Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 Homework
Uploaded by
itsheartmovingOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 Homework
Uploaded by
itsheartmovingCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy-123 Chapter 9 Homework (James Walker, 4th Edition) 3. A 26.2kg dog is running northward at 2.70m/s, while a 5.
30kg cat is running eastward at 3.04 m/s. Their 74.0kg owner has the same momentum as the two pets taken together. Find the direction and magnitude of the owners velocity.
4. Two air track carts move toward one another on an air track. Cart 1 has a mass of 0.35kg and a speed of 1.2 m/s. Cart 2 has a mass of 0.61kg. (a) What speed must cart 2 have if the total momentum of the system is to be zero? (b) Since the momentum of the system is zero, does it follow that the kinetic energy of the system is also zero? (c) Verify your answer to part (b) by calculating the systems kinetic energy.
5. A 0.150kg baseball is dropped from rest. If the magnitude of the baseballs momentum is 0.780 just before it lands on the ground, from what height was it dropped?
6. A 285g ball falls vertically downward, hitting the floor with a speed of 2.5m/s and rebounding upward with a speed of 2.0m/s. (a) Find the magnitude of the change in the balls momentum. (b) Find the change in the magnitude of the balls momentum. (c) Which of the two quantities calculated in parts (a) and (b) is more directly related to the net force acting on the ball during its collision with the floor? Explain.
15. A 0.50 kg croquet ball is initially at rest on the grass. When the ball is struck by a mallet, the average force exerted on it is 230 N. If the balls speed after being struck is 3.2 m/s, how long was the mallet in contact with the ball?
17. A 15.0g marble is dropped from rest onto the floor 1.44m below. (a) If the marble bounces straight upward to a height of 0.640m, what are the magnitude and direction of the impulse delivered to the marble by the floor? (b) If the marble had bounced to a greater height, would the impulse delivered to it have been greater or less than the impulse found in part (a)? Explain.
21. In a situation similar to (Example 9-3), suppose the speeds of the two canoes after they are pushed apart are 0.58 m/s for canoe 1 and 0.42 m/s for canoe 2. If the mass of canoe 1 is 320kg, what is the mass of canoe 2?
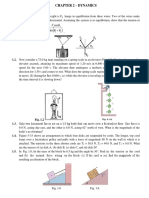
26. An 85kg lumberjack stands at one end of 380kg floating log, as shown in Figure 9-15. Both the log and the lumberjack are at rest initially. (a) If the lumberjack now trots toward the other end of the log with a speed of 2.7m/s relative to the log, what is the lumberjacks speed relative to the shore? Ignore friction between the log and the water. (b) If the mass of the log had been greater, would the lumberjacks speed relative to the shore be greater than, less than, or the same as in part (a)? Explain. (c) Check your answer to part (b) by calculating the lumberjacks speed relative to the shore for the case of a 450kg log.
28. A cart of mass m moves with a speed v on a frictionless air track and collides with an identical cart that is stationary. If the two carts stick together after the collision, what is the final kinetic energy of the system?
32. A bullet with a mass of 4.0g and a speed of 650 m/s is fired at a block of wood with a mass of 0.095kg. The block rests on a frictionless surface, and is thin enough that the bullet passes completely through it. Immediately after the bullet exists the block, the speed of the block is 23 m/s. (a) What is the speed of the bullet when it exits the block? (b) Is the final kinetic energy of this system equal to, less than, or greater than the initial kinetic energy? Explain. (c) Verify your answers to part (b) by calculating the initial and final kinetic energies of the system.
33. A 0.420kg block of wood hangs from the ceiling by a string, and a 0.0750kg wad of putty is thrown straight upward, striking the bottom of the block with a speed of 5.74 m/s. The wad of putty sticks to the block. (a) Is the mechanical energy of this system conserved? (b) How high does the putty-block system rise above the original position of the block?
34. A 0.430kg block is attached to a horizontal spring that is at its equilibrium length, and whose force constant is 20.0 N/m. The block rests on a frictionless surface. A 0.0500kg wad of putty is thrown horizontally at the block, hitting it with a speed of 2.30 m/s and sticking. How far does the putty-block system compress the spring?
37. A 732kg car stopped at an intersection is rear-ended by a 1720kg truck moving with a speed of 15.5 m/s. If the car was in neutral and its brakes were off, so that the collision is approximately elastic, find the final speed of both vehicles after the collision.
70. A car moving with an initial speed v collides with a second stationary car that is onehalf as massive. After the collision the first car moves in the same direction as before with a speed of v/3. (a) Find the final speed of the second car. (b) Is this collision elastic or inelastic?
71. A 1.35kg block of wood sits at the edge of a table, 0.782 m above the floor. A 0.0105kg bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 715 m/s embeds itself within the block. What horizontal distance does the block cover before hitting the ground?
84. The three air carts shown in Figure 9-27 have masses, reading from left to right of m, 2m, and 4m, respectively. Initially, the cart on the right is at rest, whereas the other two carts are moving to the right with a speed of v0. All carts are equipped with putty bumpers that give completely inelastic collisions. (a) Find the final speed of the carts. (b) Calculate the ratio of the final kinetic energy of the system to the initial kinetic energy of the system.
You might also like
- Unit 5 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- PH600 CH 9 Problems PDFDocument3 pagesPH600 CH 9 Problems PDFMike GaoNo ratings yet
- Assing 4Document2 pagesAssing 4KazaValiShaikNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Extra Study Questions: Short AnswerDocument109 pagesDynamics Extra Study Questions: Short Answeramitdeo99No ratings yet
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDocument7 pagesCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariNo ratings yet
- Energy WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnergy WorksheetAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Momentum: 1 - Praveen AlwisDocument7 pagesMomentum: 1 - Praveen Alwispraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- 153 20101029141059 PDFDocument6 pages153 20101029141059 PDFMeerreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document20 pagesChapter 07Shehryar AliNo ratings yet
- ANSWER: (A) 67 M/s (B) - X (C) 1.2 KN (D) - XDocument2 pagesANSWER: (A) 67 M/s (B) - X (C) 1.2 KN (D) - XThu HòaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Problems Ch04Document19 pagesProblems Ch04John100% (1)
- HW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSDocument4 pagesHW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSmaalmeida85No ratings yet
- Homework #5 MomentumDocument10 pagesHomework #5 MomentumNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- Practice Test2 ps150Document3 pagesPractice Test2 ps150Antoine S. NdiayeNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerDocument3 pages2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerBEN CHILUFYANo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Mamun ShahNo ratings yet
- Phys1101 Worksheeti 2014 EDocument6 pagesPhys1101 Worksheeti 2014 Ejhxnrx48f8No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsDocument1 pageAssignment 2 Chapter 7 and 8 ProblemsmlondiyaseenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch04Document2 pagesTutorial Ch04khxrsvrgb6No ratings yet
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford ManisanNo ratings yet
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford ManisanNo ratings yet
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford Manisan0% (1)
- 1.4.2 Momentum 00-10Document10 pages1.4.2 Momentum 00-10Murray PhysicsNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument8 pagesQuestionHimanshuTripathiNo ratings yet
- Phys10 Chap8 MomentumImpulse&CollisionsDocument6 pagesPhys10 Chap8 MomentumImpulse&CollisionsEngelbert Bicoy AntodNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 MomentumDocument4 pagesTutorial 7 Momentumapi-3827354No ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 2 F DynamicsDocument2 pagesLaboratory No. 2 F Dynamicsjutr ruyluNo ratings yet
- Week#4 Wednesday Chapter6SETBDocument4 pagesWeek#4 Wednesday Chapter6SETBmanadaNo ratings yet
- Wilson, College Physics - Chapter 6, ExercisesDocument23 pagesWilson, College Physics - Chapter 6, ExercisesJohnatan AgudeloNo ratings yet
- Subjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesSubjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionAniket PalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Windi Wandira100% (1)
- Problems Vibrations and Waves - Physics - 7 - Ed Serway-2 PDFDocument7 pagesProblems Vibrations and Waves - Physics - 7 - Ed Serway-2 PDFNathalia AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Questions:: University of Zambia School of Natural Sciences Department of PhysicsDocument2 pagesConceptual Questions:: University of Zambia School of Natural Sciences Department of PhysicsAngel JereNo ratings yet
- Dynamic 3Document3 pagesDynamic 3Gaozheng RelinquishNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 8Document5 pagesPhysics Chapter 8doctorssdatNo ratings yet
- Cantidad de MovimientoDocument6 pagesCantidad de MovimientoSebastianNo ratings yet
- Ch.5lawsofmotionDocument4 pagesCh.5lawsofmotionsamahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Semester 1 ReviewDocument20 pagesAP Physics Semester 1 ReviewAngelo PinerNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 02 Momentum & Energy Extra Study QuestionsDocument141 pages02 Momentum & Energy Extra Study QuestionsTheBigbrains Aceo50% (2)
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBacillus SubtilisNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Worksheetpackage - 1 Newtons LawsDocument1 pageUnit 3 - Worksheetpackage - 1 Newtons LawsAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- EOC Exercise 1Document11 pagesEOC Exercise 1Lukhman Al AmeenNo ratings yet
- PC1431 Term Test 2012Document10 pagesPC1431 Term Test 2012MrshuaiNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL SHEET ON Dynamics and Linear Momentum & Collisions-1Document4 pagesTUTORIAL SHEET ON Dynamics and Linear Momentum & Collisions-1Princess Ruth MangenaNo ratings yet
- Homework: Set 8-Linear Momentum & CollisionsDocument2 pagesHomework: Set 8-Linear Momentum & CollisionsNikhil MinhasNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Colm-05 - Cbse LevelDocument2 pagesColm-05 - Cbse LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving With Newton'S Laws NameDocument4 pagesProblem Solving With Newton'S Laws Nameganesh guptaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PhysicsDocument10 pagesReviewer PhysicsYeho ShuaNo ratings yet
- Wiley Part2Document9 pagesWiley Part2Andrian Dean Handika CsTahtaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Physics 01 012022Document2 pagesAssignment Physics 01 012022Trương Đức HiếuNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lab 2 Dynamics MEC424Document16 pagesLab 2 Dynamics MEC424Zeno SebastianNo ratings yet
- 10-09-23 - Sr. Elite & Target (C-120, C-Ipl, Ipl-Ic) - Jee-Main - ctm-02 - Key & Sol'sDocument12 pages10-09-23 - Sr. Elite & Target (C-120, C-Ipl, Ipl-Ic) - Jee-Main - ctm-02 - Key & Sol'sNavyasri NavyasriNo ratings yet
- Pump Calculations EquationDocument3 pagesPump Calculations EquationToan LeNo ratings yet
- Easa Parte 66 M1-Sample QuestionsDocument19 pagesEasa Parte 66 M1-Sample QuestionsAl Pec100% (1)
- Diode Ir1fDocument6 pagesDiode Ir1fedgarlibanioNo ratings yet
- NP7 121Document2 pagesNP7 121Owen MontillaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VII Direct Current CircuitsDocument28 pagesCHAPTER VII Direct Current CircuitsNandya GuvitaNo ratings yet
- Aspen Plus Simulation of A Low Capacity Organic Rankine Cycle Heated by Solar EnergyDocument6 pagesAspen Plus Simulation of A Low Capacity Organic Rankine Cycle Heated by Solar EnergySẵffǿủ JặmếsNo ratings yet
- PCC Retaining WallDocument129 pagesPCC Retaining WallSUJEET DUBEY100% (1)
- Hardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 To 200 KW) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 To 200 HP)Document174 pagesHardware Manual ACS800-01 Drives (0.55 To 200 KW) ACS800-U1 Drives (0.75 To 200 HP)virgil guimanNo ratings yet
- IGBT Module Selection and ApplicationDocument7 pagesIGBT Module Selection and Applicationvdsantos74No ratings yet
- SHURE 98 108 MicrofonoDocument2 pagesSHURE 98 108 MicrofonoDiego MarchantNo ratings yet
- Amanda Astracia Final IADocument15 pagesAmanda Astracia Final IAMukesh PantNo ratings yet
- Diep - Io ClassessDocument4 pagesDiep - Io ClassessIvanNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S.Prakash and Hari D Sharma PDFDocument784 pagesPile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S.Prakash and Hari D Sharma PDFHayro Copacalle50% (4)
- Extensometr TypeDocument19 pagesExtensometr TypeMoaz HussainNo ratings yet
- V An de G Raff G Enerator SF-9722Document4 pagesV An de G Raff G Enerator SF-9722JonhGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Appropriate Technology - Electric Power From The Wind - Prepper Survivor UpAndRunningDocument42 pagesAppropriate Technology - Electric Power From The Wind - Prepper Survivor UpAndRunningBen LernerNo ratings yet
- Description:: Model 3629B 1 of 18 Part No. 5000095-1070-7 S:/Data/Manuals/3629/I3629B.p65 11.23.1999Document20 pagesDescription:: Model 3629B 1 of 18 Part No. 5000095-1070-7 S:/Data/Manuals/3629/I3629B.p65 11.23.1999Jose Roberto Villegas MNo ratings yet
- 220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportDocument45 pages220 KV GSS Heerapura ReportMohit Bhavsar63% (8)
- The Ground Power Unit To Supply AircraftsDocument64 pagesThe Ground Power Unit To Supply AircraftsWilliam Jaldin CorralesNo ratings yet
- Chinhat G.S.S (220 KV) : Submitted By: Ashutosh Singhal 08EJEEE015 Ivth YearDocument20 pagesChinhat G.S.S (220 KV) : Submitted By: Ashutosh Singhal 08EJEEE015 Ivth YearSandeep Sharma100% (1)
- Product Data - Sound Intensity Probe Kit - Type 3599, Sound Intensity Microphone Pair - Type 4197, Dual Preamplifier - Type 2683 (Bp1880)Document8 pagesProduct Data - Sound Intensity Probe Kit - Type 3599, Sound Intensity Microphone Pair - Type 4197, Dual Preamplifier - Type 2683 (Bp1880)DanielSierraNo ratings yet
- ECE482 Homework 1 SolDocument4 pagesECE482 Homework 1 SolsuhaaasNo ratings yet
- Mil HDBK 83575 PDFDocument29 pagesMil HDBK 83575 PDFLohith GowdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Plane Electromagnetic Waves and Wave Propagation: An Historical PerspectiveDocument23 pagesChapter 7: Plane Electromagnetic Waves and Wave Propagation: An Historical PerspectiveNiranjan DaradeNo ratings yet
- Physics SolutionDocument5 pagesPhysics Solutionprince ian cruzNo ratings yet
- Analisis Termodinamika Sistem Hibrida PV T Berdasarkan Model TermalDocument11 pagesAnalisis Termodinamika Sistem Hibrida PV T Berdasarkan Model TermalANA MARDIANANo ratings yet
- Power Supply EmersonDocument20 pagesPower Supply Emersonindra gunawanNo ratings yet
- Getinge Ultrasonic Cleaner - Service ManualDocument62 pagesGetinge Ultrasonic Cleaner - Service Manualgustavoesanchez100% (1)