Professional Documents
Culture Documents
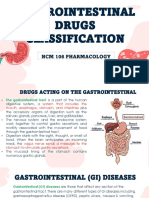
Drugs
Uploaded by
Marnelie Guerrero AbuanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drugs
Uploaded by
Marnelie Guerrero AbuanCopyright:
Available Formats
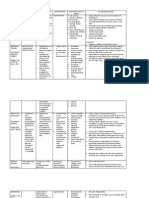
METOCLOPRAMIDE:
MOA: Stimulates motility of upper GI tract without stimulating gastric, billiary, or pancreatic secretions; appears to sensitize tissues to action of acetylcholine; relaxes pyloric sphincter, which, when combined with effects on motility, accelerates gastric emptying and intestinal transit; little effect on gallbladder or colon motility; increases lower esophageal sphincter pressure; has sedative properties; induces release of prolactin INDICATION: Relief of symptoms of acute and recurrent diabetic gastroparesis Short-term therapy for adults with symptomatic GERD who fail to respond to conventional therapy- Prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with emetogenic cancer chemotherapy- Prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting when nasogastric suction is undesirable- Facilitation of small-bowel intubation whentube does not pass the pylorus with conventional maneuvers- Stimulation of gastric emptying and intestinal transit of barium when delayed emptying interferes with radiologic examination of the stomach or small intestine- Unlabeled uses :Improvement of lactation; treatment of nausea and vomiting of a variety of etiologies :hyperemesis gravidarum, gastric ulcer, anorexia nervosa CONTRAINDICATION; - Allergy to metoclopramide- GI hemorrhage- Mechanical obstruction or perforation- Pheochromocytoma- Epilepsy Precaution - Previously detected breastcancer - Lactation- Pregnancy- Fluid overloadRenal impairment NSG CONSIDERATION Before Observe 15 rights in drugadministration.- Assess for allergy to metoclopramide.- Assess for other contraindications.- Keep diphenhydramine injection readilyavailable in case extrapyramidalreactions occur (50 mg IM).- Have phentolamine readily available incase of hypertensive crisis. During - Monitor BP carefully dring IVadministration.- Monitor for extrapyramidal reactions,and consult physician if they occur.- Monitor diabetic patients.Give direct IV doses slowly over 1-2minutes.- For IV infusion, give over at least 15minutes.
LEVOFLOXACIN
Drug classes: Antibiotic, Fluoroquinolone Therapeutic actions Bactericidal: interferes with DNA by inhibiting DNA synase replication in susceptible gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, preventing cell reproduction. Indications Treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia, acute maxillary sinusitis caused by susceptible bacteria Treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis caused by susceptible bacteria Treatment of complicated and uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible bacteria Treatment of complicated and uncomplicated UTIs and acute pyelonephritis caused by susceptible bacteria Treatment of nosocomial pneumonia due to methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas strains, Serratia, E. coli, Klebsiella, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae Adverse effects Headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, somnolence, blurred vision Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, diarrhea, abdominal pain (occur less with this drug than with oflaxacin), constipation, flatulence Elevated BUN, AST, ALT, serum creatinine, and alkaline phosphatase; neutropenia, anemia Fever, rash, photosensitivity, muscle and joint tenderness Nursing considerations Arrange for culture and sensitivity tests before beginning therapy. Continue therapy as indicated for condition being treated. Administer oral drug 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals with a glass of water; separate oral drug from other cation administration, including antacids, by at least 2 hr. Ensure that patient is well hydrated during course of therapy. Discontinue drug at any sign of hypersensitivity (rash, photophobia) or at complaint of tendon pain, inflammation, or rupture. Monitor clinical response; if no improvement is seen or a relapse occurs, repeat culture and sensitivity test.
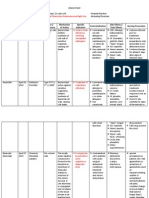
OXYCOTIN
The precise mechanism of the analgesic action is unknown. However, specific CNS opioid receptors for endogenous compounds with opioid-like activity have been identified throughout the brain and spinal cord and are thought to play a role in the analgesic effects of this drug. Indication OxyContin is indicated for the management of moderate to severe pain when a continuous, around-the-clock opioid analgesic is needed for an extended period of time. S/E
Seizures
SAGOBION
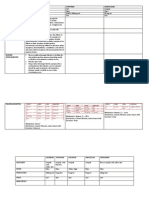
Sangobion is organic iron Sangobion is ferrous gluconate and not ferrous sulfate. This organic iron formulation allows for better absorption* inside the body and has less gastrointestinal side effects than ferrous sulfate. *Haler, David (1952). The Therapeutic Response of Secondary Anemias to Organic and Inorganic Iron Salts. British Medial Journal, United Kingdom.
Respiratory depression [see BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, and OVERDOSAGE] CNS depression [see DRUG INTERACTIONS, and OVERDOSAGE] Hypotensive effects [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, and OVERDOSAGE] Drug abuse, addiction, and dependence [see Drug Abuse and Dependence] Gastrointestinal Effects [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Sangobion has Vitamins and Minerals Sangobion is packed with Vitamin C, Folic acid, Vitamin B12, Copper sulfate, and Manganese sulfate. Sangobion contains SORBITOL A common side effect of most iron supplements is constipation. Sangobions Sorbitol component acts as an anti-constipating agent. Sorbitol is naturally found in edible fruits and vegetables
You might also like
- Ofloxacin Drug Class and Mechanism of ActionDocument5 pagesOfloxacin Drug Class and Mechanism of ActionSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyMelissa DavidNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Motility Disorders of The GITDocument57 pagesMotility Disorders of The GITMahmoud AjinehNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases - 2Document63 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases - 2Varunavi SivakanesanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyLj PingoyNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDocument7 pagesNeuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyJomabee TuArNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Peptic UlcersDocument9 pagesDrugs for Peptic UlcersSaud AlamNo ratings yet
- Git Diseases OralrevDocument30 pagesGit Diseases OralrevRafi AcostaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin treats infectionsDocument4 pagesCiprofloxacin treats infectionsbibet_martijaNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY AmpicillinsodiumDocument3 pagesDRUGSTUDY AmpicillinsodiumMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- OFLOXACINDocument3 pagesOFLOXACINfayrouz fathiNo ratings yet
- Silver Sulfadiazine Cream Prevents Burn InfectionsDrug NameDosageTherapeuticActionIndicationContraindicationAdverse EffectNursing ConsiderationDocument11 pagesSilver Sulfadiazine Cream Prevents Burn InfectionsDrug NameDosageTherapeuticActionIndicationContraindicationAdverse EffectNursing ConsiderationKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- LIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDocument5 pagesLIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib uses, dosage, side effectsDocument4 pagesCelecoxib uses, dosage, side effectsAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument51 pagesGerdHoney LaxNo ratings yet
- PANCREATITISDocument45 pagesPANCREATITISMaisonNo ratings yet
- Drugs Fall 2014: Pharm ListDocument31 pagesDrugs Fall 2014: Pharm Listashleynorris1403No ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument5 pagesPharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal SystemShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- GI Drugs Classification GuideDocument29 pagesGI Drugs Classification GuideJeneyse Ajap BalcenaNo ratings yet
- Doms DrugsDocument5 pagesDoms DrugsMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin medication guideDocument15 pagesGabapentin medication guideTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Nursing Care Guide: Uses, Side Effects & ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesOxytocin Nursing Care Guide: Uses, Side Effects & ResponsibilitiesCieLouie Cauilan-DomingoNo ratings yet
- Analgesics ContentDocument11 pagesAnalgesics ContentELISION OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Drugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Esophagus & GasterDocument83 pagesKelainan Esophagus & GasterajikwaNo ratings yet
- Relieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureDocument6 pagesRelieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureBij Hilario100% (1)
- Note for Pregnancy and AnxietyDocument1 pageNote for Pregnancy and Anxietyasmatmasoom5566No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMarielle Denise Tagtag BugtongNo ratings yet
- LEVOFLOXACIN MonographDocument3 pagesLEVOFLOXACIN Monographfayrouz fathiNo ratings yet
- Antidiarrhoeal DrugsDocument15 pagesAntidiarrhoeal DrugsJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument36 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseAlexNo ratings yet
- Case Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisDocument34 pagesCase Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisVivian Montesena BreganzaNo ratings yet
- Nausea & VomittingDocument55 pagesNausea & VomittingAsti Gusni DharmawatiNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkier khierNo ratings yet
- DS OfloxacinDocument2 pagesDS OfloxacinjessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Garopride ManualDocument16 pagesGaropride Manualsherif_awadNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument42 pagesAntifungal AgentsOluwatobi AyomideNo ratings yet
- Piroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsDocument3 pagesPiroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsBheiatriz de VeraNo ratings yet
- Betnesol InjectionDocument7 pagesBetnesol Injectionhiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeDocument5 pagesTreatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- Cefradime, Paracetamol, KetorolacDocument10 pagesCefradime, Paracetamol, KetorolacMae_Sheryn_Lip_1795No ratings yet
- Penicillin-resistant Staphylococcal Infections TreatmentDocument2 pagesPenicillin-resistant Staphylococcal Infections TreatmentRoanne LaguaNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCebu Normal University: Drug StudyGwen Marie Taboada100% (1)
- Lec9 د ذو الفقارDocument4 pagesLec9 د ذو الفقارMohammed JaberNo ratings yet
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandLaryngopharyngeal Reflux, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Ethnic Dances: Pandanggo, Sayaw, CariñosaDocument1 pageEthnic Dances: Pandanggo, Sayaw, CariñosaMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Flags SsDocument1 pageFlags SsMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ERDocument4 pagesDrug Study ERMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- What Is GriefDocument4 pagesWhat Is GriefMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Table FsDocument2 pagesTable FsMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- OrgDocument37 pagesOrgMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Ballet Dance (1) DnceDocument2 pagesBallet Dance (1) DnceMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University School of Nursing Baguio City BSN Iv-L1Document2 pagesSaint Louis University School of Nursing Baguio City BSN Iv-L1Marnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- IntoDocument1 pageIntoMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Pro LifeDocument2 pagesPro LifeMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument6 pagesNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityRowell Zaragoza91% (11)
- Ri SeDocument1 pageRi SeMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- CgordsDocument3 pagesCgordsMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- CgordsDocument3 pagesCgordsMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- IBD (ER Journal)Document11 pagesIBD (ER Journal)Marnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- OrgDocument37 pagesOrgMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- BusDocument1 pageBusMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareDocument6 pagesNursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Instuments (D&C, NSVD)Document5 pagesInstuments (D&C, NSVD)Marnelie Guerrero Abuan67% (3)
- Instuments (D&C, NSVD)Document5 pagesInstuments (D&C, NSVD)Marnelie Guerrero Abuan67% (3)
- God Is AbleDocument2 pagesGod Is AbleMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocument1 pageOxytocin Drug Studysweetpixie1887% (15)
- Developmental ChartDocument4 pagesDevelopmental ChartMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Ri SeDocument1 pageRi SeMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Community JournalDocument6 pagesCommunity JournalMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- Get Oracle Order DetailsDocument4 pagesGet Oracle Order Detailssiva_lordNo ratings yet
- Evaluative Research DesignDocument17 pagesEvaluative Research DesignMary Grace BroquezaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of PIADocument16 pagesRatio Analysis of PIAMalik Saad Noman100% (5)
- Duca Industries March 2023 pay slip for Dipankar MondalDocument1 pageDuca Industries March 2023 pay slip for Dipankar MondalPritam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Alignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFDocument18 pagesAlignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFAshutosh MauryaNo ratings yet
- AD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash PointDocument4 pagesAD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash Pointyb3yonnayNo ratings yet
- 7 Aleksandar VladimirovDocument6 pages7 Aleksandar VladimirovDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Committee History 50yearsDocument156 pagesCommittee History 50yearsd_maassNo ratings yet
- A Database of Chromatographic Properties and Mass Spectra of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters From Omega-3 ProductsDocument9 pagesA Database of Chromatographic Properties and Mass Spectra of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters From Omega-3 ProductsmisaelNo ratings yet
- Google Earth Learning Activity Cuban Missile CrisisDocument2 pagesGoogle Earth Learning Activity Cuban Missile CrisisseankassNo ratings yet
- A Guide To in The: First AidDocument20 pagesA Guide To in The: First AidsanjeevchsNo ratings yet
- Bad DayDocument3 pagesBad DayLink YouNo ratings yet
- Basic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Document10 pagesBasic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Asif Hasan DhimanNo ratings yet
- AA ActivitiesDocument4 pagesAA ActivitiesSalim Amazir100% (1)
- Sinclair User 1 Apr 1982Document68 pagesSinclair User 1 Apr 1982JasonWhite99No ratings yet
- Lewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Document8 pagesLewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Om Prakash100% (1)
- CFO TagsDocument95 pagesCFO Tagssatyagodfather0% (1)
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument2 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledCesar ValeraNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesLecture NotesRawlinsonNo ratings yet
- Alternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesDocument96 pagesAlternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesPedro de CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxDocument52 pagesLaryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxjialeongNo ratings yet
- Kalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFDocument49 pagesKalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFjulio cesar calveteNo ratings yet
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocument164 pagesUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- THE DOSE, Issue 1 (Tokyo)Document142 pagesTHE DOSE, Issue 1 (Tokyo)Damage85% (20)
- Applied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesApplied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFteri.sanborn87695% (44)
- HSSC English Model PaperDocument32 pagesHSSC English Model PaperMaryam Abdus SalamNo ratings yet
- Beauty ProductDocument12 pagesBeauty ProductSrishti SoniNo ratings yet
- Efaverenz p1Document4 pagesEfaverenz p1Pragat KumarNo ratings yet
- Mounting InstructionDocument1 pageMounting InstructionAkshay GargNo ratings yet
- Astm D7928 - 17Document25 pagesAstm D7928 - 17shosha100% (2)