Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)
Uploaded by
Yee Kai TanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)
Uploaded by
Yee Kai TanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:_______________________
Class: _______
Index no.: _______
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2 2011 Secondary Four Express/ Five Normal Academic SCIENCE CHEMISTRY- PAPER 3 23 August 2011 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Section A Answer all questions Write your answers in the spaces provided on the question paper. Section B Answer any two questions. Write your answers on the writing paper provided. At the end of the examination, fasten any separate answer paper used securely to the question paper. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The number of marks is given in bracket [ ] at the end of each question or part question. A copy of the Periodic Table is attached on page 14. Paper 1 Paper 3:Section A Paper 3:Section B Total Marks 5116/03 and 5118/03 1 hour 15 min
This question paper consists of 14 printed pages including the cover page Candidates Name: _______________________ Pg 1 of 14 Index No: ____________
Section A: 45 marks Answer ALL the questions in this section. A1 Choose from the following elements to answer the questions below. aluminum iodine bromine iron calcium chlorine hydrogen oxygen magnesium nitrogen [4]
Each element can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Name an element which : (a) (b) (c) (d) forms two different positive ions; forms an amphoteric oxide; is the most reactive metal in the list; forms a diatomic molecule with a triple bond; ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________
A2
Sodium is stored under oil because it rapidly oxidizes to form sodium oxide, Na2O.
(a)
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in sodium oxide, Na 2O. You only need to show outer shell electrons. [2]
Pg 2 of 14
Sodium oxide reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide. (b) Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. [1] _____________________________________________________________ (c) 62g of sodium oxide are used to make 2 dm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide. What is the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution in mol/dm 3? [2]
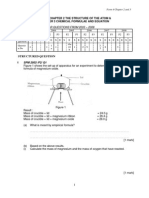
A3
Phosphorus is a non-metal. This diagram shows the structure of one molecule of phosphorus (III) oxide.
(a)
Give the molecular formula of phosphorus (III) oxide.
[1]
_____________________________________________________________ (b) Explain why phosphorus (III) oxide has the properties given below. Property 1 Phosphorus (III) oxide is acidic. [2]
Explanation __________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Property 2 Phosphorus (III) oxide has a low melting point.
Explanation __________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Pg 3 of 14
A4
Complete the following table. Particle Fe N 313 27 proton number 26 38 mass number 56 protons Number of neutrons electrons 50 7 38 10
[4]
A5 The table below gives the results of the experiments between three metals and aqueous solutions of their salts. [4] aqueous X salt aqueous silver salt aqueous magnesium salt (a) (i) (ii) What would be the result in A : ___________________________________________________ B : ___________________________________________________ silver no reaction no reaction no reaction metal X no reaction displacement reaction occurred A magnesium displacement reaction occurred B no reaction
(b)
Place the metals in the order of increasing reactivity. _______________________________________________________________
(c)
Write the ionic equation for the reaction between magnesium and aqueous solution of X if X has a valency of 2. _______________________________________________________________
A6 The statue of liberty in New York is made from an iron frame covered with copper plates. In 2004, work had to be carried out to stop the iron frame from rusting away. Pg 4 of 14
The iron frame was rusting much faster than normal where it was in contact with the copper. (a) Explain why copper, in contact with iron, causes the iron to rust faster than normal. [2] ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________
(b)
Would you expect the copper, in contact with the iron, to corrode faster or slower than normal? Explain your reasoning. [1] _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________
A7
This question is about making salts. For each salt, suggest the name of the missing reagent and briefly describe how to obtain the solid product from the reaction mixture. [6]
(a)
salt to be made : lithium chloride. reagent 1 : dilute hydrochloric acid reagent 2 : _______________________________________________________ I could obtain solid lithium chloride crystals by : __________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________
(b)
salt to be made : barium sulfate. reagent 1 : aqueous potassium sulfate Pg 5 of 14
reagent 2 : ______________________________________________________ I could obtain solid barium sulfate by : ________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ (c) salt to be made : blue copper (II) sulfate crystals. reagent 1 : dilute sulfuric acid reagent 2 : ______________________________________________________ I could obtain blue copper (II) sulfate by : ______________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ A8 Petrol (gasoline) vapour is mixed with air before being burned in a car engine. The amount of petrol in the mixture can be varied. The amounts of pollutant gases, nitrogen oxide and carbon monoxide, in the exhaust emissions from cars depend on the mixture used, as shown in the graph
Pg 6 of 14
below.
(a) (i) Explain why some carbon monoxide is produced in a car engine.
[1]
________________________________________________________________ (ii) Using the graph, describe how the concentration of carbon monoxide varies as the percentage of petrol in the mixture increases. [1]
________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ (b) Explain how car engines produce nitrogen oxide. [1]
_________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ (c) Pollution from cars is decreased by using catalytic converters. The structure of a converter is shown below. Pg 7 of 14
Catalysts increase the rates of reaction. Suggest two other reasons why the reactions in catalytic converters are very fast. [2]
_______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________
A9 State if the following reactions are exothermic or endothermic reactions: (a) (b) (c) Dissolving ammonium nitrate in water : ________________________ Melting ice Respiration : ________________________ : ________________________
[3]
A10 During cracking, molecules of nonane, C9H20, produce three different products: butane, ethane and product X. (a) Complete the equation to show the formula of product X. crack nonane butane + ethane + product X [1]
C9H20 C4H10 + C2H4 + ____________ Structural formula of ethene Structural formula of product X (b) Draw the structural formulae of ethene and product X in the boxes below.[2]
Pg 8 of 14
A11
The table contains some information about two addition polymers and the monomers from which they are made. Complete the table below by filling in the empty boxes. [3]
(a)
(i) Explain what is meant by the term monomer.
[1]
______________________________________________________________ (ii)Both of the polymers in the table are addition polymers. Pg 9 of 14
Explain what is meant by addition polymerization.
[1]
______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________
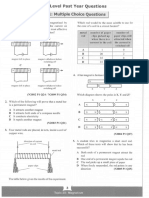
Section B: 20 marks Answer any TWO questions in this section on the writing paper provided. B1 An excess of zinc was added to 10cm3 of 0.5 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid, using the apparatus below.
Pg 10 of 14
(a)
Calculate the maximum volume of hydrogen which could be produced in the reaction at r.t.p. The graph shows how the volume of hydrogen changed during the reaction. [3]
(b)
(i) Describe how the rate of reaction changes as the reaction progresses. (ii) Suggest a reason for this change. [2]
(c)
The experiment was repeated using dilute sulfuric acid of the same concentration. (i) (ii) Write a balanced equation for the reaction between zinc and sulfuric acid. Suggest how both the rate of reaction and the total volume of hydrogen obtained would differ from the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid. (iii) Explain your reasoning. [5]
B2 (a)
Chlorine, bromine and iodine are elements in Group VII of the Periodic Table. A series of experiments were carried out to determine the reactivity of these three elements, using the reagents shown in the table below.
Pg 11 of 14
Reagents used Aqueous potassium chloride Aqueous potassium bromide Aqueous potassium iodide (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
Aqueous chlorine -
Aqueous bromine -
Aqueous iodine
Copy and complete the table, showing the observations you would expect to see when the respective reagents react. List the elements in order of increasing chemical reactivity. Write a chemical equation, with state symbols, for any one of the reactions that occurred in part (i). Hence write an ionic equation for the chemical reaction in part (iii) [1] [2] [3] [1]
(b)
Chlorine reacts with water to make a solution that can be used as a bleach. The equation is shown below. Cl2 + H2O HCl + ClOH Use oxidation numbers to show that chlorine is both oxidized and reduced in this reaction. [3]
Pg 12 of 14
B3
The diagram shows a fractionating column for the separation of crude oil.
The following fractions leave the column. fraction naphtha paraffin diesel oil number of carbon atoms 7-14 9-16 15-25 boiling range / oC 90 - 150 150 - 240 220 - 250 [1] [3]
(a) Which fractions leave the column at each of the points A, B and C? (b) Explain how the fractionating column is able to separate the crude oil mixture. hydrocarbons in ship fuel. Pg 13 of 14
(c) Octane, C8H18, is a hydrocarbon in petrol. Hexadecane, C 16H34, is one of the
(i)
Show, by calculation, that hexadecane contains a higher percentage of carbon by mass than octane.
This is the equation for the complete combustion of octane. 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) (ii) Copy and complete the following equation for the complete combustion of hexadecane. 2C16H34 (l) + ___O2 (g) ___ CO2 (g) + ___ H2O (g) (iii) (d) Use the equations to explain why hexadecane burns with a smokier flame than octane. Name two fuels, suitable for cars, which may not be produced from crude oil. [1] [5]
THE END
Pg 14 of 14
You might also like
- Matrix Math: Addition, Subtraction, and PropertiesDocument7 pagesMatrix Math: Addition, Subtraction, and PropertiesMohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFDocument39 pagesO LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFSONo ratings yet
- 2235 2012Document33 pages2235 2012poh_elsenNo ratings yet
- 2020 Revision For Chapter 3 PDFDocument3 pages2020 Revision For Chapter 3 PDFTimothy Handoko0% (1)
- BT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsDocument70 pagesBT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsSean Ng Jun JieNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSDocument29 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSNicholas Ow100% (1)
- Answers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Document99 pagesAnswers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Ruel Arila Jr.No ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)Document12 pagesH2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)iuhihzNo ratings yet
- Nyjc - 2007 Jc1 h2 Promo p3 - AnswerDocument4 pagesNyjc - 2007 Jc1 h2 Promo p3 - AnswerSudibyo GunawanNo ratings yet
- Siglap Secondary School: Go Forth With Wisdom and CourageDocument9 pagesSiglap Secondary School: Go Forth With Wisdom and CourageLim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Mid-Year Examination (E)Document10 pagesIT Chem F5 Mid-Year Examination (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- HCI H3 PHY 9811 EoMP QP PDFDocument12 pagesHCI H3 PHY 9811 EoMP QP PDFLeng RyanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Nov 2006Document6 pagesPaper 2 Nov 2006MSHNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesAcids and Bases Chapter SummaryjihuhuNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics NotesDocument40 pagesReaction Kinetics Notesapi-234602673No ratings yet
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Document27 pagesStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1718 V2 EoS1 Past PaperDocument12 pagesChemistry 1718 V2 EoS1 Past PaperjcyNo ratings yet
- 2014 YJC Prelim H2 Chem P1 W AnsDocument18 pages2014 YJC Prelim H2 Chem P1 W AnswaimoeNo ratings yet
- 2009 Nov H2 Chemistry Paper 2Document6 pages2009 Nov H2 Chemistry Paper 2nncy_rox3478565No ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry PaperDocument13 pagesH2 Chemistry PaperChong56No ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Chemistry 6031/3Document12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Chemistry 6031/3takundavs100% (2)
- Catholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Document13 pagesCatholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 5090 w01 QP 2Document12 pages5090 w01 QP 2Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- 2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsDocument3 pages2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Unit 1 OCR Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesJune 2016 QP - Unit 1 OCR Chemistry A-Levelmark sjsieuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem (With Solution) 2Document75 pagesOrganic Chem (With Solution) 2vlNo ratings yet
- Alkane Alkene QuestionsDocument10 pagesAlkane Alkene QuestionsormattNo ratings yet
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDocument12 pagesH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurequestions PDFDocument42 pagesAtomicstructurequestions PDFNfor KlinsmanNo ratings yet
- H2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFDocument78 pagesH2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFBobNo ratings yet
- Emath Sec4 Sa2 2012 Cedar GirlsDocument31 pagesEmath Sec4 Sa2 2012 Cedar GirlsrofinaNo ratings yet
- 2012 JC1 Promo RevisionDocument477 pages2012 JC1 Promo RevisionVincent SeeNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 9Document23 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 9Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument113 pagesOrganic ChemTrúc Hồ0% (1)
- Sec 3NA Quiz IDocument4 pagesSec 3NA Quiz ISharizah Bte Md AminNo ratings yet
- VJC 2007Document14 pagesVJC 2007sswee_1No ratings yet
- Year 8 - Atoms and Elements and Compounds and MixturesDocument8 pagesYear 8 - Atoms and Elements and Compounds and MixturesAbhiraj SamantaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 SLDocument16 pagesChemistry Paper 2 SLSonia InezaNo ratings yet
- Acid and AlkaliDocument9 pagesAcid and Alkali云吸仓鼠吉尼斯保持者No ratings yet
- Preparation of Soluble SaltsDocument23 pagesPreparation of Soluble SaltsFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals and Their PropertiesDocument22 pagesTransition Metals and Their PropertiesPeng Jia XinNo ratings yet
- Sec 2NT Science CT1 Revision WSDocument4 pagesSec 2NT Science CT1 Revision WSdenlinNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 20 Answer SchemeDocument19 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 20 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- JC H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocument13 pagesJC H2 Chemistry Prelim Paperschong56No ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedDocument21 pagesOxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedKaroline UhlemannNo ratings yet
- 4047 SP 01Document6 pages4047 SP 01MaverickNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Electrolysis Worksheet with Past Paper QuestionsDocument53 pagesIGCSE Electrolysis Worksheet with Past Paper Questionsaqsa chaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Level H2 Paper 2Document6 pagesA Level H2 Paper 2newtonian_physics100% (1)
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Document4 pagesO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurNo ratings yet
- Che 02Document5 pagesChe 02lakashl14No ratings yet
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDocument18 pagesAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- AnglesDocument23 pagesAnglesJoann NgNo ratings yet
- 2021 S.3 1st Term TestDocument11 pages2021 S.3 1st Term Testirene fungNo ratings yet
- G. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceDocument9 pagesG. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceGervent GayleNo ratings yet
- Energetics Revision Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesEnergetics Revision Exam QuestionsDulshan JayNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Working OutDocument117 pagesOxidation and Reduction Working Outnathan100% (1)
- Acjc h2 Chem p2 AnswersDocument18 pagesAcjc h2 Chem p2 AnswersZach EganNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseDocument13 pagesChemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseKrishvardhan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- R WeidenfellerDocument2 pagesR WeidenfellerYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimDocument18 pages4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Gan Eng Seng SCH Sec 4 e Maths 2nd Prelim Exam Paper 1 With AnswersDocument16 pages2009 Gan Eng Seng SCH Sec 4 e Maths 2nd Prelim Exam Paper 1 With AnswersYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument46 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesRenée ReimiNo ratings yet
- Prelim Scichem P5 2012Document2 pagesPrelim Scichem P5 2012Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 4E&5NA SC (Chem) Prelim P3 10 Ans LDocument10 pages4E&5NA SC (Chem) Prelim P3 10 Ans LYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimDocument18 pages4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes v1.6 ExtraDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes v1.6 Extraarj77No ratings yet
- Prelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeDocument1 pagePrelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- BSS2012 Prelim Exam Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesBSS2012 Prelim Exam Marking SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Science Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Document8 pagesScience Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim Scichem P5 2012Document2 pagesPrelim Scichem P5 2012Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Test No. Test Observations Remarks: /black Solid FormedDocument3 pagesTest No. Test Observations Remarks: /black Solid FormedYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeDocument1 pagePrelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Kranji Prelim09 5116 P1 - With KeysDocument9 pagesKranji Prelim09 5116 P1 - With KeystopcatNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsDocument9 pagesPreliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- MHSS Prelim06 5152 P1Document8 pagesMHSS Prelim06 5152 P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision NotesDocument20 pagesQuick Revision NotesYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases & SaltsDocument19 pagesAcids Bases & SaltsMuhammadAbutalibKazmiNo ratings yet
- BP Prelim05 5152 P1Document10 pagesBP Prelim05 5152 P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Science Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Document8 pagesScience Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 0653 s13 GT Science-CombinedDocument2 pages0653 s13 GT Science-CombinedYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Westwood 4NA Prelim2010 P3 MCQDocument10 pagesWestwood 4NA Prelim2010 P3 MCQYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 4 E5 NSci Phy Prelim IIP12012 AnswersDocument1 page4 E5 NSci Phy Prelim IIP12012 AnswersYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Pure Geog P1 AnsDocument27 pagesPure Geog P1 AnsYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Metals (Key Points and Q&A)Document7 pagesMetals (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Systems and Processes: Types of WavesDocument2 pagesCoastal Systems and Processes: Types of WavesYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 2010 Prelim2 ScChem 4E5N.P1Document15 pages2010 Prelim2 ScChem 4E5N.P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Sec 4Ex/5NA Science (Physics) Prelim ANSWERDocument4 pages2012 Sec 4Ex/5NA Science (Physics) Prelim ANSWERYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- G 4852 Microalloy Material DatasheetDocument8 pagesG 4852 Microalloy Material Datasheetasirul_meNo ratings yet
- A SWOT Analysis of Indian Mining IndustryDocument3 pagesA SWOT Analysis of Indian Mining Industryravenrulez67% (6)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Sarah KKC0% (1)
- Unistrut: Application, Installation, Specification GuideDocument20 pagesUnistrut: Application, Installation, Specification GuideCAR6No ratings yet
- A102Document3 pagesA102SUNIL BINDNo ratings yet
- Production of Magnesia - Methods and ProcessesDocument2 pagesProduction of Magnesia - Methods and ProcesseszamburittiNo ratings yet
- Casting defect causes and typesDocument7 pagesCasting defect causes and typesSama UmateNo ratings yet
- The Solvent Extraction of Some Major MetalsDocument37 pagesThe Solvent Extraction of Some Major MetalsSimi SichulaNo ratings yet
- PREN Value (Duplex)Document4 pagesPREN Value (Duplex)onkarNo ratings yet
- 05 Petrucci10e CSMDocument45 pages05 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- 567 TDSDocument1 page567 TDSPete DechaNo ratings yet
- 0620 Sow Unit 11 Redox Electrochemistry Group VIIDocument7 pages0620 Sow Unit 11 Redox Electrochemistry Group VIIPakardan TeaNo ratings yet
- CLASS-10TH - CHAPTER - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument3 pagesCLASS-10TH - CHAPTER - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsTanmay LahaNo ratings yet
- Net Smelter ReturnDocument7 pagesNet Smelter Returnsunpit100% (2)
- Periodic Table of ElementalsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of ElementalsXhian TadzNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Analysis ReportGlient: Here is a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document:TITLE IGAS Research Reports Aluminum Alloy Purity and PropertiesDocument3 pagesAluminum Analysis ReportGlient: Here is a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document:TITLE IGAS Research Reports Aluminum Alloy Purity and PropertiessalmanNo ratings yet
- p-100 Vol2 1935 Part5Document132 pagesp-100 Vol2 1935 Part5Matias MancillaNo ratings yet
- Materials and Mechanical Properties in Additive ManufacturingDocument36 pagesMaterials and Mechanical Properties in Additive ManufacturingHalyna HafiychukNo ratings yet
- BS 3882 Soil AnalysisDocument3 pagesBS 3882 Soil AnalysisHansika JayathilakaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Metals: An Introduction to Metallurgy and Metal PropertiesDocument11 pagesThe Science of Metals: An Introduction to Metallurgy and Metal PropertiesFran jimenezNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry LabDocument6 pagesCalorimetry LabchristineNo ratings yet
- Workshop PresentationDocument27 pagesWorkshop PresentationMUHAMMAD UMAR FAYYAZNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsDocument8 pagesCH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsBeth0% (1)
- Structural Steel Shapes: Standard Specification ForDocument3 pagesStructural Steel Shapes: Standard Specification ForNgoc BuiNo ratings yet
- Dental Cement Types and PropertiesDocument17 pagesDental Cement Types and PropertiesMella Bella WilsonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis reactions and observationsDocument35 pagesElectrolysis reactions and observationsBOOKwormNo ratings yet
- A New Type of Scandium Mineralization in PhoscoritesDocument10 pagesA New Type of Scandium Mineralization in PhoscoritesŞerifKayaNo ratings yet
- Steel Castings, General Requirements, For Pressure-Containing PartsDocument12 pagesSteel Castings, General Requirements, For Pressure-Containing PartsMarco A. R. JimenesNo ratings yet
- Answers For Group VII Problem-Solving QuestionsDocument9 pagesAnswers For Group VII Problem-Solving QuestionsTan Song Kai100% (1)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document18 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)