Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Momentum
Uploaded by
Surya PrakashCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Momentum
Uploaded by
Surya PrakashCopyright:
Available Formats
HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will be able to...
understand that forces can act over time (impulse) resulting in changes in momentum identify characteristics of motion with respect to momentum in a collision distinguish between elastic and inelastic collisions state the Law of Conservation of Momentum SKILLS Students will be able to... use appropriate metric units for given measurements use steps for solving physics problems solve problems using mass, velocity, momentum and conservation of momentum for inelastic collisions conduct experiments relating to momentum collect and display experiment data develop models of inelastic collisions VOCABULARY Newtons Third Law momentum impulse law of conservation of momentum collision Impulse-Momentum theorem perfectly Inelastic collision HOMEWORK The Impulse-Momentum Change Theorem #1: Momentum, reading and homework #2: Momentum and Impulse Connection, reading and homework #3: Real-World Applications, reading The Law of Momentum Conservation #4: The Law of Action-Reaction (Revisited), reading and homework #5: Momentum Conservation Principle, reading #6: Isolated Systems, reading #7: Using Equations as a "Recipe", reading and homework 1, homework 2 #8: Using Equations as a Guide, reading and homework 1 #9: Momentum Conservation in Explosions, reading
CONTENT OUTLINE I. The Impulse-Momentum Change Theorem A. Momentum a. Defined b. Calculating B. Impulse a. Defined b. Calculating C. Relation between impulse and momentum The Law of Conservation of Momentum A. Connection to Newtons Third Law B. Momentum Conservation Principle C. Isolated Systems a. Collision and Impulse Problems b. Perfectly inelastic collisions in one dimension
II.
Chapter Questions 1. What is formula for momentum? What is the unit of momentum? 2. What is the difference between momentum and mass? 3. Which has greater mass, a bowling ball at rest or a rolling basketball? Which has greater momentum? 4. *Is linear momentum conserved, when two objects collide and stick together? Is kinetic energy conserved? 5. *Why, when you release an inflated but untied balloon, does it fly across the room? 6. *How can a rocket change direction when it is far out of space and is essentially in a vacuum? 7. *A boy stands in the middle of a perfectly smooth, frictionless, frozen lake. How can he set himself in motion? 8. *When rain falls from the sky, what happens to its momentum as it hits the ground? 9. *What is impulse? What is the unit of impulse? 10. *What is the difference between impulse and momentum? How does impulse relate to momentum? 11. *When a glass falls, will the impulse be greater if it lands on a plush carpet than if it lands on a hard floor? 12. *When a small car meshes with a large truck in a head-on collision, which of these two experiences greater change in momentum?
Chapter Problems Momentum of a Single Object 13. What is the momentum of a 3000 kg truck traveling at 25 m/s? 14. A 1500 kg ferryboat has a momentum of 25000 kgm/s. What is the speed of the ferryboat? 15. A car travels at a constant speed of 24 m/s and has a momentum of 28800 kgm/s. What is the mass of the car? 16. An 8 kg bowling ball rolls at a constant speed of 3 m/s. What is the momentum of the ball? 17. A bicyclist travels at a constant speed of 7 m/s. What is the total mass of the bicycle and the boy, when the total momentum is 490 kgm/s? 18. When a 45 kg cannon ball leaves a barrel it has a momentum of 14000 kgm/s. What is the speed of the ball at the end of the barrel? 19. A 45 kg woman runs at a speed of 5.6 m/s. What is her momentum? 20. A certain bowling ball rolls at a constant speed of 5 m/s. If the momentum of the ball is 42.5 kgm/s, what is its mass? 21. What is the speed of a 0.25 kg arrow with a momentum of 8 kgm/s? 22. A 1500 kg car travels 400 m in 12 s. What is its momentum? 23. An electron has a mass of 9.1x10-31 kg. What is its momentum if it is travelling at a speed of 3.5x106 m/s? 24. A 3 kg stone is dropped from a height of 4 m. What is its momentum as it strikes the ground? Momentum of a System of Objects 25. Determine the momentum of a system that consists of two objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 6 kg and a velocity of 13 m/s towards the east and a second object, m2, has a mass of 14 kg and a velocity of 7 m/s in that same direction. 26. Determine the momentum of a system that consists of two objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 6 kg and a velocity of 13 m/s in the direction of the positive x-axis and a second object, m2, has a mass of 14 kg and a velocity 7 m/s in the direction of the negative x-axis. 27. Determine the momentum of a system that consists of three objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 7 kg and a velocity 23 m/s towards the north, a second object, m2, has a mass of 9 kg and a velocity 7 m/s towards the north and the third object, m3 has a mass of 5 kg and a velocity of 42 m/s towards the south . 28. Determine the momentum of a system of the two objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 35 kg and a velocity of 3.7 m/s towards the east and the second object, m2, has a mass of 57 kg and a velocity of 4.3 m/s towards the west. 29. Determine the momentum of a system of the two objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 35 kg and a velocity of 3.7 m/s towards the north and the second object, m2, has a mass of 57 kg and a velocity of 4.3 m/s towards the south.
30. Determine the momentum of a system that consists of three objects. One object, m1, has a mass of 12 kg and a velocity 120 m/s towards the east, a second object, m2, has a mass of 25 kg and a velocity 18 m/s towards the west and the third object, m3 has a mass of 1 kg and a velocity of 350 m/s towards the east. Conservation of Momentum and Perfectly Inelastic Collisions 31. *A 13,500 kg railroad freight car travels on a level track at a speed of 4.5 m/s. It collides and couples with a 25,000 kg second car, initially at rest and with brakes released. What is the speed of the two cars after collision? 32. *A 40 kg girl skates at 3.5 m/s on ice toward her 65 kg friend who is standing still, with open arms. As they collide and hold each other, what is the speed of the couple? 33. *A 50 kg boy jumps off the front of a 1.5 kg skateboard moving forward. Find the skateboards velocity immediately after the boy jumps, assuming that the skateboards initial velocity is 3.5 m/s and the boys velocity when jumping off the front is 5 m/s. 34. *A 0.01 kg bullet has a speed of 700 m/s before it strikes a 0.95 kg wooden block that is stationary on a horizontal frictionless surface and remains inside of it. What is the speed of the block after the bullet becomes embedded in it? 35. *A cannon ball with a mass of 100 kg flies in horizontal direction with a speed of 600 m/s and strikes a railroad freight car filled with sand and initially at rest. The total mass of the car and sand is 25,600 kg. Find the speed of the car after the ball becomes embedded it the sand. 36. *A 0.01 kg bullet is fired at a 0.5 kg block initially at rest. The bullet, moving with an initial speed of 400 m/s, emerges from the block with a speed of 300 m/s. What is the speed of the block after the collision? 37. *A 50 kg boy jumps off the back of a 1.5 kg skateboard moving forward. Find the skateboards velocity immediately after the boy jumps, assuming that the skateboards initial velocity is 3.5 m/s and the boys velocity when jumping off the back is 5 m/s. 38. *Two football players with mass 85 kg and 110 kg run directly toward each other with speeds 4 m/s and 7 m/s respectively. If they grab each other as they collide, what is the combined speed of the players just after the collision? 39. *An air track car with a mass of 0.55 kg and velocity of 5.8 m/s to the right collides and couples with a 0.45 kg car moving to the left with a velocity of 3.9 m/s. What is the combined velocity of the cars just after the collision? 40. *An air track car with a mass of 0.25 kg and velocity of 3.4 m/s to the right collides and couples with a 0.45 kg car moving to the left with a velocity of 3.9 m/s. What is the combined velocity of the cars just after the collision? 41. *A 15000 kg railroad car travels on a horizontal track with a constant speed of 12 m/s. A 6000 kg load is dropped onto the car. What will be the cars speed? 42. *A 55 kg skater at rest on a frictionless rink throws a 3 kg ball, giving the ball a velocity of 8 m/s. What is the velocity of the skater immediately after?
43. *A 0.015 kg bullet is fired at a 1.5 kg block initially at rest. The bullet, moving with an initial speed of 500 m/s, emerges from the block with a speed of 400 m/s. What is the speed of the block after the collision? 44. *A 40 kg surfer jumps off the front of a 20 kg surfboard moving forward. Find the surfboards velocity immediately after the girl jumps, assuming that the surfboards initial velocity is 8 m/s and the girls velocity when jumping off the front is 3 m/s. 45. *A 40 kg surfer jumps off the back of a 20 kg surfboard moving forward. Find the surfboards velocity immediately after the girl jumps, assuming that the surfboards initial velocity is 8 m/s and the girls velocity when jumping off the back is 3 m/s. Elastic Collision Problems (without masses) 46. *Two objects have an elastic collision. Before the collision they approach one another with a velocity of 45 m/s. With what velocity will they be separating after the collision? 47. *Two objects, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +8.0 m/s and of m2 is -4.0 m/s. After the collision, the velocity of m1 is +5.0m/s. What is the velocity of m2? 48. *Two objects, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is -12.0 m/s and of m2 is +8.0 m/s. After the collision, the velocity of m1 is +9.0m/s. What is the velocity of m2? 49. *Two objects with identical masses, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +20 m/s and of m2 is +9.0 m/s. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m1? 50. *Two objects with identical masses, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +20 m/s and of m2 is +9.0 m/s. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 51. *Two objects have an elastic collision. The mass of m1 is much greater than that of m2, so that the velocity of m1 is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +10 m/s and m2 is initially at rest. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 52. *Two objects have an elastic collision. The mass of m1 is much greater than that of m2, so that the velocity of m1 is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of m2 is +10 m/s and m1 is initially at rest. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 53. *A bat has a nearly elastic collision with a baseball. The velocity of the bat is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of the bat is 10 mph and that of the baseball is 30 mph. What is the speed of the ball leaving the bat? 54. *Two objects have an elastic collision. Before the collision they approach one another with a velocity of 18 m/s. With what velocity will they be separating after the collision? 55. *Two objects, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +6.0 m/s and of m2 is +4.0 m/s. After the collision, the velocity of m1 is +5.0m/s. What is the velocity of m2? 56. *Two objects, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is -5.0 m/s and of m2 is +8.0 m/s. After the collision, the velocity of m1 is +7.0m/s. What is the velocity of m2? 57. *Two objects with identical masses, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is -9.0 m/s and of m2 is -3.0 m/s. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m1?
58. *Two objects with identical masses, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is -9.0 m/s and of m2 is -3.0 m/s. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 59. *Two objects have an elastic collision. The mass of m1 is much greater than that of m2, so that the velocity of m1 is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of m1 is +20 m/s and m2 is initially at rest. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 60. *Two objects have an elastic collision. The mass of m1 is much greater than that of m2, so that the velocity of m1 is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of m2 is +20 m/s and m1 is initially at rest. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m2? 61. *A bat has a nearly elastic collision with a baseball. The velocity of the bat is barely affected by the collision. The initial velocity of the bat is 25 mph and that of the baseball is 80 mph. What is the speed of the ball leaving the bat? Elastic Collision Problems (with masses) 62. *A ball of mass 0.34 kg moving with a speed of 2.7 m/s to the right collides head on with a 0.24 kg ball at rest. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after the collision? 63. *An ice puck of mass 0.54 kg moving with a speed of 5m/s to the right collides with a 0.28 kg piece of ice moving with a speed of 4.2 m/s to the right. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after the collision? 64. *An air track car with a mass of 0.75 kg and velocity of 8.5 m/s to the right collides elastically with a 0.65 kg car moving to the left with a velocity of 7.2 m/s. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after the collision? 65. *An air track car with a mass of 0.85 kg and velocity of 3.4 m/s to the right collides elastically with a 0.95 kg car moving to the left with a velocity of 4.9 m/s. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after the collision? 66. *A ball of mass 6.5 kg moving with a speed of 15 m/s to the right collides head-on with a 3.5 kg ball which is at rest. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after the collision? 67. *An ice puck of mass 7.5 kg moving with a speed of 18 m/s to the right collides with a 2.5 kg piece of ice moving with a speed of 4.2 m/s to the right. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each mass after the collision? Change of Momentum and Impulse 68. *A 1200 kg car accelerates from 13 m/s to 17 m/s. Find the change in momentum of the car. 69. *A small object with a momentum of 6 kgm/s to the west approaches head-on a large object at rest. The small object bounces straight back with a momentum of 5 kgm/s. What is the change in the momentum of the small object? What is the impulse exerted on the small ball? What is the impulse exerted on the large object? 70. *A 0.03 kg golf ball is hit off the tee at a speed of 34 m/s. The golf club was in contact with the ball for 0.003 s. What is the average force on ball by the golf club?
71. *A toy rocket achieves a velocity of 55 m/s after 3 s, when fired straight up. If the average force exerted by the engine is 28 N, what is the toys mass? 72. *A 15000 kg air jet accelerates from rest to 45 m/s before it takes off. What is the change in momentum of the jet? 73. *A 0.025 kg piece of clay is thrown into a wall and has a speed of 9 m/s before it strikes the wall. Find the change in momentum of the clay and the impulse exerted on the clay if it does not bounce from the wall. 74. *A small bouncy ball with a momentum of 8 kgm/s to the left approaches head-on a large door at rest. The ball bounces straight back with a momentum of 6 kgm/s. What is the change in the momentum of the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the door? 75. *A 0.07 kg tennis ball leaves a racket with a speed of 56 m/s. If the ball is in contact with the racket for 0.04 s, what is the average force on the ball by the racket? 76. *A 0.145 kg baseball reaches a speed of 36 m/s when a bat strikes. If the average force of 500 N was applied on the ball by the bat, what is the impact time? 77. *A 0.17 kg hockey puck slows down from 54 m/s to 35 m/s when it slides on horizontal ice surface. Find the change in momentum of the puck? 78. *A 0.01 kg bullet is fired at 250 m/s into a wooden block that is fixed. The bullet emerges from the block with a speed of 120 m/s. What is the change in momentum of the bullet? 79. *A 0.05 kg tennis ball moves at a speed of 10 m/s and is struck by a racket causing it to rebound in the opposite direction at a speed 16 m/s. What is the change in momentum of the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the ball? What is the impulse exerted on the racket? 80. *A 0.25 kg beach ball rolling at a speed of 7 m/s collides with a heavy exercise ball at rest. The beach ball bounces straight back with a speed of 4 m/s. That is the change in momentum of the beach ball? What is the impulse exerted on the beach ball? What is the impulse exerted on the exercise ball? 81. *A 0.16 kg hockey puck is moving on an icy horizontal surface with a speed of 5 m/s. A player strikes the puck by a hockey stick, after the impact the puck moves in opposite direction with a speed of 9 m/s. If the puck was in contact with the stick for 0.005 s, what is the average force on the puck by the stick? 82. *A constant force of 12 N acts for 5 s on a 5 kg object. What is the change in objects velocity? 83. *A small object with a mass of 1 kg moves in a circular path with a constant speed of 5 m/s. What is the change in momentum during of period; one period?
General Problems
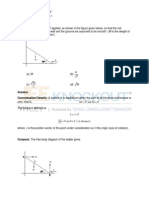
84. The diagram above shows a ballistic pendulum. A 10 g bullet is fired into the suspended 2 kg block of wood and remains embedded inside it (a perfectly inelastic collision). After the impact of the bullet, the block swings up to a maximum height h. If the initial speed of the bullet was 35 m/s: a. What was the momentum of the bullet before the collision? b. What was the kinetic energy of the bullet before the collision? c. *What was the velocity of the bullet-block system just after the collision? d. *What was the total kinetic energy of the bullet-block system after the collision? e. *What is the maximum possible potential energy of the bullet-block system when it reaches its maximum height? f. *What is the maximum possible height of the bullet-block system?
85. Two objects, A and B, with masses of 3.2 kg and 1.8 kg, move on a frictionless horizontal surface. Object A moves to the right at a constant speed of 5.1 m/s while object B moves to the right at a constant speed 1.4 m/s. They collide and stick together (a perfectly inelastic collision). a. Determine the total momentum of the system (both objects) before the collision b. Determine the total kinetic energy of the system before the collision c. *Find the speed of the two objects after the collision d. *Find the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision. e. *Is the kinetic energy of the system conserved? Explain.
86. A small cube, with a mass of 25 g, slides along a frictionless horizontal surface at a constant speed of 18 m/s until it collides with, and sticks to, a large wooden 3.5 kg block. The large block is attached to the left end of a spring with a spring constant of 100 N/m as shown above. a. What is the momentum of the cube before the collision? b. What is the kinetic energy of the cube before the collision? c. *Find the speed of the combined cube and block system just after the collision. d. *Find the kinetic energy of the cube-block system just after the collision. e. *What is the maximum potential energy that can be stored in the spring due to this collision? f. *How far will the cube-block system move before it stops?
87. A track consists of a frictionless incline plane, which is a height of 0.5 m, and a rough horizontal section with a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.02. Block A, whose mass is1.5 kg, is released from the top of the incline plane, slides down and collides instantaneously and inelastically with identical block B at the lowest point. The two blocks move to the right through the rough section of the track until they stop. a. Determine the initial potential energy of block A. b. Determine the kinetic energy of block A at the lowest point, just before the collision. c. *Find the speed of the two blocks just after the collision. d. *Find the kinetic energy of the two blocks just after the collision. e. *How far will the two blocks travel on the rough section of the track?
f.
*How much work will the friction force do during this time?
88. A bullet of mass 0.01 kg is moving horizontally with a speed of 100 m/s when it hits a block of mass 2 kg that is at rest on a horizontal surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.4. After the collision the bullet becomes embedded in the block. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. What is the net momentum of the bullet-block system before the collision? What is the net momentum of the bullet-block system after the collision? *What is the speed of the bullet-block system after the collision? *Find the total energy of the bullet-block system before the collision? *Find the total energy of the bullet-block system after the collision? *Is the total energy conserved during the collision? *Find the maximum traveled distance of the bullet-block after the collision?
89. A 35 kg child moving at 5 m/s jumps onto a 40 kg sled that is initially at rest on a horizontal ice surface with the coefficient of friction of 0.02. a. Determine the total momentum of the child-sled system before the child jumps onto the sled. b. Determine the total momentum of the child-sled system after the child jumps onto the sled. c. *Determine the velocity of the child-sled system after the child jumps onto the sled. d. *Determine the total energy of the child-sled system before the child jumps onto the sled. e. *Determine the total energy of the child-sled system after the child jumps onto the sled. f. *Determine the maximum horizontal distance that child-sled can go after the child jumps onto the sled?
90. A 10 g piece of sticky clay moving horizontally with a speed of 12 m/s strikes a pendulum bob and sticks to the bob. The pendulum bob has a mass of 50 g and it is suspended from a 0.7 m string. a. Find the momentum of the clay before the collision. b. *Find the momentum of the clay-bob system after the collision. c. *Find the velocity of the clay-bob system after the collision. d. *Find the kinetic energy of the clay-bob system after the collision. e. *Find the maximum height of the clay-bob system that they deflect after the collision. f. *What velocity should the clay have before the collision in order for the clay-bob system to complete one circle?
91. As shown above, a 0.35 kg cart is moving on a horizontal, frictionless track with a speed of 5 m/s when it hits and sticks to a 1.6 kg cart initially at rest on the track. The 1.6 kg cart is connected to one end of a massless spring with a spring constant 80 N/m. a. b. c. d. e. f. Determine the momentum of the 0.35 kg cart before the collision. Determine the kinetic energy of the 0.35 kg cart before the collision. Determine the momentum of the carts after the collision. *Determine the kinetic energy of the carts after the collision. *Is the kinetic energy conserved during the collision? Explain you reasoning. *Determine the maximum displacement of the spring after the collision.
Practice Multiple Choice Questions 1. A freight car of mass 20,000 kg moves along a frictionless level railroad track with a constant speed of 15 m/s. What is the momentum of the car? A. 30,000 kgm/s B. 3,000 kgm/s C.300,000 kgm/s D. 3,000,000 kgm/s E. 300 kgm/s
2. A 500 kg sailboat moves with a momentum of 150,000 kgm/s? What is the velocity of the boat? A.300 m/s B. 3 m/s C. 30 m/s D. 3,000 m/s E. 30,000 m/s
3. The momenta of two different objects are presented by on the diagram. Which of the following is the net momentum of the system of two objects?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
4. The momenta of two different objects are presented by on the diagram. Which of the following is the net momentum of the system of two objects?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
5. A cannon fires a cannonball and recoils backward. Which of the following statements is true about the cannon recoil? A. It happens because the energy of the system is conserved B. It happens because the energy of the system is increased C. It happens because the momentum of the system is not conserved D. It happens because the momentum of the system is conserved E. It happens because the momentum of the system is increased
6. An air balloon hovers at a certain altitude above the ground. A pilot throws a sand bag down from the balloon. What is the direction of the balloons velocity just after the bag was thrown?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
7. What is the momentum of the cannon after firing a cannon ball with an initial momentum of 5,000 kgm/s to the right? A. 5,000 kgm/s to the right D. 2,500 kgm/s to the right B. 5,000 kgm/s to the left E. 2,500 kgm/s to the left C. zero
8. A platform moves at a constant velocity on a horizontal surface. What happens to the velocity of the platform after a sudden rain falls down? A. It increases because the energy is conserved B. It decreases because the energy is conserved C. It remains constant because the momentum is conserved D. It increases because the momentum is conserved E. It decreases because the momentum is conserved
9. A stationary skateboarder I with a mass of 50 kg pushes a stationary skateboarder II with a mass of 75 kg. After the push the skateboarder II moves with a velocity of 2 m/s to the right. What is the velocity of the skateboarder I? A. 3 m/s to the left B. 2 m/s to the left C. 1 m/s to the right D. 3 m/s to the right E. 2 m/s to the right
10. A loaded freight car A with a mass of 24,000 kg moves at a constant velocity of 8 m/s on a horizontal railroad track and collides with an empty stationary car B with a mass of 8,000 kg. After the collision the cars stick to each other and moves like one object. What is the velocity of two cars after the collision? A. 2 m/s B. 4 m/s C. 6 m/s D. 8 m/s D. 12 m/s
11. A 40 kg skateboarder runs at a constant velocity of 0.12 m/s and jumps of a stationary skateboard with a mass of 8 kg. What is the velocity of the skateboard after the jump? A. 0.12 m/s B. 0.90 m/s C. 0.60 m/s D. 0.20 m/s E. 0.10 m/s
12. An 80 kg diver jumps off a moving boat. The boat has a mass of 400 kg and moves at a constant velocity of 2 m/s. What is the velocity of the boat after the jump if the diver jumps with a velocity of 3 m/s in opposite direction to the initial velocity of the boat? A. 2 m/s B. 3 m/s C. 4 m/s D. 5 m/s E. 6 m/s
13. Block A with a mass 2m moves on a frictionless horizontal surface at a constant speed v and collides inelastically with B of mass m. What is the velocity of two blocks after the collision? C. v D. v E. v A. v B. v
14. Block A with a mass m moves on a frictionless horizontal surface at a constant velocity v and collides elastically with an identical block B. What is the velocity of block A after the collision? D. v E. v A. 0 m/s B. v C. v
15. Block A with a mass m moves on a frictionless horizontal surface at a constant velocity v and collides elastically with an identical block B. What is the velocity of block B after the collision? D. v E. v A. 0 m/s B. v C. v
16. A 10 kg object moves at a constant velocity 2 m/s to the right and collides with a 4 kg object moving at a velocity 5 m/s to the left. Which of the following statements is correct? A. The total momentum before and after the collision is 20 kgm/s B. The total momentum before and after the collision is 40 kgm/s C. The total momentum before and after the collision is 10 kgm/s D. The total momentum before and after the collision is 30 kgm/s E. The total momentum before and after the collision is zero
17. When two objects collide elastically the momentum is conserved. Which of the following is true about the kinetic energy during the collision? A. The kinetic energy is conserved B. The kinetic energy is lost C. The kinetic energy is gained D. The kinetic energy completely transforms into thermal energy E. More information is required 18. When two objects collide inelastically the momentum is conserved. Which of the following is true about the kinetic energy during the collision? A. The kinetic energy is conserved B. The kinetic energy is not conserved C. The kinetic energy is gained D. The kinetic energy completely transforms into thermal energy E. More information is required
19. A light beach ball moving with a velocity 2 m/s to the right collides elastically with a stationary bowling ball. After the collision the bowling ball remains stationary. What is the velocity of the beach ball after the collision? A. 0 m/s B. 2 m/s to the left C. 4 m/s to the left D. 3 m/s to the left E. 1 m/s to the left
20. A bowling ball moving with a constant speed v collides elastically with a stationary beach ball. After the collision the bowling ball barely slows down. What is an approximate speed of the beach ball after the collision? C. v D. 2v E. 3v A. v B. v
21. A big truck collides inelastically with a small car. Which of the following statements is true? A. The truck experiences the greater magnitude of impulse during the collision B. The car experiences the greater magnitude of impulse during the collision C. They experience the same magnitude of impulse during the collision D. The impulse of each object is zero during the collision E. More information is required
22. A tennis ball approaches a racket with a momentum of 5 kgm/s and bounces back with a momentum of 6 kgm/s after the collision with the racket. What is the change in momentum of the tennis ball? A. 1 kgm/s B. 5 kgm/s C. 6 kgm/s D. 11 kgm/s E. 0 kgm/s
23. A rubber ball moving with an initial momentum Pi collides elastically with a vertical wall. Which of the following is correct about the vector of impulse that the ball experiences during the collision?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
24. A piece of clay moving with an initial momentum Pi collides with a vertical wall and sticks to it. Which of the following is correct about the vector of impulse that the clay experiences during the collision?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
25. The force as a function of time is presented by the graph. What is the impulse exerted on the object during first six seconds? A. 40 Ns B. 80 Ns C. 120 Ns D. 240 Ns E. 360 Ns
Answers 1) 75,000 kgm/s 2) 16.7 m/s 3) 1200 kg 4) 24 kgm/s 5) 70 kg 6) 311 m/s 7) 252 kgm/s 8) 8.5 kg 9) 32 m/s 10) 50,000 kgm/s 11) 3.185x10-24 kgm/s 12) 26.6 kgm/s 13) 176 kgm/s 14) -20 kgm/s 15) 14 kgm/s 16) -115.6 kgm/s 17) -115.6 kgm/s 18) 1340 kgm/s 19) 1.58 m/s 20) 1.33 m/s 21) -46.5 m/s 22) 7.29 m/s 23) 2.33 m/s 24) 2 m/s 25) 286.83 m/s 26) -2.2 m/s 27) 1.435 m/s 28) -1.29 m/s 29) 8.57 m/s 30) -.44 m/s 31) 1 m/s 32) 18 m/s 33) 30 m/s 34) 45 m/s 35) 17 m/s 36) -11 m/s 37) 9 m/s 38) 20 m/s 39) 40) 41) 42) 43) 44) 45) 46) 47) 48) 49) 50) 51) 52) 53) 54) 55) 56) 10 m/s 10 m/s 40 mph 18 m/s 7m/s -6 m/s -3 m/s -9 m/s 40 m/s 20 m/s 130 mph V1f = .46 m/s V2f = 3.16 m/s V1f = 4.454 m/s V2f = 5.253 m/s V1f = -6.07 m/s V2f = 6.2475 m/s V1f = -5.36 m/s V2f = 2.791 m/s V1f = 4.5 m/s V2f = 19.5 m/s V1f = -11.1 m/s V2f = 24.9 m/s p=4800 kgm/s 71) p1/2 period = -10 kgm/s p1 period = 0 72) a) .35 Kgm/s b) 6.125 J c) .17 m/s d) .03 J e) .03 J f) .0015 m 73) a) 18.84 kgm/s b) 43.4 J c) 3.768 m/s d) 35.5 J e) No 74) a) .45 kgm/s b)4.05 J c).128 m/s d).0289 J e).0289 J f) .074m 75) a) 7.35 J b) 7.35 J c) 1.57 m/s d) 3.7 J e) 6.25 m f) 3.675 J 76) a) 1 kgm/s b) 1 kgm/s c) 0.5 m/s d) 50 J e) 0.25 J f) No g) 0.03 m 77) a) 175 kgm/s b) 175 kgm/s c) 2.33 m/s d) 437.5 J e) 203.584 J f) 13.84 m 78) a) 0.12 kgm/s b) 0.12 kgm/s c) 2 m/s d) 0.12 J e) 0.2 m f) 26.4 m/s 79) a) 1.75 kgm/s b) 4.375 J c) .897 kgm/s d) 0.78 J e) No f) 0.14 m
57) psmall = 11 kgm/s Ismall = 11 kgm/s Ilarge = -11 kgm/s 58) 340 N 59) 1.527 kg 60) 675,000 kgm/s 61) p = -.225 kgm/s I = -.225 kgm/s 62) p = 14 kgm/s IB = 14 kgm/s Idoor = -14 kgm/s 63) 98 N 64) .01044 s 65) -3.23 kgm/s 66) -1.3 kgm/s 67) p = -1.3 kgm/s Iball = -1.3 kgm/s Iracket = 1.3 kgm/s 68) p = -2.75 kgm/s IBB = -2.75kgm/s IEB = 2.75kgm/s 69) -448 N 70) 12 m/s
You might also like
- Momentum ProblemsDocument5 pagesMomentum ProblemsawbNo ratings yet
- JEE BooksDocument1 pageJEE BooksSurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Momentum WorksheetsDocument7 pagesMomentum WorksheetsRyan QuimoNo ratings yet
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - ScienceDocument57 pagesClass 9 - ScienceA AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualDocument100 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualMitchell Cifuentes100% (4)
- Momentum Worksheet PacketDocument10 pagesMomentum Worksheet PacketsmexiiloriNo ratings yet
- Raymondi and Boyd GraphDocument0 pagesRaymondi and Boyd Graphdsathiya100% (1)
- ch4 - 1d MomentumDocument8 pagesch4 - 1d Momentumapi-301275445No ratings yet
- Problems MomentumDocument9 pagesProblems Momentumpkhanna25No ratings yet
- Abp - Momentum Chapter Problems - 2019 02 28Document11 pagesAbp - Momentum Chapter Problems - 2019 02 28John SurdovalNo ratings yet
- Momentum ProblemsDocument14 pagesMomentum ProblemsHasmaye PintoNo ratings yet
- Abp Momentum Chapter Problems 2021-01-06Document11 pagesAbp Momentum Chapter Problems 2021-01-06whis2022No ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum Skill Based Problems 2023-10-28Document13 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum Skill Based Problems 2023-10-28whis2022No ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20Document14 pagesAp Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20黃吏維No ratings yet
- 7 Momentum HWDocument5 pages7 Momentum HWampay ayubNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument34 pagesMomentumGreenMatterNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion Holiday Home WorkDocument3 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Holiday Home Workanon_963134920No ratings yet
- Project in Science 9Document9 pagesProject in Science 9Susan Vivas MagpantayNo ratings yet
- 3.may Physics Notes and Practice ProblemsDocument2 pages3.may Physics Notes and Practice Problemsapi-309597212No ratings yet
- Moment, Impulse and MomentumDocument5 pagesMoment, Impulse and Momentumcarls burg a. resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Elastic and Inelastic Colls QsDocument4 pagesElastic and Inelastic Colls Qsqtkdn5dfryNo ratings yet
- Physiscs NumericalsDocument7 pagesPhysiscs Numericalsoscar wildeNo ratings yet
- Collisions & CM WorksheetDocument10 pagesCollisions & CM WorksheetMona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Collision PracticeDocument11 pagesCollision PracticeYohanes Ratnodiyanto100% (1)
- Momentum CW HW 1 Problems 2021-07-14Document16 pagesMomentum CW HW 1 Problems 2021-07-14whis2022No ratings yet
- MomentumDocument4 pagesMomentumijaddjuesNo ratings yet
- Unit VIII Worksheet 2 Name: - "Conservation of Momentum" PeriodDocument4 pagesUnit VIII Worksheet 2 Name: - "Conservation of Momentum" PeriodBhanu AdaveniNo ratings yet
- Elastic Inelastic CollisionsDocument3 pagesElastic Inelastic Collisionssaud ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam For Review 2019Document2 pagesMechanics Exam For Review 2019John Derick LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- 69Document5 pages69Josh Dominic TeleronNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Newton S 3 Laws 2014Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Newton S 3 Laws 2014Aditi BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Kinetic and Potential ProblemsDocument1 pageMechanical Kinetic and Potential Problemsnicolasenciso.alumNo ratings yet
- Blake Jewell - Chapter 3 Section 6 ClassworkDocument3 pagesBlake Jewell - Chapter 3 Section 6 Classworkapi-305220205No ratings yet
- Forces & Motion Classwork & Homework-2013!07!30Document10 pagesForces & Motion Classwork & Homework-2013!07!30Boldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- DC Honors Physics Final Exam Practice Problems - May 15Document6 pagesDC Honors Physics Final Exam Practice Problems - May 15webelo1998No ratings yet
- Conceptual QuestionsDocument4 pagesConceptual QuestionssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Worksheet - 4.4 CollisionsDocument2 pagesUnit 4 - Worksheet - 4.4 CollisionsTaylorNo ratings yet
- Physics! Unit 05 MTM Packet 2012Document12 pagesPhysics! Unit 05 MTM Packet 2012Kelly O'Shea100% (1)
- Momentum WorksheetDocument4 pagesMomentum WorksheetemilyNo ratings yet
- Fisica PCCNSDocument4 pagesFisica PCCNSMarieli FigueroaNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument5 pagesReviewejNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document3 pagesPhysics 1zebingwuNo ratings yet
- Impulse and MomentumDocument2 pagesImpulse and MomentumRyu Casper L DasilioNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Extra Study Questions: Short AnswerDocument109 pagesDynamics Extra Study Questions: Short Answeramitdeo99No ratings yet
- Work Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Document21 pagesWork Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Liam ReillyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- Gen PhysicsDocument6 pagesGen PhysicsKristina PazNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document2 pagesExercise 5ebina aomiNo ratings yet
- Force (WS)Document2 pagesForce (WS)Mukhlish PrihartonoNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Mamun ShahNo ratings yet
- Momenum Ws 3 - Elastic and Inelastic CollisionsDocument2 pagesMomenum Ws 3 - Elastic and Inelastic Collisionsdilini0% (1)
- Worksheet Science (Speed & Acceleration) : Each Questions Has 10 PointsDocument3 pagesWorksheet Science (Speed & Acceleration) : Each Questions Has 10 PointsJason AntonioNo ratings yet
- Foundational Physics Midterm ReviewDocument4 pagesFoundational Physics Midterm ReviewMichael ClarkNo ratings yet
- Physics Exercise Force and MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Exercise Force and MotionAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Concept Check #4Document3 pagesConcept Check #4zhan sunNo ratings yet
- Precalc 3Document28 pagesPrecalc 3ApichayaNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 6 - Test A: Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionDocument3 pagesPhysics Chapter 6 - Test A: Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionCamdrn WrightNo ratings yet
- 6 - 3 - Momentum FPS3Document2 pages6 - 3 - Momentum FPS3clxudsy.brownzNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems For KinematicsDocument43 pagesSample Problems For Kinematicsdavid jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion: Ans. (A) A Stone of The Same SizeDocument2 pagesForce and Laws of Motion: Ans. (A) A Stone of The Same SizeMonika SanghviNo ratings yet
- Resonance DPPDocument25 pagesResonance DPPSurya Prakash67% (3)
- AITS PT II MainDocument21 pagesAITS PT II MainSurya Prakash100% (1)
- Aits PT IiDocument27 pagesAits PT IiSurya Prakash50% (2)
- 11studying Batch Question Paper (22. 12 08)Document2 pages11studying Batch Question Paper (22. 12 08)Pawan BabelNo ratings yet
- Solving Friction ProblemsDocument6 pagesSolving Friction ProblemsSurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument46 pagesAnalytical GeometryChinmay SwainNo ratings yet
- General Instructions For Kvpy Test Paper (Stream-Sa) YEAR: 2011Document13 pagesGeneral Instructions For Kvpy Test Paper (Stream-Sa) YEAR: 2011Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Bodies in Equilibrium: Physics Question - 52Document2 pagesBodies in Equilibrium: Physics Question - 52Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Solving Friction ProblemsDocument6 pagesSolving Friction ProblemsSurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- At 1314 Sample Paper IX - Going To X - IQ+S&M - AIEEEDocument15 pagesAt 1314 Sample Paper IX - Going To X - IQ+S&M - AIEEENaveen ShettyNo ratings yet
- Electric Drive Systems: What Is A Drive System?Document10 pagesElectric Drive Systems: What Is A Drive System?Emirhan AlmaNo ratings yet
- DownloadLecture 9 - Second Law Corollaries, Thermodynamic Temperature ScaleDocument4 pagesDownloadLecture 9 - Second Law Corollaries, Thermodynamic Temperature Scaleeuglena6No ratings yet
- 2 Steam TurbineDocument46 pages2 Steam TurbineWahyu MxNo ratings yet
- Shindengen: Super Fast Recovery RectifiersDocument7 pagesShindengen: Super Fast Recovery RectifiersCharbel TadrosNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 Projectile Motion: Vertical PositionDocument28 pagesPhysics Grade 11 Projectile Motion: Vertical Positionsrinidhi innaniNo ratings yet
- EM&IDocument34 pagesEM&IAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- High Frequency High VoltageDocument13 pagesHigh Frequency High VoltageSharif UllahNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuit AnalysisDocument20 pagesDiode Circuit AnalysisAsmaa WajeahNo ratings yet
- 0625 w15 Ms 33Document7 pages0625 w15 Ms 33Hany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Service Code in Electrical System (Short-Circuiting in Governor Motor Phase A and Phase B) E318Document2 pagesService Code in Electrical System (Short-Circuiting in Governor Motor Phase A and Phase B) E318ariy yuli styawanNo ratings yet
- 2016 Dse Phy 1Document31 pages2016 Dse Phy 1RAKIB AL MAHDINo ratings yet
- Wiley - Power System Relaying, 4th Edition - 978!1!118-66200-7Document2 pagesWiley - Power System Relaying, 4th Edition - 978!1!118-66200-7Aung Kyaw KhineNo ratings yet
- 7I Energy ResourcesDocument25 pages7I Energy ResourcesChristineNo ratings yet
- Switched Mode Regulated Power Supply (SMPS)Document36 pagesSwitched Mode Regulated Power Supply (SMPS)Vipin NathNo ratings yet
- Mi3290 Earth Analyser DatasheetDocument4 pagesMi3290 Earth Analyser DatasheetErick LopezNo ratings yet
- Martin de WitDocument200 pagesMartin de WitDimitris Sampatakos100% (1)
- Electro Magnetic Theory and Transmission - 1Document2 pagesElectro Magnetic Theory and Transmission - 1Ravindra NathNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- MD 1 Final Exam 2nd Sem 2021Document3 pagesMD 1 Final Exam 2nd Sem 2021Grido FinoNo ratings yet
- Product Specsheet PD SGS New 3 Button VersionDocument2 pagesProduct Specsheet PD SGS New 3 Button VersionjuanmalegreNo ratings yet
- wph12 01 Rms 20190815Document16 pageswph12 01 Rms 20190815NairitNo ratings yet
- ErrorsDocument8 pagesErrorsnorhazli ibrahimNo ratings yet
- L C R Circuit Series and Parallel1Document6 pagesL C R Circuit Series and Parallel1krishcvrNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Chemistry Matter and MeasurementDocument13 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Chemistry Matter and MeasurementMichael Jerwin AbellaNo ratings yet
- LADS Modular 1K Online UPS ManualDocument27 pagesLADS Modular 1K Online UPS ManualSab BahNo ratings yet
- 3x25mm FCU-PVC-PVC 1 KV (TD)Document2 pages3x25mm FCU-PVC-PVC 1 KV (TD)HaikalNo ratings yet
- Final Coaching 4Document12 pagesFinal Coaching 4Cliff Sotto Omayan100% (1)
- Chap 14P Semiconductor Devices & Digital Circuits Arvind 2023Document93 pagesChap 14P Semiconductor Devices & Digital Circuits Arvind 2023Yash JoshiNo ratings yet