Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Okan
Uploaded by
Gökhan YüksekOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Okan
Uploaded by
Gökhan YüksekCopyright:
Available Formats
EEE454 High Voltage Techniques 2013
Prof.Dr.Aydoan ZDEMR
Department of Electrical Engineering
Istanbul Technical University
34469 Maslak, ISTANBUL
Tel: 212 285 6758
High Voltage Laboratory-ITU Gmsuyu Campus
Tel 212 252 2220
Email : ozdemiraydo@itu.edu.tr
Website : http://www.elk.itu.edu.tr/~ozdemir
Grading Policy
Midterm test : 25 %
2 Homeworks : 5% + 5%
1 group project : 15%
Final test : 50%
Week Date Subject
1 06.02.2013 Introduction and Timelines of Electricity
2 13.02.2013
Basic concepts of electrostatic field, Laplace's and Poisson's equations in
different coordinate systems. Basic equations of electrostatic fields. Planar
electrode systems.
3 20.02.2013 Concentric spherical electrode systems.
4 27.02.2013 High Voltage Laboratory Visit
5 06.03.2013 Coaxial cylindrical electrode systems.
6 13.03.2013
Non-coaxial cylindrical electrode systems: eccentric and parallel cylindrical
electrode systems.
7 20.03.2013
Approximate calculation of maximum electric field strength for different
electrode systems. Electrode systems with multi-dielectrics: planar
electrode systems.
8 27.03.2013 Midterm test
9 03.04.2013
Electrode systems with multi-dielectrics: coaxial cylindrical systems with
multi-dielectrics. Uniformly stressed cylindrical electrode systems
10 10.04.2013
Uniformly stressed cylindrical electrode systems. Numerical methods for
electrostatic field calculations.
11 17.04.2013 Numerical methods for electrostatic field calculations.
12 24.04.2013 Conduction and breakdown in gases.
13 01.05.2013
Conduction and breakdown in gases (cont.). Corona discharges, surface
discharges and lightning discharges. Breakdown in liquid and solid
dielectrics
14 08.05.2013 Project presentation
There may small revisions in the program. Please check it every week.
References
1. Prof.Dr.Muzaffer ZKAYA, Yksek Gerilim Teknii : Cilt 1, Birsen Yaynevi, stanbul 1996.
2. Akpnar S., Yksek Gerilim Teknii, Karadeniz Teknik niv., Trabzon, 1997.
3. Gnen .., Yksek Gerilim Teknii, Cilt 1: Statik Elektrik Alan ve Basit Elektrot Sistemleri,
.T.. Ktphanesi, Say:1085, stanbul, 1977.
4. E. Kuffel, W. S. Zaengl, J. Kuffel , Yksek Gerilim Mhendislii Temelleri, Tercme yayn EMO
Yaynlar, 2008.
5. E. Kuffel, W. S. Zaengl, J. Kuffel, High Voltage Engineering Fundamentals, Pergamon Press,
Oxford, 2000.
6. M. S. Naidu, V. Kamaraju, High Voltage Engineering, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 1997.
7. M. Abdel-Salam, H. Anis, A. El Morshedy, R. Radwan, High Voltage Engineering: Theory and
Practice, Marcel Dekker, New York, 2000.
8. Kind, D., Feser, K., High-Voltage Test Techniques, SBA Publ./Vieweg, 2. Ed. 1999.
9. M. Khalifa, High Voltage Engineering, Theory and Practice, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1990.
10. H. M. Ryan, High Voltage Engineering and Testing, Peter Peregrinus Ltd., London, 2001.
11. C. L. Wadhwa, High Voltage Engineering, New Age Int. Ltd., 2
nd
Edition, New Delhi, 2007.
12. Subir Ray, An Introduction to High Voltage Engineering, Printice Hall of India, New Delhi 2004
March 6, 2013
HOMEWORK #1
1. Potential distribution of an electrode system for a voltage of U=200 kV is given as follows,
| | | | cm y cm x y x kV
y x
b
a y x v , , 9 4 ; 1 . ) , (
2 2
2 2
s + s
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
a) Determine the constants ( a and b) if v(0 , 2 cm)=200 kV and v(3 cm , 0)=0 kV.
b) Determine and sketch the equipotential curves of v
1
=0 kV, v
2
=200 kV and v
3
=100 kV .
c) Determine the field strength vector E
and
min max
, E E
. da
2. a) Outer sphere radius of a concentric spherical electrode system is given to be r
2
= 15 cm. Determine
the maximum voltage that can safely be applied to the system if the dielectric strength of the
insulation is E
d
= 30 kV/cm.
b) Determine the inner radius of the system in order to apply U=100 kV.
c) Evaluate the system from the point of discharge phenomena (will there be a discharge, if so the type)
for the inner radiuses of r
1
= 2 cm , r
1
= 7 cm and r
1
= 14 cm.
3. a) Given that the maximum voltage that can safely be applied to an air-insulated (E
d
= 30 kV/cm)
coaxial cylindrical system is 300 kV. Determine the inner radius of the system in order to apply
U=250 kV.
b) Evaluate the maximum field strengths for an inner radius of r
1
and for an increased outer radiuses of
r
2
= 1.5* r
2
, r
2
= 2.0* r
2
, r
2
= 3.0* r
2
and r
2
= 4.0* r
2
; where r
1
and r
2
are the inner and
outer radiuses calculated in b). What can you say about the maximum field strength versus outer
radius of the system?
Due date : March 13, 2013
HOMEWORK #1 SOLUTIONS
1. a) cm 3 b and kV 400 a solved if
0
3
1
3
. ) 0 , 3 (
200
2
1
2
. ) 2 , 0 (
= =
= =
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
|
.
|
\
|
=
a
ab b
a v
kV a
ab b
a v
b) cm 3 of radius a with Circle 3 1
3
. 400 0
2 2 2
2 2
1
= +
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= = y x
y x
kV v
cm 2 of radius a with Circle 2 1
3
. 400 200
2 2 2
2 2
2
= +
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= = y x
y x
kV v
cm 2.4 of radius a with Circle 4 . 2 1
3
. 400 100
2 2 2
2 2
3
= +
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= = y x
y x
kV v
c)
| | | |
j
y x
y
i
y x
x
j
y
v
i
x
v
v grad E
y x
v
2 / 3 2 / 3
2 2 2 2
2 2
1200 1200
1
3
. 400
+
+
+
=
(
c
c
+
c
c
= =
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
| |
cm kV E E cm kV E E
y x
y x
y x
y x
y x E
y x y x
/ 3 . 133 , / 300
3 2
1200
* 1200 ) , (
9 4
3
2 2 2 2
min max
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
= = = =
s + s
+
=
+
+
=
= + = +
2. a) Maximum voltage can be applied when cm r r 5 . 7 2
2 1
= =
kV E U E
r r
r r
U E
d d
m r
m r
5 . 112
5 . 7 / 15
5 . 7 15 /
max
5 . 7
1
15
2 1 2
1 2
max
=
= s
=
=
=
b) 10 , 5 30
15
/ 15
100
/
12 11
1
1
15
1 2
1 2
max
2
cm r cm r
r
r
E
r r
r r
U E
d
cm r
= = s
=
=
12 1 11
r r r < <
v
2
= 200 kV
v
1
= 0 kV
v
3
= 100 kV
c)
2
since discharge partial a be will There 7 . 57
/
15
2
2
1
1 2
1 2
max
2
1
r
r E
cm
kV
r r
r r
U E
cm r
cm r
d
< > =
=
)
`
=
=
discharge be t won' There 8 . 26
/
15
7
1 2
1 2
max
2
1
< =
=
)
`
=
=
d
E
cm
kV
r r
r r
U E
cm r
cm r
2
since breakdown total a be will There 0 . 107
/
15
14
2
1
1 2
1 2
max
2
1
r
r E
cm
kV
r r
r r
U E
cm r
cm r
d
> > =
=
)
`
=
=
3. a) Maximum voltage can be applied when e r r
2 1
=
cm r e r cm r
cm
kV
E
r
U
r
r
Ln r
U
E
d
e
r
r
18 . 27 * , 10
30
300
30
1 2 1
1
max
2
1
1
2
1
max
max
> = = > = s =
(
=
=
cm r cm r solved if E
r Ln r
E kV U For
d
8 . 4 , 3 . 16
) / 18 . 27 (
250
250
12 11
1 1
max
= = s = =
12 1 11
r r r < <
b)
) / (
, 250 , 8 . 4
1 2 1
max 1
r r Ln r
U
E kV U cm r = = =
cm kV E cm r
cm kV E cm r
cm kV E cm r
cm kV E cm r
/ 7 . 16 7 . 108 18 . 27 * 0 . 4
/ 3 . 18 5 . 81 18 . 27 * 0 . 3
/ 4 . 21 4 . 54 18 . 27 * 0 . 2
/ 3 . 24 8 . 40 18 . 27 * 5 . 1
4 max 2
3 max 2
2 max 2
1 max 2
= = =
= = =
= = =
= = =
Increasing r
2
decreases E
max
. However decreasing rate decreases as r
2
increases and therefore r
2
is not
an effective means of reducing E
max
, especially after a certain value.
March 27, 2013
High Voltage Technique, Midterm Test
1. Potential function for an electrode system is given as, v(x,y) = a.xy + b xy > 1 cm
2
a) Determine a and b if v
1
(1 cm,1 cm) = 0 kV and v
2
(2 cm, 2 cm) = 60 kV (5)
b) Determine and sketch v
1
= 0 kV and v
2
= 60 kV equipotential curves. (10)
c) Determine the electric field expression and calculate the values at points A(1 cm,1 cm) and
B(2 cm, 2 cm) (10)
2. a) Maximum discharge voltage of an air-insulated co-axial cylindrical electrode system is 240
kV. Determine the radius of the inner cylinder for a test voltage of U = 200 kV. (10)
b) Two parallel-axis cylindrical electrodes having radiuses r
1
= 10 cm and r
2
= 25 cm are
placed one inside another. Minimum spacing between the electrodes is a = 5 cm. Calculate
the maximum field strength, equivalent spacing, system efficiency and unit length
capacitance if U = 100 kV is applied to the system (15).
3.a) U = 50 kV is applied to a sphere-plane electrode system having a spacing of a = 5 cm.
Calculate the approximate values of the maximum field strength, equivalent spacing and
system efficiency if the sphere radius is r = 10 cm. (15)
b) Calculate the same quantities if the sphere was replaced by a cylinder of the same diameter.
(10)
4. Consider a two layer inclined-planar electrode system composed of transformer oil ( c
r1
= 2.5)
and porcelain (c
r2
= 5) insulations. Electric filed strength in transformer oil makes an angle of
37
o
with the boundary surface and has a magnitude of 80 kV/cm.
a) Calculate the tangential and the normal components of the field strengths at both layers (10).
b) Calculate the angle between the electric field strength in porcelain layer and the boundary
surface. (5)
c) What happens if the normal or tangential field strengths exceed the dielectric strengths of the
materials? (10)
Notes are open and test duration is 90 minutes.
MIDTERM TEST SOLUTIONS
1.a)
b)
y=1 y=1/x
d)
) kV/cm
2.a) Maximum voltage can be applied when e r r
2 1
=
For U=200 kV
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6 2 2.4 2.8
y [cm]
x [cm]
v1=0 kV
b)
2 1 1 2 2 1 1
2
1
2
1
1
2 1
1 1
1
2
1
2
1
1
2
1
5 20 100 25
25
20
5 2
2
b b b b b b b
b
b
b
b
k
b a r
b r
l
l
b a
b
l
l
B A
+ = +
+
=
+
=
+ +
= =
+
=
2 1 2 2 1 1 2
2
1
2
1
2
2 2
1 2
2
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
45 50 5 250
50
45 5
2
2
b b b b b b b
b
b
b
b
k
b r
b a r
l
l
b
b a
l
l
B A
= + + +
+
=
+
=
+
= =
+
=
If organized cm b cm b
b b b b
b b b b
25 , 5 . 7
250 2 40 50
100 2 20 30
2 1
2 1 2 1
2 1 2 1
= =
)
`
= +
= +
,
cm
b b a d
75 . 18
2 2
2 1
=
+ +
= =
m C q kV
q q
b
b a
b
b a
Ln
q
U / 015 . 8 , 27 . 144
2
693147 . 0
2 2
1
2
2
1
tc tc tc
= = =
(
+ +
=
cm kV
x
q
E E
b x
A
/ 04 . 24
2
2
1
1
2 2
max
=
= =
=
tc
m pF
U
q
C
a
cm
E
U
E
U
A
/ 15 . 80 , 83 . 0 , 16 . 4
1
max
= = = = = = =
o
q o
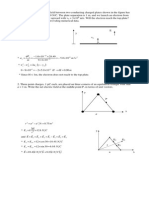
3.a)
b)
d=2
b
2
a
b
1
c
A
2
A
1
B
1
B
2
r
2
r
1
y
x
-q q
U
r
1= 10 cm
r
2= 25 cm
a
= 5 cm
U
= 100 kV
4.
a)
b)
c) If the normal field strength exceeds the dielectric strength of the material, it creates
discharges inside the insulator; whereas if the tangential field strength exceeds the
surface dielectric strength, it creates surface discharges along the boundary surface.
April 17, 2013
High Voltage Technique, Midterm-Make up Test
1. a) Maximum withstand voltage of an air-insulated ( E
d
= 30 kV/cm) concentric spherical
electrode system is 1000 kV. Determine the inner and the outer radiuses of the system. (10)
b) Keep the outer radius constant and determine the inner radius of the system for a system
voltage of 800 kV. (10)
c) Keep the outer radius constant and discuss the existence and the type of the discharges for
an inner radiuses of r
1A
= 10 cm and r
1B
= 110 cm for U = 600 kV. (10)
2. U = 240 kV is applied to an oil-insulated (c
r
= 2.5, E
d
= 75 kV/cm) co-axial electrode
systems with an inner radius of r
1
= 20 cm.
a) Determine the outer radius of the system to keep the maximum field strength less than 35
kV/cm. (10)
b) Discuss the existence and the type of the discharge for an outer radius of 25 cm. (10)
c) Assume that the outer radius is r
2
= 30 cm and the inner cylinder is covered by a 5 mm
solid dielectric (c
r
=4, E
d
=100 kV/cm). Calculate the maximum and the minimum field
strengths for both layers. (10)
3. U = 200 kV is applied to an electrode system comprising two parallel cylindrical electrodes
with a spacing of 6 cm. The radiuses of the cylinders are r
1
= 8 cm and r
2
= 12 cm,
respectively.
a) Determine the location and the value of the maximum and the minimum electric field
strengths. Calculate the equivalent spacing, system efficiency and unit length capacitance
of the system. (10)
b) Calculate the approximate maximum field strength and corresponding error. (10)
c) Calculate the approximate value of the maximum field strength and the efficiency of
sphere to plane electrode system where sphere radius is 10 cm and electrode spacing is 5
cm. Applied voltage is 100 kV (10)
d) Calculate the approximate value of the maximum field strength and the efficiency of
sphere to cylinder electrode system. The radiuses of the sphere and the cylinder are 10 cm
and electrode spacing is 5 cm. Applied voltage is 100 kV (10)
Notes are open and test duration is 90 minutes.
April 17, 2013
HOMEWORK #2
1. Use Finite Difference Method (FDM) to determine the potentials and electric field
magnitudes at free nodes (node-a, b, c and d) and on the electrode surfaces (e,f,g and h) in the
Cartesian electrode system. (Note: h = 2 cm, k = 2 cm. Assume that the z-axes is infinite
length, and the electric potential is a function of x and y).
2. Solve the same question for h=3 cm and k = 2 cm
c d
V = 10 kV
V = 5 kV
V
=
0
V
=
2
k
V
x
y
(0, 0)
h
k
a b
Dielectric
e
f
g
h
HOMEWORK #2 SOLUTIONS
1.
if solved,
For all points
c d
V = 10 kV
V = 5 kV
V
=
0
V
=
2
k
V
x
y
(0, 0)
h
k
a b
Dielectric
e
f
g
h
e
h
g
f
2.
if solved,
For all points
May 22, 2013
High Voltage Technique - Final test
1. Maximum breakdown voltage of a compressed-gas high voltage capacitor
(c
r
= 1.0) comprising an equi-center spherical electrode system and a co-
axial cylindrical electrode system is 1800 kV.
a) Determine the radiuses r
1
, r
2 ,
r
3
ve r
4
(E
d
= 80 kV/cm), and calculate
the system capacitance. (15)
b) Determine r
2
and r
4
for a system voltage of 1200 kV, assuming that r
1
,
r
3
and L are constant. (10)
2. U = 140 kV is applied to an oil-insulated (c
r
= 2.5) coaxial cylindrical electrode system having
an outer cylinder radius of r
2
= 20 cm.
a) Determine the value (range) of the inner cylinder radius so that the E
max
is kept less than 30
kV/cm. (10)
b) Assume that the inner cylinder radius is 3 cm. Determine the maximum and the minimum field
strengths at both layers, if the inner cylinder is covered with 2 cm solid dielectric (c
r
= 4.0, E
d
=
100 kV/cm ). (15)
3.a) Calculate the breakdown voltage, breakdown field strength and Townsends first ionization
coefficient of an air-insulated electrode system having an electrode spacing of a = 2.5 cm at T
= 273
o
K and p = 760 mmHg. (A(T = 273
o
K) = 24.4 1/cm.Torr , B(T = 273
o
K) = 341.6
V/cm.Torr, = 1/5000). (10)
b) Calculate the same values for the ambient conditions of T = 283
o
K and p = 750 mmHg (5)
c) Calculate the critical pressure and corresponding breakdown voltage and breakdown field
strength (5).
d) Give a half page summary of your term project (5).
4. Use Finite Difference Method (FDM) to determine the potentials at a and b; and calculate the
field strengths at a, b, c, and e in the following electrode system. (Note: h = 2 cm, k = 2 cm.
Assume that the z-axes is infinite length, and the electric potential is a function of x and y) (25).
Test period: 120 minutes. Books and the notes are open.
V = 0 kV
V = 10 kV
x
y
(0, 0)
h
k
a b
c
f
h
d
e
g
V
=
2
k
V
2r
1
2r
2
2r
3
2r
4
L=1m
Final test problem solutions
1.a) For equi-center spherical electrode system:
cm
r
r cm r
r
r
r
r r
r r
U E
d d
45
2
, 90
80
1800 * 4
2 /
2
1800
2
/
2
1 2
2
2
1
1 2
1 2
max
= = = = =
=
=
For co-axial cylindrical electrode system:
cm
e
r
r cm r
e
r
e
r
r
r
r
Ln r
U
E
d
d
5 . 22 , 16 . 61
80
1800 * 718 . 2 1800
*
4
3 4
4
3
4
3
4
3
max
= = = = =
=
=
pF pF pF
r r Ln
L
r r
r r
C C C
c s
5 . 155 5 . 55 0 . 100
) / (
2
4
4 3 1 2
2 1
= + = +
= + =
tc
tc
b) For equi-center spherical electrode system:
cm r
r
r
cm r
r r
r r
U E
d
5 . 67
3
80
3600 80
45
/
2
2
2
1
1 2
1 2
= =
=
=
For co-axial cylindrical electrode system:
cm
E
U
r
cm r
r r Ln r
U
E
d
d
82 . 43
) * 5 . 22
exp * 5 . 22
5 . 22
) / ( *
4
3
3 4 3
=
(
=
=
=
2.a) cm r cm r i
r
Ln r
cm
kV
r r Ln r
U
E 49 . 14 , 05 . 2 solved f
30
140
)
20
( * 30
) / ( *
12 11
1
1
1 2 1
max
= = > < =
cm r r cm r 49 . 14 05 . 2
12 1 11
= < < =
b) It will be a 2-layer system with cm r cm r R cm r 20 , 0 . 5 2 , 0 . 3
2 1 1
= = + = =
m pF
C C
C C
C m pF
R r Ln
C m pF
r R Ln
C
s
/ 4 . 81 , / 2 . 100
) / (
2
, / 0 . 435
) / (
2
2 1
2 1
2
0
2
1
1
=
+
= = = = =
tc tc
kV U
C
C
U kV U
C
C
U 8 . 113 , 2 . 26
2
1
1
1
= = = =
cm kV
r R RLn
U
E cm kV
r R Ln r
U
E / 3 . 10
) / (
, / 1 . 17
) / (
1
1
min 1
1 1
1
max 1
= = = =
cm kV
R r Ln r
U
E cm kV
R r RLn
U
E / 1 . 4
) / (
, / 4 . 16
) / (
2 2
2
min 2
2
2
max 2
= = = =
3.a) kV
Ln
Ln
Ln
Apa
Ln
Bpa
U
d
452 . 75
) 5000 1 (
5 . 2 * 760 * 4 . 24
5 . 2 * 760 * 6 . 341
) / 1 1 (
=
(
+
=
(
+
=
s e e Ap cm kV
a
U
E
p E
B
d
d
/ 1 41 . 3 * 760 * 4 . 24 * , / 181 . 30
5 . 2
452 . 75
760 / 30181
6 . 341
/
= = = = = =
o
b) Torr cm
T
T
C T A C T A . / 1 54 . 23
283
273
* 4 . 24 * ) 0 ( ) 10 (
0 0 0
= = = = =
Torr cm V
T
T
C T B C T B . / 53 . 329
263
273
* 6 . 341 * ) 0 ( ) 10 (
0 0 0
= = = = =
kV
Ln
Ln
Ln
Apa
Ln
Bpa
U
d
240 . 72
) 5000 1 (
5 . 2 * 750 * 54 . 23
5 . 2 * 750 * 53 . 329
) / 1 1 (
=
(
+
=
(
+
=
s e e Ap cm kV
a
U
E
p E
B
d
d
/ 1 41 . 3 * 750 * 54 . 23 * , / 896 . 28
3
853 . 84
750 / 28896
53 . 329
/
= = = = = =
o
c) Torr
Ln
Aa
Ln e
p
cr
38 . 0
5 . 2 * 4 . 24
) 5001 ( * 718 . 2 ) / 1 1 ( *
= =
+
=
cm V a U E
V a p B U
d d
cr d
/ 130 5 . 2 / 1 . 324 /
1 . 324 5 . 2 * 38 . 0 * 6 . 341 * *
min min
min
= = =
= = =
d) Refer your term project
4.
if solved,
For all points
TERM PROJECT
1. Term projects will be prepared by the groups listed below.
2. The first student is the group leader and responsible from the organization. Please get in
contact with him/her for the organization.
3. Project reports should be prepared in accordance with the following format.
Project name
Group members and the responsibilities
Contents
1. Introduction
2. Report of the studies, calculations, simulations etc.
3. The results and the discussion
4. References
4. The responsibility and the activity of each group member should be clearly stated in the
report.
5. The projects will be presented in the class on May 8, 2013. All the group members should
share the presentation. Presentations must not exceed 15 minutes. Power point presentation
is required.
6. Project report should be signed by all group members and delivered on the date of final
test.
G NO NAME SURNAME
PROJECT
1
M.Kemal GNAY,
mkgunay2003@gmail.com
Travelling waves in transmission lines
Burak Zobi
Arif nel
Alkn Karata
Sekin Uyank
2
Simge TRKKAN,
simgeturkkan.4@gmail.com
Generation and measurement of High
Direct Voltages
Din Kuruay
M.Serdar DLAVER
lhan Top
smail Kovalk
3
Harun KEEC,
harunkececi.10@hotmail.com
Generation and Measurement of AC high
voltages
R.Anl OKTAY
Recepan GNAY
Samet ZENR
Kemal GZEL
4
Ali KSE,
akose@stu.okan.edu.tr
Partial discharge phenomena in solid
dielectrics
Yiit Zengin
Erkan stn
Yavuz eliker
Mikail Cem Szen
5
Ozan Ayaz,
ozan_ayaz07@hotmail.com
Measurement of Impulse Voltages Talha Doan
Ali YAMAN
Koray Koal
6
Sercan TUNCER,
sercanntuncer@gmail.com
Lightning Protection of the Buildings
Uur etin
Mehmet Ali Perk
Rdvan zcan
7
Serhad Bilim,
serhadbilim87@gmail.com
Surge arresters and Protection against
overvoltages
Ercan Kasm
Levent Bahadr
S.Tabu Ongwaya
8
Tayfun MERAL,
tayfunmeral@yandex.com
Generation of Impulse Voltages
Turgut Canikli
Gkhan Aydn
Semih Sancakl
Hw
#1
MT
Hw
#2
Project
Final
Pres. Rep.
80203003 Ozan Ayaz
36 85 70 45 33
80203006 Tayfun MERAL 39
50 45 70 60 36
80203009 Burak Zobi
55 80 75 28
80203012 Talha Doan
39 50 45 21
80203016 Harun KEEC 48
35 45 80 52 30
80203018 Alkn Karata
35 45 75 38
80203019 Mehmet Ali Perk
37 50 45 38
80203020 Ercan Kasm
45 60 65 29
80203022 Ali KSE 62
35 50 50 50 47
80203026 Simge TRKKAN 87
88 100 90 85 96
80203029 Gkhan Aydn
66 60 60 19
80203030 R.Anl OKTAY 84
34 45 50 52 49
80203031 Mikail Cem Szen
80
M
55 50 36
80203033 smail Kovalk
55 45 40 85 18
80203035 lhan Top
48 70 85 20
80203039 Koray Koal
53 55 45 21
80203047 M.Serdar DLAVER 42
40 45 70 85 41
80203049 Semih Sancakl
32 45 80 60 48
80207001 Recepan GNAY 60
42 50 60 52 33
90203200 Yiit Zengin
28 45 40 50 32
90203203 Levent Bahadr
16 45 70 65 31
90203204 Erkan stn
31 45 40 50 31
90203208 Arif nel
28 45 75 30
90203218 Yavuz eliker
40 45 70 50 19
90207002 Sercan TUNCER 59
37 50 60 45 25
100203024 Din Kuruay
30 45 85 42
100203026 Rdvan zcan
29 45 50 45 16
100203031 Turgut Canikli
40 45 50 60 19
100203033 Kemal GZEL 42
28 45 40 52 35
100203037 S.Tabu Ongwaya 92
87 90 90 65 60
100203040 Uur etin
44 45 40 45 25
100203042 Serhad Bilim
36 45 80 65 33
100203043 Ali YAMAN 47
50 45 70 45 38
100203050 Sekin Uyank
30 75 23
110203054 M.Kemal GNAY 81
36 90 85 75 45
Samet ZENR** 57
45 45 50 52 26
Atilla Korlar*,**
40 23
You might also like
- Earthing CalculationDocument14 pagesEarthing CalculationNatarajan Ramakrishnan100% (18)
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ieee Gold Book Standard 493 2007Document3 pagesIeee Gold Book Standard 493 2007Patricia0% (2)
- Earthing Calculations for 110KV SwitchyardDocument8 pagesEarthing Calculations for 110KV SwitchyardGarmangh GersNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Electrical Schematic Connection Diagrams ANDDocument27 pagesElectrical Schematic Connection Diagrams ANDntdien923100% (2)
- Short Circuit Force CalculationDocument11 pagesShort Circuit Force CalculationAchint Kumar100% (2)
- 160.00-m3 Vs Oil PumpDocument16 pages160.00-m3 Vs Oil PumpArshad Mahmood100% (2)
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Learning SimulinkDocument572 pagesLearning Simulinkmarrakamasutras100% (28)
- Chapter 06 p060-073Document14 pagesChapter 06 p060-073umamgis3304100% (1)
- KFUPM EE340 Electromagnetics Lab ManualDocument31 pagesKFUPM EE340 Electromagnetics Lab ManualAhmed Al-ShwmiNo ratings yet
- Siemens - CCDocument11 pagesSiemens - CCtrymskvedaNo ratings yet
- University Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFDocument1 pageUniversity Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFMohammed Rashwan32% (19)
- Modeli̇ng Cs İn MatlabDocument1 pageModeli̇ng Cs İn MatlabGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Iec 60027 Iec 60034 Iec 60038Document6 pagesIec 60027 Iec 60034 Iec 60038Sabir NaseerNo ratings yet
- UEE403 Feb2004Document3 pagesUEE403 Feb2004sliit2008No ratings yet
- CHPT 3 PDFDocument8 pagesCHPT 3 PDFYahya Faiez WaqqadNo ratings yet
- Exam MEP1553 Apr2010Document7 pagesExam MEP1553 Apr2010Abid JamaliNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual-2nd EdDocument55 pagesSolution Manual-2nd EdSami Rajput50% (2)
- 9397physics Paper 2 (2012) With SolutionsDocument5 pages9397physics Paper 2 (2012) With SolutionsdannycbsNo ratings yet
- Rr310203 Power Systems IIDocument8 pagesRr310203 Power Systems IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Uee403 - High Voltage Engineering: University of Moratuwa, Sri LankaDocument3 pagesUee403 - High Voltage Engineering: University of Moratuwa, Sri LankaSarinda JayasingheNo ratings yet
- A2 Unit 4 Topic 2 Electric and Magnetic FieldsDocument13 pagesA2 Unit 4 Topic 2 Electric and Magnetic FieldsattzsdNo ratings yet
- EEE (May 2023)Document298 pagesEEE (May 2023)Durjoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Greconici PDFDocument7 pagesGreconici PDFDayan YasarangaNo ratings yet
- BSc Engineering Degree UEE403 AnswersDocument16 pagesBSc Engineering Degree UEE403 AnswersNipuna Lakmal WeerakkodyNo ratings yet
- HV Sheets (2015) A FDocument7 pagesHV Sheets (2015) A FMANS عسيريNo ratings yet
- Mock Test-3 CBSEDocument2 pagesMock Test-3 CBSEAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 07a51402-Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pages07a51402-Finite Element Methodswebs6000No ratings yet
- Reg No Manipal Institute of Technology ECE-207 ExamDocument2 pagesReg No Manipal Institute of Technology ECE-207 ExamShobhit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Ground CalculationDocument12 pagesGround CalculationafmNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1 Correct PubDocument8 pagesElectrical Machines 1 Correct PubJean-paul NgouneNo ratings yet
- Fourth Question (Total 15 Marks) 4) Answer The Following QuestionsDocument10 pagesFourth Question (Total 15 Marks) 4) Answer The Following QuestionsRadak RuduNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Transient Overvoltage Stresses On 132 KV Power Transmission NetworkDocument8 pagesEvaluation of The Transient Overvoltage Stresses On 132 KV Power Transmission NetworkIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Section5 1Document22 pagesSection5 1sonti11No ratings yet
- Evaluating Induced Voltages in PipelinesDocument9 pagesEvaluating Induced Voltages in PipelinessajuaanalsaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PHYSICSDocument5 pagesSample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PHYSICSAnirudh MuraliNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 3rd Partial NotesDocument18 pagesElectricity and Magnetism 3rd Partial NotesZoteloNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Revision BookletDocument19 pagesPhysics 2 Revision BookletkhadhiNo ratings yet
- Visual PreviewDocument4 pagesVisual PreviewjeovanevsNo ratings yet
- 2008 Final Exam PaperDocument9 pages2008 Final Exam PaperKurisu KrisNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP)Document4 pagesElectrostatic Precipitators (ESP)Ahmed Al-jouboriNo ratings yet
- P 9Document1 pageP 9szoylentgreenNo ratings yet
- IEEE-TPC Tutorial Line Losses 26 July 2010 Final2Document27 pagesIEEE-TPC Tutorial Line Losses 26 July 2010 Final2Dale DouglassNo ratings yet
- Uee403 - High Voltage Engineering: University of Moratuwa, Sri LankaDocument4 pagesUee403 - High Voltage Engineering: University of Moratuwa, Sri LankaSarinda JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Ferroresonance Susceptibility of Electrical NetworksDocument7 pagesFerroresonance Susceptibility of Electrical Networksmohammadi123456No ratings yet
- r05310203 Power Systems IIDocument8 pagesr05310203 Power Systems IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Electrical System Design-I EE782: Topic: Designing of A SubstationDocument25 pagesElectrical System Design-I EE782: Topic: Designing of A SubstationSantanu BhadraNo ratings yet
- Design of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using Ie3d SoftwareDocument5 pagesDesign of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using Ie3d SoftwareAnkitPatelNo ratings yet
- BEngTech Electrical/Mechanical/Industrial Engineering module testDocument3 pagesBEngTech Electrical/Mechanical/Industrial Engineering module testSims Gift ShibaNo ratings yet
- EE343 Energy Conversion 1 (First Midterm Exam Solutions) Spring2006Document7 pagesEE343 Energy Conversion 1 (First Midterm Exam Solutions) Spring2006Saied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Menoufia University Final Term Exam Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesMenoufia University Final Term Exam Power ElectronicsMaher Gomaa IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- NEET_2023_Solutions_Code_E1_db303618abfc1622fcf62f0c8f0d9fdbDocument25 pagesNEET_2023_Solutions_Code_E1_db303618abfc1622fcf62f0c8f0d9fdbankurkumar296296No ratings yet
- A.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Document6 pagesA.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Maulana MalikNo ratings yet
- R7 210205 Electromagnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesR7 210205 Electromagnetic FieldssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Problems Chapter 2-Ofc KeiserDocument6 pagesProblems Chapter 2-Ofc KeiserVentri Galuh DikaraNo ratings yet
- Report on calculating surface electric field strengthDocument9 pagesReport on calculating surface electric field strengthIsmail ÖzkanNo ratings yet
- University of Moratuwa, Sri Lanka: B. Sc. Engineering Degree Course Final Part III Examination 1996/97Document3 pagesUniversity of Moratuwa, Sri Lanka: B. Sc. Engineering Degree Course Final Part III Examination 1996/97Sarinda JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Potential ProblemsDocument5 pagesElectric Field and Potential ProblemsMahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Breakdown in Insulations 2011 Update - QuizDocument23 pagesBreakdown in Insulations 2011 Update - QuizKung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsFrom EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Supercapacitors As New Power Sources in Hybrid Energy Storage Systems For Electric VehiclesDocument4 pagesAn Overview of Supercapacitors As New Power Sources in Hybrid Energy Storage Systems For Electric VehiclesGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Energy Storage Review For Renewable Energy System Technologies and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesHybrid Energy Storage Review For Renewable Energy System Technologies and ApplicationsGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- A Review of Energy Storage System StudyDocument6 pagesA Review of Energy Storage System StudyGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: β=tan w σDocument1 pageFormula Sheet: β=tan w σGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Lab # 4 Time Response AnalysisDocument7 pagesLab # 4 Time Response AnalysisGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Motor Driver TestDocument1 pageMotor Driver TestGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Z Transform Analysis and Design Using MatlabDocument6 pagesLaplace and Z Transform Analysis and Design Using MatlabGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Switch Realization Methods for DC-DC Converter ProblemsDocument2 pagesSwitch Realization Methods for DC-DC Converter ProblemsBraxt MwIra GibecièreNo ratings yet
- Lab # 4 Time Response AnalysisDocument7 pagesLab # 4 Time Response AnalysisGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Type3CompensatorDesign PDFDocument6 pagesType3CompensatorDesign PDFGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Mood and Emotions in SportDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Mood and Emotions in SportGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Type3CompensatorDesign PDFDocument6 pagesType3CompensatorDesign PDFGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument1 pageLicenseHafeez AnsariNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Analysis of A Three-Phase Cycloconverter Under VariDocument87 pagesPower Quality Analysis of A Three-Phase Cycloconverter Under VariGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument22 pagesLab ManualGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Lecture3-Network Matrices, The Y-Bus Matrix Tap Changing TransformersDocument13 pagesLecture3-Network Matrices, The Y-Bus Matrix Tap Changing Transformersleo232No ratings yet
- EulaDocument1 pageEulaGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Bisun Duo XL 325 Duo enDocument2 pagesBisun Duo XL 325 Duo enGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Vocabooster Adjectives-1 Exercises by Celal YiğitDocument1 pageVocabooster Adjectives-1 Exercises by Celal YiğitGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Geeks3d Gputest LogDocument2 pagesGeeks3d Gputest LogGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram and Truth TableDocument3 pagesPin Diagram and Truth TableGökhan YüksekNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument2 pagesReadmeMae Sntg OraNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Technical Note: Microstepping Myths and RealitiesDocument4 pagesStepper Motor Technical Note: Microstepping Myths and Realitiesmixarim100% (1)
- InfiniSolar V II-3P-6KW-9KW-15KWDocument1 pageInfiniSolar V II-3P-6KW-9KW-15KWHusam Apoud100% (1)
- Requirement-Supply of Line Materials To TUMKUR Circle For FY 11-12 Till 24.02.2012Document27 pagesRequirement-Supply of Line Materials To TUMKUR Circle For FY 11-12 Till 24.02.2012Bescom GmprocurementNo ratings yet
- Physiological Effects of Electricity HazardsDocument26 pagesPhysiological Effects of Electricity HazardsMinh Thuan HuynhNo ratings yet
- Template QuizizzDocument6 pagesTemplate QuizizzFachri AbilfidaNo ratings yet
- 9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TDocument26 pages9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TpeterfunNo ratings yet
- UAA180 Based VU Meter - EEWeb CommunityDocument1 pageUAA180 Based VU Meter - EEWeb CommunityRicardo Alberto BarralNo ratings yet
- Wbut Measurement Question (EE402)Document7 pagesWbut Measurement Question (EE402)Debdeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Motorized Solutions For Interior BlindsDocument52 pagesMotorized Solutions For Interior BlindsMonty Va Al MarNo ratings yet
- Electrical safety checklist for working on high voltage equipmentDocument3 pagesElectrical safety checklist for working on high voltage equipmenttksundaravelNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Oxygen-Free Copper Cu-OF - Luvata Alloy OF-OKDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Oxygen-Free Copper Cu-OF - Luvata Alloy OF-OKMuhammad Asif IqbalNo ratings yet
- 3+2 Multiphase PWM Regulator For Intel Imvp8™ Desktop Cpus: DatasheetDocument2 pages3+2 Multiphase PWM Regulator For Intel Imvp8™ Desktop Cpus: DatasheetTomy Aditya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Split Phase Motor ExplainedDocument1 pageSplit Phase Motor ExplainedJenny MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Amateur Radio Licensing Examitation Question BankDocument183 pagesAmateur Radio Licensing Examitation Question BankSuvendu SahaNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Electronics ToolboxDocument1 pageBuild Your Own Electronics ToolboxLady Mae DomingoNo ratings yet
- Print View Options ECET Hall TicketDocument2 pagesPrint View Options ECET Hall TicketsareenckNo ratings yet
- 7 True/False Questions: Name: ScoreDocument4 pages7 True/False Questions: Name: ScoreAtharv GandhiNo ratings yet
- EEE342 - Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing: Lab Report # 06Document15 pagesEEE342 - Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing: Lab Report # 06Siddique Haider MashwaniNo ratings yet
- CD4016Document8 pagesCD4016api-3708997100% (1)
- Introduction To NI ELVISDocument136 pagesIntroduction To NI ELVISchrsolvegNo ratings yet
- McIntosh MDA5000 Car Source Mobile Digital To Analog ConvertorDocument2 pagesMcIntosh MDA5000 Car Source Mobile Digital To Analog ConvertorNicolus CageNo ratings yet
- LMV358Document25 pagesLMV358Roozbeh BahmanyarNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Electromagnetic Rotor Material PropertiesDocument4 pagesCharacterization of Electromagnetic Rotor Material PropertiesSteve OoiNo ratings yet
- Unit III Sensors and Machine VisionDocument120 pagesUnit III Sensors and Machine VisionVinoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft GFI Relay OperationDocument3 pagesAircraft GFI Relay Operationraghav787No ratings yet