Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Cell Observations
Uploaded by
Dwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Cell Observations
Uploaded by
Dwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'Copyright:
Available Formats
BLOOD CELL OBSERVATIONS
Purpose Problem Formulation Hypothesis
: to watch the red blood cell and white blood cell. : How is the red blood cell and white blood cell? : in the blood cell, there is a lot of red blood cell, and little white blood cell that have blue color because white blood cell absorb the color of methylene blue. :
Based theory
We have about 5 dm3 of blood in our body, weighting about 5 kg. Suspended in the blood plasma, we have around 2.5 x 1013 red blood cells, 5 x 1011 white blood cell and 6 x 1012 platelets. Red blood cells are also called erythrocytes, which simply means red cells. Their red color is caused by the pigment hemoglobin, a globular protein. Red blood cells are very small. The diameter of a human red blood cell is about 7m. Red blood cells are shaped like a biconcave disc. White blood cells are sometimes known as leucocytes, which just means white cells. Most white blood cells are larger than red blood cells. White blood cells are either spherical or irregular in shape. White blood cell have ability to absorb color substance.
Tools and materials : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Glass object Glass cover Microscope Pipette Methylene blue 6. Cotton 7. Alcohol 70% 8. Blood lancet 9. Blotting paper / tissue 10. Toothpick
Procedure : 1. Dampening cotton with alcohol 70%, then wiping to the tip of finger. 2. Sticking the fingertip by using blood lancet. 3. Putting the blood on the glass objects and then dropping a little methylene blue. When methylene blue excess, blotting with tissue/ blotting paper and flattening with a toothpick. 4. Closing blood with glass cover, and then observing under a microscope. 5. Documenting the observations. 6. Creating reports results of the experiment.
Experiment Table :
Data analyze :
Conclusion :
OBSERVATIONS OF BLOOD GROUPS
Purpose Problem Formulation Hypothesis Based theory
: to determine ABO blood group system and Rhesus system. : how to determine ABO blood system and Rhesus system. : :
A blood group is
Tools and Materials 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cotton Alcohol Blood lancet Agglutinin A/ anti-A substances Agglutinin b/ anti-B substances Anti-D / Rhesus Toothpick Glass object (3)
Procedure :
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
7. 8.
Dampening cotton with 70% alcohol Sticking the fingertip by using blood lancet Putting the blood on the three of glass objects. Squirting agglutinin A in the blood which is in the glass tops objects. Then, stirring with a toothpick. Observing what happens( clotting or not). Squirting agglutinin B in blood which is in the second object glass. Stirring it with toothpick. Observing what happens. Putting anti-D in the blood which is in the third object glass. Stirring in long time with toothpick. Observing what happens. If there clotting, so the rhesus is positive. And if there is no clumping, so the rhesus is negative. Documenting the observations. Creating the report of the experiment.
Experiment Table :
Data Analyze :
Conclusion :
EFFECT OF ACTIVITY ON PULSE BEAT
Purpose Problem Formulation Hypothesis Variable Manipulation Control Response Based theory
: to determine the influence of activity on the pulse. : How the influence of activity to the pulse beat? : if the activity get harder, so the pulse beat will increase. : : kind of activity : the human, the time of activity : the pulse beat :
Tools and Materials : 1. Stopwatch 2. A human Procedure : 1. Calculating the veins throbbing in 1 minute by holding the wrist with three fingers(not thumb and little finger) before doing the activity. Then doing the same for 1 minute second, and 1 minute third. After that, calculating the average. 2. Doing the activity : a. Up and down stairs for 5 minutes. Calculating the pulse first in 1 minute, 1 minute second, and third. After that, calculating the average. b. Jogging for 5 minutes. Calculating the pulse first in 1 minute, 1 minute second, and third. After that, calculating the average. c. Jumping in place for 5 minutes. Calculating the pulse first in 1 minute, 1 minute second, and third. After that, calculating the average. 3. Recording all results in the table. 4. Creating a report of the experiment. Experiment table :
Data Analyze :
Conclusion :
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoGlenn_Ancheta_2074100% (1)
- 2) Strategy Analysis.& FormulationDocument51 pages2) Strategy Analysis.& FormulationDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Introduction to Engineering Systems and System DynamicsDocument27 pagesIntroduction to Engineering Systems and System DynamicsDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ErgonomicsDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Ergonomicsdumiran18No ratings yet
- Cell Components: See This VideoDocument28 pagesCell Components: See This VideoDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- BuildingDocument34 pagesBuildingDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Out 4Document17 pagesOut 4Dwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- 2) Strategy Analysis.& FormulationDocument51 pages2) Strategy Analysis.& FormulationDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Proceedings of The Institution of Mechanical Engineers Mar 2005 219, 3 Proquest Science JournalsDocument1 pageProceedings of The Institution of Mechanical Engineers Mar 2005 219, 3 Proquest Science JournalsDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Out 3Document7 pagesOut 3Dwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- DevelopmentDocument18 pagesDevelopmentkashifbutty2kNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument7 pagesJurnalDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Origami DragonDocument3 pagesOrigami DragonThauffig ExjerkNo ratings yet
- BREATHING & GASES EXCHANGEDocument7 pagesBREATHING & GASES EXCHANGEKankana Biswas100% (1)
- Temperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsDocument24 pagesTemperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsKiran Hassan0% (1)
- Lab 8Document6 pagesLab 8Naz PulatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of PCAPDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of PCAPMads0% (1)
- The essential components and functions of human bloodDocument51 pagesThe essential components and functions of human bloodAlvinTercianoVitugNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory and Circulatory System Ver FinalDocument33 pagesScience 9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory and Circulatory System Ver FinalNoah SmithNo ratings yet
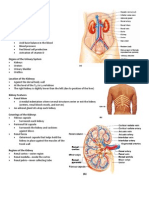
- Handouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Document7 pagesHandouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Kelly Trainor100% (2)
- 3edited My Class Note 1 On Blood BankDocument46 pages3edited My Class Note 1 On Blood BankmatewosNo ratings yet
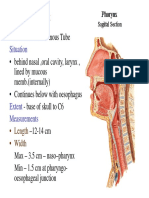
- H & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFDocument17 pagesH & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFRamin AmirkhiziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Prepared By: Mark Christian N. LunaDocument28 pagesLesson 1: Prepared By: Mark Christian N. LunaJohn Mark CelosaNo ratings yet
- Lab ResultDocument1 pageLab Resultrakibul islamNo ratings yet
- CSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesCSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetC ROBERTSNo ratings yet
- Trazodone InsomniaDocument5 pagesTrazodone InsomniaShahriar NiloyNo ratings yet
- DLL - SCIENCE - Q2 - W2Document8 pagesDLL - SCIENCE - Q2 - W2Carole FuentesNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Pola Tidur Pada Kelompok Usia Lanjut Dan PenatalaksanaannyaDocument9 pagesGangguan Pola Tidur Pada Kelompok Usia Lanjut Dan PenatalaksanaannyaEntri Sulistia ParirakNo ratings yet
- Basic Nursing Skills: Nurse CourseDocument46 pagesBasic Nursing Skills: Nurse CoursedatmojoNo ratings yet
- Indah Yulianti - 012011041 - Kep A1'20 - Resume Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesIndah Yulianti - 012011041 - Kep A1'20 - Resume Respiratory SystemIndah YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Exer 11Document9 pagesExer 11Matthew DenusNo ratings yet
- SBL Report7Document10 pagesSBL Report7api-383715002No ratings yet
- Digestive System Lab ReportDocument6 pagesDigestive System Lab Reportapi-296590009No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Biology - Transportation in Human BeingsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Biology - Transportation in Human BeingsmrneetgamerNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- OV - Basic Anatomy and FunctionDocument25 pagesOV - Basic Anatomy and FunctionhpmonkeyzNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Functions Immune ProtectionDocument4 pagesLymphatic System Functions Immune ProtectionMelljonhNo ratings yet
- No Significant Correlation Between Procalcitonin and Leukocyte Levels in Sepsis PatientsDocument4 pagesNo Significant Correlation Between Procalcitonin and Leukocyte Levels in Sepsis PatientsIlham Habib DjarkoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Student Version The Respiratory System 2020.ppt (1186)Document18 pagesChapter 13 Student Version The Respiratory System 2020.ppt (1186)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation: Mammals Are EndothermicDocument4 pagesThermoregulation: Mammals Are EndothermicSamraNo ratings yet
- Affinities of CyclostomesDocument11 pagesAffinities of Cyclostomesalmas shaikhNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology of SleepDocument37 pagesNeurophysiology of SleepTripat SinghNo ratings yet