Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK SKEMA K1 K2 K3 SET B
Uploaded by
Cikgu FaizalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK SKEMA K1 K2 K3 SET B
Uploaded by
Cikgu FaizalCopyright:
Available Formats
PROGRAM PENINGKATAN PRESTASI AKADEMIK SPM
TAHUN 2013
SET B
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
Paper 1
1 D 26 A
2 B 27 B
3 A 28 D
4 C 29 B
5 B 30 C
6 A 31 A
7 C 32 C
8 D 33 B
9 B 34 B
10 C 35 A
11 C 36 C
12 B 37 A
13 C 38 C
14 A 39 C
15 D 40 A
16 B 41 C
17 D 42 A
18 A 43 D
19 D 44 B
20 C 45 A
21 B 46 A
22 A 47 D
23 B 48 A
24 A 49 B
25 B 50 A
FIZIK
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
PROGRAM PENINGKATAN PRESTASI AKADEMIK SPM
TAHUN 2013
SET B
FIZIK
Kertas 2
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
Peraturan pemarkahan ini mengandungi 10 halaman bercetak
Set B
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
2
PHYSICS
Paper 2
SECTION A
NO. MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
1 (a) State the sensitivity of the metre rule correctly
- 0.1 cm 1
(b) (i) State the diameter of five ball bearings correctly
- 3.1 cm 1
(ii) State the diameter of one ball bearing correctly
- 0.62 cm 1
(c) State the instrument correctly
- Vernier calipers // micrometer screw gauge 1 4
2(a) (i) State the explanation correctly 1
- energy is used to break the bonds//change the state of matter
(ii) State the explanation correctly 1
- energy is used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules
(b) Correct substitution 1
- 0.2 x 3.36 x 10
5
Correct answer and correct unit 1
- 6.72 x 10
4
J
(c) Mark on the box correctly 1
- There is no net transfer of energy between the water and the
surroundings
5
3(a) Name the mirror correctly 1
- convex mirror
(b) State the focal length correctly 1
- f = 10 cm
(c) Ray diagram draw correctly 1
- ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected and pass through the
principal focus
Marks the image correctly 1
- intersection of the ray with the given ray
(d) State two characteristics of the image correctly 2 6
- virtual / smaller (diminished) / upright
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
3
NO. MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
4(a) Name the process correctly
- Thermionic emission 1
(b) (i) Describe the motion correctly
- Uniform acceleration 1
(ii) Describe the motion correctly
- Uniform velocity 1
(c) (i) State the correct answer
- Alternating current 1
(ii) Calculate the period correctly
T = 3 x 0.02 = 0.06 s 1
State the frequency and unit correctly
f =
1
T
=
1
0.06
= 16.7 Hz
1
(iii) Sketch the waveform correctly
- Sinusoidal with one complete cycle 1 7
NO. MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
5(a) (i) State the function correctly
- To supply heat 1
(ii) State the comparison of reading correctly
- Same 1
(iii) State the explanation correctly
- Heat is used to break the bonds/weaken the force of attraction 1
(b)
State two common characteristics correctly
0.01
s / div
4
V / div
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
4
Change in state//mass decreases
Heat is absorbed, temperature remains unchanged
1
1
(c) State the heat involved correctly
- (Specific) latent heat 1
(d) State explanation correctly
Snow requires heat to melt
Heat is absorbed from the surroundings
1
1
8
6(a) State the meaning correctly 1
- Time for the activity of the radioactive substance to become half of
the original activity // Time taken for half of the mass of radioactive
substance to decay
(b) (i) State the half life correctly
- X : 10 minutes
- Y : 5 minutes
1
1
(ii) State the answer correctly
- X : 50 %
- Y : 25 %
1
1
(c) State the comparison correctly 1
- The decay rates for substance X is slower//vice versa
State the relationship correctly 1
- The shorter the half life, the higher the decay rate
(d) Give the reason correctly 1
- Background radiation 8
7(a) State the meaning correctly 1
- the capacity to do work
(b) Correct expression 1
-
2
20 049 . 0
2
1
Correct answer 1
- 9.8 J
(c) State the transformation correctly 2
- Kinetic energy potential energy kinetic energy
(d) State a suitable suggestion and reason 2
- bigger force
- ball has more kinetic energy / momentum
State a suitable suggestion and reason 2
- use a heavier golf club // raise the golf club higher / at a bigger angle
- more energy is transferred to the golf ball
(e) State the correct factor 1 10
- angle of projection // any suitable factor not mentioned above
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
5
NO. MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
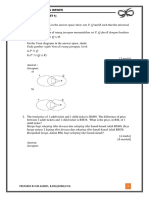
8(a) State the phenomenon correctly 1
- Electromagnetic induction
(b) State the terminals correctly 1
- W and Z
- X and Z
(c) (i) State the terminals correctly 1
- W and Z
(ii) Give the reason correctly 2
- Highest ratio of number of turns of secondary coil to number of turns
of primary coil // highest
P
S
N
N
(d) (i) Complete the values of P
in
correctly 1
- A : 60 W
B : 60 W
C : 72 W
D : 72 W
All values of P
in
calculated correctly
Complete the values of e correctly 2
- A : 0.80
B : 0.90
C : 0.80
D : 0.90
All values of e
calculated correctly, 2 marks
2 or 3 calculated correctly, 1 mark
(ii) Give the choice correctly 1
- A and B (accept e.c.f.)
(iii) Give the choice correctly 1
- B and D (accept e.c.f.)
(iv) Give the reason correctly 1
- Highest efficiency
(v) Give the choose of the most suitable bulb correctly 1 12
- Transformer B
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
6
SECTION B
NO MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
9(a) (i) State the light phenomenon correctly
- Total internal reflection 1 1
(ii) State the function of objective lens correctly
- used to produce a real, inverted and magnified image // intermediate
image
1
State the function of eyepiece correctly
- as a magnifying glass 1 2
(iii) State two advantages of using fibre optics correctly
- can carry large amount of data/information 1
- transmit signals with very little loss of energy 1
- can transmit large amount of signals at one time
- very much thinner and lighter 2
(b) (i) Compare the size of object and the size of image correctly
- in diagram 9.2/9.3 the size of object is equal to the size of image 1
(ii) Compare the object distance and the image distance correctly
- in diagram 9.2/9.3 the object distance is equal to the image distance 1 2
(c) (i) Compare the focal lengths correctly
- Focal length of lens X is shorter than the focal length of Y 1
(ii) Compare the thickness of lens correctly
- Lens X is thicker than lens Y 1
(iii) Relate the focal length to the thickness correctly
- The thicker the lens, the shorter the focal length 1 3
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
7
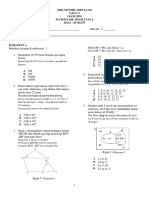
(d) (i) Draw the ray diagram of a compound microscope correctly
- R as an eye piece and T as an objective lens
- F
e
and F
o
are not overlapped
- Light rays to form first image
- First image formed shown
- Light rays to form final image
- Final image formed shown
1
1
1
1
1
1
State the characteristics of final image correctly
Virtual, magnified and inverted
(Any two) 2 8
(ii) Suggestion on the modification to produce bigger image
By using more powerful // shorter focal length lenses 1
Suggestion on modification to produce brighter image
By using a plane mirror near the object to reflect more rays / a lamp near
the object / Objective lens of bigger diameter
1 2
20
Object
T
F
e
F
o
R Eye
Image2
Object
T
F
e
F
o
R Eye
F
o
F
e
Final
Image
First
Image
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
8
NO MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
10(a) (i) State the reason correctly 1 1
- To ensure constant velocity of water wave / ripple.
(ii) Name the water wave phenomenon correctly 1 1
- Interference
(iii) State the amplitude of wave correctly 1 1
- Zero or minimum
(iv) Diagram showing superposition of a crest and a trough 1
Diagram showing the resultant amplitude 1 2
- zero // minimum // smaller than the original amplitude
(b) (i) Compare the distance between vibrators correctly 1
- The distance in Diagram 10.1 is higher
(ii) Compare the distance between the adjacent nodal line correctly 1
- The distance in Diagram 10.1 is smaller
(iii) Compare the wavelength correctly 1
- Same
(iv) State the relationship between a and x correctly 1 5
- The higher the a, the smaller the x // a inversely proportional to x
// a
x
1
Reject Equation
D
ax
=
(c) (i) Suggest the number of loudspeakers correctly 1
- Increase the number of loudspeakers // use more loudspeakers
Give the reason correctly 1
- To produce louder sound // Sound transmitted covers a bigger
area
(ii) Suggest position of the loudspeaker correctly 1
- Placed at all corners // different locations
Give the reason correctly 1
- Cover a bigger area // the spectators around the area can hear
clearly
(iii) Suggest the amplification correctly 1
- High amplification
Give the reason correctly 1 6
- to produce louder sound // sound can travel further
(d) Give the choice of D correctly 1
- Large/big
Give the reason correctly 1
- Less diffraction // spreading // sound travels straight
Give the choice of L correctly 1
- Large/big
Give the reason correctly 1 4
- Vibrates more air // produces louder sound
20
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
9
SECTION C
NO MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
11(a) (i) State the meaning correctly
- Archimedes principle states that the buoyant force on an object
immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of fluid displaced by the
object.
1
1
(ii) Explain why a balloon filled with helium gas rises up in the air
correctly
- The balloon acted by two forces: Upthrust and the weight of the
balloon
1
- The density of helium gas is less than the density of surrounding air
1
- Upthrust equals to the weight of the air displaced by the ballloon
1
- Upthrust is higher than the weight of the balloon 1 4
(b) M1 States a suitable size of the balloon
- Large balloon 1
M2 State the reason for M1 correctly
- To produce bigger buoyant / upthrust // Increase the volume of the air
displaced
1
M3 State a suitable number of the burner
- Use 2 burners // Many burners 1
M4 State the reason for M3 correctly
- To produce bigger flame // heat up the gas in the balloon faster
1
M5 State a suitable type of fabric of the balloon
- Synthetic nylon 1
M6 State the reason for M5 correctly
- Light-weight, strong and air-proof material 1
M7 State a suitable temperature of the air in the balloon
- High temperature of the air in the balloon 1
M8 State the reason for M7 correctly
- Reduce the density /weight of the air in the balloon 1
M9 Choose the most suitable hot air balloon
Hot air balloon Q is chosen 1
M10 State the reason correctly
Large balloon, use 2 burners / many burners, use synthetic nylon and has
high temperature of the air in the balloon // or combination of the
reasons
1
10
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
10
(c) (i) Giving a correct equation
Weight = buoyant force / weight of the water displaced 1
Substitute the equation correctly
m x 10 = (10 x 2 x 10
-6
) x 1000 x 10 1
Correct answer with unit
m = 0.02 kg /20 g 1
(ii) Show a correct substitution
20 = (12 x 2) 1
Correct answer with unit
= 0.83 g cm
-3
1 5
20
12(a) State the two properties and explanations correctly
- High melting point
- Can withstand high temperature / heat // does not melt easily
- Not easily oxidized
- Can last longer
1
1
1
1
4
(b) (i) State the meaning correctly 1
- Maximum current flowing through the fuse is 0.5 A
(ii) State the suitable melting point and reason correctly 1+1
1 Low melting point
2 Can melt easily
State the suitable specific heat capacity and reason correctly 1+1
3 Low specific heat capacity
4 Can heat up easily
State the suitable diameter and reason correctly 1+1
5 Small
6 High resistance // more heat released // easy to break
State the suitable resistivity and reason correctly 1+1
7 High
8 High resistance // more heat released
State most suitable choice of generator and justification correctly 1+1 10
9 Z
10 Low melting point, low specific heat capacity, small diameter and
high resistivity
(c) (i) Correct substitution 1
-
240
500
Correct answer and unit 1
- 2.08 A
(ii) State correctly 1
- Not suitable
(iii) Correct substitution 1
- 500 x (10x60)
Correct answer with unit 1 5
- 300 000 J
20
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
1
PROGRAM PENINGKATAN PRESTASI AKADEMIK SPM
TAHUN 2013
SET B
FIZIK
Kertas 3
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
Peraturan pemarkahan ini mengandungi 3 halaman bercetak
Set B
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
2
Section A
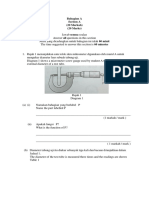
1 (a) (i) Length // L 1
(ii) Current // I 1
(iii) diameter of wire // type of material of wire 1
(b) (i) X = 0.2 1
(ii)
L / cm
1 -
cm /
1
L
i / A I / A
0.2 5.00 2.0 1.8
0.3 3.33 1.4 1.2
0.4 2.50 1.1 0.9
0.5 2.00 0.9 0.7
0.6 1.67 0.8 0.6
4 columns with labels L / cm,
1 -
cm /
1
L
, i / A, I / A 1
5 values of
L
1
correct 1
5 values of i correct 1
5 values of I correct [4 correct 1 mark] 2
all values of
L
1
to 1, 2 or 4 decimal places 1
all values of i correct to 1 decimal place 1
(c) I at the vertical axis,
L
1
at the horizontal axis 1
Vertical axis labeled I / A, horizontal axis
1 -
cm /
1
L
1
Uniform scale 1
5 points plotted correctly 1
best straight line 1
(d) I is directly proportional to
L
1
1
17
[Maximum = 16]
2 (a) (i) Decreases 1
(ii) Show intraplolation line 1
76 1
(iii) 28 1
(iv) 42 1
(b) (i) shown on graph 1
Correct expression, e.g.
0 200
28 70
1
Correct answer, e.g. 0.21 1
(ii) Correct substitution, e.g.
21 . 0 20 . 0
48
1
Correct answer and unit, e.g. 1143 J kg
1
o
C
1
1+1
(c) The liquid is stirred continuously so that its temperature is uniform //
The eye is at the same level as the meniscus of the mercury in the thermometer 1
[12]
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
3
Section B
3 (a) The pressure affects the volume the of the air 1
(b) The higher the pressure, the smaller the volume 1
(c) (i) To investigate the relationship between the pressure and volume of air 1
(ii) MV : Pressure 1
RV : Volume 1
CV : Mass // Temperature 1
(iii) Glass syringe, Bourdon gauge, rubber tube 1
(iv) Labeled diagram 1
(v) The piston is pushed slowly inwards until the pressure is 120 kPa 1
The volume of the air in the syringe is recorded. 1
The above steps are repeated with pressure 140 kPa, 160 kPa, 180 kPa and 200 kPa 1
(vi) Table with 2 columns for pressure and volume. Values of pressure written. 1
(vii) Draw a graph of volume against pressure 1
[Part (c): 11 marks, Max. 10] 12
4 (a) The thickness affects the resistance of the wire 1
(b) The bigger the thickness, the smaller the resistance 1
(c) (i) To investigate the relationship between the thickness and resistance 1
(ii) MV : thickness 1
RV : resistance 1
CV : length // temperature // type of material 1
(iii) Five pieces of eureka wires, ammeter, voltmeter, battery, connecting wires, switch, micrometer
screw gauge 1
(iv) Labeled diagram 1
(v) The micrometer screw gauge is used to measure the thickness, t
1
, of the eureka wire 1
The current, I, and potential difference, V, are measured with the ammeter and voltmeter.
The resistance is calculated,
I
V
R =
1
The above steps are repeated with thickness t
2
, t
3
, t
4
, and t
5
1
(vi) Table with 4 columns for t, I, V and R. Values of t written. 1
(vii) Draw a graph of R against t 1
[Part (c): 11 marks, Max. 10] 12
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
w
w
w
.
m
y
s
c
h
o
o
l
c
h
i
l
d
r
e
n
.
c
o
m
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
o
a
l
a
n
l
a
i
n
d
i
:
M
u
a
t
t
u
r
u
n
(
p
e
r
c
u
m
a
)
s
k
e
m
a
l
a
i
n
d
i
You might also like
- Skema P2 Melaka 2022Document10 pagesSkema P2 Melaka 2022GAN KHEK SEONG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Skema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMDocument8 pagesSkema K2 Set B JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 2 Form 4Document21 pagesMath Paper 2 Form 4Heng ChungNo ratings yet
- SPM P2 Section A (Set 1)Document48 pagesSPM P2 Section A (Set 1)Kaness TanabaluNo ratings yet
- Jawapan - Modul Fizik - Soalan Berformat SPMDocument7 pagesJawapan - Modul Fizik - Soalan Berformat SPMYuvitha SureshNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Modul Pan Asia - FizikDocument7 pagesJawapan Modul Pan Asia - FizikNURFATIN NABILAH BINTI YUNOS MoeNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test Basic ScienceDocument3 pagesAchievement Test Basic ScienceShabeeb MohamedNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Document14 pagesSkema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Cheah Soon TikeNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K1 K2 K3 SET BDocument0 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K1 K2 K3 SET BCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Perkampungan Ilmu Fizik p2Document28 pagesPerkampungan Ilmu Fizik p2friday k zamanNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 1 (Malacca)Document19 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Physics Paper 1 (Malacca)StephyNo ratings yet
- Ujian 2 Math Form 4Document7 pagesUjian 2 Math Form 4Nur Abidah Mat TawilNo ratings yet
- K2 Fizik F5 2014Document23 pagesK2 Fizik F5 2014Ilya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Sains K2 Trial Perlis 2019Document16 pagesSains K2 Trial Perlis 2019Atiq IshakNo ratings yet
- Fizik k2 PPC SPMDocument25 pagesFizik k2 PPC SPMTS ShongNo ratings yet
- Fizik p3 f4 Final SBP 07Document18 pagesFizik p3 f4 Final SBP 07shazillaNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan TopikalDocument247 pagesKoleksi Soalan TopikalKwai Ying Abdul Aziz100% (2)
- Bab 1 - Penyiasatan Saintifik (Pengukuhan-Skema)Document35 pagesBab 1 - Penyiasatan Saintifik (Pengukuhan-Skema)NUR FAIZAH BINTI ZAINAL ABIDEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Soal Fisika 11 PAS 2122Document4 pagesSoal Fisika 11 PAS 2122KridNo ratings yet
- PB SainsDocument8 pagesPB SainsMUHAMAD ZULHAZIQ HADI BIN ASRULHADI Moe100% (1)
- Nurul Fisika RelativitasDocument9 pagesNurul Fisika Relativitasamalia100% (1)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K2 SET ADocument0 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K2 SET ACikgu Faizal0% (1)
- MRSM 2014Document33 pagesMRSM 2014Cheng WLNo ratings yet
- Fast RevisionDocument14 pagesFast RevisionM ZackyNo ratings yet
- Soalan Set 1 Modul CemerlangDocument20 pagesSoalan Set 1 Modul Cemerlangwww.tuitionking7637No ratings yet
- PENJELMAANDocument7 pagesPENJELMAANNurul Huda Che HamzahNo ratings yet
- Kertas PenilaianDocument9 pagesKertas PenilaianKero Malek50% (2)
- PAT T1 Maths 2019Document19 pagesPAT T1 Maths 2019NOOR FARIZA BINTI MD SAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Ujian Penilaian 1 SC t1 23Document9 pagesUjian Penilaian 1 SC t1 23Bazli HafizuddinNo ratings yet
- Praktis Ekstra Ting 5 Bab 7Document6 pagesPraktis Ekstra Ting 5 Bab 7DIANANo ratings yet
- 1 2 Unit PengukuranDocument5 pages1 2 Unit Pengukuranslokkro100% (2)
- Ujian 1 Tingkatan 2 2019Document11 pagesUjian 1 Tingkatan 2 2019gaya379yahooNo ratings yet
- Fizik Exam 01Document11 pagesFizik Exam 01Firdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- 962/1 STPM 2021Document12 pages962/1 STPM 2021Legends Ryan50% (2)
- PartA PBD Form4Document9 pagesPartA PBD Form4Az RinaNo ratings yet
- Skema Ar1Document7 pagesSkema Ar1eveNo ratings yet
- Final 20Document19 pagesFinal 20NURSHATHIRAH BINTI ZULKEFELY KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- W23 Revision Exercise 10 June 2022Document7 pagesW23 Revision Exercise 10 June 2022bidarihassanNo ratings yet
- Math F3 2022 - SoalanDocument30 pagesMath F3 2022 - SoalanGiy IngNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Fizikf 4Document6 pagesUjian 1 Fizikf 4eriire79No ratings yet
- Koefisien EkstensiDocument3 pagesKoefisien Ekstensitensura slime1No ratings yet
- Fizik Paper 3 KedahDocument19 pagesFizik Paper 3 KedahnizamNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology A+ Level Sure QuestionsDocument144 pagesSSLC Biology A+ Level Sure QuestionsGautham Ram RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Rumussssssss 15: Bahagian ADocument5 pagesRumussssssss 15: Bahagian Amimi mohdNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 SBP 2012Document65 pagesKertas 2 SBP 2012Amy HenryNo ratings yet
- Modul Pelajar Potensi PDFDocument104 pagesModul Pelajar Potensi PDFSaidah Bt MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Wa0002Document4 pagesWa0002tiara8heldinaNo ratings yet
- Sri Aman MM k2 2018Document25 pagesSri Aman MM k2 2018Olzen Khaw Tee SengNo ratings yet
- Uji Kompetensi 1 VektorDocument13 pagesUji Kompetensi 1 VektortriNo ratings yet
- ME 09 Perambatan Gelombang ElektromagnetikDocument26 pagesME 09 Perambatan Gelombang Elektromagnetikhendrian15No ratings yet
- Kimia FizikDocument8 pagesKimia FizikNUR AIN FARHANA BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Perlis 2010 FIZIK2Document28 pagesPerlis 2010 FIZIK2kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- SET 2 K2 & JawapanDocument20 pagesSET 2 K2 & JawapanSamion Awaldin0% (1)
- PAT Sains K2 17Document8 pagesPAT Sains K2 17Nur Qaisara Bt Rozman100% (1)
- Revision Paper 2 Form 4 Mathematics KSSMDocument9 pagesRevision Paper 2 Form 4 Mathematics KSSMazlinasmsspNo ratings yet
- KP Tegasan Dan Terikan Sk3021Document19 pagesKP Tegasan Dan Terikan Sk3021En Salleh Ilpkk0% (1)
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Document30 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Menyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqDocument6 pagesMenyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqPhysics MGCM100% (1)
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Document14 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaDocument12 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Document23 pagesTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Document22 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument18 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Document58 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (7)
- Modul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Document6 pagesModul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 SkemaDocument83 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (4)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument41 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument42 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- Contoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatDocument17 pagesContoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- Sejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Document47 pagesSejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Dyieba LatifNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Document24 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)Document13 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)gunaNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument19 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument47 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument40 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument46 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Bahasa Melayu K1 Set 1Document4 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Bahasa Melayu K1 Set 1Autumn SanNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument39 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014 SkemaDocument23 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Document56 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (4)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Bahasa Melayu K1 Set 1 SkemaDocument9 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Bahasa Melayu K1 Set 1 SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Soalan Praktis Bestari BM 1, Set 3Document4 pagesSoalan Praktis Bestari BM 1, Set 3Muhamad FarisNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusDocument219 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusCikgu Faizal100% (3)