Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of Software System
Uploaded by
cap2010Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of Software System
Uploaded by
cap2010Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF PROFESSIONAL STUDIES, ACCRA
Lecture 3
OVERVIEW OF SOFTWARE SYSTEMS
Lecture 3 -1
Learning Objectives
Describe several important trends occurring in computer software Give examples of several major types of application and system software Explain the purpose of several popular software packages for end user productivity and collaborative computing
Lecture 3 -2
Learning Objectives
Define and describe the functions of an operating system Describe the main uses of computer programming software, tools, and languages Describe the issues associated with open source software
Lecture 3 -3
Definition
A software is a set of machine-readable instructions that directs a computer's processor to perform specific operations. The term is used to contrast with computer hardware, which are the physical objects (processor and related devices) that carry out the instructions. Hardware and software require each other; neither has any value without the other
Lecture 3 -4
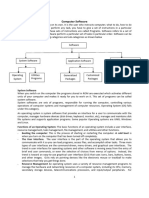
Types of Software
There are 2 main types of software. They are the Application software and System Software. The application software performs information processing task for end-users such as preparation documents and or calculation of figures. The system software System software is a type of computer program that is designed to run a computers hardware and applications such as word processors
Lecture 3 -5
Types of Software
Types of Application Software
General Application: As the name implies they are software that anybody at can use for either business or personal purposes, e.g word processor, browser etc Application Specific: These are software used for specific business purposes. Individuals normally do not use these applications. They include marketing and accounting software
Lecture 3 -6
Types of Software
Types of System Software
System Management Software. It enables IT support staff to manage network systems. They include server software, Operating systems, Database Management systems System Development Software: It enables IT staff to develop software applications such as e-commerce software, websites, banking and finance software. Experts who develop these software are called programmers or software developers. They use programming software such as HTML, Java and Java Script Lecture 3 -7
Types of Application & System Software
Lecture 3 -8
Examples of Business Application Software
Application Specific Software Customer Relationship Management Human Resource Supply Chain Management Web-enabled electronic commerce
Lecture 3 -9
Examples of General Purpose Software
Software Suites Browsers Search Engines E-mail/Instant Messaging Word Processing/Desktop Publishers Spread Sheets/Presentation Graphics Personal Information Managers Groupware
Lecture 3 -10
Software Suites, Integrated Packages
A software suite or Integrated software package is software that merges several applications in one program and is accessed via a common launching pad. They typically provide at least word processing, spreadsheet and database management, presentation graphics, page layout, paint, calendar, address book, e-mail as well as other applications.
Lecture 3 -11
Examples of Top Software Suites
Lecture 3 -12
Web Browsers
Software used to locate, retrieve and also display content on the World Wide Web It is the universal platform from which end users launch Information searches E-mail Multimedia file transfer Discussion groups Other Internet-based applications
Lecture 3 -13
Search Engines
Computer program that searches databases and internet sites for the documents containing keywords specified by a user.
Google, Ask Jeeves, Look Smart (Business), Lycos, Overture, Yahoo! Using search engines to find information has become an indispensable part of Internet, intranet, and extranet applications
Lecture 3 -14
E-mail, Instant Messaging
E-mail
Sending and receiving messages and attachments via the Internet, intranet, or extranet
Instant messaging (IM)
A software that allows users connected to the Internet or a corporate network to send text messages and files between other IM users e.g is Yahoo messenger, Google Talk, Whatsapp, Skype,
Lecture 3 -15
Word Processing/Desktop Publishing
Word Processing
Software that enable a user to Create, edit, revise, and print documents E.g., Microsoft Word, Lotus WordPro, Corel WordPerfect
Desktop Publishing
Produce printed materials that look professionally published E.g., Adobe PageMaker, Microsoft Publisher, QuarkXPress
Lecture 3 -16
Electronic Spreadsheets
Used by virtually every business for calculations, analysis, planning, modeling Worksheet of rows and columns Can be stored on local computers or a network Requires designing format and developing the relationships (formulas) Most help you develop charts and graph displays of spreadsheet results Supports what-if questions
Lecture 3 -17
Presentation Graphics
Software that converts numeric data into graphics
Common presentation graphics packages
Microsoft PowerPoint, Lotus Freelance, Corel Presentations
Top packages can tailor files for transfer in HTML format to websites
Are used to create multimedia presentations of graphics, photos, animation, video
Lecture 3 -18
Personal Information Managers
Software for end user productivity and collaboration Stores information about clients Manages schedules, appointments, tasks Most have ability to access the Web and e-mail Some support team collaboration by sharing information with other PIM users e.g., Lotus Organizer, Microsoft Outlook
Lecture 3 -19
Groupware
Software that helps workgroups collaborate on group assignments
E-mail, discussion groups, databases, audio, and video conferencing E.g., Lotus Notes, Novell GroupWise, Microsoft Exchange Windows SharePoint Services and WebSphere both allow teams to create websites for information sharing and document collaboration
Lecture 3 -20
Cloud Computing
Software and virtualized hardware resources are provided as a service over the Internet. It is the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server. It advantages include:
No technology knowledge, expertise, or control needed. Pay-for-use avoids capital expenditures Capacity can be scaled upward almost instantly Immediate access to broad range of applications Contracts can generally be terminated Lecture at any time 3 -21
Software Licensing
A software is licensed, which involves Intellectual property rights Copyright and trademark Trade secrets So you dont buy software You buy a license to use the software Licensed to protect vendors property rights
Lecture 3 -22
System Software
System Management Programs
Manages hardware, software, network, and data resources of computer systems Operating systems, network management programs, database management systems, system utilities Helps users develop IS programs and procedures, and then prepare them for processing Includes language translators and editors, and programming tools
System Development Programs
Lecture 3 -23
Operating Systems (OS)
It is system of programs that
Controls the input/out, storage resources, and activities of the computer system Provides support services as the computer executes application programs
Manages the operations of the CPU
Without an OS, all software applications cannot be operated
Lecture 3 -24
Operating Systems
There are two main types of Operating System. They are:
Desktop OS: It runs on a single desktop PC, or laptop . Examples are Windows XP and Windows 7. When that single PC or laptop is on a network, the OS enables the PC to access resources on a Server. Server OS: It runs on a server which is a higher capacity PC. Examples are Windows 2008 Server, Linux, and Unix
Lecture 3 -25
Popular Operating Systems
Windows
It has Graphical User Interface, multitasking, networking, multimedia Different versions manage servers
Standard, enterprise, data center, Web
Unix
Multitasking, multi-user, network-managing Portable - can run on mainframes, midrange, and PCs
Lecture 3 -26
Popular Operating Systems
Linux
Founded by Linus Torvalds Low-cost, powerful, reliable, Unix-like operating system Open-source
MAC OS X
Apple operating system for the iMac GUI Multitasking Multimedia
Lecture 3 -27
OS for Smartphone and Tablets Computers
ios by Apple Android by Google (Open Source) Symbian by Nokia ( Sold to Microsoft in August 2013) Windows Phone by Microsoft Bada meaning sea or ocean in Korean by Samsung
Lecture 3 -28
Open Source Software
Open-source software is computer software with its source code made available and which the copyright holder provides the rights to anyone to study, change and redistribute the software to anyone and for any purpose The basic idea is that when programmers can modify and redistribute source code, the software evolves quickly. This can happen at astonishing speed and produces better software than the traditional commercial (closed) model
Lecture 3 -29
Open-Source Licensing Characteristics
The License
The program must include the source code and allow distribution in source code as well as compiled form It shall not restrict any party from selling or giving away the software as a component of another software distribution. Must allow modifications and redistribution under the same terms as the license of the original software Must not discriminate against any person or any group of persons Must not restrict anyone from making use of the program in a specific field of endeavor
Lecture 3 -30
Examples of Open Source Software
Open Office
Can be used for any purpose: domestic, commercial, educational, or public administration. Made up of Writer, Calc, Impress, Draw and Base
Mac OS X
Based on a form of UNIX Advanced Graphical User Interface Supports multi-tasking and multimedia Integrated Web browser, e-mail, instant messaging, search engine, digital media player, and more Includes software development tools
Lecture 3 -31
System Monitoring Software
Utilities
Miscellaneous housekeeping functions Example: Norton utilities includes data backup, virus protection, etc.
Performance Monitors
Programs that monitor and adjust computer system to keep them running efficiently
Security Monitors
Monitor and control use of computer systems to prevent unauthorized use of resources
Lecture 3 -32
Programming Languages
Lecture 3 -33
Object-Oriented Languages
Most widely used software development languages
Easier to use and more efficient for graphicsoriented user interfaces Reusable: can use an object from one application in another application Examples: Visual Basic, C++, Java Most object-oriented languages provide a GUI that supports visual programming
Lecture 3 -34
Web Languages
HTML
A page description language that creates hypertext documents for the Web
Java
Object-oriented programming language that is simple, secure, and platform independent Java applets can be executed on any computer
Lecture 3 -35
Language Translator Programs
Translate instructions written in programming languages into machine language
Assembler Translates assembler language statement
Compiler Translates highlevel language statements
Interpreter A compiler that translates and executes each statement in a program, one at a time
Lecture 3 -36
Programming Tools
Help programmers identify and minimize errors while they are programming
Graphical programming interfaces Programming editors Debuggers
Lecture 3 -37
END OF LECTURE
Lecture 3 -38
You might also like
- Computer Software Class NotesDocument7 pagesComputer Software Class Notesgerrad cortezNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals (Midterm)Document4 pagesComputer Fundamentals (Midterm)JanJan AbuzoNo ratings yet
- SOFTWARE BASICS LESSON 2Document6 pagesSOFTWARE BASICS LESSON 2Prody LacasaNo ratings yet
- ITB Part 02a SoftwareDocument16 pagesITB Part 02a Softwaretalha gillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Software OverviewDocument14 pagesChapter 5 Software Overviewmunashe francisNo ratings yet
- Application Software (App For Short) IsDocument22 pagesApplication Software (App For Short) Isjayagokul saravananNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument3 pagesComputer SystemEmmanuel SaweNo ratings yet
- Software and Operating Systems (Document19 pagesSoftware and Operating Systems (izzieraeyNo ratings yet
- Computer Software-ICT ClassDocument4 pagesComputer Software-ICT Classkentbabayson15No ratings yet
- Assignment Work DocumentDocument6 pagesAssignment Work DocumentKarabo moetiNo ratings yet
- Software Concepts ExplainedDocument30 pagesSoftware Concepts ExplainedJustin Ryan DisquitadoNo ratings yet
- Salahaddin University-Erbil Collage of Arts Social Work Department SoftwareDocument9 pagesSalahaddin University-Erbil Collage of Arts Social Work Department SoftwareZA IDNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Computer SoftwareDocument12 pagesLesson 6 - Computer SoftwareErick KadohNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Computer SoftwareDocument27 pagesUnit - 3 Computer SoftwareSanket GangalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document4 pagesChapter 4ShohagNo ratings yet
- Software: Presented By: Group 3Document25 pagesSoftware: Presented By: Group 3Pauline BobisNo ratings yet
- Software: Program Studi Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Sains Dan Teknologi Universitas Teknologi Yogyakarta 2010Document9 pagesSoftware: Program Studi Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Sains Dan Teknologi Universitas Teknologi Yogyakarta 2010LUTVIINo ratings yet
- Learning GuideDocument19 pagesLearning GuidehakiNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesPage 1 of 6Æbeni DaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Software PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Software PDFPoonam GiteNo ratings yet
- TCC ReviewerDocument10 pagesTCC Revieweryohan gauranaNo ratings yet
- in PeoplewareDocument40 pagesin PeoplewareGlenda C. Flores0% (1)
- There Are Three Basic Components of System Software That You Need To Know AboutDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Basic Components of System Software That You Need To Know AboutJPIA Scholastica DLSPNo ratings yet
- Installation Software and ApplicationDocument20 pagesInstallation Software and ApplicationKiya Abdi100% (3)
- Topic 3 - ReviewDocument12 pagesTopic 3 - ReviewRahul NarayanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Application Software and Software IssuesDocument23 pagesPresentation On Application Software and Software Issuesginish12No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document3 pagesLecture 1Samita MukeshNo ratings yet
- Homework No.1 OF System Programming: Submitted To: Submitted By: Mandeep Kaur Surendra Mca 4 SEM D3804A15 10806601Document9 pagesHomework No.1 OF System Programming: Submitted To: Submitted By: Mandeep Kaur Surendra Mca 4 SEM D3804A15 10806601Surendra Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Software: Scope of The ModuleDocument25 pagesThe Software: Scope of The Modulejane quiambaoNo ratings yet
- MO 01 Business Technology and Equpment TTLMDocument13 pagesMO 01 Business Technology and Equpment TTLMDebebe DanielNo ratings yet
- Name: Syeda Laiba Zaidi STUDENT ID: 62759 Course: Sab Instructor: Muhammad Waqas Pasha Assignment No: 01Document7 pagesName: Syeda Laiba Zaidi STUDENT ID: 62759 Course: Sab Instructor: Muhammad Waqas Pasha Assignment No: 01Laiba ZaidiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 1PGDCA1 1DCA1 EnglishDocument21 pagesUNIT-3 1PGDCA1 1DCA1 EnglishVikram ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Install Software Application Lo1Document20 pagesInstall Software Application Lo1Mebratu Goa ThyNo ratings yet
- ITB. 4 NewDocument32 pagesITB. 4 NewRb REJANNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document52 pagesLesson 1Bernadette Concepcion Abo-aboNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document11 pagesModule 8bscomputersciencelsstiNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER APPLICATION PACKAGES 1 Notes-1Document51 pagesCOMPUTER APPLICATION PACKAGES 1 Notes-1Abubakarabdulrazaq17No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - SoftwareDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - SoftwareMaurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Ilide - Info LM Lesson 8Document14 pagesIlide - Info LM Lesson 8laikhadasoxxNo ratings yet
- CProgchap 1notesDocument11 pagesCProgchap 1notesraghavNo ratings yet
- Review Questions For Chapter 5 Business Information SystemsDocument3 pagesReview Questions For Chapter 5 Business Information Systemsrobj20076404No ratings yet
- History of SoftwareDocument8 pagesHistory of SoftwareASHLEY SUSANA URBINANo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers - Software Concepts PDFDocument4 pagesBasics of Computers - Software Concepts PDFMarz CasipongNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument6 pagesComputer Softwarepowelljean16No ratings yet
- Managers Overview: CreateDocument47 pagesManagers Overview: CreateahmadfirozNo ratings yet
- TEJ2O Day 11 - Software - 2020Document18 pagesTEJ2O Day 11 - Software - 2020mike simsonNo ratings yet
- Week 04 MISDocument44 pagesWeek 04 MISbayzidNo ratings yet
- Operating System - Study MaterialDocument6 pagesOperating System - Study MaterialShreya MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument18 pagesComputer SoftwareArtur100% (56)
- Education Technology II DOcumentationDocument4 pagesEducation Technology II DOcumentationMylene Sunga AbergasNo ratings yet
- Types of Software - System & ApplicationDocument7 pagesTypes of Software - System & Applicationyleno_meNo ratings yet
- Software and Its EvolutionDocument11 pagesSoftware and Its EvolutionPraveen Kumar NalliNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument22 pagesComputer SoftwareAli SyedNo ratings yet
- Types of computer softwareDocument3 pagesTypes of computer softwareROLLIN RAMUS NDAYO FONTENGNo ratings yet
- Assignments: Subject Code - MI0024 MBA - III Semester (3credits) Set 1 Marks 30 Subject Name-Software EngineeringDocument6 pagesAssignments: Subject Code - MI0024 MBA - III Semester (3credits) Set 1 Marks 30 Subject Name-Software EngineeringSelvakani KandeebanNo ratings yet
- Application Software, Also Known As An Application or An "App", Is ComputerDocument2 pagesApplication Software, Also Known As An Application or An "App", Is ComputerGrace Bogbog-CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Course Name: Information Technology For Business Value Course Code: BUS 7103 Submitted ToDocument8 pagesAssignment: Course Name: Information Technology For Business Value Course Code: BUS 7103 Submitted ToRashmi RiztanNo ratings yet
- Operating System.: Information DataDocument11 pagesOperating System.: Information DataHaider Ali MinhasNo ratings yet
- Disposal of All Electrical Equipment at Bisa Nyame Shop Opposite Sabo Zongo Market Stores - AccraDocument1 pageDisposal of All Electrical Equipment at Bisa Nyame Shop Opposite Sabo Zongo Market Stores - Accracap2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document51 pagesChapter 03cap2010No ratings yet
- Hardware & Networking NotesDocument75 pagesHardware & Networking Notesvsprasad5969% (16)
- 14 CM0340 SummaryDocument7 pages14 CM0340 Summarycap2010No ratings yet
- Digital Audio EffectsDocument47 pagesDigital Audio Effectscap2010100% (1)
- Overview of Computer Graphics & Multimedia: © 2008 Prentice-Hall, IncDocument49 pagesOverview of Computer Graphics & Multimedia: © 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inccap2010No ratings yet
- Audio SynthesisDocument80 pagesAudio Synthesiscap2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: SQL: ©silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan 4.1 Database System ConceptsDocument98 pagesChapter 4: SQL: ©silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan 4.1 Database System Conceptscap2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document26 pagesChapter 06cap2010No ratings yet
- Welcome: - IntroductionDocument7 pagesWelcome: - Introductioncap2010No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabuscap2010No ratings yet
- Welcome: - IntroductionDocument7 pagesWelcome: - Introductioncap2010No ratings yet
- MultimediaDocument18 pagesMultimediagurudatha265100% (3)
- Computer Graphics and MultimediaDocument11 pagesComputer Graphics and Multimediacap2010No ratings yet
- 01 RasterDocument7 pages01 Rastercap2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Multimedia Authoring and ToolsDocument50 pagesChapter 02 - Multimedia Authoring and Toolsa_setiajiNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Security Threats To E-Commerce-Requirements DefinitionDocument8 pagesSecurity Threats To E-Commerce-Requirements Definitioncap2010No ratings yet
- Project AssignmentDocument2 pagesProject Assignmentcap2010No ratings yet
- Manage farm business info with MISDocument17 pagesManage farm business info with MISKisilu MbathaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Information Technology in IndustryDocument14 pagesApplications of Information Technology in Industryali_punjabian1957No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Programming Research PDFDocument10 pagesGrade 11 Programming Research PDFTanya MiyaNo ratings yet
- VMware Shortlist For Online TestDocument40 pagesVMware Shortlist For Online TestArushi ParasharNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technology Ict IgcseDocument3 pagesEmerging Technology Ict IgcseOsama Al-MadanatNo ratings yet
- Commodore 64 OmnibusDocument516 pagesCommodore 64 OmnibuslordbubsyNo ratings yet
- Computer, ScienceDocument16 pagesComputer, ScienceAnonymous Cw1DGmRfNo ratings yet
- Cpen 106 LecDocument4 pagesCpen 106 LecJaysonNo ratings yet
- Tracking System Monitors VehiclesDocument38 pagesTracking System Monitors VehiclesTommy Bui57% (7)
- Design Program Logic 1Document9 pagesDesign Program Logic 1lemuel sardualNo ratings yet
- Information Communication Technology: Answer All QuestionsDocument5 pagesInformation Communication Technology: Answer All QuestionsRishanRulzNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture NotesDocument45 pagesComputer Architecture Notesbt2O1O5131 AnshulNo ratings yet
- The Computer EnvironmentDocument12 pagesThe Computer EnvironmentJung jeonNo ratings yet
- 9609 w17 Ms 22Document19 pages9609 w17 Ms 22mrsundeepsNo ratings yet
- JAVA HandoutsDocument189 pagesJAVA HandoutsIbrar Gul YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Batuan Elementary School Enrollment SystemDocument22 pagesBatuan Elementary School Enrollment SystemRyan SuganobNo ratings yet
- Abb PCSDocument43 pagesAbb PCSSwathi KondaNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument5 pagesProject Proposalpapa zolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 ComprogDocument25 pagesLesson 6 ComprogmarkvillaplazaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Networks: What Is A Network?Document3 pagesThe Concept of Networks: What Is A Network?Ias Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary MemoryDocument23 pagesPrimary and Secondary MemoryALINo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Instructions Architecture SetDocument105 pagesChapter2 Instructions Architecture SetTrần Đăng KhoaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledLeomar AfallaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 17Document6 pagesĐỀ 17Nam Du NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Python Ch1Document37 pagesPython Ch1Kleven carl GindapNo ratings yet
- Engineering Technician Diploma ProgramsDocument4 pagesEngineering Technician Diploma ProgramsJadeLamorellNo ratings yet
- Course Descrption Fall 2018 BSITDocument311 pagesCourse Descrption Fall 2018 BSITHussainNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument6 pagesNetworksscribdNo ratings yet
- Siprotec 7sk80Document490 pagesSiprotec 7sk80Sunny SinghNo ratings yet
- BSC IT COURSE SYLLABUSDocument11 pagesBSC IT COURSE SYLLABUSKiambisNo ratings yet
- AfiFArm 3 05 InstallationDocument33 pagesAfiFArm 3 05 Installationgro_mirNo ratings yet