Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ja Assignment3
Uploaded by
BookMaggotOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ja Assignment3
Uploaded by
BookMaggotCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
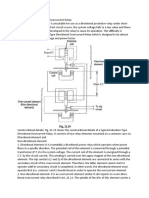
Describe how does the Vibrating Contact Type Voltage Regulator maintain the output generator at constant value (28Vdc)?
The vibrating control regulator is a type of voltage regulator that is used in an excitation system to both supply and regulate the direct current in the rotor windings. Also, as the name suggests, it is a type of regulator with vibrating contacts whose excitation current and pole field strength are automatically controlled using voltage regulating components. Current in this vibrating contact type voltage regulator can flow in two path way which is through contact point or through resistance itself. So, in order to maintain the values of current at 28Vdc, this device has several important component combined together to maintain this current values. In the voltage regulator, the charging current does not flow through the regulator winding. The winding on the core consists of a voltage coil of fine wire. The two ends of the voltage coil are connected across the generator brushes and in parallel with the battery. Instead, the current will flow to through contact points and then directly to the shunt field. When the speed of generator increases, the voltage has a tendency to go above 28 volt dc. When the value of current as long as value of voltage, increasing in magnetic pull of the core on the contact armature will overcome the spring tension and pull armature towards the core. This reaction will create a condition of open the contacts and insert a resistance in the vibrating generator circuit. By this way, the added current will be lowered by this insert resistance in the field winding, thus the developed voltage will be drop at 28 volt dc. In addition to that, when the voltage of generator decreased due to the speed of the generator, the pull of spring on the regulator armature will overcomes the magnetic pull of the core and thus closed the contact as its original position (closed contact). This condition will lead to short-circuit of the resistances unit and allow the field current to increase as long as its voltage value. In the nutshell, in order to protect the electronics devices in aircraft, this vibrating voltage regulator will react rapidly in order to maintain 28 Vdc and prevent the excessive build up of
voltage which can damaged some component which led to failure. This process will react rapidly. 2. Describe the operation of a Reverse Current Cut-Out Relay (RCCR) in DC generator circuit when: a) Generator voltage is higher than the battery voltage. b) Battery voltage is higher than the generator voltage.
Reverse Current Cut-Out Relay(RCCR) is one of the unit in the three unit regulator. The Reverse Current Cut-Out relay is used to prevent battery from discharging through the generator if output voltage falls below the battery output. When this occurs the battery attempts to drive the generator as a motor. This action is called motoring the generator and unless prevented, the battery discharges in a short time. The Reverse Current Cut-Out Relay is normally open rather than the two other units in the three unit regulator that is normally closed. When the generator at a stationary position, the generator warning light will illuminate. When voltage began to produce in the generator, the contact will be closed due to the electromagnetic field produced. On the condition of overvoltage where generator voltage is higher than the battery voltage, the Reverse Current Cut-Out relay will remain closed. Meanwhile the Voltage Regulator voltage coil produces enough magnetic fields to open the points. The Voltage and Current Regulator will thus control the generator value to the appropriate value. As for when the condition where the battery voltage is higher than the generator voltage, the initial current from battery will flow through the Reverse Current Cut-Out Relays current coil and neutralize the magnetic field from the voltage coil. Thus the contact point will be opened by the spring and prevent battery from discharging through the armature and motor. The remaining current will be routed to the generator warning light.
3. Describe how does the Carbon Pile Voltage Regulator (CPVR) maintain the output generator at constant value (28Vdc)? a) Generator at constant speed
When the generator is at constant speed, it will supply a fix amount of voltage which is 28 volt. In this case, the voltage is maintained at 28 volt by using carbon stack, where this carbon stack acts as a resistance and it is fitted with spring to produce a spring tension. The movement of the carbon stack, or carbon pile, is controlled by the electromagnetic coil, where the electromagnetic force produced will expand or contract the cabon stack. In the meantime, this electromagnetic force is regulated by the rheostat, where it will control the amount of current from the armature that flow to the electromagnetic coil. b) Generator speed increased
So, when the generator speed increased, also known as overvoltage condition, the output voltage will also be increased up to 30 volt. Therefore, the current from armature is higher than what is supposed to be. In order to reduce the output voltage back to 28 volt, the current from the armature flow to the electromagnetic coil and provide the magnetic field that is strong enough to pull the carbon pile against the spring tension and hence, increase the resistance. Then, the field current passing through the carbon pile is decreased and there is corresponding decrease in the field magnetic coil strength and eventually results in a drop in generator output which is 28 volt.
c) Generator speed decreased
Other than that, if the system is having undervoltage condition, or the generator speed decreased, the output voltage to the load will decrease to 26 volt. Due to this circumstance, the current provided to the electromagnetic coil, which is from the armature, is low and unable to pull the carbon pile. This will cause the carbon pile to contract due to spring tension and give a lower resistance to the field current. Finally, the field current passing through the carbon pile will increase and results in an increase of field magnetic coil strength. So, the generator output will gradually increase until it obtained 28 volt of output voltage.
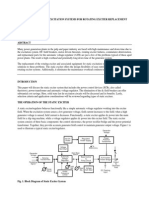
4. Describe the operation of a DC Brushless Alternator below.
The DC Brushless alternator is mainly used for high-output DC. In most operations, it consist two alternators in the same housing, one alternator produces DC for the load, and the other is controlled by the voltage regulator to provide excitation voltage for the output. The larger of the two sections is the main alternator and the smaller one is the exciter. The exciter is stationary and receives field DC from the voltage regulator. If output is low, the regulator will supply a larger amount of current and vice versa. The magnetic field of the exciter stator is cut by the exciter rotor and the resulting threephase AC is rectified by the three diodes which act as a half wave rectifier. The rectified output of the exciter rotor flows into the output field windings, which are also a part of the rotor. This field creates north and south poles on the rotor frame, and as it rotates within the three-phase stator, generates it becomes DC for the output circuit. In addition to that, a capacitor is placed across the output of the alternator to prevent voltage surges from destroying the rectifying diodes.
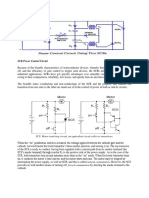
5. Describe the whole operation of the aircrafts external power circuit below.
When plug in, it make solid contact with 2 larger plugs but ext. power relay still open ( no current flow) until the plug is forced all the way and the smaller pin makes contact. When the interlock pin is engaged the ext. power relay in the aircraft is energized, only then the current flow from GPU into the aircraft system. The third small pin will supply current to the conductor coil to close the contactor. For battery, a circuit consists of: A diode (D2) A current limiter resistor A fuse
This circuit allows enough current to energized contactor coil, in case the battery is completely discharged. Reverse polarity/Diode D1 to prevent external power contactor to close if wrong polarity power source installed. Diode D2 to prevent positive pin of the external power receptacle from being HOT when no external power connected to the aircraft. External source supplies power for starting and at the same time for charging the battery. CAUTION: Be sure to use the correct external power voltage for the aircraft. 12V or 24V? Since it can damage sensitive electrical equipment.
You might also like
- Physics Paper 1 TZ1 HL PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics Paper 1 TZ1 HL PDFdrive wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Impulse Generator Practical Course WorkDocument8 pagesImpulse Generator Practical Course WorkKapila Kumara100% (1)
- High Voltage Testing of GeneratorDocument28 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of GeneratorbuntysuratNo ratings yet
- Optimize Magnetic GapDocument45 pagesOptimize Magnetic GapteomondoNo ratings yet
- Charging System NotesDocument5 pagesCharging System Notesmoyocarnage409No ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationRDocument4 pagesExcitationRDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationsysDocument5 pagesExcitationsysDan GrayNo ratings yet
- Static Relays: Static Relays Are Superior To Electro-Magnetic Relays in The Following AspectsDocument7 pagesStatic Relays: Static Relays Are Superior To Electro-Magnetic Relays in The Following AspectsKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- How Is Ac Voltage Produced?Document4 pagesHow Is Ac Voltage Produced?Mariappan NaNo ratings yet
- Charging Systems For AutomobilesDocument56 pagesCharging Systems For AutomobilesIshu PattanayakNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument4 pagesExcitationDan GrayNo ratings yet
- CAT 910 Charging SystemDocument15 pagesCAT 910 Charging SystemYober Emilio Nato AcostaNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationDocument7 pagesSingle-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationKhushbakht KhushiNo ratings yet
- Electronic IgnitionDocument17 pagesElectronic IgnitionMitsos TakisNo ratings yet
- Basic of ElectricalDocument10 pagesBasic of ElectricalAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Charging SystemDocument22 pagesCharging SystemTrần Văn ChươngNo ratings yet
- Mod 4Document41 pagesMod 4Ayush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- LopDocument4 pagesLopD SNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Generation and Excitation SystemDocument20 pagesElectric Power Generation and Excitation SystemMansen NsubugaNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsDocument19 pagesPower Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsEr. Piush Jindal100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTENo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument26 pagesDocumentPurbita ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ee0041l Finals (Fa) KilakigaDocument19 pagesEe0041l Finals (Fa) KilakigaKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTENo ratings yet
- Application of Static ExcitationDocument18 pagesApplication of Static ExcitationMohamed RashidNo ratings yet
- The Charging SystemDocument15 pagesThe Charging SystemRuth MwendaNo ratings yet
- BVCDocument4 pagesBVCD SNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Capacitor Bank Value To Maintain Unity Power Factor With Some Suitable ExampleDocument5 pagesHow To Calculate Capacitor Bank Value To Maintain Unity Power Factor With Some Suitable Examplesaran100% (1)
- Application of Static Excitation Systems For Rotating Exciter Replacement R.C. SchaeferDocument14 pagesApplication of Static Excitation Systems For Rotating Exciter Replacement R.C. SchaeferyaayNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation System-AMTECHDocument24 pagesStatic Excitation System-AMTECHsssduduNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Types of AlternatorsDocument12 pagesTypes of AlternatorsHamoudRazaMazherNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machines PDFDocument34 pagesRotating Machines PDFphanindraNo ratings yet
- Carbon Pile RegulatorsDocument4 pagesCarbon Pile RegulatorsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Experiment Three: Charging System: DynamoDocument12 pagesExperiment Three: Charging System: Dynamoمحمد القدوميNo ratings yet
- Investigate The DC Motor CharacteristicDocument7 pagesInvestigate The DC Motor CharacteristicAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- AlternatorDocument28 pagesAlternatorbebekNo ratings yet
- Pilot ExciterDocument6 pagesPilot ExciterRudy HerreraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Automatic Voltage Regulation of Alternator or GeneratorDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The Automatic Voltage Regulation of Alternator or GeneratorJohn Fredy Martínez CardonaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Pile Voltage Regulator Use in A Heavy Duty Generators SystemDocument1 pageCarbon Pile Voltage Regulator Use in A Heavy Duty Generators SystemBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Emergency Diesel Generator The Generator, Exciter, and Voltage RegulationDocument34 pagesEmergency Diesel Generator The Generator, Exciter, and Voltage RegulationCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Operating Principles of DC GeneratorsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Operating Principles of DC GeneratorsRenz MykoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 4 PDFMuhamad AmmarNo ratings yet
- RpsDocument15 pagesRpsMuhammad Omer IshfaqNo ratings yet
- Charging SystemDocument28 pagesCharging SystemAnanta Kumar NandiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document8 pagesAssignment 3Renz MykoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On DVR, JS Saroya, CS Singh, 03.12.11Document75 pagesPresentation On DVR, JS Saroya, CS Singh, 03.12.11Amit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Group-2 Two and Three Wheeled Vehicle Assignment PresentationDocument20 pagesGroup-2 Two and Three Wheeled Vehicle Assignment PresentationTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- Solar Grass CutterDocument75 pagesSolar Grass CutterRajreddy100% (4)
- Lab 14 - 3-Phase AlternatorDocument7 pagesLab 14 - 3-Phase AlternatorjalilemadiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Ignition1 Ed.15-06-18Document27 pagesElectronic Ignition1 Ed.15-06-18collins arogoNo ratings yet
- Charging and TestingDocument77 pagesCharging and TestingHinsermu NeftalemNo ratings yet
- Automatic Voltage RegulatorsDocument7 pagesAutomatic Voltage RegulatorsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Question ElectricDocument12 pagesQuestion Electricmaxime78540No ratings yet
- Experiment - 07 Open and Short Circuit of 3 Phase AlternatorDocument8 pagesExperiment - 07 Open and Short Circuit of 3 Phase Alternatorcharanrck10No ratings yet
- Battery Charger CKT Using SCRDocument20 pagesBattery Charger CKT Using SCRSai Shashank AkulaNo ratings yet
- SCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsDocument5 pagesSCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsMark Kenneth Apuyan100% (1)
- DC MachinesDocument23 pagesDC MachinesNoyaNo ratings yet
- Ggenerator AlternatorDocument4 pagesGgenerator AlternatorShakir FadzliNo ratings yet
- Stepping Motor Control CircuitsDocument9 pagesStepping Motor Control CircuitsrfcbaccaratNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMDocument11 pagesPower Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMShashankNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers-STATICSDocument15 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers-STATICSBookMaggot0% (1)
- Why Choose MBA MSC BUSDocument1 pageWhy Choose MBA MSC BUSBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concept of The Gear Ratio: 1.27 Inches / 2 0.635 InchesDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Concept of The Gear Ratio: 1.27 Inches / 2 0.635 InchesBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument7 pagesQuestionaireBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Seat Pitch Position On Two Seats, One Behind The Other - It Is NOT The Legrest Area As SomeDocument3 pagesSeat Pitch Position On Two Seats, One Behind The Other - It Is NOT The Legrest Area As SomeBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Project p-37Document2 pagesProject p-37BookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Typical Aircraft Charging CircuitDocument1 pageTypical Aircraft Charging CircuitBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Report Landing Gear Sek AkuDocument3 pagesReport Landing Gear Sek AkuBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Aircraft PneumaticDocument3 pagesAircraft PneumaticBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Ata Presentation Power PointDocument9 pagesAta Presentation Power PointBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current I: Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1Document19 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current I: Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1 Activity 13.1Saurabh KoranglekarNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Subjective & Obj.Document10 pagesMagnetism Subjective & Obj.Aviram YadavNo ratings yet
- LM 5116Document28 pagesLM 5116rmoscibdNo ratings yet
- Lab 11: The Biot Savart Law: PurposeDocument7 pagesLab 11: The Biot Savart Law: PurposeÂn HoàngNo ratings yet
- 25510-A New Calculation For Designing Multilayer Planar Spiral Inductors PDF PDFDocument4 pages25510-A New Calculation For Designing Multilayer Planar Spiral Inductors PDF PDFAnonymous Kti5jq5EJINo ratings yet
- Bd9483f Leds DriverDocument32 pagesBd9483f Leds Driveraries2010mx0% (1)
- OSS Engineering Control Ver 2 1 PNDocument80 pagesOSS Engineering Control Ver 2 1 PNRagav SasthriNo ratings yet
- Free Energy TheoryDocument112 pagesFree Energy TheoryJohn TurnerNo ratings yet
- Miniature InductiveDocument5 pagesMiniature InductivePrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- 2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2Document5 pages2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2soumya vollalaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Flyback Converter With Peak Current Mode ControlDocument6 pagesSimulation of Flyback Converter With Peak Current Mode ControlAbhijit SinghNo ratings yet
- Motor and Drive System Resonance Problems and SolutionsDocument4 pagesMotor and Drive System Resonance Problems and SolutionsYernohjNo ratings yet
- AME EXAM Module 3 MCQDocument258 pagesAME EXAM Module 3 MCQkunnannNo ratings yet
- MD PresentationDocument7 pagesMD PresentationHanie MunirahNo ratings yet
- Data RFDocument63 pagesData RFmgitecetechNo ratings yet
- Transformer in and OutDocument214 pagesTransformer in and OutguytoughNo ratings yet
- Train Lighting ReportDocument31 pagesTrain Lighting ReportPiyush GoyalNo ratings yet
- 3A, 28V, 385Khz Step-Down Converter: The Future of Analog Ic TechnologyDocument11 pages3A, 28V, 385Khz Step-Down Converter: The Future of Analog Ic TechnologyerdaNo ratings yet
- ssp381 - Audi TT Coupé 07 - Suspension SystemDocument48 pagesssp381 - Audi TT Coupé 07 - Suspension SystemGabriel VetreneanuNo ratings yet
- 3ccc PDFDocument20 pages3ccc PDFKaka KunNo ratings yet
- What Is Magnetic Contactor and How ItDocument2 pagesWhat Is Magnetic Contactor and How Itgan100% (1)
- Aluminum Vs Copper Winding TransformersDocument4 pagesAluminum Vs Copper Winding Transformerssghori73No ratings yet
- Network Theory: Presented byDocument29 pagesNetwork Theory: Presented bySapata KumarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices, and ApplicationsDocument40 pagesElectronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices, and ApplicationsCece SolihinNo ratings yet
- ABB Guide To Harmonics With AC DrivesDocument36 pagesABB Guide To Harmonics With AC DrivesTeja KusumaNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperSaravanan BNo ratings yet