Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immunity MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)
Uploaded by
Ae BanpongCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunity MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)
Uploaded by
Ae BanpongCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Number 5.
(b)(i)
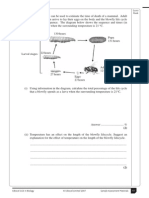
Question Explain the meaning of the term mutation. Answer 1. Change in sequence of DNA; 2. Change in {mass of DNA / number of chromosomes}; Mark 2
Question Number 5.(b)(ii)
Question Suggest why the vaccine contains a cocktail of antigens. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. mutation causes change in gene product/eq; 2. idea that structure of antigen may change (as result of mutation); 3. idea that individual will not be protected if flu virus does not have same antigens present in vaccine; 4. idea that a cocktail of antigens will increase the chance of matching antigens; Mark 2
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Edexcel Limited 2007
Sample Assessment Materials
133
Question Number 7.(a)
Question The table below lists five structural features that may be found in bacteria and viruses. Put a cross in the box if the structural feature is present. Answer Award 1 mark for each correct row in the following table. Structural feature Mesosomes Capsid Nucleic acid Cytoplasm Ribosomes Bacteria Viruses Mark 5
Question Number 7.(b)(i)
Question Describe the trends shown by the data. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. Increase in number of new cases in Africa and Europe 2. Decrease in number of new cases in Asia and South America 3. Any relevant manipulation of data Mark 2
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Edexcel Limited 2007
Sample Assessment Materials
137
Question Number 7.(b)(ii)
Question HIV positive people were excluded from the data. If they had been included suggest how the data would differ. Give an explanation for your answer. Answer Explanation: x More incidence of TB in the population/eq Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. Ref to opportunistic infection 2. HIV positive people have weakened immune system 3. A higher proportion of HIV positive people are infected by TB Mark 3
Question Number 7.(c)
Question TB is increasing in some countries which have well-funded health services. Suggest two reasons for this. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points in context to a maximum of two marks. 1. TB bacteria {mutate / become resistant to antibiotics} 2. immigration from countries with high incidence of TB 3. increased travel 4. increase in HIV infection 5. lower rates of immunisation against TB Mark 2
138
Sample Assessment Materials
Edexcel Limited 2007
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Question Number 8.(a)(i)
Question Distinguish between bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal antibiotics. Correct Answer Bacteriostatic prevent bacteria multiplying and bacteriocidal kill bacteria Mark 1
Question Number 8.(a)(ii)
Question Suggest why mammalian cells are unharmed by antibiotics. Correct Answer Award one mark for each of the following points up to a maximum of two marks. Mammalian cells: 1. are eukaryotic 2. have different enzymes 3. do not have cell walls 4. have {80s / larger/eq} ribosomes / different protein synthesis Mark 2
Question Number 8.(b)
Question Suggest ways by which doctors and patients can help to prevent the further spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points up to a maximum of three marks. 1. do not prescribe antibiotics for minor infections /viral infections 2. do not prescribe antibiotics to prevent infections 3. reference to narrow spectrum antibiotics 4. ref to rotation in the use of different antibiotics 5. {advise / take} the full course of antibiotics 6. ref to hand-washing (between patients / by visitors of hospitals) 7. use of isolation wards Mark 3
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Edexcel Limited 2007
Sample Assessment Materials
139
Question Number 8.(c)
Question Describe a procedure that you have used to investigate the effect of different antibiotics on bacterial growth. Answer Award one mark for each of the following points up to a maximum of four marks. 1. Ref. to a specific aseptic technique 2. Bacterial lawn/pour plate 3. Use of antibiotic discs / antibiotics incorporated into agar /eq 4. Incubate for 24-36 hours 5. At 25-30 C 6. Record bacterial growth/eq Mark 4
140
Sample Assessment Materials
Edexcel Limited 2007
Edexcel GCE in Biology
Question Number 6(a)
Answer
Mark
1. RNA in HIV and DNA in {bacterium / eq} ; 2. comparative description of nucleic acid e.g. circular in bacterium and linear in HIV / eq ; 3. plasmids in {bacterium / eq} and no plasmids in HIV ;
maximum (2)
Question Number 6(b)
Answer
Mark
1. {keratin / protein} in skin {surface / epidermis} ; 2. idea of forms a {hard / impenetrable / physical / eq} barrier ; (2)
Question Number 6(c)(i)
Answer 1. numbers decrease / eq ; 2. small decrease in {first week / between weeks {4 / 5} and 6} / eq ; 3. large decrease between weeks {1 / 2} to 3 / eq ; 4. credit use of manipulated figures ;
Mark
maximum (2)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 6* (c)(ii) QWC
Answer (QWC Spelling of technical terms (shown in italics) must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence) 1. {glycoprotein / gp120} on virus / eq ; 2. binds with {receptors / CD4} / eq ; 3. on (surface) membrane of lymphocytes / eq ; 4. viral RNA enters the lymphocyte / eq ; 5. viral RNA used to produce viral DNA (in lymphocyte) / eq ; 6. by action of reverse transcriptase ; 7. ref to formation of new viruses ; 8. lymphocyte destroyed when new viruses {bud out of / leave} the cell / eq ; 9. T killer {cells / lymphocytes} destroy T helper {cells / lymphocytes} / eq ;
Mark
maximum (5)
Question Number 6(c)(iii)
Answer B {cells / lymphocytes} { not activated / not stimulated / are inhibited / eq} / fewer antibodies / T killer cells {increase / multiply / eq} ;
Mark
(1)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 8(a)
Answer 1. idea of antibiotic is used to {control / kill / prevent reproduction of / eq} bacteria ; 2. bacteriostatic prevent {reproduction / division / multiplication / growth / eq} of bacteria; 3. bactericidal {destroy / kill / eq} bacteria ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 8(b)
Answer
Mark
1. idea that both more or less the same at {start / end} ; 2. idea that B is higher than A most of the time ; 3. B rises and then falls and A falls and then rises / eq ; 4. ref to both falling after April 04 / eq ; 5. comparative use of figures ; maximum (3)
Question Number 8(c)(i)
Answer D {has the lowest rate of MRSA infection (throughout) / is consistent / has less fluctuation} / eq ;
Mark
(1)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 8(c)(ii)
Answer 1. D has {stricter / eq} hygiene practices / eq ; 2. ref to hand washing regimes for {doctors / nurses / medical staff / visitors} ; 3. particularly when dealing with open {wounds / eq} / eq ; 4. ref to wearing suitable clothing ; 5. ref to antiseptic (solutions) readily available ; 6. named antiseptic e.g. gels, pastes, alcohol rubs ; 7. ref to {isolation of suspected cases / screening of admissions} / eq ; 8. D {controls / monitors} use of antibiotics / eq ; 9. fewer {patients / visitors} passing in and out ;
Mark
maximum (3)
1001 6BI0
Question Number 4(a)(i) Question Number 4(a)(ii) Question Number 4(b)(i)
Answer C; Answer A;
Mark
(1) Mark
(1) Answer Mark
D = antigens / (glyco)proteins ; E = B {lymphocytes / cells} / plasma cells ; F = antibodies / immunoglobulins ; G = macrophage / phagocyte / eq ; H = enzymes / lysozyme ; (5)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 4(b)(ii)
Answer
Mark
1. reference to protein nature of {antigens / antibodies} ; 2. antigens are specific (to each bacteria) / eq ; 3. antibodies need to be {complementary / specific} (to the antigen) ; 4. idea that {binding / eq} can take place ; 5. (some bacteria) have {different / changed} antigens / eq ; 6. idea that this is a primary infection ; 7. reference to {mucus / slime} {coat /capsule} (of bacterial cells) ; 8. idea that some bacteria are inside body cells ; 9. idea of antibodies already present e.g. from passive immunity or breast feeding ; max (3)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 8(a)
Answer
Mark
Description Enclosed by outer smooth membrane inner membrane folded forming cristae Long strand-like structure extending out from the cell Used for locomotion Small, circular loop of doublestranded DNA
Name of structure Mitochondrion / mitochondria
P, E or B E / eukaryotic
Flagellum / flagella
B / both
plasmid
P / prokaryotic (3)
1 mark for any two correct cells ;;; Question Number 8(b)(i) Question Number 8(b)(ii) 1. cell wall {weaker /cannot form properly / eq} ; 2. {cell / cell wall} bursts (easily) / eq ; 3. during division /eq ; max (2) Answer bactericidal ; (1) Answer Mark Mark
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 8(b)(iii)
Answer
Mark
1. reference to antibiotic acting as selective pressure ; 2. reference to some bacteria resistant (to antibiotic) ; 3. idea that resistant bacteria survive and {reproduce / pass on resistance / pass on gene / eq}; 4. idea that antibiotic no longer effective ; 5. reference to some infections cannot be treated with antibiotics ; max (2)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 8(c)
Answer
Mark
1. idea of bacteria distributed evenly / description of technique e.g. lawn spreading ; 2. description of method used to apply different antibiotics at known positions e.g. multidisks, wells in agar ; 3. reference to control of antibiotic concentration ; 4. reference to {sterile / aseptic} technique ; 5. reference to incubation at a suitable temperature ; 6. description of how effect is assessed e.g. measure {clear area / inhibition zone / eq} ; 7. reference to replication (with same bacterium) ; 8. reference to repetition with different bacteria ; max (4)
6BI04_01 1006
Question Number 2(a)
Answer Feature Bacteria only Viruses only Both bacteria and viruses
Mark
Glycogen granules Nucleic acids Protein coat (capsid)
X X
1 mark per row ;;; Question Number 2(b)(i) Answer 1. viruses (and bacteria) involved ; 2. (usually) antibiotics {are only effective against bacteria / do not affect viruses / eq} ; 3. {other medication / eq} needed to deal with viruses / eq ; Question Number 2(b)(ii) Answer 1. both enrofloxacin and florfenicol named ; 2. idea of {(high) effectiveness / eq} against all three bacteria / eq ; 3. above {80% / 83%} / eq / average above 90% / eq ;
(3) Mark
max (2) Mark
(3)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 2(b)(iii)
Answer 1. idea that antibiotic used is {most effective / eq} (against the known bacterium) ; 2. idea that none of the antibiotics is 100% effective / some bacteria {survive / eq} ; 3. some bacteria {are resistant / eq} ; 4. idea of resistant strain {develops / prevented} ;
Mark
max (3)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 4(a)(i)
Answer Any characteristic symptom of TB e.g. tubercules, bloody sputum, (general)body tissue wastage ;
Mark
(1) Question Number 4(a)(ii) Question Number 4(a)(iii) Answer D; (1) Answer 1. idea of {bacterium / eq} recognised as {non-self / eq} ; 2. reference to labelling of bacteria by B {lymphocytes / cells} ; 3. phagocytosis / phagocytic / phagocyte ; 4. descriptive detail of phagocytosis (involving {bacterium / eq}) ; 5. reference to formation of vacuole ; Question Number 4(a)(iv) Answer 1. {kills / eq} {bacteria / eq} in {stomach / mouth / saliva / gastric juice} ; 2. (by) {(hydrochloric) acid / lysozyme} ; (2) max (3) Mark Mark Mark
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number *4(b)QWC
Answer (QWC Spelling of technical terms must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence) Supporting the hypothesis: 1. both HIV and TB infection rates rise and then fall / eq ; 2. both HIV infection and TB infection increase {from 1990 to 2000 / for the first 10 years} / eq ; Not supporting the hypothesis: 3. TB infection falls from 2000 onwards but HIV continues to rise (until 2004) / eq ; 4. different {parameters /measures / variables / eq} for the two infections / eq ; General points: 5. idea of {more {data / information / eq} is needed / other factors (may be) involved} ; 6. reference to need for statistical {analysis / test} ; 7. such as correlation {data / test / named example} ; 8. there is no data that {links HIV infection with TB infection / shows that people with HIV also have TB / shows causal relationship / eq} ;
Mark
max (4)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 8(a)
Answer Source of antibodies Form of immunity D B C A
Mark
Note: [accept descriptions instead of letters] 4 correct = 2 marks 2 or 3 correct = 1 mark 0 or 1 correct = 0 marks ;; (2) Question Number 8(b) Answer 1. (bacterium) is made of many different {polymers / chemicals / eq} / eq ; 2. which can act as antigens / eq ; 3. reference to B {lymphocytes / cells} ; 4. reference to (individual B-lymphocytes) recognise specific antigens / antibodies are specific / eq ; 5. reference to {activation/ eq} of Blymphocytes by T {lymphocytes / cells} ; 6. reference to mitosis (in B-lymphocytes or cells) ; 7. to {form / eq} genetically identical plasma cells ; max (4) Mark
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 8(c)
Answer 1. specific {antigen / virus / pathogen / bacterium / eq} can be {identified / eq} ; 2. idea of {specific / monoclonal} antibody binds to {specific / only one} antigen ; 3. specific treatment can be given / eq ; 4. avoids unnecessary use of {drugs / treatment} / eq ; 5. more likely to be effective / eq ;
Mark
max (3)
6BI04_01 1101
Question Number 5(a)(i)
Answer 1. {competition / eq} for nutrients ; 2. {competition / eq} for space ; 3. {secretion / eq} {chemicals / substances / lysozyme / eq} OR affects {pH / eq} ; 4. {stimulation / eq} of (skin) immune system / eq ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 5(a)(ii)
Answer A;
Mark (1)
Question Number 5(b)
Answer 1. idea that influenza may allow development of other diseases e.g. opportunistic infections ; 2. antibiotics will {kill / inhibit growth of / eq} bacteria ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 5(c)(i)
Answer correct answer 37.2 / 37.17 / 37 (%) gains 2 marks 1. (226 142) / 84 ; 2. 226 to give 37.2 / 37.17 / 37 (%) ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 5(c)(ii)
Answer 1. yes ; 2. idea that if current rate continues / eq ; 3. idea of achieving lower than the target / eq; 4. credit use of supporting figures ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 5(c)(iii)
Answer 1. reference to some bacteria {can resist / are resistant to} antibiotics ; 2. idea of {resistance being genetic / can be passed on} ; 3. reference to MRSA / other named example ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 8(a)
Answer Statement HIV infects b-lymphocytes in the human immune system The genetic material in HIV is a form of RNA The enzyme, reverse transcriptase, is used by HIV 1 mark each correct row ;;; True False 3 3 3
Mark
(3)
Question Number 8(b)(i)
Answer 1. change in the {nucleotides / bases} / eq ; 2. in {RNA / DNA} / eq ; 3. which leads to change in the {sequence / eq} of amino acids in (primary structure of) a {polypeptide / protein} / eq ;
Mark
(2)
Question Number 8(b)(ii)
Answer 1. idea that HIV has {many / variety of / new / eq} {strains / types /antigens / protein coats / eq} (in infected person) ; 2. some strains {are / become} resistant to {an individual / a specific / a particular / eq} drug / eq ; 3. these would survive if (only one drug used) / eq ; 4. {mixture of drugs / eq } has more chance of getting rid of {all / more} (strains / types / eq) / eq ;
Mark
5. reference to drugs used together because of mutation ; 6. reference to rapid rate of mutation ; 7. reference to rapid rate of {multiplication / eq} of virus ; (4)
Question Number 5(a)
Answer Feature Nucleic acid Cytoplasm Protein capsid 1 mark each correct row ;;; Bacteria only Viruses only Both bacteria and viruses
Mark
(3)
Question Number 5(b)(i)
Answer 1. idea of (SCAG is) caused by {a bacterium / bacteria} ; 2. antibiotics {kill / stop reproduction / eq} of bacteria / are {bactericidal / bacteriostatic} ;
Mark
(2)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number *5(b)(ii) QWC
Answer Spelling of technical terms must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence 1. as age increases, acid secretion decreases / eq ; 2. as age increases (above 30) , stomach cancer increase / eq ; 3. as acid secretion decreases (below 120), stomach cancers increases / eq ; 4. idea that the {higher age groups (51+) have low acid and high cancer / lower age groups (up to 30) have high acid and low cancer} ; 5. Idea of {acid / low pH} (in stomach) kills {bacteria / Helicobacter} ; 6. reference to development of SCAG {inhibited / prevented / eq} (by low pH / more stomach acid) ; 7. idea of age affects the immune system ; 8. idea that the older you are acid-producing cells are less effective e.g. fewer acid-producing cells / cancer cells replace the acid-producing cells ; 9. idea that {acid / low pH} destroys cancer cells ; 10. idea that mutations (leading to cancer) more likely to occur with age ;
Mark
(5)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 7(a)
Answer C;
Mark (1)
Question Number 7(b)(i)
Answer
Mark
1. {T helper / CD4 (positive)} (cell / lymphocytes) ; 2. phagocytic cells e.g. macrophages, dendritic cell ; (2) Question Number 7(b)(ii) Answer 1. reference to (HIV) binds to (CD4) receptors on cell (surface) ; 2. ref to CD4 (receptors on cells) ; Mark
3. reference to {glycoprotein / gp120} on virus (surface) ; 4. reference to fusion of virus (envelope) with (cell surface) membrane ; 5. idea of phagocytosis (in macrophage / eq) ; (3)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 7(b)(iii)
Answer 1. reference to viral RNA ; 2. reference to production of (viral) DNA (using viral RNA as a copy) ; 3. correct ref to reverse transcriptase ; 4. reference to incorporation of viral DNA into host cells {DNA /genome } / reference to provirus / eq ; 5. correct ref to integrase ; 6. reference to production of {viruses / viral RNA and proteins} / eq ; 7. idea of infection of further (T helper) cells ; 8. reference to destruction of (T helper) cells by T killer cells OR reference to cell lysis / eq ; 9. reference to lowering of immunity ;(to other diseases ; 10. credit reference to role of T helper cells in immune response e.g. produce cytokines, activate B cells / killer cells ; 11. death is caused by e.g. opportunistic disease, pneumonia , TB, Kaposis sarcoma, cancer, dementia, extreme weight loss, meningitis, toxoplasmosis ;
Mark
(6)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 8(a)
Answer Description B and T cells are formed in the bone marrow B cells stimulate T cells to produce clones of memory cells T helper cells produce chemicals that destroy pathogens B and T cells are able to form clones by mitosis True False
Mark
1 mark each correct row ;;;;
(4) Mark
Question Number 8(b)
Answer 1. (bacteria are) too small / reference to limitation of {magnification / resolution} ; 2. (bacteria) not stained ; 3. idea of bacteria already {removed / destroyed} e.g. phagocytosis ; 4. idea that bacteria are not present in the blood e.g. only a small {region / sample} shown, reference to local infection ;
(2)
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 8(c)(i)
Answer Either: 1. idea of fewer {lymphocytes / eq} ; 2. reference to {lymphocytes / eq} no longer needed / eq ; 3. (as) {antibiotics / drugs} {kill / destroy / eq} bacteria ; Or: 4. more {lymphocytes / eq} ; 5. idea of clonal expansion (of lymphocytes) / eq ; 6. idea that the antibiotics have not killed all the bacteria yet ;
Mark
(2) Question Number 8(c)(ii) Answer 1. idea that a placebo has no effect ; 2. (therefore there will be) more bacteria / eq ; 3. (therefore there will be) more {lymphocytes / eq} ; 4. (more lymphocytes due to) clonal expansion / eq ; (2) Mark
6BI04_01 1201
Question Number 6(a)
Answer C plasma cell ;
Mark (1)
Question Number 6(b)(i)
Answer 1. idea of using {virus / PCV2} as vaccine ; 2. which is {modified / attenuated / harmless / similar / part of / eq} ; 3. idea that the vaccine contains the antigen ; 4. idea of {activation / proliferation} of (specific) {B cell / T cell / lymphocyte} ; 5. reference to production of (B / T) memory cells ; 6. idea that body now able to produce (specific) antibody {faster / at higher concentration / eq} on another exposure to PCV2 ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 6(b)(ii)
Answer 1. reference to giving a placebo (to group B) ; 2. idea that all (other) {conditions / factors / variables} should be {controlled / same as group A} ; 3. stated example e.g. food, temperature of housing / eq ; 4. reference to group B is a control group ; 5. (so that) only the (effect of) {vaccine / vaccination} is tested / eq ; 6. ref to {valid / validity} ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 6(b)(iii)
Answer 1. {Greater change / higher / eq} in group A (than B) / eq ; 2. group A rises for first 30 days, group B rises (slightly) for first 20 days / eq ; 3. (this) rise for group A is {faster / greater} than for group B / eq ; 4. (after the rise) group A falls, group B levels off / eq (until day 140) ; 5. after day 140, group A rises, group B falls / eq ; 6. credit use of comparative manipulated figures (with units) ;
Mark
(3)
Question Number 6(b)(iv)
Answer 1. idea that (antibodies present at birth as) both groups received antibodies from mother ; 2. via {placenta / blood / milk / breast feeding} ; 3. reference to passive immunity ; 4. group A concentration falls because {piglets not infected by (PCV2) virus/ antibodies excreted / passive immunity is short term} /eq ; 5. group B concentration rises because {PCV2 / virus} present / eq ;
Mark
(3)
You might also like
- Health, Safety and Environment Test For Operatives and Specialists in English - XpsDocument193 pagesHealth, Safety and Environment Test For Operatives and Specialists in English - XpsAdrian Prisecaru75% (4)
- Store Employee Safety Handbook: Dear Dollar General EmployeeDocument6 pagesStore Employee Safety Handbook: Dear Dollar General EmployeeLaura HugginsNo ratings yet
- Examiner Tips For IGCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesExaminer Tips For IGCSE BiologySunSun Hemnilrat42% (12)
- ISO 45001 Documents List of Required Policies & ProceduresDocument16 pagesISO 45001 Documents List of Required Policies & ProceduresBFNo ratings yet
- Sat Subject Tests Practice PDFDocument72 pagesSat Subject Tests Practice PDFSri KondabattulaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming Forensics QuestionsDocument136 pagesUnit 4-Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming Forensics Questionsareyouthere92100% (2)
- Photosynthesis QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document18 pagesPhotosynthesis QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Immunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document40 pagesImmunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Foronda Et Al - Cultural Humility - A Concept AnalysisDocument8 pagesForonda Et Al - Cultural Humility - A Concept AnalysisabcNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyDocument19 pagesUnit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyAe Banpong69% (13)
- Unit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyDocument19 pagesUnit 4 Notes Edexcel BiologyAe Banpong69% (13)
- EDEXCEL: AS BIOLOGY REVISION NOTES: UNIT 1 METABOLISM OVERVIEWDocument14 pagesEDEXCEL: AS BIOLOGY REVISION NOTES: UNIT 1 METABOLISM OVERVIEWAe Banpong0% (2)
- Yasmeen Sitxfa002Document35 pagesYasmeen Sitxfa002ranu jain100% (1)
- Gilbert Quizora v. Denholm Crew Management (Phils), Inc.Document2 pagesGilbert Quizora v. Denholm Crew Management (Phils), Inc.poppy2890No ratings yet
- Score Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolDocument29 pagesScore Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolThomas GiangNo ratings yet
- 6BI02 Jan 2013 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages6BI02 Jan 2013 Mark Schemecozzy'mozzy..dozzy.;No ratings yet
- 6B108 Biology 6B Mark Scheme June 2012Document12 pages6B108 Biology 6B Mark Scheme June 2012zinmNo ratings yet
- SN Unit 6 June 2008 MS PDFDocument21 pagesSN Unit 6 June 2008 MS PDFafoo1234No ratings yet
- GCE Biology (6BI02/01) January 2009 Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesGCE Biology (6BI02/01) January 2009 Mark Schemeİzem SözgenNo ratings yet
- Biology A 1520 Paper 4H: Edexcel GCSEDocument6 pagesBiology A 1520 Paper 4H: Edexcel GCSEaustowNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015Document25 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015rajmeganNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI05) Paper 01Document16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI05) Paper 01afoo1234No ratings yet
- 2012 June Edexcel Biology Unit 4 MSDocument20 pages2012 June Edexcel Biology Unit 4 MSKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- With Answers Microbiology Bailey 14th EditionDocument61 pagesWith Answers Microbiology Bailey 14th EditionrhymeNo ratings yet
- 1 Diseases Ans PDFDocument7 pages1 Diseases Ans PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- 2014 - June 2B MS PDFDocument14 pages2014 - June 2B MS PDFSimilar12345No ratings yet
- Biology 2B June 2011 MsDocument12 pagesBiology 2B June 2011 MsMeeraf AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Worksheet Answer Key CH 10 Diseases and Immunity by Ms. Amrita GMDocument3 pagesIGCSE Worksheet Answer Key CH 10 Diseases and Immunity by Ms. Amrita GMKK man OnNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Growth Answer SheetDocument3 pagesBacterial Growth Answer SheetKENT BENEDICT PERALESNo ratings yet
- Biology GCE 2008 Jan Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesBiology GCE 2008 Jan Paper 1 Mark SchemeRicky MartinNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Infection, Immunity and Disease - MsDocument8 pagesTopic 6 - Infection, Immunity and Disease - Msg8yd7q9cnmNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (RESULTS) January 2009: GCE Biology (6104/01)Document15 pagesMark Scheme (RESULTS) January 2009: GCE Biology (6104/01)Jean-Paul VincentNo ratings yet
- January 2014 - Marking Scheme - Biology 6BDocument16 pagesJanuary 2014 - Marking Scheme - Biology 6BAbdulla IkramNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology t2 sp03Document6 pages12 Biology t2 sp03HenryNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2013: GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper: 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and The EnvironmentDocument16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2013: GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper: 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and The EnvironmentMahiat Miftah ShowkatNo ratings yet
- 7040 GCE O Biology MSC 20080807Document30 pages7040 GCE O Biology MSC 20080807Mehjabeen HossainNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2012: International GCSE Human Biology (4HB0) Paper 02Document8 pagesExaminers' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2012: International GCSE Human Biology (4HB0) Paper 02Joseph LAU [11D]No ratings yet
- 0610 w07 Ms 3Document14 pages0610 w07 Ms 3Khaled SaidNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 01 Practical Biology and Research (WA)Document13 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 01 Practical Biology and Research (WA)areyouthere92No ratings yet
- Markscheme Unit4 (6BI04) June2012Document20 pagesMarkscheme Unit4 (6BI04) June2012Mahiat Miftah ShowkatNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy - Aegrotat Supplementary - Biochemistry Microbiology Immunology - PC 221 - Feb 2022Document4 pagesPharmacy - Aegrotat Supplementary - Biochemistry Microbiology Immunology - PC 221 - Feb 2022THE MASUVHELELE POSTNo ratings yet
- (ARCHIVED) 8040 9040 GCE Biology International PDFDocument33 pages(ARCHIVED) 8040 9040 GCE Biology International PDFVictor EnglishNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI07) Paper 3BDocument10 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI07) Paper 3Bafoo1234No ratings yet
- 7040 01 Rms 20080306Document14 pages7040 01 Rms 20080306MERCY LAWNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Biology (6BI01) Paper 01Document20 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Biology (6BI01) Paper 01areyouthere92No ratings yet
- 5090 s06 Ms 2Document6 pages5090 s06 Ms 2FaizanAminNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2019Document25 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2019Santi DiazNo ratings yet
- Gcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology Spec A (New) JANUARY 2012Document18 pagesGcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology Spec A (New) JANUARY 2012sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- GCE Biology (6104/02) Mark Scheme January 2008Document12 pagesGCE Biology (6104/02) Mark Scheme January 2008Mehak KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2015 - June 1BR MS PDFDocument24 pages2015 - June 1BR MS PDFSimilar12345No ratings yet
- Examiners' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback January 2012Document8 pagesExaminers' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback January 2012Similar12345No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 01 Practical Biology and Investigative SkillsDocument12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2013: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 01 Practical Biology and Investigative Skillsafoo1234No ratings yet
- June 2017 MSDocument20 pagesJune 2017 MSEefaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Resistance to Antibiotics TestDocument2 pagesBacteria Resistance to Antibiotics Testصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit-5 January 2014 Mark SchemeDocument22 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology Unit-5 January 2014 Mark SchemeAvrinoxNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Infection Immune System TB Hiv AnswersDocument25 pagesUnit 4-Infection Immune System TB Hiv Answersareyouthere92100% (6)
- 4BI0 1B MSC 20120121Document16 pages4BI0 1B MSC 20120121avishkabandaraNo ratings yet
- 2014 - June 1BR MS PDFDocument26 pages2014 - June 1BR MS PDFSimilar12345No ratings yet
- Wbi14 01 Pef 20230302Document8 pagesWbi14 01 Pef 20230302grengtaNo ratings yet
- Proteins 4 MSDocument8 pagesProteins 4 MSAktham SmairatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 January 2009 ms00Document14 pagesUnit 2 January 2009 ms00Adrian Safa khouryNo ratings yet
- 03 - Biochemistry of Corona VirusDocument1 page03 - Biochemistry of Corona VirusnarasimhahanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Document13 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Fathmath MohamedNo ratings yet
- R7212306 MicrobiologyDocument1 pageR7212306 MicrobiologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Faculty - Applied Sciences - 2023 - Session 1 - Degree - BMS545Document13 pagesFaculty - Applied Sciences - 2023 - Session 1 - Degree - BMS545adibaumairahNo ratings yet
- Gcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology (Legacy) JANUARY 2013Document46 pagesGcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology (Legacy) JANUARY 2013sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 15 International Biology Olympiad Brisbane, 2004: Competitor #Document62 pages15 International Biology Olympiad Brisbane, 2004: Competitor #martynapetNo ratings yet
- WBI14 01 Pef 20220113Document6 pagesWBI14 01 Pef 20220113the dsNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 6BDocument12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Biology (6BI08) Paper 6BMahiat Miftah ShowkatNo ratings yet
- STS10 - First Exam - Part 1 and Part 2Document6 pagesSTS10 - First Exam - Part 1 and Part 2Trisha MalaluanNo ratings yet
- IBO 2004 Theory Part 2Document62 pagesIBO 2004 Theory Part 2pdbiocompNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani immunology midterm focuses on microbial homeostasis, MHC, vaccinesDocument2 pagesBITS Pilani immunology midterm focuses on microbial homeostasis, MHC, vaccinesRAVI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Core skeletal muscles mashupDocument5 pagesCore skeletal muscles mashupAe BanpongNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument2 pagesCell StructureAe BanpongNo ratings yet
- QP Option H (2007-2013)Document70 pagesQP Option H (2007-2013)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Bmat 2017Document13 pagesBmat 2017Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- 6BI07 Jan 2013 QP PDFDocument16 pages6BI07 Jan 2013 QP PDFAe BanpongNo ratings yet
- Vaping Is Far From HarmlessDocument3 pagesVaping Is Far From HarmlessAe BanpongNo ratings yet
- Lab #11: Respiratory Physiology: BackgroundDocument12 pagesLab #11: Respiratory Physiology: BackgroundAe BanpongNo ratings yet
- Questions Section B 1993-2003Document29 pagesQuestions Section B 1993-2003Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Ecology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming QP (2010-2012)Document61 pagesEcology Evolution Ecoystems Global Warming QP (2010-2012)Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Forensic Science QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document25 pagesForensic Science QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Forensic Science MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document21 pagesForensic Science MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document16 pagesPhotosynthesis MS New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Note By4 By5Document263 pagesNote By4 By5Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- Aqa Biol1 W MS Jun11Document6 pagesAqa Biol1 W MS Jun11Ae BanpongNo ratings yet
- 2015 Special Report On Housing Characteristics PDFDocument267 pages2015 Special Report On Housing Characteristics PDFaileen_v21No ratings yet
- Anthropology: Anthropology Is The Scientific Study of Humans, Human BehaviorDocument26 pagesAnthropology: Anthropology Is The Scientific Study of Humans, Human BehaviorAliaNo ratings yet
- Good Clinical Laboratory Practice (GCLP) : Quality Demanding From Clinical LaboratoriesDocument5 pagesGood Clinical Laboratory Practice (GCLP) : Quality Demanding From Clinical LaboratoriesJaneNo ratings yet
- Health Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Document2 pagesHealth Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Randell ManjarresNo ratings yet
- Sample Script 1 EnglishDocument6 pagesSample Script 1 EnglishKelhei GabrelleNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On: "Brain Fingerprinting"Document20 pagesSeminar Report On: "Brain Fingerprinting"Priyadarshini Behera Vyas0% (1)
- WWW - Osha.gov Arc Flash HandoutDocument4 pagesWWW - Osha.gov Arc Flash Handoutraul_bsu100% (1)
- Mise Ry by Stephen King: AnalysisDocument9 pagesMise Ry by Stephen King: AnalysisMartinaNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument24 pagesPractice QuestionsMonique RapleyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Ethics Article Highlights Need for Nurses to Engage in Public Policy DevelopmentDocument11 pagesNursing Ethics Article Highlights Need for Nurses to Engage in Public Policy Developmentlorelyn cabreraNo ratings yet
- Terapi ToxoplasmosisDocument9 pagesTerapi Toxoplasmosissarah disaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument3 pagesAccomplishment ReportLorelyn CamarigNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNo ratings yet
- AG3-Lesson 6. Review of Related LiteratureDocument12 pagesAG3-Lesson 6. Review of Related LiteratureJelly CantilNo ratings yet
- Awesome: Toilet Training TipsDocument3 pagesAwesome: Toilet Training TipsBindu SripadNo ratings yet
- Growth Monitoring - GIDocument19 pagesGrowth Monitoring - GIokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice in Postgraduate Healthcare EducationDocument29 pagesEvidence Based Practice in Postgraduate Healthcare EducationGab FgilzcheNo ratings yet
- Corporate Ergonomics ProgramsDocument16 pagesCorporate Ergonomics ProgramsJharef Rupire DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 20 21 Nclex Requirements For Licensure by Examination 06-08-22. Rev. 1 1Document3 pages20 21 Nclex Requirements For Licensure by Examination 06-08-22. Rev. 1 1Sheick MunkNo ratings yet
- D. 800/1000: Climax/ 1 Trong 2 Chi Tiết Xuất Sắc NhấtDocument2 pagesD. 800/1000: Climax/ 1 Trong 2 Chi Tiết Xuất Sắc NhấtThanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Urology DNB Old QuestionsDocument8 pagesUrology DNB Old QuestionssjulurisNo ratings yet
- Importance of Nursing TheoriesDocument5 pagesImportance of Nursing TheoriesDecere PascualNo ratings yet
- AE PostGrad SyllabusDocument265 pagesAE PostGrad Syllabusaquib yousufNo ratings yet
- Practice Mock GA MayDocument124 pagesPractice Mock GA MaydatwbfaqsjvmsNo ratings yet