Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Altitudes
Uploaded by
Greg ChalikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Altitudes
Uploaded by
Greg ChalikCopyright:
Available Formats
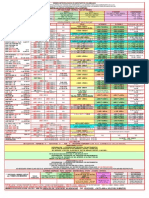
effective AA altitude 8 50 feet 100ft 147ft 250ft 328ft 500ft 699ft 899 ft 1200ft 1499ft sea-level ground level
NOE1 ground level NOE2 ground level NOE3 ground level NOE4 ground level NOE5 ground level ground level ground level ground level very-low altitude very-low altitude very-low altitude very-low altitude 5,500ft very-low altitude 2,200 m low altitude low altitude 10,000ft low altitude medium altitude medium altitude medium altitude medium-high altitude 7,160 m medium-high altitude high altitude Troposphere high altitude high altitude very-high altitude very-high altitude very-high altitude extreme altitude extreme altitude
6 12.7mm
5 20mm
3 40mm 2 88mm 90mm 1
Pressure altitude divided by 100 feet is referred to as the flight level (FL) 15 m 30m 45m 76m 100m 152m 213 m for open sea 274 m for open terrain 366 m for suburbs or low hills 457 m for large cities FL 0600 m (2,000 ft) large hills FL 0900 m (3,000 ft) low mountains FL 1200 m (3,900 ft) FL 1500 m (4,900 ft) FL 1800 m (5,900 ft) FL 2100 m (6,900 ft) mountain ranges FL 2500 m (8,200 ft) FL 3000 m (9,800 ft) FL 3300 m (10,800 ft) high mountains FL 4800 m (15,700 ft) FL 5100 m (16,700 ft) FL 5400 m (17,700 ft) FL 7200 m (23,600 ft) FL 7500 m (24,600 ft) FL 9000 m (29,500 ft) FL 9600 m (31,500 ft) FL 10200 m (33,500 ft) 36,090 ft FL 12000 m (39,400 ft) FL 12800m (42,000ft) 15,850m 18,288m (32,000km) 104,986ft 50km (31 miles) 80 kilometres (262,464ft) 80 kilometres 100 kilometres 200 kilometres 300 kilometres 400 kilometres 500 kilometres 600 kilometres
Stratosphere Mesosphere
Thermosphere 700 kilometres 800 kilometres 900 kilometres 1000 kilometres 2000 kilometres 3000 kilometres 4000 kilometres 5000 kilometres 6000 kilometres 7000 kilometres 8000 kilometres 9000 kilometres Exosphere 20000 kilometres 30000 kilometres 40000 kilometres 50000 kilometres
upper boundary of the exosphere
60000 kilometres 70000 kilometres 80000 kilometres 90000 kilometres 100000 kilometres 110000 kilometres 120000 kilometres 130000 kilometres 140000 kilometres 150000 kilometres 160000 kilometres 170000 kilometres 180000 kilometres 193,121.28 kilometer
de divided by 100 feet is referred to as the flight level (FL) at understory canopy layer or 'sea level' the standard gives a pressure of 1.013 bar and a temperature of 15C, and an initial lapse rate of -6.5 C/km to 12km Residential buildings, utility pole, telephone pole, power pole tree canopy level Tall buildings, concrete pylons with heights of up to 75 metres emergent tree layer canopy and lattice steel electricity pylon Over Populated Areas : an altitude of 500 feet AGL; 1940s transmission towers wind gradient turbulence height; modern transmission towers wind gradient turbulence height; Lowest safe altitude; wind gradient turbulence in the wind flow just a few hundred meters above the the earth's surfacethe surfac wind gradient turbulence height wind gradient turbulence height Oxford English Dictionary suggests a limit of 2000 ft (610 m) Transition altitude in Europe; highest altitude at which an aircraft in normal operation should use an altimeter pressure setting indicating height above mean sea lev Transition altitude in Europe Transition altitude in Europe Transition altitude in Europe atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)
Instrument flight rules are for low-altitude navigation and tactical training below 3050 m (10000 ft) and at airspeeds in excess of 460 km/h (250 knots) at night and i Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) refers to an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) that flies at an altitude window of 10,000 ft to 30,000 ft Atmospheric pressure decreases with height, dropping by 50% at an altitude of about 5.6 km (18,000 ft). Himalayas average 5 km above sea level 15,000 to 18,000 feet troposphere 7 km (23,000 ft) at the poles troposphere HALO/HAHO insertions, the troops are dispatched from altitudes between 25,000(circa 7500m) - 35,000ft(circa 10500m). surface to 8000 m / 5 miles at poles 18,000 m / 11 miles at equator, ending at the Tropopause. troposphere 30,000 feet; Everest, 8,848 m (29,029 feet) The common cruising altitude of commercial airliners is about 10 km in troposphere. stratosphere between about 10 km (6 miles) and 50 km (31 miles) International Standard Atmosphere
Most commercial jetliners have a ceiling of about 42,000 feet (12,802 meters) stratosphere; Above 12km the tabulated temperature is essentially constant some business jets can reach a ceiling of about 52,000 feet or higher (15,850 meters.); stratosphere 90% of the atmosphere by mass is below an altitude of 16 km 60,000 ft U.S. Standard Atmosphere is a series of models that define values for atmospheric temperature, density, pressure and other properties over a wide range of altitud Tropopause to 50 km /31 miles International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) published their "ICAO Standard Atmosphere" Stratopause to 85 km /53 miles
Mesopause to 675 km / 420 miles
Thermopause to 10,000 km /6200 miles
can be defined theoretically by the altitude (about 120,000 miles, half the distance to the Moon) at which the influence of solar radiation pressure on atomic hydrog
nitial lapse rate of -6.5 C/km to 12km
rs above the the earth's surfacethe surface layer of the planetary boundary layer
setting indicating height above mean sea level (QNH). Above the transition altitude (TA) the aircraft altimeter pressure setting should be adjusted to the standard pressure setting of 1013.2 he
xcess of 460 km/h (250 knots) at night and in foul weather.
emperature is essentially constant phere by mass is below an altitude of 16 km
other properties over a wide range of altitudes to 32km.
of solar radiation pressure on atomic hydrogen velocities exceeds that of the Earths gravitational pull.
ould be adjusted to the standard pressure setting of 1013.2 hectopascals(Milibars) or 29.92 inches of mercury and aircraft altitude will be specified as a flight level
de will be specified as a flight level
Northern hemisphere Tree Maximum Height Grasses >1m Plants >2m Bushes >3 m Saplings >5 m forest floor layer Rose-of-sharon 5 m Poison sumac 6m Pawpaw 6m Chokecherry 6m Magnolia 9m Red maple 12 m Jack pine 12 m understory canopy layer Dogwood 12 m Weeping willow 15 m Quaking aspen 15 m Sugar maple 18 m Pitch pine 18 m Live oak 18 m Catalpa 18 m White birch 24 m Red oak 24 m Douglas r 24 m Cottonwood 24 m Tupelo 30 m canopy Loblolly pine 30 m American elm 30 m White pine 34 m Bald cypress 37 m Sycamore 40 m 45 m Eucalyptus 60 m emergent layer canopy Giant redwood 100 m
effective AA altitude 50 feet sea-level ground level ground level ground level ground level ground level ground level ground level very-low altitude very-low altitude 12.7mm 5,500ft very-low altitude very-low altitude very-low altitude low altitude low altitude 10,000ft low altitude medium altitude medium altitude medium altitude 15 m 30m 76m 100m 500ft 152m 213 m for open sea 274 m for open terrain 366 m for suburbs or low hills 457 m for large cities FL 0600 m (2,000 ft) large hills FL 0900 m (3,000 ft) low mountains FL 1200 m (3,900 ft) FL 1500 m (4,900 ft) FL 1800 m (5,900 ft) FL 2100 m (6,900 ft) mountain ranges FL 2500 m (8,200 ft) FL 3000 m (9,800 ft) FL 3300 m (10,800 ft) high mountains FL 4800 m (15,700 ft) FL 5100 m (16,700 ft) FL 5400 m (17,700 ft) FL 7200 m (23,600 ft) FL 7500 m (24,600 ft) FL 9000 m (29,500 ft) FL 9600 m (31,500 ft) FL 10200 m (33,500 ft) FL 12000 m (39,400 ft) FL 12800m (42,000ft) 15 240m (50,000ft) extreme altitude 15,850m 18,288m (32,000km) 104,986ft 50km (31 miles) 80 kilometres (262,464ft)
100ft 250ft
699ft 899 ft 1200ft 1499ft
5 20mm
2,200 m
3
40mm 7,160 m
medium-high altitude medium-high altitude high altitude 88mm 90mm high altitude high altitude very-high altitude very-high altitude extreme altitude
at sea level the standard gives a pressure of 1.013 bar and a temperature of 15C, and an initial lapse rate of -6.5 C/km to 12km Residential buildings, utility pole, telephone pole, power pole Tall buildings, concrete pylons with heights of up to 75 metres lattice steel electricity pylon Over Populated Areas : an altitude of 500 feet AGL; 1940s transmission towers wind gradient turbulence height; modern transmission towers wind gradient turbulence height; Lowest safe altitude; wind gradient turbulence in the wind flow just a few hundred meters above the the earth's surfacethe wind gradient turbulence height wind gradient turbulence height Oxford English Dictionary suggests a limit of 2000 ft (610 m) Transition altitude in Europe Transition altitude in Europe Transition altitude in Europe atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)
Transition altitude in Europe; highest altitude at which an aircraft in normal operation should use an altimeter pressure setting indicating height above mean s
Instrument flight rules are for low-altitude navigation and tactical training below 3050 m (10000 ft) and at airspeeds in excess of 460 km/h (250 knots) at night Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) refers to an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) that flies at an altitude window of 10,000 ft to 30,000 ft Atmospheric pressure decreases with height, dropping by 50% at an altitude of about 5.6 km (18,000 ft). Himalayas average 5 km above sea level 15,000 to 18,000 feet troposphere 7 km (23,000 ft) at the poles troposphere HALO/HAHO insertions, the troops are dispatched from altitudes between 25,000(circa 7500m) - 35,000ft(circa 10500m). troposphere 30,000 feet; Everest, 8,848 m (29,029 feet) The common cruising altitude of commercial airliners is about 10 km in troposphere. stratosphere between about 10 km (6 miles) and 50 km (31 miles) Most commercial jetliners have a ceiling of about 42,000 feet (12,802 meters) stratosphere; Above 12km the tabulated temperature is essentially constant B-52 60,000 ft U.S. Standard Atmosphere is a series of models that define values for atmospheric temperature, density, pressure and other properties over a wide range of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) published their "ICAO Standard Atmosphere"
some business jets can reach a ceiling of about 52,000 feet or higher (15,850 meters.); stratosphere 90% of the atmosphere by mass is below an altitude of 1
ve the the earth's surfacethe surface layer of the planetary boundary layer
indicating height above mean sea level (QNH). Above the transition altitude (TA) the aircraft altimeter pressure setting should be adjusted to the standard pressure setting of
of 460 km/h (250 knots) at night and in foul weather.
00 ft to 30,000 ft
ature is essentially constant
by mass is below an altitude of 16 km
properties over a wide range of altitudes to 32km.
adjusted to the standard pressure setting of 1013.2 hectopascals(Milibars) or 29.92 inches of mercury and aircraft altitude will be specified as a flight level
e specified as a flight level
You might also like
- Rangkuman Catatan CopiedDocument6 pagesRangkuman Catatan CopiedFAHMI PRAYOGINo ratings yet
- PressureDocument35 pagesPressureHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- N Above A AircraftDocument81 pagesN Above A Aircraftpeter stanoNo ratings yet
- Baisc ParametersDocument1 pageBaisc Parametersyogi_swarnNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Air Data Instruments GuideDocument32 pagesAircraft Air Data Instruments GuideJehan IchhaporiaNo ratings yet
- Familia Avante - InglésDocument4 pagesFamilia Avante - Inglésmatteo_1234No ratings yet
- ADC How To Determine Transition LevelDocument5 pagesADC How To Determine Transition LeveljuniorNo ratings yet
- VFR MinimaDocument2 pagesVFR MinimarenatopuenteNo ratings yet
- Hitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebDocument8 pagesHitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebridofambudiNo ratings yet
- Caracteristici AeronaveDocument176 pagesCaracteristici AeronaveAnonymous 4rEDPV5No ratings yet
- AdpDocument37 pagesAdpGagan chahalNo ratings yet
- 3 Student - VFR - MinimaDocument1 page3 Student - VFR - MinimaMonish JohnsonNo ratings yet
- A319-100 / A319LR / A319CJ A320-200 A321-200: Seating CapacityDocument12 pagesA319-100 / A319LR / A319CJ A320-200 A321-200: Seating CapacityLizzy OdutolaNo ratings yet
- Abs 320 PohDocument3 pagesAbs 320 Pohjamnavy28No ratings yet
- Meteorology AtplDocument17 pagesMeteorology AtplJavier Moreno Rodríguez100% (3)
- Air law essentials for pilotsDocument37 pagesAir law essentials for pilotsmanjitha100% (1)
- Altitude - WikipediaDocument37 pagesAltitude - WikipediaSikendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Engr. Ghulam Hussain: Lecturer Civil Engineering Department The University of LahoreDocument52 pagesEngr. Ghulam Hussain: Lecturer Civil Engineering Department The University of Lahoremeghathomas77No ratings yet
- 146 Technical Data at A Glance 2Document4 pages146 Technical Data at A Glance 2Roger Burton100% (1)
- Hitachi-ZX210LC-5-Spec EN WebDocument11 pagesHitachi-ZX210LC-5-Spec EN WebHery Sanukri MunteNo ratings yet
- Cheyenne Iv Spec - PerfDocument2 pagesCheyenne Iv Spec - PerfPablo Sebastian Di GregorioNo ratings yet
- MEC 3766 Instrumentation and AvionicsDocument45 pagesMEC 3766 Instrumentation and AvionicsNur AdlinaNo ratings yet
- A) An Increase of Temperature With HeightDocument963 pagesA) An Increase of Temperature With HeightDhruv VijayNo ratings yet
- Runway With No Instrument Approach (Visual Runways) Runway With A Nonprecision Instrument Approach Runway With A Precision Instrument ApproachDocument53 pagesRunway With No Instrument Approach (Visual Runways) Runway With A Nonprecision Instrument Approach Runway With A Precision Instrument ApproachJuan ParraNo ratings yet
- 95 - 737-General-InformationDocument3 pages95 - 737-General-InformationffontanaNo ratings yet
- NelsonLayers of Atmosphere Drawing Instructions-1Document3 pagesNelsonLayers of Atmosphere Drawing Instructions-1Lily DanielsonNo ratings yet
- 1 2 4 AtmosphereDocument14 pages1 2 4 Atmosphereapi-235337654No ratings yet
- ThermExcel - Aeroduct USDocument12 pagesThermExcel - Aeroduct USTuankhanh DangNo ratings yet
- WSMR Environmental Impact StatementDocument1 pageWSMR Environmental Impact Statementpavlosmakridakis2525No ratings yet
- PP ADC Visual Flight RulesDocument3 pagesPP ADC Visual Flight RulesJuan Pablo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Reduced Vertical Separation Minima or Minimum (RVSM) Is The Reduction of The StandardDocument1 pageReduced Vertical Separation Minima or Minimum (RVSM) Is The Reduction of The StandardCerose SakilNo ratings yet
- ATPL Fragen 1Document18 pagesATPL Fragen 1martinNo ratings yet
- EP0503 - 1. What Is The Airline Industry AboutDocument59 pagesEP0503 - 1. What Is The Airline Industry AboutJackLiewNo ratings yet
- Pipeline profile and reservoir water levelsDocument7 pagesPipeline profile and reservoir water levelsPhyu Mar Thein KyawNo ratings yet
- EASA Flight RulesDocument5 pagesEASA Flight Rulesjoethompson007No ratings yet
- Question Bank Meteorology For ATPLDocument102 pagesQuestion Bank Meteorology For ATPLGaurav Sawaai100% (4)
- Atr72 Limitation Level 1,2,3Document3 pagesAtr72 Limitation Level 1,2,3Nguyen Xuan HungNo ratings yet
- Engine 160G LCDocument8 pagesEngine 160G LCapi-282795606No ratings yet
- Aircraft Type Model Price (US$) Fuselage Length (M/FT) Aircraft Height (M/FT) Wingspan (M/FT)Document13 pagesAircraft Type Model Price (US$) Fuselage Length (M/FT) Aircraft Height (M/FT) Wingspan (M/FT)BC JasonNo ratings yet
- ATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyDocument70 pagesATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyNuno Arnaud100% (1)
- QDB 15 MeteorologyDocument233 pagesQDB 15 MeteorologyKueh Chew Chai96% (25)
- 4 - NavigationDocument11 pages4 - NavigationShruti Prakasen100% (1)
- A400m - 3 MSFSDocument23 pagesA400m - 3 MSFSNiklas ObermayerNo ratings yet
- LGT3027 Lecture 4 - Aviation Meteorology PDFDocument55 pagesLGT3027 Lecture 4 - Aviation Meteorology PDFhappyguysNo ratings yet
- Cheyenne I Spec - PerfDocument2 pagesCheyenne I Spec - PerfCanal Ferreira 7700No ratings yet
- 10T Tadano Load ChartsDocument12 pages10T Tadano Load ChartsBqdcc6100% (2)
- New PPL Bifa ProflightDocument512 pagesNew PPL Bifa ProflightThomas AmisimNo ratings yet
- Engine 130GDocument6 pagesEngine 130Gapi-282795606No ratings yet
- ALBATROSS MALE UAV 25h Flight Long Endurance SurveillanceDocument2 pagesALBATROSS MALE UAV 25h Flight Long Endurance SurveillancePresa Kautsar100% (1)
- Technical Interview WIZZ - PREPDocument51 pagesTechnical Interview WIZZ - PREPRicardoNo ratings yet
- QNH CalculationDocument12 pagesQNH CalculationMask550% (2)
- Airworthiness: Involving The Aircraft's Design (Limitations, Performance DataDocument20 pagesAirworthiness: Involving The Aircraft's Design (Limitations, Performance DataThar LattNo ratings yet
- Project 100 Seated AircraftDocument14 pagesProject 100 Seated AircraftBalasastha PNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Konu Konu Ayrılmış SorularDocument278 pagesMeteorology Konu Konu Ayrılmış Sorularjames100% (1)
- Aircraft Performance - Atmosphere 2010Document4 pagesAircraft Performance - Atmosphere 2010Bali KhanNo ratings yet
- Conociminetos 5 Nociones de MeteorologiaDocument85 pagesConociminetos 5 Nociones de MeteorologiaBrunna Lopes de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Navigation Questions: A) 1950 Ft/minDocument8 pagesNavigation Questions: A) 1950 Ft/minScipioNo ratings yet
- Y-Z Y Z Y - Z Z Baq Rnav Gnss ILS: Elevacion / Sei / FrecDocument1 pageY-Z Y Z Y - Z Z Baq Rnav Gnss ILS: Elevacion / Sei / Frecavera7777No ratings yet
- Lev 430 Wtiv DataDocument6 pagesLev 430 Wtiv Datawarrimaint28094No ratings yet
- The Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsFrom EverandThe Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub - Null A Pulp Cthulhu SourcebookDocument34 pagesDokumen - Pub - Null A Pulp Cthulhu SourcebookDan TiceNo ratings yet
- GUJCET Physics and Chemistry Question Paper 1Document31 pagesGUJCET Physics and Chemistry Question Paper 1Piyush GoreNo ratings yet
- 200,000 Year Old Statue Found On Moon - ThecritDocument8 pages200,000 Year Old Statue Found On Moon - ThecritTanya Michaela KneidingerNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 122563Document5 pagesScience Reviewer 122563Gilbert Cantil100% (5)
- The PILOT - September 2023Document16 pagesThe PILOT - September 2023RSCA Redwood ShoresNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Oceanography 9th Edition Trujillo Test BankDocument7 pagesEssentials of Oceanography 9th Edition Trujillo Test Bankchristophermorgangajfdxqimp100% (16)
- Spectroscopy of Astrophysical Plasmas PDFDocument369 pagesSpectroscopy of Astrophysical Plasmas PDFarpit shrivastav100% (1)
- Simple Nakshatra Shuddhi technique for birth time verification from Uttar KalamritDocument2 pagesSimple Nakshatra Shuddhi technique for birth time verification from Uttar Kalamritcatchdgreen0% (1)
- The Northern Atlantis From Gunter BischoffDocument33 pagesThe Northern Atlantis From Gunter Bischoffneuweil1100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in ITS (Constellations)Document10 pagesLesson Plan in ITS (Constellations)Angeline MarisgaNo ratings yet
- 19 Worksheet (A2)Document2 pages19 Worksheet (A2)junfeixieNo ratings yet
- Brainpop Periodic Table WsDocument1 pageBrainpop Periodic Table WsJen A. MacauleyNo ratings yet
- HoraGanaka CalculationsDocument303 pagesHoraGanaka CalculationsZendu BalmNo ratings yet
- We Choose To Go To The MoonDocument23 pagesWe Choose To Go To The MoonDerekNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Global WarmingDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Global Warmingdeep932100% (5)
- Math Workshop For Kids by SlidesgoDocument43 pagesMath Workshop For Kids by SlidesgoLawrence MarayaNo ratings yet
- Physic Xi 2011Document230 pagesPhysic Xi 2011Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Planet Earth, Explained: Our Dance Around The SunDocument5 pagesPlanet Earth, Explained: Our Dance Around The SunAristeo EbioNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Universe - On Nasadiya SuktamDocument5 pagesOrigin of The Universe - On Nasadiya SuktamRaghava AkshintalaNo ratings yet
- Sign, Star and Sub Table - KP AstrologyDocument17 pagesSign, Star and Sub Table - KP AstrologyAmiit Luthra100% (2)
- Thrissphuta and KalachakraDocument4 pagesThrissphuta and Kalachakrats8166No ratings yet
- Nexus Nov Dec 2013 Black Hole at Heart of Atom ENGLISH PDFDocument14 pagesNexus Nov Dec 2013 Black Hole at Heart of Atom ENGLISH PDFSatwik DasNo ratings yet
- Comet andDocument31 pagesComet andAlexandre MedinaNo ratings yet
- Annalen Der Physik Volume 18 Issue 1 2009. A. Unzicker. A Look at The Abandoned Contributions To Cosmology of Dirac, Sciama, and Dicke PDFDocument14 pagesAnnalen Der Physik Volume 18 Issue 1 2009. A. Unzicker. A Look at The Abandoned Contributions To Cosmology of Dirac, Sciama, and Dicke PDFAlf SegNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument2 pagesCombustionAmer ShahNo ratings yet
- Medical Astrology Autism Ivf Narcolepsy - CompressDocument8 pagesMedical Astrology Autism Ivf Narcolepsy - CompressFawad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Apollo 13Document23 pagesApollo 13o.ONo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Fe Isotope Geochemistry: 4.1 Iron Isotope Variations in The Solar SystemDocument63 pagesHigh-Temperature Fe Isotope Geochemistry: 4.1 Iron Isotope Variations in The Solar Systemgigio marinoNo ratings yet
- Philosophia HermeticaDocument146 pagesPhilosophia HermeticaThrice_Greatest83% (6)
- Docslide - Us - The Spin Force A Collection of Articles Experiments 2nd Edition PDFDocument187 pagesDocslide - Us - The Spin Force A Collection of Articles Experiments 2nd Edition PDFAhmad Al-Kady100% (2)