational Database 2020Document26 pagesM1 LD-Relational Database 2020M.Kelvin PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Database Architecture and ASMDocument41 pagesDatabase Architecture and ASMPradpm KumNo ratings yet
- SQL InjectionsDocument1 pageSQL InjectionsNIHAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- 39524Document16 pages39524Lakshman ANo ratings yet
- Microsoft AccessDocument20 pagesMicrosoft Accessbansaliresh1No ratings yet
- Queries On BANK DatabaseDocument8 pagesQueries On BANK DatabaseVenkataramana BattulaNo ratings yet
- How To Retrieve Entire SQLDocument17 pagesHow To Retrieve Entire SQLpaulfer0376No ratings yet
- Adapters DB 307 ExpertPollingDocument8 pagesAdapters DB 307 ExpertPollingRKNo ratings yet
- DBMS CSE Digital Notes 2020-2021 - March 9th 2021Document155 pagesDBMS CSE Digital Notes 2020-2021 - March 9th 2021swetha sastryNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological Universityyicef37689No ratings yet
- Joins and Sub QueriesDocument10 pagesJoins and Sub Queriesganesh_g_1No ratings yet
- Android DatabaseDocument22 pagesAndroid DatabaseshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- Gathers Schema StatsDocument30 pagesGathers Schema StatsSiddharth ChopraNo ratings yet
- Nov Dec 2018 PDFDocument4 pagesNov Dec 2018 PDFAbhijeet Dhanraj SalveNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 CS PRACTICAL MysqlDocument10 pagesCLASS 12 CS PRACTICAL Mysqlrohitvk92No ratings yet
- Example Health Check ReportDocument22 pagesExample Health Check ReportTechypyNo ratings yet
- Aginity Netezza Workbench DocumentationDocument8 pagesAginity Netezza Workbench Documentationvanptl9361No ratings yet
- Advanced SQL Injection Victor Chapela Sm4rt Security Services Victor@Document93 pagesAdvanced SQL Injection Victor Chapela Sm4rt Security Services Victor@Anonim MinonaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: Submitted by Submitted To Class Semester Roll NoDocument15 pagesAssignment # 1: Submitted by Submitted To Class Semester Roll NoNABEEL BHATTINo ratings yet
- Mini-Project 231-CIS - LAB SET-BDocument3 pagesMini-Project 231-CIS - LAB SET-BHakim Al-HuribiNo ratings yet