Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PM - Reading 42 PDF
Uploaded by
Vũ Lan PhươngOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PM - Reading 42 PDF
Uploaded by
Vũ Lan PhươngCopyright:
Available Formats
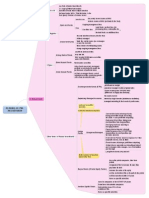
one form of pooled investments What is it? i.e.
single portfolio that contains investment funds from multiple investors Net asset value NAV = Total Net value in the fund (pool) / Number of shares issued
Investors can
buy newly issued shares at NAV redeem shares at NAV (sell back to the fund) Load funds: up-front fees (for purchasing fees), redemption fee No-load funds: no additional fees
Open-end funds Fees 2 categories
Ongoing management fees One-time fees
No new investment money into the fund Actively managed Closed-end funds trade like equity shares (on exchanges or over-the counter) fixed number of outstanding shares charge ongoing management fees short-term debt securities Money Market Funds very low risk NAV usually DOWN when securities value DECREASED Bond Mutual Funds 3 types fixed-income securities Index funds passively managed: portfolio is constructed to match the performance of particular index Actively managed funds: select individual securities, producing greater return than benchmark index Higher management fess higher turnover of portfolio securities greater tax liabilities traded in market: traded as equity shares, sold short, purchased on margin passively managed: match a typical index Shares market price DIFFERS NAV (difference in Supply and Demand) No shares issued
Stock Mutual Funds
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
d. Mutual funds
Separately Managed Accounts
owned by single investor (individual or institution) managed according to their needs & preferences
READING 42. PM AN OVERVIEW
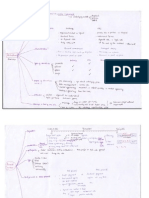
sold only to qualified investors minimum investment required Convertible bond arbitrage funds: buying convertible bonds and selling the stock -> earn profit from mispricing Dedicated Short Bias: taking more short positions than long positions Emerging markets: investing in emerging markets Hedge Funds Other forms of Pooled Investments Categories/Strategies Equity Market Neutral: eliminate market movement by OFFSETTING long positions by short positions (by the same amount) Event Driven Funds: invest in response to 1-time corporate events, such as M&A Fixed-Income Arbitrage: profit from mispricing Global Macro: speculate on international interest and exchanges rates changes, use of derivatives and leverage Long/Short funds: buy and sell limited number of investors invest in the fund buy entire public companies, take them private reorganised firm to increase its cash flow Buyout funds (Private Equity Funds) pay down its debt increase the value of its equity sell the restructured firm or its parts to the public exit this investment after 3-5 years focus on specific industries Invest in companies in their START-UP phase Grow them into valuable companies Venture Capital Funds Sold publicly via an IPO or to an established firm. focus on specific industries
You might also like
- NISMDocument167 pagesNISMprashant_agharkar9257No ratings yet
- Sta A4187876 21425Document2 pagesSta A4187876 21425doud98No ratings yet
- Investing Made Simple - Warren Buffet Strategies To Building Wealth And Creating Passive IncomeFrom EverandInvesting Made Simple - Warren Buffet Strategies To Building Wealth And Creating Passive IncomeNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC GAMING Technical Tutorial 1 - Drawing Game Statistics From Diversity Multigame StatisticsDocument4 pagesATOMIC GAMING Technical Tutorial 1 - Drawing Game Statistics From Diversity Multigame StatisticsmiltoncgNo ratings yet
- BAR Digest MenuDocument4 pagesBAR Digest MenuFloila Jane YmasNo ratings yet
- TEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 16 Motivating EmplDocument37 pagesTEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 16 Motivating Emplpolkadots939100% (1)
- Bernardo Corporation Statement of Financial Position As of Year 2019 AssetsDocument3 pagesBernardo Corporation Statement of Financial Position As of Year 2019 AssetsJean Marie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ebook The Managers Guide To Effective Feedback by ImpraiseDocument30 pagesEbook The Managers Guide To Effective Feedback by ImpraiseDebarkaChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Amfi Exam Nism V ADocument218 pagesAmfi Exam Nism V AUmang Jain67% (6)
- MUTUAL FUND GUIDEDocument16 pagesMUTUAL FUND GUIDEjineshshajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-23 - Mutual Fund OperationsDocument21 pagesChapter-23 - Mutual Fund OperationsZareen TasfiahNo ratings yet
- 4 MutualFundsDocument22 pages4 MutualFundsSimhadri AshokNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds and Other Investment CompaniesDocument47 pagesMutual Funds and Other Investment Companiesshao9213No ratings yet
- Mutual Fund Guide on Concepts, Types and StructuresDocument210 pagesMutual Fund Guide on Concepts, Types and StructuresarmailgmNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Investment CompaniesDocument16 pagesChapter - Investment CompaniesAminul Haque RusselNo ratings yet
- NISM MF Distributors Certification - Learn Key ConceptsDocument167 pagesNISM MF Distributors Certification - Learn Key ConceptsSachin Kumar100% (2)
- Investment Companies & Pension Funds Chapter SummaryDocument31 pagesInvestment Companies & Pension Funds Chapter SummarySantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Investment Companies: Jones, Investments: Analysis and ManagementDocument14 pagesInvestment Companies: Jones, Investments: Analysis and ManagementnensirsNo ratings yet
- Invest in Mutual Funds for Long Term Growth (40 charactersDocument20 pagesInvest in Mutual Funds for Long Term Growth (40 charactersAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund - PPT TSMDocument30 pagesMutual Fund - PPT TSMGopi NathNo ratings yet
- Activity 05252023Document4 pagesActivity 05252023Fire burnNo ratings yet
- Banking PresentationDocument56 pagesBanking PresentationRabia KhanNo ratings yet
- 050 Chapter 12Document20 pages050 Chapter 12Izwa BaizuraNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds ExplainedDocument3 pagesMutual Funds ExplainedafreenessaniNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument3 pagesDefinitionsMohammad MedlejNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document14 pagesCH 08Md.Rakib MiaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund: Presented byDocument34 pagesMutual Fund: Presented byAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Investment in Mutual Funds: "It's All About Money, Honey "Document20 pagesInvestment in Mutual Funds: "It's All About Money, Honey "vineethkmenon0% (1)
- Glossary Investment TermsDocument15 pagesGlossary Investment TermsBehroozRaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 19 NotesGloria HuNo ratings yet
- Investments Essentials Chapter 1-5 SummaryDocument12 pagesInvestments Essentials Chapter 1-5 Summaryagrawal3436No ratings yet
- Mutual fund basicsDocument10 pagesMutual fund basicsI love strawberry berry berry strawberryNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument5 pagesMutual Fundssabhirami34No ratings yet
- Mutual Fund Investment Guide: Risks, Returns & StrategiesDocument20 pagesMutual Fund Investment Guide: Risks, Returns & Strategiesatik0909No ratings yet
- Investment in Mutual FundsDocument20 pagesInvestment in Mutual FundsDhamotharan GurusamyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mutual Fund?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Mutual Fund?uzmanickNo ratings yet
- AMFI Mutual Fund (Advisor) Module: Preparatory Training ProgramDocument231 pagesAMFI Mutual Fund (Advisor) Module: Preparatory Training Programallmutualfund100% (5)
- Investment 1Document26 pagesInvestment 1anupan92No ratings yet
- Lect 2Document37 pagesLect 2mahamamir012No ratings yet
- Asset Classes: Understanding Securities and InvestmentsDocument26 pagesAsset Classes: Understanding Securities and InvestmentsAatish PanditNo ratings yet
- CH 03 Indirect InvestingDocument38 pagesCH 03 Indirect Investingmalikawais1100% (1)
- Quiz 4 Name: Ahmed Niaz Roll No.: 180762 Class: BSAF 5BDocument2 pagesQuiz 4 Name: Ahmed Niaz Roll No.: 180762 Class: BSAF 5BAhmed NiazNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument95 pagesProject ReportsaivasuNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument24 pagesMutual Fundstejas1989No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Investment FundsDocument45 pagesLecture 2 Investment Fundsnoobmaster 0206No ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument31 pagesMutual FundsSonia LawsonNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund InvestmentDocument24 pagesMutual Fund Investmentpooja22No ratings yet
- Lax MiDocument78 pagesLax MivsabhijitNo ratings yet
- What Are Mutual FundsDocument8 pagesWhat Are Mutual Fundsrushi4youNo ratings yet
- MUTUAL FUNDS Lecture - Indirect Investing & TypesDocument17 pagesMUTUAL FUNDS Lecture - Indirect Investing & TypesSami119No ratings yet
- Finance Concept (PGEXE)Document10 pagesFinance Concept (PGEXE)Abhiruchi DawraNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mutual Funds-By HDFC AMCDocument41 pagesBasics of Mutual Funds-By HDFC AMCRupanjali Mitra BasuNo ratings yet
- MF Module 1Document75 pagesMF Module 1Gouri K MakatiNo ratings yet
- 2 Mutual FundDocument10 pages2 Mutual FundNorjie AcolNo ratings yet
- Asset-Management Chapter 5Document5 pagesAsset-Management Chapter 5kaylee dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Investing in Mutual Funds and EtfsDocument16 pagesInvesting in Mutual Funds and EtfssumihosaNo ratings yet
- CHPT 03Document16 pagesCHPT 03raheelmalik32No ratings yet
- MFS, Etfs, HfsDocument25 pagesMFS, Etfs, HfsAriful Haidar MunnaNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: Group Members: Abdullah Saleem (15223) Khuzaima Faraz (17687)Document8 pagesMutual Funds: Group Members: Abdullah Saleem (15223) Khuzaima Faraz (17687)Abdullah SaleemNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Investment SettingDocument61 pagesUnit-1: Investment SettingKarthika NathanNo ratings yet
- BFF3121 Lecture 2Document10 pagesBFF3121 Lecture 2Jeremy LoboNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds and Other Investment CompaniesDocument5 pagesMutual Funds and Other Investment Companiespiepkuiken-knipper0jNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds: A Beginner'S ModuleDocument53 pagesMutual Funds: A Beginner'S ModuleNITIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Mastering the Markets: Advanced Trading Strategies for Success and Ethical Trading PracticesFrom EverandMastering the Markets: Advanced Trading Strategies for Success and Ethical Trading PracticesNo ratings yet
- Mastering the Market: A Comprehensive Guide to Successful Stock InvestingFrom EverandMastering the Market: A Comprehensive Guide to Successful Stock InvestingNo ratings yet
- Anh Khong Doi Qua - Karik FT OnlyCDocument2 pagesAnh Khong Doi Qua - Karik FT OnlyClinh2271991No ratings yet
- PM - Reading 42 PDFDocument1 pagePM - Reading 42 PDFVũ Lan PhươngNo ratings yet
- Major Return Measures and Portfolio Risk AnalysisDocument1 pageMajor Return Measures and Portfolio Risk AnalysisVũ Lan PhươngNo ratings yet
- Derivatives - SummaryDocument6 pagesDerivatives - SummaryVũ Lan PhươngNo ratings yet
- Someone Like YouDocument7 pagesSomeone Like YouVũ Lan PhươngNo ratings yet
- Lec - Ray Theory TransmissionDocument27 pagesLec - Ray Theory TransmissionmathewNo ratings yet
- Fabric Bursting StrengthDocument14 pagesFabric Bursting StrengthQaiseriqball100% (5)
- Aptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User ManualDocument42 pagesAptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User Manualdhirender karkiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Qus OnlyDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Qus OnlySaksharNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Complete Fittings CatalogDocument224 pagesAlfa Laval Complete Fittings CatalogGraciele SoaresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 HExDocument16 pagesTutorial 5 HExishita.brahmbhattNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1Document7 pagesDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1api-235617848No ratings yet
- Circular 09/2014 (ISM) : SubjectDocument7 pagesCircular 09/2014 (ISM) : SubjectDenise AhrendNo ratings yet
- Project The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDDocument7 pagesProject The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDmorraz360No ratings yet
- Learning HotMetal Pro 6 - 132Document332 pagesLearning HotMetal Pro 6 - 132Viên Tâm LangNo ratings yet
- CFEExam Prep CourseDocument28 pagesCFEExam Prep CourseM50% (4)
- QSK45 60 oil change intervalDocument35 pagesQSK45 60 oil change intervalHingga Setiawan Bin SuhadiNo ratings yet
- 9 QP - SSC - MOCK EXAMDocument5 pages9 QP - SSC - MOCK EXAMramNo ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic Foundations TheoryDocument15 pagesBeams On Elastic Foundations TheoryCharl de Reuck100% (1)
- As 1769-1975 Welded Stainless Steel Tubes For Plumbing ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAs 1769-1975 Welded Stainless Steel Tubes For Plumbing ApplicationsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteraciesDocument27 pages21st Century LiteraciesYuki SeishiroNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument14 pagesMarketing ManagementShaurya RathourNo ratings yet
- Elementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterDocument1 pageElementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterRonilo DagumampanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Real-Time Systems ARTIST Project IST-2001-34820 BMW 2004Document372 pagesAdvanced Real-Time Systems ARTIST Project IST-2001-34820 BMW 2004كورسات هندسيةNo ratings yet
- Notes On Lesson: Faculty Name Code Subject Name CodeDocument108 pagesNotes On Lesson: Faculty Name Code Subject Name CodeJeba ChristoNo ratings yet
- ANDRITZ Company Presentation eDocument6 pagesANDRITZ Company Presentation eAnonymous OuY6oAMggxNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rocks ImagesDocument7 pagesMetamorphic Rocks Imagesapi-289985616100% (1)
- SAP ORC Opportunities PDFDocument1 pageSAP ORC Opportunities PDFdevil_3565No ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugSaleha YounusNo ratings yet